Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Psychrometric Chart Analysis of Air-Water Sample
Hochgeladen von
Janry EfriyantoOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Psychrometric Chart Analysis of Air-Water Sample
Hochgeladen von
Janry EfriyantoCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1.
280
0. l5
,8000
-l
260
I ,.1
0
0.
tt
l.l
6000
-5
00r1
40{)0
220
200
!_
'J.
11.
l: I
l0
1000
2
000
sL'
180
0.
;
tl
i60
:> :o >'; EU ,]t ll i).9 \
100 140
0.09
000
008
O.OJ
s 800
(r00
:00
.1( )(
I ,
tr'-r
80
,'iO
0.{).1
40 20
0
0.lr c.0
LJ.0l
80 tl
90
\.'zi-l
{-1
100
*t
(il)
Flgure .5 (a) Psychrometric chart for air-water vapor, I std atrn abs, in Sl units
r30
0.I4
1500
t000
I5
[0
IIO
'a
0Ll
()(l
0l: 0il
0 t0
009
o ori 0.07 0 0{'
0.0 5
000
E00
:
d
t
)
a;
I00 9')
c lr0 70 60 50 40 fa. 30
(,00 400
c t c
il
.l0o
l0r I
I
E
l5{l
IO0
!
il
!-
0.04 0
0..]
:0
00:
0 0l
1..
30 40 50 60 ?0 80 90 100 I t0 Il0 130 140 r50 l('0 170 180 I90 200 210 120 130 140 250 160
Tcmperature
oF
.
Flgure
(b)
?5 (6) Psychromctric chart for air-water vapor, I std atm abs, in English engineering units.
23
uass-rn,tNsFER opERATToNS
at I std atm pressure
Table 7.1 Psvchrometric relations for t}e syslem air (B)-water (A)
SI rrnit5 6[9, m, N, "C)
English
cnpnering mia
(Btu, fr3, lh. "F.
tVinr)
M^
MB
18.02
kg/kmol, H2O
18.02
lbllb
mol. HrO
28-97
kg/kmo| air
O.622pH.o
28.97
lb/lb mol, air
lb
Y'
l.0t33xtd-Fu,o
O.522ps,o 1.0133
kg HrO/kg air
0.622FH{
ta"ra -;
0.622pn-n
H:o/lb
air
v'
x Id -/s,o
+
0.0O456
kg HrO/kg
an
ib H.O/tb air
aH
(0.00283
)/'Xrc + 273) f3 mixrure/kg air (0.0252 +
0.24
0.0405
Xlro + 460) ft3 mixture/lb
air
cs
to
l0O5
1884
),'J for mixrure/(kg art . .C
+ 0.45Y'Btu for mirture/Qb an) . "F
0'c
2 502 3U
(1005
J
32"F
Io H
/kg
1075.8
Btullb
1884y')tc
+ Z 502 3C,y'
(0.24
J for nlxture,/l6g air, referred to gaseous air and
+ O.45y'Xr6
satuated liquid H.O, 0"C
H
Btu for mixrurc/lb ai, referred to ga.eous r,ir and l-quid H2O, 32"F
- j:) + 1075.8 r,
r,'c
0
Hi, I/kg
9
4'79
t, "F
32
H:.
4.074
7._s45
l0
20 40
50
29 3@
57 570
100 030 166 790
40 60
80 100
It
7RN
36.020
60
275 580 461 500
J
6{.090
1
t20
l.lrC
12.00
98.40
hc/ k'y 95O
/kg . K
0.227
Btu/lb . "F
purposes these can be considereaui curves vapor-gas mi_xture per unit mass of gas.
absorure humri\iity 0030 kg
necessar]'. The series of curves marked '.adiabatic-saturation cufv.es,, on the chart s'ere plotted accorcing.lo gq. (1 .2t),-n be considered
of
1:r:r. For nost
constanr .rrJuipy
for
the
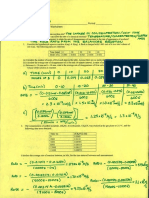
Ilhxrredoa 7'6 A:r air @)-water-vapor (A) sample haq a cin.-r,.lb teapcr=:ure 55.c aad aa water/kga.yu;
SoLt-no:{ T-r. point of coordilates
chan
"-'ria atm pressure. Tabu.rar i,s characteristics. /c:55.C, y,:0.030 is locared ihe psychrometric fig' ?'f a\. 2 56[s641ic version oiwhich rt rn"*r in Fig. ?.6. This ison pc"int D ir Fig. 7.6.
_-a
:'.i.'
",..n,
t{U}{lDIFlC.\llON OI'ITRAIIONS Ltf,
{,)
ta li? i:
i
o.
9
E
,1,,
i: i. 1o
)P
" a.::'
92
f ntbolp
I I
I
I
6l
55
Igmpgr6llrg
Ffture 7.6 Solutions to Illustrations 1.6 and
1.7.
(a) By vertical interpolation berween the adjacent curves of coDstant percnt humidity, tile sample has a percentage humidity :26.17o' Alternatively, tle saturadon humidity at 55'C rs y; : 0.1 15, and the percenl.age humidity at , is therefore (0.03010'l i5)1ffi : 26'lV"'
(D)
The rnolal absolute humidity : Y : Y'(MB/ M
0.tx82 k-mol water/kmol dry ar. (c) The partial pressure of water vapor in the sample, by E4. fi'E)'
^)
0.030(28.97
is
/18.C2)
F^:
.c^. The relative humidity
(d) The vapor Pressure of water at
(e) Dew poi_nt. From poiot D proceed at constant humidity to the saturation c'rve at point E, at which the dew point temperature is 31.5"C. O I{umid voluae.,\t 55"C, the specific vclume of dry air is a'% n3/kg' The h:'nid volume of saturated air - l.l0 m3,/kc dry air. Interpolatingfct 76'I% humidity,
55'C: l18 mmHg or ll8(li3 l) : F^(|ffi)/p^: 466q100)/15 730:79'6%-
#i:
qo4q'?l.l#I8+'O
= 4660 Nr/m:
15 730
N/m2
or :
(g)
Cs
0.93
+ (1.10 -
0.93X0.261)
0'974 rarilkg
dj) air
Hunid heaq Eq. (7.10):
Cs
+ Y'C^-
1005
+ 0.030(1884): 106l.5J(forwet"n)/(rgdrvan)'K
(l) Enrhalpy. Ar 55"C, the en'.halpy of dry air is 56000 l/kSu:- air; that for saturated air is 352 000 N'm/kg dry at. Interpolating for 26.19':humidity gives H' : 56 000 + (352 0@ - 56 0mX0.261) : ll3 300 J.i"kg drv air
.{lternatively, Eq. (7.13) or Table 7.1:
H' = CsUo - ,J + r'\:
(1005
+ tg8/Y')tc + 2 502 3{0r'
133'a
[1005
18&4(0'030)]5 5
+ 7 5OZ lux0'030) =
U/kg drv ar
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- UEMK1113 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING APPENDICESDokument25 SeitenUEMK1113 INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL ENGINEERING APPENDICESTie Teck HoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Gas DynamicsDokument11 SeitenApplied Gas DynamicsAishwarya RaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fugas de VaporDokument2 SeitenFugas de VaporMariano PiccardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hglii A: .Irij.IDokument1 SeiteHglii A: .Irij.IFiel A'nNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book 07 - Flight Performance & Planning 2Dokument30 SeitenBook 07 - Flight Performance & Planning 2Daniel Ognenoski100% (2)
- CH 02Dokument132 SeitenCH 02Paul Mj Robertson81% (16)
- Fluid Mechanics Homework SolutionsDokument9 SeitenFluid Mechanics Homework SolutionsnidhalsaadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1ft's fttnd'/lP/1 F: P) Fe'li't1f-Ln? Lit (I Inee)Dokument18 Seiten1ft's fttnd'/lP/1 F: P) Fe'li't1f-Ln? Lit (I Inee)Yuan-Po LinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lampiran PraktikumDokument3 SeitenLampiran PraktikumAhmad Fahmi IrfandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sol 05Dokument13 SeitenSol 05Ricky HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Engineering 2Dokument28 SeitenMechanical Engineering 2Aashrith ParvathaneniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treybal DistDokument5 SeitenTreybal DistJay CeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowDokument40 SeitenChapter 8 Fundamentals of Fluid FlowNader Alaa66% (38)
- Pe04024 QaDokument22 SeitenPe04024 QaSona SithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 - Dec.08-Jan.09-ME45Dokument3 Seiten2008 - Dec.08-Jan.09-ME45nitte5768Noch keine Bewertungen
- Capillary TubeDokument8 SeitenCapillary Tubeziko23100% (2)
- 2 GasDokument14 Seiten2 GasSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007Dokument4 SeitenME132 Thermodynamics Nov Dec 2007ARUNGREESMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Volume CalculationDokument123 SeitenGas Volume CalculationZulfitrizulkarnain ZulkarnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix A: - .Sizing of Distillation ColumnsDokument14 SeitenAppendix A: - .Sizing of Distillation ColumnsBlack WidowNoch keine Bewertungen
- SM ch01Dokument45 SeitenSM ch01Seth Hallam0% (1)
- Ex Problem 10 - Countercurrent Packed Tower For Absorption of Ammonia Gas (Pilat)Dokument5 SeitenEx Problem 10 - Countercurrent Packed Tower For Absorption of Ammonia Gas (Pilat)joesuhreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 3 SolDokument10 SeitenAssignment 3 SolHadi SobianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Fluid MechanicsDokument4 SeitenTest Fluid MechanicsFarrukhakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer through a Glass WindowDokument4 SeitenHeat Transfer through a Glass WindowAlexander Yauri Gomez50% (2)
- 2009 Sem 2 - CA1 & 2Dokument8 Seiten2009 Sem 2 - CA1 & 2Khim YangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetics Refresher WS Answer KeyDokument2 SeitenKinetics Refresher WS Answer KeyIchwan Permana MadaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Chap08 053Dokument10 SeitenHeat Chap08 053Kerem GönceNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDPE Pipe Fittings - 2Dokument5 SeitenHDPE Pipe Fittings - 2Sami ThirunavukkarasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final 103 2555Dokument8 SeitenFinal 103 2555Mikey PanupongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermo NaswersDokument98 SeitenThermo NaswersJapril AgustinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sava TabliceDokument13 SeitenSava TabliceMalinaGreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Simulink PDFDokument32 Seiten10 Simulink PDFAugusto De La Cruz Camayo100% (1)
- (Ethyl-Benzene Recovery) : Major Equipment DesignDokument35 Seiten(Ethyl-Benzene Recovery) : Major Equipment DesignKrishnan AnanthanarayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- HITACHIKH2sOHD 65-ton crawler craneDokument7 SeitenHITACHIKH2sOHD 65-ton crawler craneKOKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linear Expanison Worksheet (Key)Dokument3 SeitenLinear Expanison Worksheet (Key)MCH100% (7)
- Chapter 2Dokument43 SeitenChapter 2radoslav121Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculate Saturated-Gas Loads For Vacuum SystemsDokument3 SeitenCalculate Saturated-Gas Loads For Vacuum SystemsFred FaberNoch keine Bewertungen
- MIDTERM 2-3rd ASSIGNMENTDokument10 SeitenMIDTERM 2-3rd ASSIGNMENTNazenin GüreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiling Point and Vapor Pressure CalculationsDokument28 SeitenBoiling Point and Vapor Pressure CalculationsFiqa Success89% (9)
- THD291Z 2009 10 e 1Dokument15 SeitenTHD291Z 2009 10 e 1kasturiep15Noch keine Bewertungen
- ACC DHP Kelas Y Praktikum Asidi Alkalimeetri 2022Dokument3 SeitenACC DHP Kelas Y Praktikum Asidi Alkalimeetri 2022lol lolNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADVANCED COMBUSTION ENGINESDokument0 SeitenADVANCED COMBUSTION ENGINESBalvinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Engineer IN G: One Marks QuestionsDokument11 SeitenChemical Engineer IN G: One Marks Questionsrahulsaini855Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chem 400 Prereq RVW KeyDokument9 SeitenChem 400 Prereq RVW KeyMiguel A. ChávezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mae3309 All TestsDokument26 SeitenMae3309 All TestsDerek Ogburn100% (1)
- Egt End Sem 2014Dokument3 SeitenEgt End Sem 2014Umang PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Heat Pump Data and ResultsDokument1 SeiteExperimental Heat Pump Data and ResultsJRAWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Exchanger DesignDokument35 SeitenHeat Exchanger Designdarkbreaker3244Noch keine Bewertungen
- Design Calculation of HEDokument8 SeitenDesign Calculation of HEandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gasdinamica: Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria AerospazialeDokument4 SeitenGasdinamica: Laurea Magistrale in Ingegneria AerospazialeDavid BrandãoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingVon EverandGas Hydrates 1: Fundamentals, Characterization and ModelingDaniel BrosetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Concept of Chemical ExergyDokument17 SeitenConcept of Chemical ExergyJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KRS 03101402064 Semester 6 2012-2013Dokument4 SeitenKRS 03101402064 Semester 6 2012-2013Janry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 TA Spnsor UNSRI FlyerDokument1 Seite2014 TA Spnsor UNSRI FlyerJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Producing Automatic Diarylic Acid Diblock CopolymersDokument1 SeiteProducing Automatic Diarylic Acid Diblock CopolymersJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Table 3 Karakter RsinDokument6 SeitenTable 3 Karakter RsinJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Krs UnsriDokument3 SeitenKrs UnsripertiwidwianugrahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laporan KEGIATAN: Mahasiswa Teknik Kimia Fakultas Teknik Unsri Kampus Palembang 2010/2011Dokument1 SeiteLaporan KEGIATAN: Mahasiswa Teknik Kimia Fakultas Teknik Unsri Kampus Palembang 2010/2011Janry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Universitas Sriwijaya Fakultas Teknik Jurusan Teknik Kimia: Diagram Alir Proses Pembuatan DinitrotoluenaDokument2 SeitenUniversitas Sriwijaya Fakultas Teknik Jurusan Teknik Kimia: Diagram Alir Proses Pembuatan DinitrotoluenaJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Passive VoiceDokument6 SeitenPassive VoiceJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KRS 03101402064 Semester 6 2012-2013Dokument4 SeitenKRS 03101402064 Semester 6 2012-2013Janry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- KRS 03101002075 Semester 6 2012-2013Dokument4 SeitenKRS 03101002075 Semester 6 2012-2013Janry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM APPLICATIONDokument12 SeitenUNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM APPLICATIONJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurva Karakteristik Fuel GasDokument1 SeiteKurva Karakteristik Fuel GasJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kurva Karakteristik Fuel GasDokument1 SeiteKurva Karakteristik Fuel GasJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CF WW SystemsDokument32 SeitenCF WW SystemsJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Test Whru 2010 Ua: Boiler Feed Water (BFW)Dokument2 SeitenPerformance Test Whru 2010 Ua: Boiler Feed Water (BFW)Janry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- CompressedDokument1 SeiteCompressedJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- NO. Kode Batuan Beku PDokument6 SeitenNO. Kode Batuan Beku PJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cover KalkulusDokument1 SeiteCover KalkulusJanry EfriyantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final ReviewDokument104 SeitenFinal Reviewzhou wangchaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAB 2513 Hydraulic Chapter 4Dokument33 SeitenSAB 2513 Hydraulic Chapter 4Tuan Jalai100% (1)
- Trainig Report For IoclDokument30 SeitenTrainig Report For IoclAshish Jha67% (3)
- Chiller OperationDokument6 SeitenChiller OperationKannan Vellasamy67% (3)
- P133 Pressure Regulator Specifications and ApplicationsDokument12 SeitenP133 Pressure Regulator Specifications and ApplicationsNag RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3DG-B32-00004 Crude & Vacuum UnitsDokument32 Seiten3DG-B32-00004 Crude & Vacuum UnitsCarlos0% (1)
- Institution Registration Number Name Course Unit Name Unit Code LecturerDokument9 SeitenInstitution Registration Number Name Course Unit Name Unit Code LecturerJosline MuriikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Capillary PressureDokument39 SeitenUnderstanding Capillary PressureDarshak SakhreliyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Conveying Systems..Dokument61 SeitenPneumatic Conveying Systems..efka808Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz - Pumps and Pumping SystemsDokument3 SeitenQuiz - Pumps and Pumping SystemsFawaaz Khurwolah0% (1)
- Brochure B1500 All Fire PumpsDokument4 SeitenBrochure B1500 All Fire Pumpseng_elbarbaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hierarchy of O2 Delivery SystemsDokument1 SeiteHierarchy of O2 Delivery SystemsRevNoch keine Bewertungen
- Patente Proceso aMDEA de BASFDokument9 SeitenPatente Proceso aMDEA de BASFizurietaeduardoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Company Profile Pt. Bangun Barat IntinusaDokument24 SeitenCompany Profile Pt. Bangun Barat IntinusaLeider ParhusipNoch keine Bewertungen
- CW PumpsDokument21 SeitenCW PumpsRaja RamachandranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daftar Isi HydraulicDokument4 SeitenDaftar Isi HydraulicYhuto W. PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cve 240-Assignment 5 - Chapter 4Dokument3 SeitenCve 240-Assignment 5 - Chapter 4Ehab Wilson0% (1)
- TC Fls Sihi Lem Lel 91 To 161 THR enDokument13 SeitenTC Fls Sihi Lem Lel 91 To 161 THR enIamandii RoxanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Relief Valves HenryDokument7 SeitenPressure Relief Valves HenryOSCAR ASIAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- A 272Dokument1 SeiteA 272AnuranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- XSteam Excel v2.6Dokument9 SeitenXSteam Excel v2.6Yos Cornel TariganNoch keine Bewertungen
- KMP Medium Profile Unit Cooler Data SheetDokument36 SeitenKMP Medium Profile Unit Cooler Data SheetVíctor HugoNoch keine Bewertungen
- T16 Liquid Density PDFDokument26 SeitenT16 Liquid Density PDFVictor Enrique Rosales ParadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Various Types of Y Plan Shaped Tall BuildingDokument25 SeitenVarious Types of Y Plan Shaped Tall BuildingPrasenjit SanyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts List Manual: I A C TS20C/V200TSDokument108 SeitenParts List Manual: I A C TS20C/V200TSMarcos CabreraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sizing Calculation Turbine Meter Project Perbaikan Dan Penggantian: Sistim Meter LPG Pert Amina Up-Ii DumaiDokument2 SeitenSizing Calculation Turbine Meter Project Perbaikan Dan Penggantian: Sistim Meter LPG Pert Amina Up-Ii DumaiNurdeny PribadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Apollo Safety Valves Serie 19Dokument5 SeitenApollo Safety Valves Serie 19Daniel SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boiler Log DailyDokument2 SeitenBoiler Log Dailymohamed abd el attyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic Conveying of Fly Ash With Various Diameter of The PipelineDokument5 SeitenPneumatic Conveying of Fly Ash With Various Diameter of The PipelineIndra D. WinarkoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Details DeaeratorDokument3 SeitenConstruction Details DeaeratorpawangwlNoch keine Bewertungen