Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mate141 Midterm1 sp11
Hochgeladen von
Moath OthmanOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Mate141 Midterm1 sp11
Hochgeladen von
Moath OthmanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
MatE 141
Midterm 1
Spring 2012
You have 1 hour, 15 minutes to complete this test. Show all your work! The neater and clearer
your work is, the more partial credit you will receive. Check all your math after you have
completed the test. Read and sign the honor code below.
I have received no information about the exact questions on this test. I realize that if I am found
to reference the work of my students during the test, I will receive a zero grade for this midterm
and be reported through the University channels for academic dishonesty.
Signature: _______________________________
Print Name: ________________________________
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
2
1. A x-ray tube with a copper target is operated at 40,000 volts and 44 milliamps (20 points)
a. Calculate the short wavelength limit in for x-rays produced by this x-ray tube
o
o
o
3
A 31 . 0
Volt 40000
Volt A 12400
Volt A 10 40 . 12
= =
=
swl
swl
V
b. If the binding energy of a Cu 1s electron is 8979 eV, what is the minimum tube
voltage required to produce characteristic x-rays?
c. If the x-ray tube current was reduced to 40 milliamps, what will be the percent change
in the number of Cu K
o
x-rays that are produced?
d. What would be the advantage of using a rotating anode x-ray source with a Cu target?
A rotating anode source can be operated at higher currents than a sealed x-ray tube ,
therefore more CuKo can be produced, which allows detection of diffraction from
weaker peaks or smaller samples.
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
3
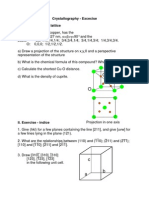
2. Draw an orthorhombic unit cell below, including a set of lattice basis vectors which are
specific and to scale (i.e. make up values for a, b, and c). In the unit cell show the following
planes and directions (you can draw them in different unit cells to make it easier to see). Be
sure to show your coordinate system. Be sure that the way you draw these planes and
directions is consistent with your coordinate system. (20 points)
(100) (112) (131)
[010] [211] [332]
3. Draw the reciprocal space unit cell for the orthorhombic unit cell shown in #2 above. What
are the reciprocal space coordinates of the lattice planes given in #2? (20 points)
1 1 1
4
1 1
*
3
1 1
*
2
1 1
*
= = = = = = A
c
c A
b
b A
a
a
(100)(1,0,0) (112)(1,1,2) (131)(1,3,1)
a*
b*
c*
x
y
z
[010] [211] [332]
(100)
(112)
(131)
a
b
c
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
4
4. You are designing a filter window for a Co x-ray source. You have been provided a copy of
Appendix 8 of Cullity for your calculations. (20 points)
a. What is the most common choice of material for this filter window?
The most common filter choice is Z-1. So that would be 27-1=26, Fe iron.
b. What thickness of the filter will transmit 90% of the Co Ko peak?
If we want to use the Co Ko wavelength as our source, we need to transmit a lot of it
(here this is estimating 90%). The transmission factor, TF, needs to be 0.9. / and
can be found in Appendix 8 (for Feor whatever you answered for part a). Then you
rearrange to solve for x.
m 38 . 2 m 10 38 . 2 cm 10 38 . 2
cm
g
87 . 7
g
cm
25 . 56
) 9 . 0 ln( ) TF ln(
x
x ) TF ln(
e
I
I
TF
6 4
3
2
x
0
x
= = =
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
= =
|
.
|
\
|
c. What is the transmission factor for the Co K peak for your filter?
To create a monochromatic beam, you need to effectively block out (have a low
transmission factor) for the other wavelengths of the Co source.
Now you use the data Co K wavelength on the Fe filter.
524 . 0 e e
I
I
TF
cm 10 38 . 2
cm
g
87 . 7
g
cm
5 . 345
x
0
x
4
3
2
= = = =
|
|
.
|
\
|
|
.
|
\
|
It will transmit 52% (block 48%) of the unwanted Co K wavelength.
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
5
5. Below is shown a 2D projection of a tetragonal unit cell for rutile (TiO
2
). The z-axis is out of
the page, and the z-coordinate of each atom is marked in the center of each atom (either z=0 or
z= ). (20 points).
a. Draw a 3D sketch of this unit cell.
b. What symmetry elements are present in the unit cell shown below? Indicate where the
elements are on either your sketch or the original drawing.
The space group of rutile is P4
2
/mnm, which has 15 symmetry elements not including the
identity operator (1). I have shown 7 symmetry elements in the 3D drawing of the unit cell: one
inversion center (i), three mirror planes (m), and three two-fold rotation axes (2). If you got these
7 symmetry elements, you got full credit. The other 8 symmetry elements for this space group
are the two 4
2
screw axes, two n glide planes, two
roto-inversion axes, and two 2
1
screw axes,
which are harder to visualize in a single unit cell.
x
y
Ti
O
0.5
0.5
0.5
0
0
0
0
0 0
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
6
x
y
T
i
O
m
m
x
y
Ti
O
y
x
m
2
2
z
i
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
From Tau Beta Pi SJSU Exam Library: http://exams.tbpsjsu.org
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NYA Winter 08 Unit Test 1Dokument5 SeitenNYA Winter 08 Unit Test 1Dr. Michael LautmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytical ChemistryDokument6 SeitenAnalytical ChemistryRodney Salazar0% (1)
- Crystallography ExceciseDokument12 SeitenCrystallography ExceciseJuan Javier Marrugo Hernandez0% (1)
- The Principles of Exercise Therapy TextDokument306 SeitenThe Principles of Exercise Therapy TextVivian Nehal50% (2)
- Practice Final ExamDokument17 SeitenPractice Final ExamSaied Aly SalamahNoch keine Bewertungen
- IIT-JEE 2009 Question Paper With Answer KeyDokument34 SeitenIIT-JEE 2009 Question Paper With Answer KeyAbhishek AnandNoch keine Bewertungen
- 07-Élec-A7 (Version Anglaise) - Novembre 2011Dokument5 Seiten07-Élec-A7 (Version Anglaise) - Novembre 2011andrytahiryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.302 Feedback SystemsDokument8 Seiten6.302 Feedback SystemsLuis AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- C 1 Quadratic InterpolationDokument18 SeitenC 1 Quadratic InterpolationSukuje Je100% (1)
- Advanced Systems Lab Exercises From The Book - VISkiDokument10 SeitenAdvanced Systems Lab Exercises From The Book - VISkiChandana NapagodaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE 134 Homework 1Dokument2 SeitenEE 134 Homework 1Poy LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 2010Dokument8 SeitenFinal 2010Hakkı ÇelimliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper-Ii Electronic Science: Instructions For The CandidatesDokument8 SeitenPaper-Ii Electronic Science: Instructions For The CandidatesKrishna PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xii-Neet Final Question Paper - 10.10.2021Dokument19 SeitenXii-Neet Final Question Paper - 10.10.2021N GANESHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee610 hw2 Au23Dokument3 SeitenEe610 hw2 Au23Manish kumawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 5307 HomeworksDokument15 SeitenEe 5307 HomeworksManoj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Lab Electric Fields and Potentials 2 PDFDokument7 SeitenOnline Lab Electric Fields and Potentials 2 PDFAlphaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EUF Out2011inglesDokument8 SeitenEUF Out2011inglesHenry Yul De AriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power System Analysis and Design 6th Edition Glover Test BankDokument14 SeitenPower System Analysis and Design 6th Edition Glover Test BankMatthewGreenefgjtb100% (22)
- An Introduction To Electrostatic ActuatorDokument32 SeitenAn Introduction To Electrostatic Actuatormujeeb.abdullah2830Noch keine Bewertungen
- PhysicsDokument13 SeitenPhysicsAbhijit JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: - Student IDDokument7 SeitenName: - Student IDinrhgoiwnowbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Engineering, Environment and Computing 310SE Advanced Digital Systems Open Time Constrained AssessmentDokument6 SeitenFaculty of Engineering, Environment and Computing 310SE Advanced Digital Systems Open Time Constrained Assessmentkelvin mwanikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE5802 - Structural Health Monitoring: Final ExamDokument5 SeitenCE5802 - Structural Health Monitoring: Final ExamAnonymous ep7LE5ZdP5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Dynamic Differential Evolution and Asynchronous Particle Swarm Optimization For Inverse ScatteringDokument4 SeitenComparison of Dynamic Differential Evolution and Asynchronous Particle Swarm Optimization For Inverse Scatteringsuper_montyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Es - 101Dokument8 SeitenEs - 101Subrata PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- hw4 2015Dokument2 Seitenhw4 2015Mario XiaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mid Term (Nov 2009)Dokument9 SeitenMid Term (Nov 2009)Astiger IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM Exam With SolutionDokument8 SeitenFEM Exam With SolutionArifian Agusta100% (2)
- Section - I Qa & Di: SolutionDokument6 SeitenSection - I Qa & Di: SolutionSonakshi BehlNoch keine Bewertungen
- F Fxe DX: Sin QDokument3 SeitenF Fxe DX: Sin QSang Min LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MT 2 Exam 2005 - Answer KeyDokument8 SeitenMT 2 Exam 2005 - Answer KeySamuel WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient Modeling of Spatially Incoherent Sources Based On Wiener Chaos Expansion Method For The Analysis of Photonic Crystal SpectrometersDokument8 SeitenEfficient Modeling of Spatially Incoherent Sources Based On Wiener Chaos Expansion Method For The Analysis of Photonic Crystal Spectrometersjulianli0220Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Circuits: Physics Lab Report - Grade 9Dokument4 SeitenElectric Circuits: Physics Lab Report - Grade 9Stuart CamposNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Oslo: Faculty of Mathematics and Natural SciencesDokument4 SeitenUniversity of Oslo: Faculty of Mathematics and Natural Sciencesasalifew belachewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport Fall 2021 PS 2 2Dokument9 SeitenTransport Fall 2021 PS 2 2Jocelyn Grisel García GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- NYCSampleFinalExam v2Dokument22 SeitenNYCSampleFinalExam v2Pi-ey En-jiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Be Midterm Spring KeyDokument11 SeitenA Be Midterm Spring KeyRex ChemNoch keine Bewertungen
- EE132 Lab1 OL Vs CLDokument3 SeitenEE132 Lab1 OL Vs CLthinkberry22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Graphics (ECS-504) 2011-12-2Dokument4 SeitenComputer Graphics (ECS-504) 2011-12-2Ajay YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- ODE Systems of LCC Type and StabilityDokument13 SeitenODE Systems of LCC Type and StabilitylambdaStudent_eplNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEM For Beams (Finite Element Method) Part 3Dokument4 SeitenFEM For Beams (Finite Element Method) Part 3Вячеслав ЧедрикNoch keine Bewertungen
- Qusetion 111 2 Data Analysis Assignment (問題卷)Dokument4 SeitenQusetion 111 2 Data Analysis Assignment (問題卷)huangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Building Services: Dublin Institute of Technology Bolton Street, Dublin 1Dokument6 SeitenBachelor of Engineering (Honours) in Building Services: Dublin Institute of Technology Bolton Street, Dublin 1Dar RylNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13122023013802physics Practice Paper 1Dokument8 Seiten13122023013802physics Practice Paper 1Srushti ChouguleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Darve Cme104 MatlabDokument24 SeitenDarve Cme104 MatlabArjun KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study - Material - 1st Year 1 Sem All Paper (2020-21) 1619326582759Dokument33 SeitenStudy - Material - 1st Year 1 Sem All Paper (2020-21) 1619326582759khuship200102Noch keine Bewertungen
- NEET Ka Feel (04-05-2023) FNLDokument42 SeitenNEET Ka Feel (04-05-2023) FNLVaradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ugc Net December 2012Dokument8 SeitenUgc Net December 2012nanda_kavalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tma, MPH-005 (2023-24)Dokument4 SeitenTma, MPH-005 (2023-24)AmleshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jee Advanced Paper 2 of 2016 With AnswerDokument20 SeitenJee Advanced Paper 2 of 2016 With AnswerKartick GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inpho11 QPDokument28 SeitenInpho11 QPAkshay PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- TMA1Dokument6 SeitenTMA1Idiots IdiotssNoch keine Bewertungen
- NYA Winter 08 Unit Test 1bDokument5 SeitenNYA Winter 08 Unit Test 1bDr. Michael LautmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Physics B Lab ProblemsDokument3 SeitenAP Physics B Lab ProblemsmashumeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Set No: 2 R10Dokument6 SeitenSet No: 2 R10Viswa ChaitanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerVon EverandStandard and Super-Resolution Bioimaging Data Analysis: A PrimerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsVon EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Von EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Motion in 1 - D.Dokument20 SeitenMotion in 1 - D.Ipshita PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Sequences & SeriesDokument6 SeitenGeometric Sequences & SerieswolfretonmathsNoch keine Bewertungen
- NTN Pillow BlockDokument54 SeitenNTN Pillow BlockteguheafNoch keine Bewertungen
- Envelope Acceleration LDokument10 SeitenEnvelope Acceleration Lsumeet_soporiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GE Apr 2011 Revisions To BS8006 For Reinforced Soil What Do These Mean For The Industry Corbet Jenner HorganDokument5 SeitenGE Apr 2011 Revisions To BS8006 For Reinforced Soil What Do These Mean For The Industry Corbet Jenner HorganAnonymous wD7ndVs3D7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Geochemistry Interview Questions and Answers 1931 PDFDokument12 SeitenGeochemistry Interview Questions and Answers 1931 PDFpeterjo raveloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mil STD 202g Method 301Dokument3 SeitenMil STD 202g Method 301ytumayNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCIT MCQDokument3 SeitenNCIT MCQyogesh deoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9709 s10 QP 42Dokument4 Seiten9709 s10 QP 42Abrar JahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Druck - UPS IIDokument2 SeitenDruck - UPS IIbugoff700Noch keine Bewertungen
- Slope Stations Lab: Station Description Teacher's Initials SDokument9 SeitenSlope Stations Lab: Station Description Teacher's Initials SheathermkohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial PymolDokument16 SeitenTutorial PymolfahraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aryabhatiya With English Commentary TextDokument293 SeitenAryabhatiya With English Commentary Textmd ctbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematical Model of Inverted Pendulum SystemDokument18 SeitenMathematical Model of Inverted Pendulum SystemMajid Mehmood100% (1)
- Earth Mat Design 33-11KV SSDokument5 SeitenEarth Mat Design 33-11KV SSDipak BandyopadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Capacity Lab 02 14 09Dokument5 SeitenHeat Capacity Lab 02 14 09api-210028385Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exp 1 Concentric Tube Heat ExchangerDokument21 SeitenExp 1 Concentric Tube Heat ExchangerHusna IzzatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- UG11T2702 Advanced Marine Control Engg & AutomationDokument3 SeitenUG11T2702 Advanced Marine Control Engg & AutomationSrinivasan PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Physics and Fiction, A Wormhole IsDokument5 SeitenIn Physics and Fiction, A Wormhole IsSouktik_Roy_2983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Six Leg Kinematic Moving MachineDokument12 SeitenSix Leg Kinematic Moving MachineShubham Bonde100% (1)
- HVD-10 50MP ApDokument4 SeitenHVD-10 50MP Apdinhhai1613Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schrodinger EquationsDokument3 SeitenSchrodinger EquationsNatheesh TpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plastic AnalysisDokument23 SeitenPlastic AnalysisPraveen Kumar R100% (1)
- CVDokument2 SeitenCVRizki HidayatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measurement of Skin Effects Using The Bode 100: AbstractDokument8 SeitenMeasurement of Skin Effects Using The Bode 100: AbstractSilvia De La CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phenolphthalein NaOH KineticsDokument7 SeitenPhenolphthalein NaOH KineticsjoevinngglNoch keine Bewertungen
- MODULE 2 Forces and MotionDokument36 SeitenMODULE 2 Forces and MotionCatherine LaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Duo Binary Modulation For Optical SystemsDokument10 SeitenDuo Binary Modulation For Optical SystemsErasmo VizzaccaroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Riemannian Curvature: 1 Parallel Transport Around A Small Closed LoopDokument7 SeitenRiemannian Curvature: 1 Parallel Transport Around A Small Closed LoopdheerajkmishraNoch keine Bewertungen