Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemistry Activity 3.4 CuO
Hochgeladen von
Zarina IdrisCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemistry Activity 3.4 CuO
Hochgeladen von
Zarina IdrisCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Two experiments can be carried out to determine the empirical formula of oxides of metal (a) Reducing a known mass
of the metal oxide in hydrogen gas (for less reactive metal : Cu, b, !n) "etal oxide # $ydrogen gas metal # water
%xample: Copper oxide # hydrogen copper # water Cu& # $' Cu # $' &
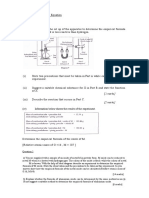
Copper oxide #histle funnel Burning of excess H2 gas (blue flame) Combustion tube Heating Anhydrous calcium chloride to dry $orcelain dish
Zn + H2 !"
the H2 gas
(ctivity )*+ (im: (pparatus "aterials rocedure
recautions ,* ass $ydrogen gas through the combustion tube for a few minutes before the copper oxide is heated* Reason: To remove the air in the combustion tube (the mixture of hydrogen and air can cause explosion when lighted)*
'* The flow of hydrogen gas must be continued throughout heating* Reason: To ensure that air does not enter the combustion tube* )* The hot copper metal is allowed to be cooled in !tream((-.R(/) of hydrogen gas* Reason: To ensure the oxygen from the air does not oxidise the hot copper to copper oxide again*
0ata and &bservation : (pg '+) 0escription ,* Combustion tube # porcelain dish '* Combustion tube # porcelain dish # copper(..) oxide, Cu& )* Combustion tube # porcelain dish # copper, Cu +* Copper 4* &xygen
"ass 1 g ,2*34 ( x ) '5*34 ( y ) '5*)4 (6)
(6 7 x) (y 7 6)
Calculation:
%lement "ass1 g /o* of moles !implest mol ratio %mpirical formula Copper, Cu '5*)4 7 ,2*34 8 ,*9 ,*9 1 9+ 8 5*5'4 , 8 &xygen, & '5*34 7 '5*)4 8 5*+ 5*+ 1,9 8 5*5'4 ,
0iscussion:
,* $ow to ensure copper oxide is completely reduced by hydrogen: (nswer: Repeat heating, ;;** and ;;** until a constant mass (of combustion tube, porcelain dish and copper) is obtained* <'* Copy the question pg24 (i) Collect a sample of $' from the small hole of the combustion tube* (ii) Test the gas by placing a lighted wooden splinter near the mouth of the test tube* (iii) .f the gas burns =uietly without pop sound, this means all the air has been removed completely* 0iscussion ,* The flow of hydrogen gas must be continued throughout the experiment* This is to ensure that air does not enter the combustion tube and mix with hydrogen gas* This may cause explosion '* 0uring cooling, the flow of hydrogen is continued to ensure the oxygen from the air does not oxidise the hot copper to copper(..) oxide* )* The heating, cooling, and weighing processes are repeated until a constant mass is obtained to ensure that all of the copper(..) oxide has been reduced into copper* Conclusion: %mpirical formula of copper oxide is
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Blast Furnace Year 10Dokument10 SeitenBlast Furnace Year 10Neldson TrancosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xi Neet Iseet Chemistry PDFDokument21 SeitenXi Neet Iseet Chemistry PDFFATHIMA80% (5)
- Chemistry Exercise - Chap 3Dokument2 SeitenChemistry Exercise - Chap 3eddielawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reducing agent in copper nitrate reactionDokument18 SeitenReducing agent in copper nitrate reactionrania samirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 1212 Exam KeyDokument6 SeitenChem 1212 Exam KeyChris HeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blast FurnaceDokument91 SeitenBlast FurnaceSarbajitManna100% (1)
- Ultimate AnalysisDokument11 SeitenUltimate Analysisgiridaran100% (1)
- On Steel MakingDokument58 SeitenOn Steel Makingallan arthur bare100% (1)
- Smelting Is A Form Of: Blast FurnaceDokument31 SeitenSmelting Is A Form Of: Blast FurnaceLalaine Arabit100% (1)
- Latihan Empirical FormulaDokument11 SeitenLatihan Empirical FormulaRusdi Chodeng100% (1)
- Revision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsDokument4 SeitenRevision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsJiaRenTeohNoch keine Bewertungen
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Chemical Reactions and Equations PDFDokument4 SeitenCBSE Class 10 Chemistry Worksheet - Chemical Reactions and Equations PDFMalancha high school HS0% (1)
- SPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsDokument80 SeitenSPM Chemistry Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundsManisha Sekaran MuniandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rate of ReactionDokument20 SeitenRate of ReactionHAKIMIN_KHAIRUL3674Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Empirical Formula of Copper II OxideDokument4 SeitenThe Empirical Formula of Copper II Oxideみゆ マイクロNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - DwiDokument2 SeitenModule 62 Rate of Reaction Concentration Effect - Dwirudi_zNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 SchemeDokument41 SeitenChemistry Module Perfect Score 2009 Schemespm_victim2010100% (5)
- A567 ORP Management in Wastewater As An Indicator of Process EfficiencyDokument2 SeitenA567 ORP Management in Wastewater As An Indicator of Process EfficiencyFelipe BrainNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is a Blast Furnace? The Extraction of IronDokument10 SeitenWhat is a Blast Furnace? The Extraction of IronSapan KansaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 - Salts (+experiment)Dokument4 SeitenForm 4 - Salts (+experiment)kanryu_zonasNoch keine Bewertungen
- PEKA Form 4 Chemistry Experiments ListDokument14 SeitenPEKA Form 4 Chemistry Experiments Listmagentiran100% (1)
- Analysing electric fields and charge flowDokument45 SeitenAnalysing electric fields and charge flowNormawarni HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soluble and Insoluble Salts GuideDokument5 SeitenSoluble and Insoluble Salts GuideAzrel YusoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIChO 2013 Results ReportDokument16 SeitenMIChO 2013 Results ReportYau Ching KoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Add Maths Paper 1 Marking SchemeDokument6 SeitenSPM Percubaan 2007 SBP Add Maths Paper 1 Marking SchemeChinWynn.com50% (2)
- Chemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07Dokument21 SeitenChemistry Answer Scheme P123 Trial SBP 07hudazzakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GasDokument12 SeitenGasJesza Mei GanironNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS Addm Paper2 Trial SPM 08Dokument13 SeitenMS Addm Paper2 Trial SPM 08Mohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- Answer Booklet Sem 2 BOOK PDFDokument17 SeitenAnswer Booklet Sem 2 BOOK PDFBryanLeeChienYungNoch keine Bewertungen
- MRSM Add Maths p1 2004Dokument11 SeitenMRSM Add Maths p1 2004murulikrishan100% (3)
- Physics Chapter 4 Form 4 DEFINITIONDokument3 SeitenPhysics Chapter 4 Form 4 DEFINITIONAnnie HonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems and Solutions To The MIChO Selection Camp 2015: Third PhaseDokument38 SeitenProblems and Solutions To The MIChO Selection Camp 2015: Third PhaseYau Ching Koon100% (1)
- Nov 2006 Paper 3 Mark SchemeDokument12 SeitenNov 2006 Paper 3 Mark SchemeilnukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix: Data BookletDokument13 SeitenAppendix: Data BookletAbdullah Nazir100% (1)
- STPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme TerengganuDokument17 SeitenSTPM Trials 2009 Chemistry Answer Scheme Terengganusherry_christyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet 1 Chemistry F4 Chapter3 Chemical Equation AnswerDokument2 SeitenWorksheet 1 Chemistry F4 Chapter3 Chemical Equation AnswerIpul Catur0% (1)
- JUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaDokument14 SeitenJUJ Pahang SPM 2014 Biology K3 Set 2 SkemaCikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2012 PSPM Kedah AddMath 2 W AnsDokument31 Seiten2012 PSPM Kedah AddMath 2 W Ansjee2kk50% (4)
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2Dokument11 SeitenSPM Chemistry Form 5 Chapter 2kslpeter87Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionDokument22 SeitenSPM Chemistry Form 5 – Oxidation and ReductionCk OoiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Johor-Answer P2-Trial SPM 2007Dokument8 SeitenJohor-Answer P2-Trial SPM 2007kamalharmozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PMTLDokument314 SeitenPMTLRahoul Chicharito RooneyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integration SPM ADokument1 SeiteIntegration SPM ARosmizar Ahmad0% (1)
- 2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim1Dokument3 Seiten2012 TJC MA H2 P1 Prelim1focuscharade_8247490Noch keine Bewertungen
- STPM Che2 Ans (SBH)Dokument8 SeitenSTPM Che2 Ans (SBH)SimPor100% (3)
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 12 Solution of TrianglesDokument5 SeitenForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 12 Solution of TrianglesManisha Sekaran MuniandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 BerjawapanDokument15 SeitenSPM 4551 2006 Biology k2 Berjawapanpss smk selandarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SPM 2016 SaltDokument2 SeitenChemistry SPM 2016 SaltAzie Nurul AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Experiment Is Conducted To Determine The Rate of Reaction Between 25 CMDokument3 SeitenAn Experiment Is Conducted To Determine The Rate of Reaction Between 25 CMJuni FarhanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ModulDokument39 SeitenModulThanabalan MunuswamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)Dokument12 SeitenH2 Chemistry Prelims 2011 (Planning)iuhihzNoch keine Bewertungen
- 46M PDFDokument106 Seiten46M PDFpei qiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acids and Bases Chapter SummaryDokument3 SeitenAcids and Bases Chapter SummaryjihuhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module The MoleDokument44 SeitenModule The MoleChin Chin YipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determining the Empirical Formula of CuODokument4 SeitenDetermining the Empirical Formula of CuOみゆ マイクロNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3Dokument3 SeitenTopic 3Kaiswan GanNoch keine Bewertungen
- By Chan, Sam and EllyDokument10 SeitenBy Chan, Sam and EllyrajatguptNoch keine Bewertungen
- CFN05 ThereductionofcopperoxideDokument5 SeitenCFN05 Thereductionofcopperoxidechikohoraarnold268Noch keine Bewertungen
- Extracting metals from oresDokument4 SeitenExtracting metals from oreshnl27Noch keine Bewertungen
- Blastfurnace 140331091507 Phpapp02Dokument10 SeitenBlastfurnace 140331091507 Phpapp02Farah Moiz AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solid FuelsDokument5 SeitenSolid FuelsPritamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaseous FuelsDokument8 SeitenGaseous FuelsvaibhavNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIR AND WATER COMPOSITIONDokument16 SeitenAIR AND WATER COMPOSITIONtavongaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Studies of A Quenched Cupola: Ricardo E. Aristizábal, Paula A. Pérez Seymour Katz Mark E. BauerDokument10 SeitenStudies of A Quenched Cupola: Ricardo E. Aristizábal, Paula A. Pérez Seymour Katz Mark E. BauerDiego MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- The History of Oxygen-Acetylene WeldingDokument3 SeitenThe History of Oxygen-Acetylene WeldingNur Halizha ErilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prime Number Maze: Name: DateDokument2 SeitenPrime Number Maze: Name: DateZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- WhymathisimportantDokument6 SeitenWhymathisimportantZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polygons: Daily Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 1 2009Dokument4 SeitenPolygons: Daily Lesson Plan Mathematics Form 1 2009Zarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Label PDP Abad 21Dokument7 SeitenLabel PDP Abad 21Zarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itemanalisismath pt1 Pat 2015 F1zarinaDokument63 SeitenItemanalisismath pt1 Pat 2015 F1zarinaZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Integer LemahDokument2 SeitenInteger LemahZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide (MgODokument4 SeitenDetermination of the Empirical Formula of Magnesium Oxide (MgONaqibah AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra Nota 3Dokument1 SeiteAlgebra Nota 3Zarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Worksheet on Algebraic Expressions and EquationsDokument1 SeiteMath Worksheet on Algebraic Expressions and EquationsZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRYDokument36 SeitenCHEMISTRYZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peka 1 (Activity 2.4)Dokument9 SeitenPeka 1 (Activity 2.4)Zarina Idris50% (2)
- MGODokument5 SeitenMGOZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Score A Chemstry ADokument10 SeitenHow To Score A Chemstry AZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- State Rate of Diffusion: Solid Liquid GASDokument4 SeitenState Rate of Diffusion: Solid Liquid GASZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exerciese 5.1. The Electron Arrangement of Elements With Proton Number 1 To 20. Number of Valence ElectronsDokument2 SeitenExerciese 5.1. The Electron Arrangement of Elements With Proton Number 1 To 20. Number of Valence ElectronsZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3.2 MgoDokument2 SeitenActivity 3.2 MgoZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Activity 3.2 MgoDokument2 SeitenActivity 3.2 MgoZarina IdrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- A_level_Chemistry_Core_Practical_10_-_Electrochemical_CellsDokument5 SeitenA_level_Chemistry_Core_Practical_10_-_Electrochemical_CellsshellodkomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduction Swelling of Iron OxidesDokument32 SeitenReduction Swelling of Iron OxidesMuykundan MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanism of Rusting of Iron Electrochemical Theory of RustingDokument2 SeitenMechanism of Rusting of Iron Electrochemical Theory of RustingJai BharatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bioenergetics and Biological Oxidation 2: Biochemistry: Shift 1 - Trans 4Dokument9 SeitenBioenergetics and Biological Oxidation 2: Biochemistry: Shift 1 - Trans 4Gemay DanglayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculation of The Platinum's Active Surface PDFDokument3 SeitenCalculation of The Platinum's Active Surface PDFUriel Cedeño AntunezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 - ElectrochemicalDokument29 SeitenChapter 2 - ElectrochemicalEDU Academic Programs CoordinatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxidation and Dissolution of Tungsten Carbide Powder in WaterDokument9 SeitenOxidation and Dissolution of Tungsten Carbide Powder in WaterManea MihaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes English Medium by Goswami SirDokument20 SeitenChemistry Notes English Medium by Goswami SirManoj GoswamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- iGCSE Chemistry Extraction of MetalsDokument57 SeiteniGCSE Chemistry Extraction of MetalsJuman AlbuhaisiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology An Australian Focus 5th Edition Knox Test BankDokument30 SeitenBiology An Australian Focus 5th Edition Knox Test BankAndrewMorrisbknaf100% (16)
- BLB 14e Ch20 Worked ExamplesDokument47 SeitenBLB 14e Ch20 Worked ExamplesthebestNoch keine Bewertungen
- P-Block Elements and Group TrendsDokument5 SeitenP-Block Elements and Group TrendsSnehashish PandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Corrosion PDFDokument18 SeitenFundamentals of Corrosion PDFAmrul KaishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reduction of Nitrate by Zero Valent Iron (ZVI) - Based MaterialsDokument16 SeitenReduction of Nitrate by Zero Valent Iron (ZVI) - Based MaterialsTatiana ArturiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRX127 Data SheetDokument8 SeitenPRX127 Data Sheettomgreen2011Noch keine Bewertungen
- PMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Dokument46 SeitenPMC National MDCAT Syllabus 2020 19-10-2020Mughees AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tabakovic 2018Dokument36 SeitenTabakovic 2018hayet debbichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solutions For Battery Electric VehiclesDokument16 SeitenSolutions For Battery Electric VehiclesPankaj DuttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science PQ2Dokument10 SeitenScience PQ2satyabrata sahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDokument51 SeitenAqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenGopi SureshNoch keine Bewertungen
- State-Of-The-Art of Battery State-Of-Charge DeterminationDokument19 SeitenState-Of-The-Art of Battery State-Of-Charge Determinationyasvanthkumar sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Durability of Materials in Molten Aluminum AlloysDokument11 SeitenReview Durability of Materials in Molten Aluminum AlloysJavier Alejandro Araujo MoreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxid Numb AnsDokument3 SeitenOxid Numb AnsUday Prakash Sahu100% (2)
- Szabo articolChemicalPapersDokument4 SeitenSzabo articolChemicalPapersTaufik HidayatullohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Preparation of 0.05M Standard Solution of Ferrous Ammonium SulfateDokument3 SeitenPreparation of 0.05M Standard Solution of Ferrous Ammonium SulfateCR7STUDIO 7Noch keine Bewertungen