Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Insurance Note Taking Guide
Hochgeladen von
api-252391503Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Insurance Note Taking Guide
Hochgeladen von
api-252391503Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
7.10.1.
L1 Note taking guide
Types of Insurance Essentials Note-Taking Guide
Payton Name__________________
39 Total Points Earned Total Points Possible Percentage
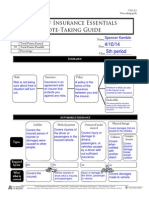
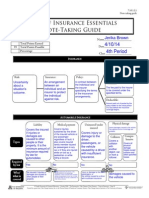
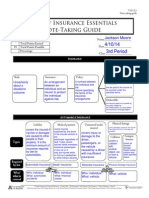
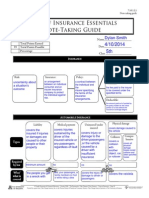
INSURANCE Policyholder:
Person who purchased the contract or 'policy'.
10/4/14 Date__________________
Career Prep Class _________________
Risk:
Insurance:
Policy:
Contract between the individual and the insurer varifying the terms of the insurance arrangements.
When you are not sure about a situations outcome.
Arrangement between individual and insurer.
Premium:
Money paid to ensure the specified terms.
Deductible:
Pocket money paid by policy holder.
AUTOMOBILE INSURANCE Liability Medical payment Uninsured/under insured Physical damage
Covers injuries or damage caused to other people.
Types
Covers injuries sustained by the driver of insured vehicle no matter whose fault it was.
Vehicles damage
Collision Comprehensive
Covers drivers, passenger, or vehicle when it is driver with unsufficient insurance's fault.
Collision with another object
all physical damage losses
Required by law Who/ what is covered
yes
no
no
no
Injured or damaged person.
Driver of insured vehicle
Driver, passenger, or vehicle
Vehicle
Family Economics & Financial Education October 2010 The Essentials to Take Charge of Your Finances Types of Insurance Page 10 Funded by a grant from Take Charge America, Inc. to the Norton School of Family and Consumer Sciences Take Charge America Institute at The University of Arizona
7.10.1.L1 Note taking guide
HEALTH INSURANCE Why is it important to purchase health insurance? Provides protection against: May cover: How may health insurance be purchased?
It gives you coverage for emergency or routine medical expenses.
Financial losses from injury or illness.
Hospital, surgical, dental, vision, long-term care, prescription, and major expenditures
By individual or through their employer
Children may stay on their parents health insurance until:
They are 19 or in college.
LIFE INSURANCE Life insurance:
Is a contract between an insurer and policyholder specifying a sum to be paid to a beneficiary upon the insureds death.
Beneficiary:
Dependent:
Recipient of any policy if insured person dies.
Person who depends on someone else financially.
Who should purchase life insurance?
Person with dependant spouse or dependant children.
DISABILITY INSURANCE Disability insurance: If needed, how much does disability insurance pay an individual?
Replaces a portion of ones income if they cant work due to illness or injury.
60-70%
HOMEOWNERS AND R ENTERS INSURANCE Peril:
Something that causes a financial loss. Ex: fire.
Renters insurance:
Keeps insured people from losing contents of dwelling.
Why is it important for a renter to purchase renters insurance?
landlords insurance policy on the dwelling does not cover the renters personal possessions
Homeowners insurance:
Combines property and liability insurance into one policy to keep a home from damage costs due to perils.
Property insurance:
Protects the insured from financial loss due to tearing down or damaging to property or possessions
Liability insurance:
Keeps the insured party from being held liable for others financial loss
Covers:
Major perils
Family Economics & Financial Education October 2010 The Essentials to Take Charge of Your Finances Types of Insurance Page 11 Funded by a grant from Take Charge America, Inc. to the Norton School of Family and Consumer Sciences Take Charge America Institute at The University of Arizona
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Property, Liability and Auto Insurance: A Handbook and Guide for Insurance Concepts and Coverage!Von EverandProperty, Liability and Auto Insurance: A Handbook and Guide for Insurance Concepts and Coverage!Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252988764Noch keine Bewertungen
- Life, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesVon EverandLife, Accident and Health Insurance in the United StatesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- InsuranceDokument2 SeitenInsuranceapi-252391740Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252387344100% (1)
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252392987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252460708Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252384953Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252384641Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252377919Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-2523918430% (1)
- Insurance Note Taking GuideDokument2 SeitenInsurance Note Taking Guideapi-252390333100% (1)
- Insurance SheetDokument2 SeitenInsurance Sheetapi-252377967Noch keine Bewertungen
- UGA RMIN 4000 Exam 2 Study GuideDokument13 SeitenUGA RMIN 4000 Exam 2 Study GuideBrittany Danielle ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Dokument11 SeitenInsurance & Risk Management JUNE 2022Rajni KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3 Insurance Transaction DocumentsDokument6 SeitenChap 3 Insurance Transaction DocumentsAmrutha YNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance BasicsDokument24 SeitenInsurance BasicsKomal LalwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insuranc 1Dokument10 SeitenInsuranc 1zunaira sarfrazNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Health Insurance Project Swati Sarang (Tybbi) UmDokument64 SeitenNew Health Insurance Project Swati Sarang (Tybbi) UmMikant Fernando63% (8)
- The Characteristics of Insurance ContractsDokument4 SeitenThe Characteristics of Insurance Contractsvij_puvva6446Noch keine Bewertungen
- Law of Insurance AnswersheetDokument55 SeitenLaw of Insurance Answersheetkhatriparas71Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance and Risk Management w24YgEaPRNe6Dokument7 SeitenInsurance and Risk Management w24YgEaPRNe6Anupriya HiranwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- $R5W2XTXDokument52 Seiten$R5W2XTXTayyab AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of Life Insurance ContractDokument26 SeitenNature of Life Insurance ContractKavita SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of LI PolicyDokument33 SeitenPrinciples of LI PolicyManik MittalNoch keine Bewertungen
- InsurancesDokument7 SeitenInsuranceskidvictor16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance BasicsDokument23 SeitenInsurance BasicsChamandeep SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance CompanyDokument25 SeitenInsurance CompanySharif UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of Insurance Law New 1Dokument20 SeitenBasic Principles of Insurance Law New 1Billiee ButccherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction of Mediclaim InsuranceDokument17 SeitenIntroduction of Mediclaim InsuranceKunal KaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2 Fundamentals of InsuranceDokument21 SeitenUnit - 2 Fundamentals of Insurancepoojaaradhya9677Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Insurance by VISHALDokument6 SeitenWhat Is Insurance by VISHALVishalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance TermsDokument3 SeitenInsurance TermsThea Espigar-VillanuevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- History and Sources of Law of InsuranceDokument4 SeitenHistory and Sources of Law of InsuranceMary-Lou Anne MohrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module V-2Dokument12 SeitenModule V-2kashifidaplNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aid To Trade Insurance: Aditva SharmaDokument20 SeitenAid To Trade Insurance: Aditva Sharmaaditva SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance TemplateDokument41 SeitenInsurance Templatereimart sarmientoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance Review SagmitDokument27 SeitenInsurance Review SagmitMirai KuriyamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMM 229 Notes Chapter 6Dokument5 SeitenCOMM 229 Notes Chapter 6Cody ClinkardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Insurance LawDokument9 SeitenUnit 2 Insurance Lawpreeti aggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit FourDokument35 SeitenUnit FourBI SH ALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance BasicsDokument5 SeitenInsurance BasicsAdriana GomezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alabama 1Dokument33 SeitenAlabama 1academicexcellence21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Insurance and Pension FundDokument44 SeitenInsurance and Pension FundFiaz Ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- InsuranceDokument2 SeitenInsuranceVAT CLIENTSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 7Dokument3 SeitenLesson 7shadowlord468Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 InsuranceDokument9 SeitenUnit 2 Insurancepreeti aggarwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 1 InsuranceDokument9 SeitenUNIT 1 InsuranceHarleenNoch keine Bewertungen
- InsuranceDokument20 SeitenInsuranceYvonne BarrackNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLOSSARY - Insurance TermsDokument76 SeitenGLOSSARY - Insurance TermsTirthajit SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Institution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesDokument16 SeitenInstitution That Offers A Person, Company, or Other Entity Reimbursement or Financial Protection Against Possible Future Losses or DamagesHrishikesh DharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3Dokument10 SeitenChap 3shanmughipriya nagarajanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Insurance: Risk Management, To HedgeDokument7 SeitenPrinciples of Insurance: Risk Management, To HedgeifthisamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essentials of An Insurance ContractDokument7 SeitenEssentials of An Insurance ContractSameer JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glossary of Insurance Terms: AbcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzDokument10 SeitenGlossary of Insurance Terms: AbcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzsebascianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phases of Development of InsuranceDokument20 SeitenPhases of Development of InsuranceJackie Don ShrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18bco32c U1Dokument14 Seiten18bco32c U1Vipul TyagiNoch keine Bewertungen
- B&I Unit 4Dokument17 SeitenB&I Unit 4saisri nagamallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4@Dokument25 SeitenUnit 4@Bikash SubbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ExerciseDokument4 SeitenExercisemuneeraaktharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard & Poors Outlook On GreeceDokument10 SeitenStandard & Poors Outlook On GreeceEuronews Digital PlatformsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Central Pharmaceuticals Limited: A Report On Performance Analysis ofDokument37 SeitenCentral Pharmaceuticals Limited: A Report On Performance Analysis ofNabila AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Goods Manufactured Schedule V13Dokument12 SeitenCost Goods Manufactured Schedule V13Osman AffanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accounting For Installment SalesDokument16 SeitenAccounting For Installment SalesLeimonadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 05 05 - Eigi - Adjusted EBITDA Is A Meaningless Metric, As It Does Not Correlate With Free Cash Flow - 4 Questions All Analyst Should Ask EIGIDokument8 Seiten2015 05 05 - Eigi - Adjusted EBITDA Is A Meaningless Metric, As It Does Not Correlate With Free Cash Flow - 4 Questions All Analyst Should Ask EIGIgothamcityresearchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Corporate Finance Asia Global 1st Edition Ross Test BankDokument25 SeitenCorporate Finance Asia Global 1st Edition Ross Test BankDonnaNguyengpij100% (60)
- Santosh VermaDokument159 SeitenSantosh VermaSantosh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - Portfolio inDokument12 SeitenChapter 7 - Portfolio intemedebereNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Implementation of Customer Due Diligence Princinple For Electronic Money As Preventive Measures of Terrorism Financing in Bank XDokument221 SeitenThe Implementation of Customer Due Diligence Princinple For Electronic Money As Preventive Measures of Terrorism Financing in Bank XOddy Ramadhika SusmoyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sun Pharma Completes Tender Offer For InSite Vision (Company Update)Dokument2 SeitenSun Pharma Completes Tender Offer For InSite Vision (Company Update)Shyam SunderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swap RevisedDokument36 SeitenSwap RevisedrigilcolacoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topeka Adhesive - Financial ForecastingDokument25 SeitenTopeka Adhesive - Financial ForecastingAlvin Francis Co100% (1)
- RBF Exchane Control BrochureDokument24 SeitenRBF Exchane Control BrochureRavineshNoch keine Bewertungen
- qX2B PJQN QnBQVKjXZ5LTt1SESnizoMtGkLWWKiEGBSA1QGVCClQblbcx6R8IDXAG3Vjerx0BmmgM9BYqjbD5y5t2A0VunOxcUzgVAa uxWA JEONWcoEwDokument6 SeitenqX2B PJQN QnBQVKjXZ5LTt1SESnizoMtGkLWWKiEGBSA1QGVCClQblbcx6R8IDXAG3Vjerx0BmmgM9BYqjbD5y5t2A0VunOxcUzgVAa uxWA JEONWcoEwNurul Hafiza ZazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reinsurance Basic GuideDokument80 SeitenReinsurance Basic GuideNur AliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBDCs and AMMDokument19 SeitenCBDCs and AMMGopal DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation - Hemas, SERVICE AND REPAIRS PDFDokument2 SeitenQuotation - Hemas, SERVICE AND REPAIRS PDFW GangenathNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCS Result Analysis 2023Dokument4 SeitenTCS Result Analysis 2023vinay_814585077Noch keine Bewertungen
- Repurchase Agreements and Money Market FundsDokument3 SeitenRepurchase Agreements and Money Market FundssdfasdfahgadsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forbes USA - 24 January 2017Dokument116 SeitenForbes USA - 24 January 2017Carlos PanaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Divi Thilina: (Terms & Conditions Applied)Dokument1 SeiteDivi Thilina: (Terms & Conditions Applied)KetharanathanSaravananNoch keine Bewertungen
- THREE Bonds and Stock Valuation.. STOCKDokument19 SeitenTHREE Bonds and Stock Valuation.. STOCKRaasu KuttyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financing For Farmer Producer Organisations PDFDokument18 SeitenFinancing For Farmer Producer Organisations PDFRaghuram BhallamudiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2312100607329500000Dokument2 Seiten2312100607329500000SHRESHTHA COLLEGESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valuation - Multiples and EV Value DriversDokument27 SeitenValuation - Multiples and EV Value DriversstrokemeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cash Book RevisionDokument2 SeitenCash Book RevisionSwati ChamariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invesco Markets ProspectusDokument104 SeitenInvesco Markets ProspectusGeorgio RomaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wells Fargo Statement - Oct 2022Dokument6 SeitenWells Fargo Statement - Oct 2022pradeep yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afm Examiner's Report March June 2022Dokument15 SeitenAfm Examiner's Report March June 2022Abha AbhaNoch keine Bewertungen