Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
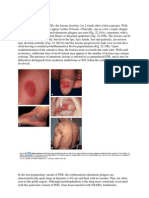
Measles Differential Diagnosis
Hochgeladen von
tobechi86Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Measles Differential Diagnosis
Hochgeladen von
tobechi86Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Differential Diagnosis of Typical Measles
Disease
Agent
Typical Season
Typica l Age
Prodrome
2-4 days of cough, conjuctivitis, and coryza
Fever
Duration of Rash (days)
Rash
Erythematous, irregular size, maculopapular; starts on temples & behind ears; progresses down from face; fades to brownish
Other Signs & Symptoms
Kopliks spots C blue-white papules (salt grains) on bright red mucosa opposite premolar teeth
Measles
Paramyxovirus Measles virus
Winter, Spring
1 to 20 years
High
5-6
Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (Kawasaki disease)
Unknown
Winter, Spring
<5 years
3 days of abrupt fever
High; fever of 5 days is key sign
5 - 7; varies
Erythematous, morbilliform, maculopapular or scarlatiniform, central distribution; erythematous, indurated palms and soles
Acute: dry, fissured & injected lips, strawberry tongue; irritability; cervical lymphadenopathy; conjunctival injection; peripheral edema Subacute: finger-tip desquamation; Complications: arthritis, carditis
Roseola Infantum (exanthem subitum)
Human herpes virus type 6
Any
6 mos. to 2 years
None
High
1-2; it follows defervescence
Discrete erythematous macules, rarely involves face, begins as fever ends
Lymphadenopathy, irritability
Rubella
Togavuris
Spring, (late winter)
7 mos. to 29 years
0 - 4 days; mild malaise, fever; absent in children
Lowgrade
1-3
Discrete, rose-pink, diffuse, maculopapular; progresses downward from face, may change quickly Scarlet sunburn with punctate papules sandpaper, circumoral pallor, increased intensity in skin folds, blanches, starts face/head/ upper trunk and progresses downward
Arthralgia (usually in adults), tender posterior cervical & suboccipital lymphadenopathy, malaise, petechiae on soft palate
Scalet Fever
-hemolytic streptococci
Winter
>2 years
0 - 1 day, marked
Low-High
2-7
Sore throat, exudative tonsillitis, vomiting, abdominal pain, lmphadenopathy, white then red strawberry tongue
Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth Disease)
Human parvovirus type B19
Spring
5 - 10 years
None usually in children, may occur in adults
None to Lowgrade
2-4
Starts as slapped cheek, maculopapular; progresses to reticular (lacy) pattern; can recur with environmental changes such as sunlight exposure Fine, pink, always affects face; variant is Boston exanthem (large ~ 1 cm, discrete maculopapules) Generalized maculopapular rash after defervescence; spares palms and soles Typically diffuse but may be concentrated in diaper area, typically no progression, erythema multiform rash can progress over a few days Trunk and proximal extremities. Rash common if Ampicillin given Starts on face and spreads down to trunk and extremities
Arthralgia/arthritis in adults, adenopathy
Enterovirus
Echovirus Coxsackie virus
Summer (Fall)
Mainly childho od
0 - 1 day fever and myalgias
Low-High
1-5
Sore throat, headache, malaies, no lymphadenopathy, gastroenteritis Headache, myalgia, abdominal pain, pharyngitis, vomiting
Dengue Fever
Dengue virus types 1 - 4 (Flavivirus)
None
High
1-5
Drug Rash
Penicillins, sulfonamide etc.
Any
Any
Possible due to underlying illness
Possible
Varies
Possibly due to underlying illness or complications
Infectious Mononucleosis
Epstein-Barr Virus Adenovirus types 2, 3, 4, 7, 7a
None
10 - 30 years
2-5 days of malaise and fatigue
Low-High
2-7
Pharyngitis, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, malaise
Pharynoconjunct ival Fever
Winter, Spring
<5 years
Low-High
3-5
Sore throat, conjunctivitis, headache, anorexia
From: Teaching Immunization for Medical Information, 2005 (http://www.atpm.org/education/TIME/ATPM_Measles-S.pdf) which adapted the information from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Epidemiology, Prevention, and Control of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 1992; Chap 9.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- #Common Childhood Rashes in General PracticeDokument5 Seiten#Common Childhood Rashes in General PracticeameerabestNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Exanthems: Sahara Tuazan AbonawasDokument75 SeitenViral Exanthems: Sahara Tuazan AbonawasMarlon Cenabre Turaja100% (1)
- Differential Diagnosis of Rash Illness: Disease Sign/Symptoms Type of Rash Other FeaturesDokument2 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Rash Illness: Disease Sign/Symptoms Type of Rash Other FeaturesCarlo CondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measles: Wilbert H. Mason Nelson's Textbook of Pediatrics 20th EditionDokument30 SeitenMeasles: Wilbert H. Mason Nelson's Textbook of Pediatrics 20th EditionEarl Mel Dustin LaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differential Diagnosis of Rash Illness: Disease Sign/Symptoms Type of Rash Other FeaturesDokument2 SeitenDifferential Diagnosis of Rash Illness: Disease Sign/Symptoms Type of Rash Other Featuresangelaemilia100% (1)
- Fever of Unknown OriginDokument25 SeitenFever of Unknown OriginAkhilMuraleedharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nelson JaundiceDokument7 SeitenNelson JaundiceJesly CharliesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral ExanthemDokument3 SeitenViral ExanthemPonchoi PintacasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Febrile Seizures, Febrile Seizure Plus, First Unprovoked Seizure WebinarDokument45 SeitenFebrile Seizures, Febrile Seizure Plus, First Unprovoked Seizure WebinarTun Paksi Sareharto100% (1)
- PPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENDokument31 SeitenPPT DIARHEA IN CHILDRENRifka AnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsMB, BSDokument33 SeitenAcute Upper Respiratory Tract InfectionsMB, BSibnbasheer83% (6)
- Perioral DermatitisDokument12 SeitenPerioral DermatitisHenny WijayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- REFERAT - Meassles - FirdaDokument19 SeitenREFERAT - Meassles - FirdaEriza LuthfansyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fever in Children and FUODokument62 SeitenFever in Children and FUOAmbartyas Niken WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Sense System Group 6Dokument24 SeitenSpecial Sense System Group 6RushdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Horner SyndromeDokument9 SeitenHorner SyndromeamiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- FEVER Approach (Paeds)Dokument3 SeitenFEVER Approach (Paeds)NorFarah Fatin AnuarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CASE 2 PneumoniaDokument12 SeitenCASE 2 PneumoniaKenneth MiguelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rule of 4 and Brainstem SyndromesDokument2 SeitenRule of 4 and Brainstem SyndromesTracie TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short StatureDokument14 SeitenShort StatureEmily EresumaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical ExaminationgiDokument61 SeitenPhysical ExaminationgiHei LeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acute Flaccid ParalysisDokument47 SeitenAcute Flaccid ParalysisVandanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ 14 Juli 2021 + Pembahasan FINALDokument50 SeitenMCQ 14 Juli 2021 + Pembahasan FINALAnonymous pJxkvPQgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fixed Drug Eruption, Bolognia DermatologyDokument2 SeitenFixed Drug Eruption, Bolognia Dermatologyjacob89Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sweet Syndrome EnglishDokument19 SeitenSweet Syndrome EnglishAsma AlwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- HepatosplenomegalyDokument49 SeitenHepatosplenomegalyTarun SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sindroamele HemoragiceDokument5 SeitenSindroamele HemoragiceIoana GalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ventikular Septal Defect FixDokument18 SeitenVentikular Septal Defect FixPutri Sari DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral ExanthemsDokument67 SeitenViral ExanthemsKay HanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal JaundiceDokument23 SeitenNeonatal JaundiceAsad M AminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Neonatal JaundiceDokument22 SeitenManagement of Neonatal JaundiceSuhazeli Abdullah100% (1)
- Tinea CorporisDokument23 SeitenTinea CorporisDita lewaherillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anemia in Newborn BabyDokument11 SeitenAnemia in Newborn BabyDana Rahmanto100% (3)
- Tourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesDokument4 SeitenTourniquet Test: Small Amount of Air Will Not Harm The TissuesjoymaeannNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Intern Guide Quick NotesDokument8 SeitenNew Intern Guide Quick NotesTrisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neonatal JaundiceDokument12 SeitenNeonatal JaundiceGiska T PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- MILIARIADokument6 SeitenMILIARIARien Anggraini RazakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skin PDFDokument13 SeitenSkin PDFLanaAmerieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anosmia and HyposmiaDokument4 SeitenAnosmia and HyposmiafaradillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meconium AspirationDokument23 SeitenMeconium AspirationWitneyGraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and AdolescentsDokument8 SeitenManagement of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in Children and AdolescentsnurlatifahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Referat Kandidosis Kutis - Dhira Dan A. Fari-70700120034 Dan 038Dokument14 SeitenReferat Kandidosis Kutis - Dhira Dan A. Fari-70700120034 Dan 038Ahmad Fari Arief LopaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyphilisDokument54 SeitenSyphilisYeyeh SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lapkas ANAKDokument40 SeitenLapkas ANAKThemySutejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.Dokument84 SeitenInfection of The Skin, Soft Tissue, Etc.fmds100% (1)
- Pathophysiology KwashirkorDokument1 SeitePathophysiology KwashirkorPATHOSHOPPENoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Asthma PDFDokument12 SeitenPediatric Asthma PDFzie_luph_taz13Noch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Abstract TEMPLATEDokument3 SeitenClinical Abstract TEMPLATEDiannesa April GolosindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral ExanthemsDokument133 SeitenViral ExanthemsDesiree AfagaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TB MeningitisDokument11 SeitenTB MeningitisMontserrat ÁlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toacs 6Dokument159 SeitenToacs 6Mobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (2)
- Checklist UKMPPD NovemberDokument6 SeitenChecklist UKMPPD Novemberuci marley100% (1)
- Acute Lobar PneumoniaDokument13 SeitenAcute Lobar PneumoniaICNoch keine Bewertungen
- Klasifikasi VitiligoDokument49 SeitenKlasifikasi VitiligoVika LeiwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differentials: Less Common InfectionsDokument6 SeitenDifferentials: Less Common InfectionsTaeyomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VPD RashchrtDokument2 SeitenVPD RashchrtMarco Ramos JacobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Red Rashes in ChildrenDokument9 SeitenSome Red Rashes in ChildrenMeidy RuthNoch keine Bewertungen
- M13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO5Dokument6 SeitenM13 v2 Dermatology & STI - LO5medipro clinicNoch keine Bewertungen
- PathologyDokument49 SeitenPathologyWarisha AmirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verbatim #1Dokument5 SeitenVerbatim #1Iosua Faur100% (4)
- NCM 109 Case Study - Sir JesusDokument25 SeitenNCM 109 Case Study - Sir JesusLance RaphaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- AfflictionsDokument12 SeitenAfflictionsshiraaazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluids and Electrolytes in Pediatrics FinalDokument41 SeitenFluids and Electrolytes in Pediatrics FinalArun GeorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head To Toe Write UpDokument3 SeitenHead To Toe Write Upapi-554096544Noch keine Bewertungen
- CharacterDokument1 SeiteCharacterPlacement officerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Angina PectorisDokument17 SeitenAngina PectorisRakesh Reddy100% (1)
- Yoga and High Blood Pressure Hypertension 2 AVonCammererDokument9 SeitenYoga and High Blood Pressure Hypertension 2 AVonCammererAndrea Van RankinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test S&HDokument5 SeitenTest S&HHf CreationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Clinical ExaminationDokument153 SeitenIntroduction To Clinical ExaminationBnB UsmleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Renap Update Pre-Kt - MDJDokument46 SeitenRenap Update Pre-Kt - MDJRenalNursesPhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isaac - Remedial Class Mock Multiple ChoiceDokument12 SeitenIsaac - Remedial Class Mock Multiple ChoiceKwabena AmankwaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenMind 3 Unit 9 Grammar and Vocabulary Test ADokument2 SeitenOpenMind 3 Unit 9 Grammar and Vocabulary Test AAna AnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- English Modul 2Dokument100 SeitenEnglish Modul 2Restian AngginiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pasar Rbe CutieDokument11 SeitenPasar Rbe CutieElla RetizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Garage Built Body Main Program GuideDokument21 SeitenThe Garage Built Body Main Program GuideNoel Martin100% (1)
- Phillipine Herbal MedicineDokument23 SeitenPhillipine Herbal MedicineCENTHREE MAGALLANESNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oklahoma's Low-THC LawDokument1 SeiteOklahoma's Low-THC LawMPPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Drug Treatment of Lipid Disorders. NIACINA. NIACINDokument14 SeitenDrug Treatment of Lipid Disorders. NIACINA. NIACINpaoloaltoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Animal Wellness Magazine February - March.2006Dokument148 SeitenAnimal Wellness Magazine February - March.2006scribuser02100% (2)
- Infection in PregnancyDokument5 SeitenInfection in PregnancyWasem A. JabbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDokument10 SeitenNCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentSheryhan Tahir BayleNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Solve An Outbreak (The Game)Dokument4 SeitenHow To Solve An Outbreak (The Game)Alina ForrayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test 1Dokument33 SeitenTest 1julialeo67% (3)
- What Is MrsaDokument17 SeitenWhat Is MrsaAnonymous NVBCqKWHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Annual Report-2016-17 Novartis India LimitedDokument139 SeitenAnnual Report-2016-17 Novartis India LimitedNitin JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 109 Upper Extremity Questions and AnswersDokument8 Seiten109 Upper Extremity Questions and AnswersChioma BenedetteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Accidents & Incidents Quiz AnswersDokument1 SeiteAccidents & Incidents Quiz AnswersMouctarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Approved Herbal Plants by DOHDokument7 Seiten10 Approved Herbal Plants by DOHjhommmmm88% (42)
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyneuropathyDokument36 SeitenChronic Inflammatory Demyelinating PolyneuropathySafitri MuhlisaNoch keine Bewertungen