Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Business Intelligence?: BI Used For?
Hochgeladen von
vijay.alloju20Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Business Intelligence?: BI Used For?
Hochgeladen von
vijay.alloju20Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Business Intelligence?
Business intelligence, or BI for short, is an umbrella term that refers to competencies, processes, technologies, applications and practices used to support evidence-based decision making in organizations. In the widest sense it can be defined as a collection of approaches for gathering, storing, analyzing and providing access to data that helps users to gain insights and make better fact-based business decisions.
BI used for?
Organizations use Business Intelligence to gain data-driven insights on anything related to business performance. It is used to understand and improve performance and to cut costs and identify new business opportunities, this can include, among many other things: Analyzing customer behaviors, buying patterns and sales trends. Measuring, tracking and predicting sales and financial performance Budgeting and financial planning and forecasting Tracking the performance of marketing campaigns Optimizing processes and operational performance Improving delivery and supply chain effectiveness Web and e-commerce analytics Customer relationship management Risk analysis Strategic value driver analysis
Basics of Business Intelligence
Gathering Data
Gathering data is concerned with collecting or accessing data which can then be used to inform decision making. Gathering data can come in many formats and basically refers to the automated measurement and collection of performance data. For example, these can come from transactional systems that keep logs of past transactions, point-of-sale systems, web site software, production systems that measure and track quality, etc. A major challenge of gathering data is making sure that the relevant data is collected in the right way at the right time. If the data quality is not controlled at the data gathering stage then it can harm the entire BI efforts that might follow always remember the old adage - garbage in garbage out Storing Data Storing Data is concerned with making sure the data is filed and stored in appropriate ways to ensure it can be found and used for analysis and reporting. When storing data the same basic principles apply that you would use to store physical goods say books in a library you are trying to find the most logical structure that will allow you to easily find and use the data. The advantages of modern data-bases (often called data warehouses because of the large volumes of data) is that they allow multi-dimensional formats so you can store the same data under different categories also called data marts or datawarehouse access layers. Like in the physical world, good data storage starts with the needs and requirements of the end users and a clear understanding of what they want to use the data for. Analyzing Data The next component of BI is analysing the data. Here we take the data that has been gathered and inspect, transform or model it in order to gain new insights that will support our business decision making. Data analysis comes in many different formats and approaches, both quantitative and qualitative. Analysis techniques includes the use of statistical tools, data mining approaches as well as visual analytics or even analysis of unstructured data such as text or pictures. Providing Access In order to support decision making the decision makers need to have access to the data. Access is needed to perform analysis or to view the results of the analysis. The former is provided by the latest software tools that allow end-users to perform data analysis while the latter is provided through reporting, dashboard and scorecard applications. *******************************************************
What
is
Data
Warehouse?
A data warehouse is a relational database that is designed for query and analysis rather than for transaction processing. It usually contains historical data derived from transaction data, but it can include data from other sources. In addition to a relational database, a data warehouse environment includes an extraction, transportation, transformation, and loading (ETL) solution, an online analytical processing (OLAP) engine, client analysis tools, and other applications that manage the process of gathering data and delivering it to business users. A data warehouse is a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non-volatile collection of data in support of management's decision making process(characteristics of Datawarehouse).
Subject-Oriented: A data warehouse can be used to analyze a particular subject area. For example, "sales" can be a particular subject. Integrated: A data warehouse integrates data from multiple data sources. For example, source A and source B may have different ways of identifying a product, but in a data warehouse, there will be only a single way of identifying a product. Time-Variant: Historical data is kept in a data warehouse. For example, one can retrieve data from 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, or even older data from a data warehouse. This contrasts with a transactions system, where often only the most recent data is kept. For example, a transaction system may hold the most recent address of a customer, where a data warehouse can hold all addresses associated with a customer. Non-volatile: Once data is in the data warehouse, it will not change. So, historical data in a data warehouse should never be altered.
*******************************************************
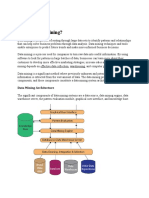
Data Warehouse Architecture
Now we are goanna define each and every terminology in the above picture to facilitate better understanding of the subject.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- What Are The Main Characteristics of Data WarehouseDokument31 SeitenWhat Are The Main Characteristics of Data WarehousekamalshrishNoch keine Bewertungen
- BA-Unit-II NotesDokument39 SeitenBA-Unit-II NotesManish RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse Essentials for Business IntelligenceDokument23 SeitenData Warehouse Essentials for Business IntelligencewanderaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Intelligence?: BI Used For?Dokument9 SeitenBusiness Intelligence?: BI Used For?Kapil GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse: Meaning, Features, Applications, Architecture, Functions, TerminologyDokument13 SeitenData Warehouse: Meaning, Features, Applications, Architecture, Functions, TerminologySunanditha SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment4 120625235331 Phpapp01Dokument12 SeitenAssignment4 120625235331 Phpapp01ChanduChandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing IntroductionDokument41 SeitenBusiness Intelligence and Data Warehousing IntroductionDouglas Albert KikonyogoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Data Warehouse?Dokument9 SeitenWhat Is Data Warehouse?bittuankitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouses and Data Marts: Key for Business IntelligenceDokument22 SeitenData Warehouses and Data Marts: Key for Business IntelligenceNøaman KayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9 Business IntelligenceDokument3 SeitenChapter 9 Business IntelligenceMardhiah RamlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BI Lab FileDokument25 SeitenBI Lab FileAniket Kumar 10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data MiningDokument142 SeitenData Miningmr2b9jfhy4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data WarehouseDokument3 SeitenData WarehouseYashi GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MC0088 Data Warehousing & Data MiningDokument10 SeitenMC0088 Data Warehousing & Data MiningGaurav Singh JantwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Banibrata Das Subject Code: MI0027 Subject Name: Registration No: 510929409 Learning Centre Set No: 01Dokument17 SeitenName: Banibrata Das Subject Code: MI0027 Subject Name: Registration No: 510929409 Learning Centre Set No: 01Pravas DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Made By:-Neha Rana Navneet Jain Paridhi Modi Pawan Deep Kaur Prachi KhandelwalDokument19 SeitenMade By:-Neha Rana Navneet Jain Paridhi Modi Pawan Deep Kaur Prachi Khandelwalnavneetjain_1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Management Information System GTU MBA Data Mining and WarehousingDokument4 SeitenManagement Information System GTU MBA Data Mining and WarehousingRushabh VoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Belga CS Elec 5Dokument4 SeitenBelga CS Elec 5kenbelga99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eserver I5 and Db2: Business Intelligence ConceptsDokument12 SeitenEserver I5 and Db2: Business Intelligence Conceptsitsme_mahe5798Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehousing ManagementDokument7 SeitenData Warehousing Managementtricia quilangNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is need of Big data in Enterprises and how it is different from Business intelligenceDokument56 SeitenWhat is need of Big data in Enterprises and how it is different from Business intelligenceCelina SawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dataware Housing and Data Mining: Homework IDokument6 SeitenDataware Housing and Data Mining: Homework IGagan RandhawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Techniques Used in BI: Data VisualizationDokument2 SeitenTechniques Used in BI: Data VisualizationShabnam KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Build a Powerful Customer DatabaseDokument4 SeitenBuild a Powerful Customer DatabaseSmriti OjhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ibm Assigment 15Dokument16 SeitenIbm Assigment 15cloey hewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics and Functions of Data WarehousesDokument13 SeitenCharacteristics and Functions of Data WarehousesMustefa MohammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dmbok - Bi & DWDokument33 SeitenDmbok - Bi & DWdivyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMIS Chapter 4 SCMSBDokument35 SeitenBMIS Chapter 4 SCMSBNainika ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference between operational CRM database and analytical CRM data warehouseDokument25 SeitenDifference between operational CRM database and analytical CRM data warehouseSiva BhandaruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Mining NotesDokument21 SeitenData Mining NotesaryanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transforming Raw Data into Meaningful Business InsightsDokument7 SeitenTransforming Raw Data into Meaningful Business InsightsMallikarjun ChagamNoch keine Bewertungen
- MI0036 CompletedDokument88 SeitenMI0036 CompletedvishaltopeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Data Analytics and Its TypeDokument9 SeitenModule 2 Data Analytics and Its Typerrrf0813Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT1Dokument37 SeitenUNIT12CSE19 Dharun P100% (1)
- Unit-I NotesDokument47 SeitenUnit-I NotesManish RautNoch keine Bewertungen
- Datamining 2Dokument5 SeitenDatamining 2Manoj ManuNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Business Intelligence?Dokument9 SeitenWhat Is Business Intelligence?Deepanshu DimriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse ConceptsDokument53 SeitenData Warehouse ConceptsVikram Singh TomarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1Dokument22 SeitenUnit 1Vishal ShivhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- BI Tools: Key Software for Business AnalyticsDokument5 SeitenBI Tools: Key Software for Business Analyticssomnath kambleNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpeechDokument3 SeitenSpeechRishabh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- BI Curs 3Dokument41 SeitenBI Curs 3crristtinaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decision Support SystemDokument60 SeitenDecision Support SystemYashaswini KnNoch keine Bewertungen
- DW OverviewDokument2 SeitenDW OverviewBindia ChandelNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Ghazwan Khalid AudaDokument17 SeitenBy Ghazwan Khalid Audaghazwan100% (1)
- Business Intelligence (BI) TechniquesDokument12 SeitenBusiness Intelligence (BI) TechniquesMukund TiwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data AnalyticsDokument5 SeitenData AnalyticsLen FCNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Concepts of Business IntelligenceDokument30 SeitenThe Concepts of Business IntelligenceKishore ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DWH Module 1Dokument29 SeitenDWH Module 1rahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Mod 3 Introduction To OLTP and OLAPDokument6 SeitenAssignment Mod 3 Introduction To OLTP and OLAPPrasad TikamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bigdata U1Dokument11 SeitenBigdata U1NNits7542Noch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse Final ReportDokument19 SeitenData Warehouse Final ReportLi BredNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Warehouse-Ccs341 MaterialDokument58 SeitenData Warehouse-Ccs341 Materialragavaharish463Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bi DW DMDokument39 SeitenBi DW DMSushant SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report For MEDokument49 SeitenProject Report For MEsumitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real-Time Analytics for Operational Intelligence (OIDokument8 SeitenReal-Time Analytics for Operational Intelligence (OIlifeofnameNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karrox Technologies LTD-: AndheriDokument21 SeitenKarrox Technologies LTD-: AndheriPrashant DevaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- FinalsDokument8 SeitenFinalsJessa Sabillo GumagdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SQL Interview QuestionsDokument1 SeiteSQL Interview Questionsvijay.alloju20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Business Intelligence and Data WarehousesDokument4 SeitenUnderstanding Business Intelligence and Data Warehousesvijay.alloju20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Batch Script For Finding New FilesDokument1 SeiteBatch Script For Finding New Filesvijay.alloju20Noch keine Bewertungen
- A QuestionsDokument1 SeiteA Questionsvijay.alloju20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Mapping Architect For Visio OverviewDokument1 SeiteUnderstanding Mapping Architect For Visio Overviewvijay.alloju20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Informatica PDFDokument38 SeitenInformatica PDFKoteswararao TirumalasettyNoch keine Bewertungen