Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Fin118 Unit 9
Hochgeladen von
ayadi_ezer6795Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Fin118 Unit 9
Hochgeladen von
ayadi_ezer6795Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Al-Imam Muhammad Ibn Saud Islamic University
College of Economics and Administration Sciences
Department of Finance and Investment
Financial Mathematics Course
FIN 118 Unit course
9 Number Unit
Compound Interest
Non annual Compound Interest
Continuous Compound Interest
Unit Subject
Dr. Lotfi Ben Jedidia
Dr. Imed Medhioub
!!! remember what we saw last time
The relationship between time and money.
The simple interest rate and the interest
amount
The present value of one future cash flow
The future value of an amount borrowed or
invested.
The relationship between Real Interest Rate,
Nominal Interest Rate and Inflation.
2
we will see in this unit
The compound interest rate and the interest
amount
How to Calculate the future value of a single
sum of money invested today for several
periods.
How to Calculate the interest rate or the
number of periods or the principal that achieve
a fixed future value.
3
Learning Outcomes
4
At the end of this unit, you should be able to:
1. Understand compound interest, including
accumulating, discounting and making comparisons
using the effective interest rate.
2. Distinguish between compound interest.
3. Identify variables fundamental to solving
interest problems.
4. Solve problems including future and present
value.
5
Definition1: In each subsequent period, the interest
amount computed is used to form a new principal sum,
which is used to compute the next interest due.
- As we said, Compound Interest uses the Sum of
Principal & Interest as a base on which to calculate new
Interest and new Principal !
n periods i i i i PV FV
ods three peri i i i PV i F FV
s two period i i PV i F FV
one period i PV FV
n n
) 1 ( ) 1 )( 1 )( 1 (
) 1 )( 1 )( 1 ( ) 1 ( V
) 1 )( 1 ( ) 1 ( V
) 1 (
3 2 1
3 2 1 3 2 3
2 1 2 1 2
1 1
+ + + + =
+ + + = + =
+ + = + =
+ =
The Compound Interest
6
Definition2: If the interest rate is constant over
different periods we have:
and
!!! Remember
( )
n
n
i PV FV + = 1
( )
n
n
i
FV
PV
+
=
1
1
1
=
n
n
PV
FV
i
( )
( ) i
PV FV
n
n
+
=
1 ln
ln
I PV FV
n
+ =
FV
n
= Principal (1+ Interest Rate)
number of Periods
The Compound Interest
i i i i i
n
= = = = = ....
3 2 1
7
The compound interest rate is a geometric sequences
but the simple interest is an arithmetic sequences.
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
V
a
l
u
e
Years
Simple Interest
Compound Interest
Simple interest: Linear growth i = 0.15
Compound interest: Geometric growth i = 0.15
Property1:
The Compound Interest
8
Example1: Future Value and Interest
How much money would you pay in interest if you
borrowed $1600 for 3 years at 16% compound
interest per annum?
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal: 16% = 0.16
( ) ( ) 434 . 2497 16 . 0 1 1600 1
3 3
3
= + = + = i PV FV
PV FV I I PV FV
n n
= + =
More Examples
The Compound Interest
4336 . 897 1600 434 . 2497 = = I
9
More Examples
Example2: Present Value
What is the present value of $150000 to be
received 5 years from today if the discount rate
(annual compounded interest) is 10%?
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal: 10% = 0.1
( ) ( )
198 . 93138 $
1 . 0 1
150000
1
5 5
5
=
+
=
+
=
i
FV
PV
The Compound Interest
10
More Examples
Example3: Interest rate
Assume that the initial amount to invest is
PV = $100 and the interest rate is constant over
time. What is the compound interest rate in
order to have $150 after 5 years?
Solution:
PV = $100 and FV
5
= $150
% 4 . 8
084 . 0 1 084 . 1 1
100
150
1 1 ) 1 (
5
1
5
1
5
5
1
5
5
5
=
= =
(
=
(
= + + =
i
i
PV
FV
i
PV
FV
i i PV FV
The Compound Interest
11
More Examples
Example4: The number of periods (n)
Find the number of periods to double your
investment at 6% compound interest per annum .
Solution:
PV = x and FV
n
= 2x
Convert the result:
11 years + 0.895 12 months= 11 years + 10.74 months
11 years + 10 months + 0.74 30 days
n = 11 years + 10 months + 22 days
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
( )
years
x x
i
PV FV
n
PV FV i n
PV
FV
i i PV FV
n
n
n
n
n
n
895 . 11
06 . 1 ln
2 ln
06 . 0 1 ln
2 ln
1 ln
ln
ln 1 ln 1 ) 1 (
= =
+
=
+
=
= +
(
= + + =
The Compound Interest
12
Question 1 ? How to calculate the FV if we have more than
one compounding periods per year ?
Response:
The table shows some common compounding periods
and how many times per year interest is paid for them.
And
If t=1 we retrieve the old formula
Compounding Periods Times per year (t)
Annually
1
Semi-annually
2
Quarterly
4
Monthly
12
t n
t n
t
i
PV FV
|
.
|
\
|
+ = 1
,
!!!
13
Example1: Future Value semi-annually
You invested $1800 in a savings account that pays
4.5% interest compounded semi-annually. Find the
value of the investment in 12 years.
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal: 4.5% = 0.045
2 12
2 , 12
,
2
045 . 0
1 1800
1
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
t
i
PV FV
t n
t n
= 1800(1 + 0.0225)
24
= 1800(1.0225)
24
= $3070.38
Non annual Compound Interest
14
Example2: Future Value Quarterly
You invested $3700 in a savings account that pays
2.5% interest compounded quarterly. Find the value of
the investment in 10 years.
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal: 2.5% = 0.025
4 10
4 , 10
,
4
025 . 0
1 3700
1
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
t
i
PV FV
t n
t n
= 3700(1 + 0.00625)
40
= 3700(1.00625)
40
= $4747.2
Non annual Compound Interest
15
Example3: Future Value monthly
You invested $1700 in a savings account that pays 1.5%
interest compounded monthly. Find the value of the
investment in 15 years.
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal: 1.5% = 0.015
12 15
12 , 15
,
12
015 . 0
1 1700
1
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
t
i
PV FV
t n
t n
= 1700(1 + 0.00125)
180
= 1700(1.00125)
180
= $2128.65
Non annual Compound Interest
16
Example4: Present Value
You expect to need $1500 in 3 years. Your bank
offers 4% interest compounded semiannually. How
much money must you put in the bank today (PV) to
reach your goal in 3 years?
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal: 4% = 0.04
t n
t n
t n
t n
t
i
FV
PV
t
i
PV FV
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
1
1
,
,
( )
957 . 1331 $
02 . 1
1500
2
04 . 0
1
1500
6 2 3
= =
|
.
|
\
|
+
=
PV
Non annual Compound Interest
17
Example5: Making a choice
Suppose a bank quotes nominal annual interest
rates on five-year of:
- 6.6% compounded annually,
- 6.5% compounded semi-annually, and
- 6.4% compounded monthly.
Which rate should an investor choose for an
investment of $10000?
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal:
6.6% = 0.066; 6.5% = 0.065 and 6.4% = 0.064
The times per year is respectively t= 1; t = 2 and
t = 12.
Non annual Compound Interest
18
Solution : continued
First proposition:
Second proposition:
Third proposition:
31 . 13765
1
066 . 0
1 10000
1 5
1 , 5
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
943 . 13768
2
065 . 0
1 10000
2 5
2 , 5
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
572 . 13759
12
064 . 0
1 10000
12 5
12 , 5
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
We choose the second proposition.
6.5% compounded semi-annually provides the best
return on investment.
t n
t n
t
i
PV FV
|
.
|
\
|
+ = 1
,
Non annual Compound Interest
Question 2 ? What would happen to our money if
we compounded a really large number of times?
Response:
We would have to compound not just every hour, or
every minute or every second but for every
millisecond. We have:
- Then with Continuous compounding interest we
have:
t n
t n
t
i
PV FV
|
.
|
\
|
+ = 1
,
i n
e PV
t
i n
t n
e PV FV
=
,
19
20
Example1: Future Value
If you invest $1000 at an annual interest rate of
5% compounded continuously, calculate the final
amount you will have in the account after five
years.
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal 5% =0.05
With continuous compounding formula we obtain
02 . 1284 $ 1000
05 . 0 5
5
= = =
e e PV FV
i n
Continuous Compound Interest
21
Example2: Finding the time
How long will it take an investment of $10000 to
grow to $15000 if it is invested at 9% compounded
continuously?
Solution:
Convert the percent to a decimal 9% =0.09
With continuous compounding formula we obtain
= 4 years + 6 months + 2 days
( )
( )
years 505 . 4
09 . 0
) 5 . 1 ln(
ln
ln
= =
= =
= =
n
i
PV FV
n PV FV i n
PV
FV
e e PV FV
n
n
n
i n i n
n
Continuous Compound Interest
22
Example3: Finding the interest rate
What is the interest rate compounded continuously
of an investment of $10000 to grow to $20000 if
it is invested for 7 years?
Solution:
( )
( )
% 9 . 9 099 . 0
7
) 2 ln(
ln
ln
= = =
= =
= =
i i
n
PV FV
i PV FV i n
PV
FV
e e PV FV
n
n
n
i n i n
n
Continuous Compound Interest
23
Example4: Making a choice
What amount will an account have after 5 years if
$100 is invested at an annual nominal rate of 8%
compounded annually? Semiannually? continuously?
Solution:
Compounded annually:
Compounded semi-annually:
Compounded continuously:
( ) 93 . 146 08 . 0 1 100
5
5
= + = FV
02 . 148
2
08 . 0
1 100
2 5
2 , 5
=
|
.
|
\
|
+ =
FV
18 . 149 100
5 08 . 0
5
= =
e FV
We choose the third proposition.
8% compounded continuously provides the best return
on investment.
Compound Interest
24
Its time to review
Compound interest Simple Interest
Continuous Compound
Interest
More than one compounding
periods per year
n i PV I =
( ) n i PV FV
n
+ = 1
I PV FV
n
+ = I PV FV
n
+ =
( )
n
n
i PV FV + = 1
t n
t n
t
i
PV FV
|
.
|
\
|
+ = 1
,
Real Interest Rate = Nominal Interest Rate - Inflation
i n
n
e PV FV
=
we will see in the next unit
Meant of simple Annuity
Simple Annuity: Ordinary Annuity,
Annuity Due (unit10)
25
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Finance for Non-Financiers 1: Basic FinancesVon EverandFinance for Non-Financiers 1: Basic FinancesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of Money - MbaDokument36 SeitenTime Value of Money - MbaFranchezka PegolloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics of FinanceDokument11 SeitenMathematics of FinanceAnis Fadzilah ZulkifleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of MoneyDokument20 SeitenTime Value of Moneyjawad_iubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of MoneyDokument40 SeitenTime Value of Moneyqrrzyz7whgNoch keine Bewertungen
- FNCE101 wk02Dokument43 SeitenFNCE101 wk02Ian ChengNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7mathematics of Finance2Dokument12 Seiten7mathematics of Finance2Jemmuel BulataoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 - TVMDokument61 SeitenTopic 1 - TVMBaby KhorNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Reporter Compound Interest .2Dokument29 SeitenFirst Reporter Compound Interest .2Golden Gate Colleges Main LibraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- First-Reporter-Compound-Interest .2Dokument25 SeitenFirst-Reporter-Compound-Interest .2Mherie Joy Cantos GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 9: Mathematics of FinanceDokument55 SeitenChapter 9: Mathematics of FinanceQuang PHAMNoch keine Bewertungen
- m2 Single Amount Finman ReportingDokument23 Seitenm2 Single Amount Finman ReportingKatring O.Noch keine Bewertungen
- BFN 2101 - B2C Financial Management: Single AmountDokument23 SeitenBFN 2101 - B2C Financial Management: Single AmountKatring O.Noch keine Bewertungen
- TTM 10 Time Value of Money - LanjutanDokument58 SeitenTTM 10 Time Value of Money - LanjutanDede KurniatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics of FinanceDokument20 SeitenMathematics of FinancekeziaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Notes in Basic FinanceDokument23 SeitenClass Notes in Basic FinanceOnat PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 10 Number Unit Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due Unit SubjectDokument26 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 10 Number Unit Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- RM Lecture 4Dokument57 SeitenRM Lecture 4觉慧Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Fin Module 4 Basic Long-Term Financial ConceptsDokument21 SeitenBus Fin Module 4 Basic Long-Term Financial ConceptsMariaShiela PascuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GR 11 L3 Financial Maths1Dokument8 SeitenGR 11 L3 Financial Maths1William NiemandNoch keine Bewertungen
- L1 R1 HY NotesDokument4 SeitenL1 R1 HY NotesboscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Time Value of Money: Money NOW Is Worth More Than Money LATER!Dokument37 SeitenThe Time Value of Money: Money NOW Is Worth More Than Money LATER!Meghashyam AddepalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Time Value of MoneyDokument70 SeitenUnit 2 - Time Value of MoneyNolan TitusNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM CHAPTER 3 THREE. PPT SlidesDokument84 SeitenFM CHAPTER 3 THREE. PPT SlidesAlayou TeferaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics of Finance: Section 2 Compound and Continuous Compound InterestDokument28 SeitenMathematics of Finance: Section 2 Compound and Continuous Compound InterestyonesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Four TVMDokument17 SeitenChapter Four TVMየሞላ ልጅNoch keine Bewertungen
- RWJ Chapter 4Dokument52 SeitenRWJ Chapter 4Parth ParthNoch keine Bewertungen
- FM I Chapter 3Dokument12 SeitenFM I Chapter 3mearghaile4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 8 - Time Value of MoneyDokument64 SeitenModule 8 - Time Value of MoneyferrarispeedsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value SolnDokument34 SeitenTime Value SolnAlim Ahmed Ansari100% (1)
- Business Finance Module 5Dokument10 SeitenBusiness Finance Module 5CESTINA, KIM LIANNE, B.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 20 Simple and Compound InterestDokument7 SeitenTopic 20 Simple and Compound InterestCarl Eugene de LemosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Winter Semester 2023-24 - MGT2006 - TH - AP2023246000029 - 2024-01-20 - Reference-Material-IDokument24 SeitenWinter Semester 2023-24 - MGT2006 - TH - AP2023246000029 - 2024-01-20 - Reference-Material-Isujithsai2004Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management Lecture 4thDokument34 SeitenFinancial Management Lecture 4thMansour NiaziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skript Translate Isnuardi Chapter 4Dokument3 SeitenSkript Translate Isnuardi Chapter 4Dian AnggrainyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 - Time Value of MoneyDokument8 SeitenChapter 4 - Time Value of MoneyGalindo, Justine Mae M.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Group 6.time Value of Money and Risk and Return - FinMan FacilitationDokument95 SeitenGroup 6.time Value of Money and Risk and Return - FinMan FacilitationNaia SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management Ii: Chapter 5 (Fundamental of Corporate Finance) Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyDokument33 SeitenFinancial Management Ii: Chapter 5 (Fundamental of Corporate Finance) Introduction To Valuation: The Time Value of MoneyEldi JanuariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 Lecture - The Time Value of Money PDFDokument26 Seiten05 Lecture - The Time Value of Money PDFjgutierrez_castro7724Noch keine Bewertungen
- Draft Jawapan Cases (Managerial Finance) Set9 Sem2 Sesi20222023 Bangi - YdDokument10 SeitenDraft Jawapan Cases (Managerial Finance) Set9 Sem2 Sesi20222023 Bangi - YdAhmad SuffianNoch keine Bewertungen
- INTERESTDokument25 SeitenINTERESTabdiel50% (2)
- Financial Mathematics Lecture Notes Fina PDFDokument71 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Lecture Notes Fina PDFTram HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discount MathematicsDokument3 SeitenDiscount MathematicsKuntugan Bekbolat UliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning and Evaluationl English 4Dokument40 SeitenPlanning and Evaluationl English 4Absa TraderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Business Finance - Simple and Compound InterestDokument42 SeitenBusiness Finance - Simple and Compound InterestJo HarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Financial MathDokument13 SeitenUnit 3 Financial Math0805640Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec1-Time Value of MoneyDokument27 SeitenLec1-Time Value of Moneyhassan baradaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of Money PDFDokument4 SeitenTime Value of Money PDFCalvin SandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin440 Chapter 5Dokument29 SeitenFin440 Chapter 5sajedulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of Money: DR. Mohamed SamehDokument22 SeitenTime Value of Money: DR. Mohamed SamehRamadan IbrahemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4Dokument41 SeitenLecture 4Tamer MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple and Compound InterestDokument46 SeitenSimple and Compound InterestAndres MabiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ppfin PDFDokument9 SeitenPpfin PDFAhmed HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of Money PV and FVDokument39 SeitenTime Value of Money PV and FVJean FlordelizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fin Man Unit 5Dokument5 SeitenFin Man Unit 5Jenelle Lee ColeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Economics Lect 3Dokument43 SeitenEngineering Economics Lect 3Furqan ChaudhryNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEE 452: Engineering Economics and Management: - Lec 9: Time Value of MoneyDokument28 SeitenEEE 452: Engineering Economics and Management: - Lec 9: Time Value of MoneyTomas KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Management 1Dokument20 SeitenFinancial Management 1Sriram_VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time Value of Money - Group 2Dokument40 SeitenTime Value of Money - Group 2Ron Andi RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- TVM Practice Problems SolutionsDokument7 SeitenTVM Practice Problems SolutionsAnne Bona100% (1)
- Risk Generating Industries For European Stock MarketsDokument14 SeitenRisk Generating Industries For European Stock Marketsayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- M01 Rejda 6117643 11 Rmi C01Dokument15 SeitenM01 Rejda 6117643 11 Rmi C01ayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Drives Systemic Bank Risk in EuropeDokument23 SeitenWhat Drives Systemic Bank Risk in Europeayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Functions and Their GraphsDokument148 SeitenFunctions and Their Graphsayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- FIN118 Unit 12Dokument22 SeitenFIN118 Unit 12ayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 7 Number Unit Sequences & Series Unit SubjectDokument27 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 7 Number Unit Sequences & Series Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 10 Number Unit Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due Unit SubjectDokument26 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 10 Number Unit Ordinary Annuity Annuity Due Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 2 Number Unit Limits of Function Continuity of Function Unit SubjectDokument35 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 2 Number Unit Limits of Function Continuity of Function Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 6 Number Unit Applications of Matrices Unit SubjectDokument21 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 6 Number Unit Applications of Matrices Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 5 Number Unit Matrices Unit SubjectDokument26 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 5 Number Unit Matrices Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 4 Number Unit Integral Calculus Unit SubjectDokument17 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 4 Number Unit Integral Calculus Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fin118 Unit 3Dokument27 SeitenFin118 Unit 3ayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 1 Number Unit Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Unit SubjectDokument16 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 1 Number Unit Linear Equations Quadratic Equations Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Financial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 0 Number Unit Introduction To The Course Unit SubjectDokument23 SeitenFinancial Mathematics Course FIN 118 Unit Course 0 Number Unit Introduction To The Course Unit Subjectayadi_ezer6795Noch keine Bewertungen
- I. Theories. Choose The Letter of The BEST Answer. No Erasures On Final AnswersDokument5 SeitenI. Theories. Choose The Letter of The BEST Answer. No Erasures On Final AnswersSheena CalderonNoch keine Bewertungen
- APSRTC - Employees Provident Fund TrustDokument1 SeiteAPSRTC - Employees Provident Fund TrustSK AKBAR BASHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini Case: Stock Valuation at Ragan Engines: Disusun OlehDokument6 SeitenMini Case: Stock Valuation at Ragan Engines: Disusun OlehricaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form XVIIDokument32 SeitenForm XVIIUmesh CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tugas Jatuh Tempo Sesi 9Dokument8 SeitenTugas Jatuh Tempo Sesi 9Araminta DewatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- University of Oxford Staff Pension Scheme (OSPS)Dokument1 SeiteUniversity of Oxford Staff Pension Scheme (OSPS)Mehran SameNoch keine Bewertungen
- G8 Term+3 Simple+and+Compound+InterestDokument33 SeitenG8 Term+3 Simple+and+Compound+InterestRam AthreyapurapuNoch keine Bewertungen
- (WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) CLERK SAMPLE 2Dokument23 Seiten(WWW - Entrance Exam - Net) CLERK SAMPLE 2Sunita Raturi0% (1)
- Orion Elevators Contracting PVT LTD: Payslip For The Month of May 2021Dokument1 SeiteOrion Elevators Contracting PVT LTD: Payslip For The Month of May 2021Monika ChoudhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maths Class Notes Simple Interest Mission & KSS Institute, JaipurDokument29 SeitenMaths Class Notes Simple Interest Mission & KSS Institute, JaipurNamn SuNoch keine Bewertungen
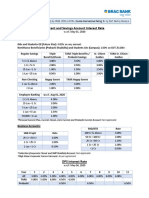
- Brac Bank Deposit Interest RateDokument2 SeitenBrac Bank Deposit Interest RateSohel RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
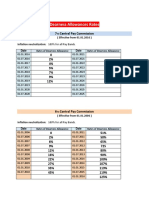
- Dearness Allowances Rates: 7 Central Pay CommissionDokument3 SeitenDearness Allowances Rates: 7 Central Pay CommissionHIRA LAL100% (1)
- Interest Rates For Fixed DepositsDokument2 SeitenInterest Rates For Fixed DepositsIndranil Roy ChoudhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- BG BPPDokument3 SeitenBG BPPHendarto WibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payslip Nov 2023Dokument1 SeitePayslip Nov 2023lonely mudasirNoch keine Bewertungen
- MySQL QueryDokument3 SeitenMySQL QueryHamesh GavaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Payslip SampleDokument1 SeitePayslip SampleWayo PhodangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rental AgreementDokument4 SeitenRental AgreementRachel PetersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- PayslipDokument1 SeitePayslipCA Manish BalaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec 23Dokument1 SeiteEc 23Jimuel Sanchez CayabasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th, 5th and 6th CPC Pay Scales and Corresponding Grade PayDokument3 Seiten4th, 5th and 6th CPC Pay Scales and Corresponding Grade PayaashuchattNoch keine Bewertungen
- W-2 Preview ADPDokument4 SeitenW-2 Preview ADPRyan AllenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenant Estoppel CertificateDokument3 SeitenTenant Estoppel Certificateholly millsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Session B - Methods To Validate Payroll EncumbrancesDokument15 SeitenSession B - Methods To Validate Payroll Encumbrancesgs2s42419Noch keine Bewertungen
- Apy Chart PDFDokument1 SeiteApy Chart PDFDeep Kumar0% (1)
- General Mathematics q2 LasDokument117 SeitenGeneral Mathematics q2 LasGian C. GuzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Per Share.: Year Devidends $ Annual GrowthDokument10 SeitenPer Share.: Year Devidends $ Annual GrowthAkuw AjahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Compound Interest: Simple Interest vs. Compound Interest Formula Sample ProblemsDokument46 SeitenCompound Interest: Simple Interest vs. Compound Interest Formula Sample ProblemsRoselle Malabanan100% (1)
- Format Rent AgreementDokument2 SeitenFormat Rent Agreementamit kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EPF Contribution Calculation: Key-In Your Basic Pay HereDokument1 SeiteEPF Contribution Calculation: Key-In Your Basic Pay HereKuzairi TokMahrajaNoch keine Bewertungen