Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
H 5
Hochgeladen von
scribd388Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
H 5
Hochgeladen von
scribd388Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
In the human body, the heart is usually situated in the middle of the thorax with the largest part
of the heart slightly offset to the left, although sometimes it is on the right (see dextrocardia), underneath the sternum. The heart is usually felt to be on the left side because the left heart (left ventricle) is stronger (it pumps to all body parts). The left lung is smaller than the right lung because the heart occupies more of the left hemithorax. The heart is fed by the coronary circulation and is enclosed by a sac known as the pericardium; it is also surrounded by the lungs. The pericardium comprises two parts: the fibrous pericardium, made of dense fibrous connective tissue, and a double membrane structure (parietal and visceral pericardium) containing a serous fluid to reduce friction during heart contractions. The heart is located in the mediastinum, which is the central sub-division of the thoracic cavity. The mediastinum also contains other structures, such as the esophagus and trachea, and is flanked on either side by the right and left pulmonary cavities; these cavities house the lungs.[16] The apex is the blunt point situated in an inferior (pointing down and left) direction. A stethoscope can be placed directly over the apex so that the beats can be counted. It is located posterior to the 5th intercostal space just medial of the left mid-clavicular line. In normal adults, the mass of the heart is 250350 grams (912 oz), or about twice the size of a clenched fist (it is about the size of a clenched fist in children), but an extremely diseased heart can be up to 1000 g (2 lb) in mass due to hypertrophy. It consists of four chambers, the two upper atria and the two lower ventricles.
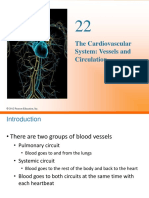
Functioning
In mammals, the function of the right side of the heart is to collect de-oxygenated blood, in the right atrium, from the Human heart removed from body (via superior and inferior vena cavae) and pump it, through the tricuspid valve, via the right ventricle, into the lungs a 64-year-old man (pulmonary circulation) so that carbon dioxide can be exchanged for oxygen. This happens through the passive process of diffusion. The left side (see left heart) collects oxygenated blood from the lungs into the left atrium. From the left atrium the blood moves to the left ventricle, through the bicuspid valve (mitral valve), which pumps it out to the body (via the aorta). On both sides, the lower ventricles are thicker and stronger than the upper atria. The muscle wall surrounding the left ventricle is thicker than the wall surrounding the right ventricle due to the higher force needed to pump the blood through the systemic circulation. Starting in the right atrium, the blood flows through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. Here, it is pumped out the pulmonary semilunar valve and travels through the pulmonary artery to the lungs. From there, oxygenated blood flows back through the pulmonary vein to the left atrium. It then travels through the mitral valve to the left ventricle, from where it is pumped through the aortic semilunar valve to the aorta. The aorta forks and the blood is divided between major arteries which supply the upper and lower body. The blood travels in the arteries to the smaller arterioles and then, finally, to the tiny capillaries which feed each cell. The (relatively) deoxygenated blood then travels to the venules, which coalesce into veins, then to the inferior and superior venae cavae and finally back to the right atrium where the process began. The heart is effectively a syncytium, a meshwork of cardiac muscle cells interconnected by contiguous cytoplasmic bridges. This relates to electrical stimulation of one cell spreading to neighboring cells.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Temple FestivalsDokument1 SeiteTemple Festivalsscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Religion in Kerala Hinduism 56.2% Islam 24.7% Christianity 19.0% Others 0.1%Dokument1 SeiteReligion in Kerala Hinduism 56.2% Islam 24.7% Christianity 19.0% Others 0.1%scribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- K 31Dokument1 SeiteK 31scribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Railways: The Main Portico of The TrivandrumDokument1 SeiteRailways: The Main Portico of The Trivandrumscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Culture: A Kathakali ArtistDokument1 SeiteCulture: A Kathakali Artistscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Government and Administration: Population Density Map of KeralaDokument1 SeiteGovernment and Administration: Population Density Map of Keralascribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fisheries: A Typical Paddy Field in KeralaDokument1 SeiteFisheries: A Typical Paddy Field in Keralascribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Climate: Periyar RiverDokument1 SeiteClimate: Periyar Riverscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- SubdivisionsDokument1 SeiteSubdivisionsscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- DemographicsDokument1 SeiteDemographicsscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Economy: Tempore Justices As of 2012Dokument1 SeiteEconomy: Tempore Justices As of 2012scribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flora and Fauna: Southwest Monsoon Clouds Over AlappuzhaDokument1 SeiteFlora and Fauna: Southwest Monsoon Clouds Over Alappuzhascribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- SecurityDokument1 SeiteSecurityscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Etymology: Ancient Religious TextsDokument1 SeiteEtymology: Ancient Religious Textsscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- Geography: Post Colonial PeriodDokument1 SeiteGeography: Post Colonial Periodscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Coconut Palms Can Be Found All Over Kerala Bharathappuzha RiverDokument1 SeiteCoconut Palms Can Be Found All Over Kerala Bharathappuzha Riverscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Pre HistoryDokument1 SeitePre Historyscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Colonial EraDokument1 SeiteColonial Erascribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Tipu Sultan's Fort at Palakkad View From Outside The Northern WallDokument1 SeiteTipu Sultan's Fort at Palakkad View From Outside The Northern Wallscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Neacyndi) .: Early Medieval PeriodDokument1 SeiteNeacyndi) .: Early Medieval Periodscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Location of Kerala (Marked in Red) in India: Coordinates (Trivandrum) : 8.5074°N 76.973°E Country IndiaDokument1 SeiteLocation of Kerala (Marked in Red) in India: Coordinates (Trivandrum) : 8.5074°N 76.973°E Country Indiascribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- KeralaDokument1 SeiteKeralascribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- See AlsoDokument1 SeiteSee Alsoscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Windows 9xDokument1 SeiteWindows 9xscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alternative ImplementationsDokument1 SeiteAlternative Implementationsscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- October 2013 Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 NT 6.3.9600 Current 11 11Dokument1 SeiteOctober 2013 Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 NT 6.3.9600 Current 11 11scribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
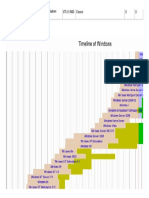
- Usage Share: The Windows Family TreeDokument1 SeiteUsage Share: The Windows Family Treescribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Windows 3.0 and 3.1: Windows 1.0, The First Version, Released in 1985Dokument1 SeiteWindows 3.0 and 3.1: Windows 1.0, The First Version, Released in 1985scribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Windows CEDokument1 SeiteWindows CEscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Timeline of ReleasesDokument1 SeiteTimeline of Releasesscribd388Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathDokument2 SeitenPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease: Chest Pain Muscle Weakness Shortness of BreathCyril Jane Caanyagan AcutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDokument3 SeitenHypertension Nursing Care Plangeng gengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Varicose VeinsDokument2 SeitenVaricose VeinsroycNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyDokument19 SeitenTest Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyMichael Burger100% (34)
- Atrial Fibrilliation Part 1 Pathophysiology C Cottrell PDFDokument5 SeitenAtrial Fibrilliation Part 1 Pathophysiology C Cottrell PDFholly theressaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Coronary Artery SpasmDokument14 SeitenManagement of Coronary Artery SpasmdcicareNoch keine Bewertungen
- IAS AneurysmDokument13 SeitenIAS AneurysmE'len HamidahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.02 Thorax - Heart - Dr. MalakDokument31 Seiten1.02 Thorax - Heart - Dr. MalakJedoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angiographic ThoracalisDokument22 SeitenAngiographic ThoracalisermaendahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- European Examination in General Cardiology (EEGC) : Jim Hall Celine CarreraDokument37 SeitenEuropean Examination in General Cardiology (EEGC) : Jim Hall Celine CarreraTasya MDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest X - RayDokument49 SeitenChest X - RayLyk TiglaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case ReportDokument9 SeitenCase ReportAlmah Mae Duro-onNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sas 12Dokument5 SeitenSas 12Sistine Rose LabajoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (Myocardial Infarction and Unstable Angina) (Clinical) - LecturioDokument36 SeitenAcute Coronary Syndrome (Myocardial Infarction and Unstable Angina) (Clinical) - Lecturiokujtimepira2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Path-09 CARDIODokument18 SeitenPath-09 CARDIOCarlos Fernando Banegas FloresNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCI9 Q1M2 PNHSDokument30 SeitenSCI9 Q1M2 PNHSsai deveraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Positioning ClientsDokument2 SeitenPositioning ClientsROBERT C. REÑA, BSN, RN, MAN (ue)100% (13)
- Chapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StripDokument7 SeitenChapter 5: Analyzing A Rhythm StriptellyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arteritis TakayasuDokument7 SeitenArteritis TakayasuGina ButronNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wingspan StentDokument6 SeitenWingspan StentneureportNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body - Heart and Circulatory System PDFDokument113 SeitenHuman Body - Heart and Circulatory System PDFWalter Silva Serrano100% (5)
- Conduction System of The HeartDokument9 SeitenConduction System of The Hearthirap0% (1)
- Simpo 14 Sept 19Dokument71 SeitenSimpo 14 Sept 19Henry SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Echocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is ADokument23 SeitenEchocardiogram: Echocardiogram, Also Known As Echocardiography, or Heart Ultrasound Is AKarl RobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A StrokeDokument10 SeitenWhat Is A StrokeRatnaPrasadNalamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine DamsDokument657 SeitenMedicine DamsSubhashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest Pain ProtocolDokument7 SeitenChest Pain Protocolomar kmr97Noch keine Bewertungen
- 22 Lecture PresentationDokument88 Seiten22 Lecture PresentationLeilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood Flow and TransportDokument7 SeitenBlood Flow and Transporttarekegn balangoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Han Cmu 0041E 10605Dokument155 SeitenHan Cmu 0041E 10605Buse Nur AkçayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Von EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionVon EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (404)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsVon EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityVon EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (31)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisVon EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (42)