Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
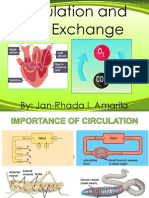
What Does The Circulatory System Do? (What Is Its Function?)
Hochgeladen von
jmmos207064Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What Does The Circulatory System Do? (What Is Its Function?)
Hochgeladen von
jmmos207064Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
What does the circulatory system do? (What is its function?) 1. Delivers food and oxygen to body cells.
2. Carries carbon dioxide and other waste products away from cells. 3. The Cardiovascular System . Three !a"or #lements $ %eart& 'lood (essels& ) 'lood 1. 1. The %eart* cardiac muscle tissue 2. highly interconnected cells 3. four chambers 1. +ight atrium 2. +ight ventricle 3. ,eft atrium . ,eft ventricle LAYERS OF THE HEART 3 layers within a sac: Endocardium (Inner !yocardium (!iddle E"icardium or #isceral "ericardium (Outer surrounded $y "arietal "ericardium !yocardium is the thic-est layer .ni/ue because of the presence of I%TER&ALATE' 'IS&S allows a single stimulation to cause all cardiac muscle fibers to contract. The 0ericardium The heart is covered by a thin& tough sac called the "ericardium( !)S&LES *ITHI% THE &HA!+ERS PAPILLARY MUSCLES , -ound within the cham$er walls E.tend into CHORDAE TENDINAE attached to #al#es 1natomy of the heart The heart has 2 atria 2upper chambers3. 'oth atria have very thin walls used to hold the blood 2waiting room3. The heart has 2 ventricles 2lower chambers3. The ventricles have very thic- walls 2blood is pumped here3. (alves The chambers of the heart are separated by valves. The valves prevent the flow of blood bac-wards. LO&ATIO% OF THE HEART Hollow/ muscular or0an 1!I is at the 2th le-t !&L *ei0hs 3 l$( F)%&TIO%S o- the Transports 42 from the lungs to tissues of the body
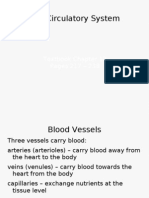
Delivers nutrients from the 56T to all systems Carries wastes from tissues to the excretory system Serves as a route for hormones& en7ymes& and other chemicals to reach target tissues 'lood (essels 3( Arteries ,,carry $lood away -rom the heart ,,usually s"urt $lood when cut ,,all e.ce"t the "ulmonary artery carry o.y0enated $lood ,,thic4 walled and elastic "ulse: e."ansion and contraction o- the artery walls in res"onse to the heart$eat 5eins ,,carry $lood toward the heart ,,contain #al#es ,,closer to the $ody sur-ace than the arteries ,,all e.ce"t the "ulmonary #ein carry deo.y0enated $lood ,,thinner/ less muscular and elastic than arteries ,,de"end u"on muscle and dia"hra0m mo#ements -or $lood -low &a"illaries ,,most numerous #essels ,,connect arteries to #eins ,,microsco"ic/ one cell thic4 walls ,,site o- much e.chan0e $etween the $lood and the intracellular -luid (lym"h $y di--usion 'lood 'lood 8 a connective tissue made up of blood cells and a li/uid called blood plasma. 1bout 9 : of your body mass 1bout .;* ;.< ,iters in an adult human !en 8 ;.< ,iters =omen 8 .; ,iters 0regnant woman 8 ;.> ,iters The ?unctions of 'lood Delivers@ 0ic-s .p@ - Autrients * waste -idneys - 4xygen& =ater& minerals * carbon dioxide lungs - %ormones and en7ymes * heat s-in - pollutants The 0arts of 'lood 1. 0lasma 8carries everything 2. +ed 'lood Cells 8 2+'C3 gas exchange 3. =hite blood Cells 8 2='C3 fight infection . 0latelets 8 clotting 'lood Composition 1lasma 226 (li7uid "art o- the $lood 8 +lood &ells 926
0lasma* nonliving Bellow li/uid 2C2: %243 D : nutrients& salts& urea& hormones Carries@ +'C& ='C& 0latelets& Carbon dioxide& food and waste ',44D C#,, TB0#S Red +lood &ells : Erythrocytes most numerous $iconca#e disc sha"ed smaller than white $lood cells/ lar0er than "latelets no nucleus when mature "roduced in the red marrow olon0 $ones destroyed in the li#er and s"leen contain the iron "rotein com"ound HE!O;LO+I% whose chie- -unction is to com$ine with o.y0en and carry it to the cells +ed 'lood Cells* living ; million in 1 drop of blood 2most common3 Shape 8 donut ,ive approximately 12>*12; days %emoglobin 8 oxygen containing pigment 'inds to oxygen and carries it to the cells 5ives red blood cells its red color =hite blood cells* living 1E1* ,eu-ocytes =hite blood cells are larger than red blood cells& but there are less of them. D>>> in one drop of blood ?unction of =hite 'lood Cells surround& engulf and digest bacteria ) viruses 2phagocytosis3 1ttac- bacteria and viruses
*hite +lood cells ,,lar0est $lood cells ,,a$out </=== "er dro" o- $lood ,,most are -ormed in the $one marrow or in the lym"h tissue ,,mostly "rotect the $ody a0ainst diseases $y -ormin0 anti$odies or en0ul-in0 $acteria Fi#e ty"es $ neutrophils& lymphocytes& eosinophils& basophils& and monocytes. 0latelets* living 'its of cells also called Aeutrophils ,ive for approximately 1> days ?unction of 0latelets creates fibrin 8 en7yme that helps clot blood 2tiny threads seal cuts3
3( 1latelets ,,smallest $lood cells (-ra0ments ,,32=/=== to 3==/=== "er dro" o- $lood ,,needed -or clottin0 >> In 0eneral/ the $lood is a -luid tissue hel"in0 to maintain homeostasis -or all cells in the $ody( 3( Trans"ort o- needed su$stances to $ody cells( (o.y0en/ amino acids/ 0lucose/ -atty acids/ 0lycerol/ salts/ etc( ?( Trans"ort o- wastes -rom cells( (urea/ water/ car$on dio.ide in the -orm o- the $icar$onate ion 3( Hel"s to maintain a constant $ody tem"erature( 9( Aids the $ody in -i0htin0 disease( +LOO' FLO* THRO);H THE HEART +O'Y (S5& @ I5& +1 tricuspid valve opens +( tricuspid valve closes +( muscles contract pulmonary semilunar valves open pulmonary artery lungs L)%;S pulmonary vein ,1 mitral valve opens ,( mitral valve closes ,( muscles contract aortic semilunar valve opens aorta distribution 3( In-erior @ su"erior #ena ca#a ?( Ri0ht atrium 3( Tricus"id #al#e 9( Ri0ht #entricle 2( 1ulmonary semilunar #al#e A( 1ulmonary arteries (+LOO' TO THE L)%;S B ;AS EC&HA%;E D E( 1ulmonary #eins <( Le-t Atrium F( +icus"id: mitral #al#e 3=( Le-t #entricle 33( Aortic semilunar #al#e 3?( Aorta
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Human Body Systems Chart With Pictures Answers-Option ADokument3 SeitenHuman Body Systems Chart With Pictures Answers-Option AJamie Sims100% (2)
- Ec LogbookDokument1 SeiteEc Logbookjmmos20706463% (8)
- Life TrapsDokument5 SeitenLife Trapsjmmos207064100% (1)
- Anatomy and Pathophysiology of AnemiaDokument9 SeitenAnatomy and Pathophysiology of AnemiaDarlen Rabano88% (8)
- Body Systems Chart KeyDokument2 SeitenBody Systems Chart KeyJamie Sims75% (4)
- Draft Concept Note On Goat RearingDokument7 SeitenDraft Concept Note On Goat Rearinganoop_100% (1)
- Osh Committee 2017Dokument3 SeitenOsh Committee 2017jmmos207064100% (2)
- OUTBREAK Movie QuestionsDokument4 SeitenOUTBREAK Movie Questionsjmmos207064100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Emergency Medical CareDokument19 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Emergency Medical Carejmmos207064100% (1)
- Equine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding, and Stud ManagementDokument383 SeitenEquine Reproductive Physiology, Breeding, and Stud Managementfrancisco_aguiar_22100% (2)
- Wings of Arian - Devri WallsDokument528 SeitenWings of Arian - Devri WallsJoseph Dela Cruz100% (4)
- Jareds BoyDokument31 SeitenJareds BoyAnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System: What Is The Job of The Circulatory System?Dokument19 SeitenCirculatory System: What Is The Job of The Circulatory System?SuaidahRahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Transport Form 5Dokument107 SeitenSPM Transport Form 5Vjayan DharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Human Circulatory System OFFICIALDokument65 SeitenGrade 9 Human Circulatory System OFFICIALEsther SparksNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.cardiovascular System (CVS)Dokument99 Seiten7.cardiovascular System (CVS)frankndunguru9519Noch keine Bewertungen
- Two Pathways: Importance of Circulatory SystemDokument32 SeitenTwo Pathways: Importance of Circulatory SystemsiennaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UK Year 6 Biology RevisionDokument9 SeitenUK Year 6 Biology RevisionabhishekkaushalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 3 Cardiovascular SytemDokument37 SeitenGroup 3 Cardiovascular Sytemsophiapelayo326Noch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Circulatory SystemDokument14 SeitenAnimal Circulatory System'Immey Ssi MoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr10 Science Exam ReviewDokument18 SeitenGr10 Science Exam ReviewPurneet Sidhu100% (1)
- Edexcel As Biology Unit 1 Exam Revision NotesDokument19 SeitenEdexcel As Biology Unit 1 Exam Revision Notesfockoffu100% (1)
- Fungsi Darah, Yaitu Sebagai BerikutDokument6 SeitenFungsi Darah, Yaitu Sebagai BerikutjokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory & Circulatory SystemDokument6 SeitenRespiratory & Circulatory SystemJanelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kelompok 2: Sirkulasi DarahDokument14 SeitenKelompok 2: Sirkulasi DarahjokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorDokument6 SeitenBone Marrow Is The Soft, Flexible, Vascular Tissue Found in The Hollow InteriorIanne Sandra SorrosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Dokument39 SeitenBiology Form 5 Notes Chapter 1Mayghen SelvanayagamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adv Bio ReportDokument26 SeitenAdv Bio ReportJan-Rhada Ilao AmarilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- HO Sistem Peredaran DarahDokument8 SeitenHO Sistem Peredaran DarahhayrachzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDokument60 SeitenCirculation and Transportation in Gen - Bio 2 For Grade 11 STEMDead Eye100% (1)
- Summary Unit 4 3esoDokument9 SeitenSummary Unit 4 3esoMeneses Oriano SaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatorysys PP White BackgroundDokument70 SeitenCirculatorysys PP White Backgroundapi-246864303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument18 SeitenCirculatory SystemLiz HackettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competitive Exams: Heart: ExamraceDokument3 SeitenCompetitive Exams: Heart: Examraceathira vijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument9 SeitenCirculatory SystemccparangueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation CSDokument21 SeitenPresentation CSJeffreyYtienzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Circulatory System L2.2Dokument53 SeitenHuman Circulatory System L2.2SUBSCRIBE TO PewDiePieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument3 SeitenCirculatory SystemtadashiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System in MammalsDokument8 SeitenCirculatory System in MammalsObiora Ekene HilaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System - Lecture IIDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular System - Lecture IIpragantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal TransportDokument20 SeitenAnimal TransportFeranmi AkinboboyeNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Medical PhysiologyDokument10 SeitenWhat Is Medical Physiologyمنتظر اللاميNoch keine Bewertungen
- CirculatoryDokument9 SeitenCirculatoryJason Vinluan Carinan100% (1)
- Circulatory SystemDokument3 SeitenCirculatory SystemJeffrey ErazoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular SystemWayneNoch keine Bewertungen
- G9 Circulatory SystemDokument16 SeitenG9 Circulatory SystemEleazar Valencia IIINoch keine Bewertungen
- B SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurDokument10 SeitenB SC 4 Sem BiotechHuman Phy Heart by DR Santosh ThakurMicaela Marcela Baldwin BarrigaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDokument12 SeitenFunctions of The Circulatory SystemJulliane OrtizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System AnatomyDokument54 SeitenCardiovascular System AnatomyAyen LatosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIO 103 Circulation, Respiration, Excretion L12 Fall, 2018Dokument29 SeitenBIO 103 Circulation, Respiration, Excretion L12 Fall, 2018Demi RoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 9 1.3 LessonDokument31 SeitenScience 9 1.3 LessonHdisbdbd NfjdnbdncNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Blood Circulation Doc2Dokument10 SeitenChapter 2 Blood Circulation Doc2Kazariyah KasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceDokument29 SeitenCirculation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceHasan Mahmud Maruf 1621513630Noch keine Bewertungen
- ABT Anatomy & PhysiologyDokument85 SeitenABT Anatomy & PhysiologyABT SchoolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument3 SeitenCirculatory SystemMark ArceNoch keine Bewertungen
- BiologyDokument5 SeitenBiologyorlaconn3Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2001 SeniorSci 2u Notes Bionics SavDokument5 Seiten2001 SeniorSci 2u Notes Bionics Savkatya15Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flowing of Blood in HeartDokument5 SeitenFlowing of Blood in HeartAkshay BahetyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 6 DLP 1 - Parts of The Circulatory System RepairedDokument11 SeitenScience 6 DLP 1 - Parts of The Circulatory System RepairedMARIFE T. BAUINoch keine Bewertungen
- Human BloodDokument3 SeitenHuman BloodAshrul Anwar MukhashenNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransportationDokument10 SeitenTransportationSarika SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- #11 - Blood: Blood and The Circulatory SystemDokument2 Seiten#11 - Blood: Blood and The Circulatory SystemrsowmyasriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument31 SeitenCirculatory SystemKalev MaricqNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Body Final DraftDokument3 SeitenThe Human Body Final DraftPratyush AcharyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparative Anatomy - Circulatory SystemDokument78 SeitenComparative Anatomy - Circulatory SystemElaine MacasaetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionVon EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human Body: 25 Fantastic Projects Illuminate How the Body WorksVon EverandThe Human Body: 25 Fantastic Projects Illuminate How the Body WorksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionVon EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- List OF Requirements: Employees' Compensation CommissionDokument2 SeitenList OF Requirements: Employees' Compensation Commissionjmmos207064100% (2)
- Scorecard For Week 16 of 2023Dokument121 SeitenScorecard For Week 16 of 2023jmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Emergency Protocol ProcedureDokument14 SeitenEmergency Protocol Procedurejmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conectys Clinic ProceduresDokument13 SeitenConectys Clinic Proceduresjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rula SheetDokument2 SeitenRula Sheetjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Employees' Compensation CommissionDokument38 SeitenEmployees' Compensation Commissionjmmos207064100% (1)
- Facilitator's Guide Phone Etiquette - Handling Difficult CustomersDokument1 SeiteFacilitator's Guide Phone Etiquette - Handling Difficult Customersjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Facilitator's Guide Phone Etiquette - Handling Difficult CustomersDokument1 SeiteFacilitator's Guide Phone Etiquette - Handling Difficult Customersjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Day 1 - History and Philosophy of Loss ControlDokument10 SeitenDay 1 - History and Philosophy of Loss Controljmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Free Policy2Dokument2 SeitenDrug Free Policy2jmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECHNRDokument1 SeiteECHNRjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Training Outline: Phone Etiquette - Handling Difficult CustomersDokument1 SeiteTraining Outline: Phone Etiquette - Handling Difficult Customersjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ways of Showing Love And-CompassionDokument17 SeitenWays of Showing Love And-Compassionjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Req. Quantit y PRICE Per PieceDokument1 SeiteDrug Req. Quantit y PRICE Per Piecejmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Requesition Slip Requesition SlipDokument2 SeitenRequesition Slip Requesition Slipjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Cooperative PledgeDokument2 Seiten1 Cooperative Pledgejmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Radiographic Technique Chart (Outbucky) : Distance: 40 Sid /machine Constant: 20masDokument2 SeitenRadiographic Technique Chart (Outbucky) : Distance: 40 Sid /machine Constant: 20masjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Supervisory Skills Training ManualDokument16 SeitenSupervisory Skills Training Manualjmmos207064100% (3)
- Operation SheetDokument2 SeitenOperation Sheetjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- MASS-SPECC CDO Training Sched January-March 2015Dokument3 SeitenMASS-SPECC CDO Training Sched January-March 2015jmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Classroom Management IIDokument42 SeitenClassroom Management IIjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rubric Online DiscusssionDokument2 SeitenRubric Online Discusssionjmmos207064Noch keine Bewertungen
- ElectronicsDokument41 SeitenElectronicsKazelle BustamanteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Med-RM - Zoo - SP-4 - Ch-17 - Strategies For Enhancement in Food ProductionDokument22 SeitenMed-RM - Zoo - SP-4 - Ch-17 - Strategies For Enhancement in Food Productionkrish masterjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Caning Dictionary Jun 16Dokument36 SeitenCaning Dictionary Jun 16Hakki YazganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Retold From The Pan Chat An Tram by Rohini ChowdhuryDokument19 SeitenRetold From The Pan Chat An Tram by Rohini ChowdhuryCatherine Degumbis PugoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Uterus - Libre PathologyDokument7 Seiten4 Uterus - Libre PathologyfadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akhal-Teke (Horse)Dokument11 SeitenAkhal-Teke (Horse)Amy KlezanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leo GoatDokument5 SeitenLeo GoatIndre IndraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branchial Cleft CystsDokument8 SeitenBranchial Cleft CystsHere LeafsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Anatomy & Physiology: The Central Nervous System: Part BDokument37 SeitenHuman Anatomy & Physiology: The Central Nervous System: Part Bminhmap90_635122804Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11.2 MovementDokument24 Seiten11.2 MovementAndyChoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Final Exam - Glory 2017 PDFDokument14 SeitenPhysiology Final Exam - Glory 2017 PDFMohammad BarakatNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Paper 2 Form 3 Term 1 Exam 2017Dokument5 SeitenEnglish Paper 2 Form 3 Term 1 Exam 2017Godfrey MuchaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proper Posture and AlignmentDokument3 SeitenProper Posture and Alignmentschorleworle100% (1)
- The Brain Comparative Vertebrates Sem1Dokument5 SeitenThe Brain Comparative Vertebrates Sem1Rashmi SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- English TestDokument13 SeitenEnglish TestDJ MRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Testing EssayDokument2 SeitenAnimal Testing EssayMohamed AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- SITHCCC014 Prepare Meat DishesDokument50 SeitenSITHCCC014 Prepare Meat Dishesrajgill1808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Koinophilia and Human Facial AttractivenessDokument9 SeitenKoinophilia and Human Facial AttractivenessDeadly Fruit JuiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pest Control Services - ISSHIcareDokument11 SeitenPest Control Services - ISSHIcarepromos10Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hatching and BroodingDokument22 SeitenHatching and BroodingToha PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inguino Scrotal SwellingDokument3 SeitenInguino Scrotal SwellingYurni Dwi AstutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Birds of Van ViharDokument8 SeitenBirds of Van ViharDurgesh Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 The Physiology of FitnessDokument11 SeitenUnit 2 The Physiology of FitnessIas UpscNoch keine Bewertungen
- Poultry Science: Sex Identification of Barred Plymouth Rock Baby Chicks by Down, Shank, and Beak CharacteristicsDokument6 SeitenPoultry Science: Sex Identification of Barred Plymouth Rock Baby Chicks by Down, Shank, and Beak CharacteristicsbillyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full PRE-TT-1P Term Test 1 Plus Without Answers ADokument7 SeitenFull PRE-TT-1P Term Test 1 Plus Without Answers ABodoquitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdomen - Pelvis: Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Wahyuni Lukita Atmodjo, PH.DDokument33 SeitenAbdomen - Pelvis: Lecturer: Prof. Dr. Wahyuni Lukita Atmodjo, PH.DAgatha FeliciaNoch keine Bewertungen