Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
IB Waves Objectives in Word
Hochgeladen von
AMITAV JENA0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
28 Ansichten3 Seitenwave notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenwave notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
28 Ansichten3 SeitenIB Waves Objectives in Word
Hochgeladen von
AMITAV JENAwave notes
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
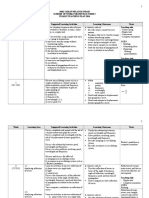
Topic 4: Oscillations and waves (10 hours)
4.1 Kinematics of simple harmonic motion (SHM)
2 hours
Aim 7: Many computer simulations of SHM are availale!
Assessment statement Teachers notes
4.1.1 "escrie e#amples of oscillations!
4.1.2 "efine the terms displacement$ amplitude$
frequency$ period and phase difference!
The connection etween fre%uency and
period should e &nown!
4.1.3 "efine simple harmonic motion (SHM) and
state the definin' e%uation as
Students are e#pected to understand the
si'nificance of the ne'ative si'n in the
e%uation and to recall the connection
etween and T!
4.1.4 Solve prolems usin' the definin' e%uation for
SHM!
4.1.5 (pply the e%uations
as solutions to the definin' e%uation for SHM!
4.1.6 So lve prolems$ oth 'raphically and y
calculation$ for acceleration$ velocity and
displacement durin' SHM!
4.2 Energ changes !uring simple harmonic motion (SHM)
1 hour
Assessment statement Teachers notes
4.2.1 "escri#e the interchange #et$een %inetic
energ an! potential energ !uring SHM.
4.2.2 Appl the e&pressions
for the %inetic energ of a particle
un!ergoing SHM'
for the total energ an!
for the potential energ.
4.2.3 Sol(e pro#lems' #oth graphicall an! #
calculation' in(ol(ing energ changes !uring
SHM.
4.) *orce! oscillations an! resonance
) hours
Assessment statement Teachers notes
4.3.1 State what is meant by damping. It is sufficient for students to know that
damping involves a force that is always in the
opposite direction to the direction of motion of
the oscillating particle and that the force is a
dissipative force.
4.3.2 Describe eamples of damped
oscillations.
!eference should be made to the degree of
damping and the importance of critical
damping. " detailed account of degrees of
damping is not re#uired.
4.3.3 State what is meant by natural fre#uency of
vibration and forced oscillations.
4.3.4 Describe graphically the variation with forced
fre#uency of the amplitude of vibration of an ob$ect
close to its natural fre#uency of vibration.
Students should be able to describe #ualitatively
factors that affect the fre#uency response and
sharpness of the curve.
4.3.% State what is meant by resonance.
4.3.& Describe eamples of resonance where the effect is
useful and where it should be avoided.
'amples may include #uart( oscillators)
microwave generators and vibrations in
machinery.
4.4 +a(e characteristics
2 hours
Assessment statement Teachers notes
4.4.1 "escrie a wave pulse and a continuous
pro'ressive (travellin') wave!
Students should e ale to distin'uish
etween
oscillations and wave motion$ and
appreciate that$ in many e#amples$ the
oscillations of the particles are simple
harmonic!
4,4,2 State that pro'ressive (travellin') waves
transfer ener'y!
Students should understand that there is no
net motion of the medium throu'h which
the wave travels!
4.4.3 "escrie and 'ive e#amples of transverse and
of lon'itudinal waves!
Students should descrie the waves in
terms of
the direction of oscillation of particles in the
wave relative to the direction of transfer of
ener'y y the wave! Students should &now
that sound waves are lon'itudinal$ that li'ht
waves are transverse and that transverse
waves cannot e propa'ated in 'ases!
4.4.4 "escrie waves in two dimensions$ includin'
the concepts of wavefronts and of rays!
4.4.5 "escrie the terms crest$ trou'h$ compression
and rarefaction!
4.4.6 "efine the terms displacement$ amplitude$
frequency$ period$ wavelength$ wave speed
and intensity!
Students should &now that
intensity amplitude)!
4.4.7 "raw and e#plain displacement*time 'raphs
and displacement*position 'raphs for
transverse and for lon'itudinal waves!
4.4.8 "erive and apply the relationship etween
wave speed$ wavelen'th and fre%uency!
4.4.9 State that all electroma'netic waves travel with
the same speed in free space$ and recall the
orders
of ma'nitude of the wavelen'ths of the
principal radiations in the electroma'netic
spectrum!
4., +a(e properties
2 hours
Assessment statement Teachers notes
4!+!1 "escrie the reflection and transmission of
waves at a oundary etween two media!
This should include the s&etchin' of
incident$
reflected and transmitted waves!
4!+!) State and apply Snell,s law! Students should e ale to define refractive
inde# in terms of the ratio of the speeds of
the wave in the two media and also in
terms of the an'les of incidence and
refraction!
4!+!- .#plain and discuss %ualitatively the diffraction
of waves at apertures and ostacles!
The effect of wavelen'th compared to
aperture or ostacle dimensions should e
discussed!
4!+!4 "escrie e#amples of diffraction!
4!+!+ State the principle of superposition and e#plain
what is meant y constructive interference and
y
destructive interference!
4!+!/ State and apply the conditions for constructive
and for destructive interference in terms of
path
difference and phase difference!
4!+!0 (pply the principle of superposition to
determine the resultant of two waves!
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Assessment 1.6Dokument2 SeitenAssessment 1.6Gohed BraunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems - Solutions To Physics of Semiconductor DevicesDokument23 SeitenProblems - Solutions To Physics of Semiconductor Deviceswazwy50% (2)
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices - ZeghbroeckDokument692 SeitenPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices - Zeghbroeckapi-371735350% (2)
- Physics 10th Class NotesDokument102 SeitenPhysics 10th Class Noteskareem345680% (5)
- Scheme of Work f5Dokument21 SeitenScheme of Work f5Eunice TangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work f5Dokument22 SeitenScheme of Work f5Asma AliasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Physics Yearly Lesson Plan 2009: Week Learning 0bjective Learning Outcome NoteDokument8 SeitenForm 5 Physics Yearly Lesson Plan 2009: Week Learning 0bjective Learning Outcome Notechekgu_2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 Wave Anatomy & Wave SpeedDokument6 Seiten1 Wave Anatomy & Wave SpeedrebbiegNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavesDokument1 SeiteWavesapi-199066238Noch keine Bewertungen
- Important Long Questions: 3. What Is Meant by Centripetal Force? Derive Relation For Centripetal Force and Acceleration?Dokument3 SeitenImportant Long Questions: 3. What Is Meant by Centripetal Force? Derive Relation For Centripetal Force and Acceleration?danialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching Plan f5 2010Dokument9 SeitenYearly Teaching Plan f5 2010zflankerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching Plan 3B.1 Wave Phase and SuperpositionDokument15 SeitenTeaching Plan 3B.1 Wave Phase and SuperpositionLiang LuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Fizik 2013 Form 5Dokument18 SeitenYearly Fizik 2013 Form 5Fazillah AziziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Teaching Plan f5 2011Dokument9 SeitenYearly Teaching Plan f5 2011zflankerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Unit PDFDokument102 SeitenWave Unit PDFPrensess BerfinNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2014: Learning Area: 1. WavesDokument15 SeitenSMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2014: Learning Area: 1. WavesaidilnurNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDCAT Curriculum 2022 Physics SyllabusDokument7 SeitenMDCAT Curriculum 2022 Physics Syllabusmunim1086Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015: Learning Area: 1. WavesDokument15 SeitenSMK Iskandar Shah Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015: Learning Area: 1. WavesTee Ting QINoch keine Bewertungen
- Students Should Be Able To Apply Their Knowledge of Simple Harmonic Motion To The Case of A Mass On A Spring, So They CanDokument1 SeiteStudents Should Be Able To Apply Their Knowledge of Simple Harmonic Motion To The Case of A Mass On A Spring, So They Canapi-199066238Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Jalan Tiga Bandar Baru Bangi Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson Plan 2009 Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Notes and VocabularyDokument25 SeitenSMK Jalan Tiga Bandar Baru Bangi Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson Plan 2009 Week Learning Area Learning Outcomes Suggested Learning Activities Notes and VocabularyGerardo Lozano GuetaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 Year 9 Physics Waves Success CriteriaDokument2 Seiten2020 Year 9 Physics Waves Success Criteriaapi-356655652Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan - Physics Form 5: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VDokument16 SeitenYearly Plan - Physics Form 5: I. Ii. Iii. Iv. VSalmizam IzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH3151 Engineering Physics Question Bank 2Dokument10 SeitenPH3151 Engineering Physics Question Bank 2p67398368Noch keine Bewertungen
- Long Questions Part 1Dokument3 SeitenLong Questions Part 1Sajid AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light and The Electromagnetic SpectrumDokument5 SeitenLight and The Electromagnetic SpectrumKavitha KaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- OCR As and A Level Physics A Delivery Guide - WavesDokument30 SeitenOCR As and A Level Physics A Delivery Guide - WavesNazib UchchhasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learning Outcome: Students Are Able ToDokument2 SeitenLearning Outcome: Students Are Able ToAlan KhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PH3151 QB 01Dokument5 SeitenPH3151 QB 01mayankraj1744Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physcs LONG QUESTIONSDokument2 SeitenPhyscs LONG QUESTIONSpaggal janNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPH (F5) PhysicsDokument8 SeitenRPH (F5) PhysicsidulNoch keine Bewertungen
- DP1 Unit Planner Topic 4Dokument23 SeitenDP1 Unit Planner Topic 4Mona Mohamed Safwat100% (1)
- Entire Lesson - Waves and Wave Properties - TeachEngineeringDokument5 SeitenEntire Lesson - Waves and Wave Properties - TeachEngineeringChris SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- JR Phy Impshort Answer QuestionsDokument1 SeiteJR Phy Impshort Answer Questionsrkstudyc_gmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013Dokument17 SeitenYearly Plan Physics Form 5 2013qq2350% (1)
- Physics: Waves Whole Unit Overview: Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities ResourcesDokument2 SeitenPhysics: Waves Whole Unit Overview: Learning Outcomes Suggested Teaching Activities ResourceszahraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Required Practical Investigating Stationary WavesDokument6 SeitenRequired Practical Investigating Stationary WavesIts AxstroZzz-Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wawe UnitDokument104 SeitenWawe UnitEMMABOICUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edited - Frequency and Pitch January 12Dokument5 SeitenEdited - Frequency and Pitch January 12tudor.chirivilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Key Points CAT II US v4.1Dokument18 SeitenKey Points CAT II US v4.1Fifth AnalistNoch keine Bewertungen
- 48 Demo of Wave TypesDokument6 Seiten48 Demo of Wave TypesChess ManNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigation 11 - Experience 1Dokument31 SeitenInvestigation 11 - Experience 1weldeenytNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 WavesDokument114 Seiten4 WavesArrush AhujaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CE 634 / OC 634 Long Wave Mechanics 3 CreditsDokument2 SeitenCE 634 / OC 634 Long Wave Mechanics 3 CreditsSyazwan BazliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shri Shankaracharya Group of Institutions B.E. - II Semester (Sec-I)Dokument3 SeitenShri Shankaracharya Group of Institutions B.E. - II Semester (Sec-I)Anonymous l5X3VhTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Waves-Unit 2Dokument35 SeitenIntroduction To Waves-Unit 2Graham NicholsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Curriculum 20201598663140Dokument18 SeitenPhysics Curriculum 20201598663140TariqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bme7001-Te CN 21 22Dokument4 SeitenBme7001-Te CN 21 22Sunil Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.1 - Waves - Sound: IB Physics Content GuideDokument4 Seiten7.1 - Waves - Sound: IB Physics Content GuideShivang KeshriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Go Enzo Nathan - WAES - Asynch-02Dokument4 SeitenGo Enzo Nathan - WAES - Asynch-02enzonathan.goNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronics, John Wiley and Sons, 1994Dokument3 SeitenElectronics, John Wiley and Sons, 1994Fere GodspowerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDokument16 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiHelmi TarmiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Dokument17 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5Salmizam IzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Fizik 5 2019Dokument17 SeitenRPT Fizik 5 2019Mashithoh RosliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Form 5 Yearly Lesson PlanDokument22 SeitenPhysics Form 5 Yearly Lesson PlanMohd Khairul Anuar100% (6)
- Yearly Lesson Plan (Physics F5) 2016Dokument28 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan (Physics F5) 2016qq235100% (1)
- AQA Physics Unit 6 Waves Student Progress SheetDokument7 SeitenAQA Physics Unit 6 Waves Student Progress SheetGabriel HoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fis 1Dokument33 SeitenFis 1syafrina novitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Sc. Ed. 422. Physics IIDokument15 SeitenFinal Sc. Ed. 422. Physics IItikaram gautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMK Methodist Ayer Tawar Perak Scheme of Work Form 5 Physics YEAR 2020Dokument22 SeitenSMK Methodist Ayer Tawar Perak Scheme of Work Form 5 Physics YEAR 2020khalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Standing Wave An Upright WaveDokument7 SeitenStanding Wave An Upright WavekamiruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 SmktpiDokument16 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Physics Form 5 2015 Smktpihelmi_tarmiziNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulse and Fourier Transform NMR: Introduction to Theory and MethodsVon EverandPulse and Fourier Transform NMR: Introduction to Theory and MethodsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Report of Online Class - Amitav JenaDokument1 SeiteReport of Online Class - Amitav JenaAMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp DealerDokument4 SeitenComp DealerAMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Online Class-10 - 23 April 2020Dokument1 SeiteOnline Class-10 - 23 April 2020AMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- What Makes Polarized Lenses So Protective: By:Alistair FlynnDokument9 SeitenWhat Makes Polarized Lenses So Protective: By:Alistair FlynnAMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- IndicDokument1 SeiteIndicAMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Comp DealerDokument4 SeitenComp DealerAMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusDokument1 SeiteSyllabusAMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- EE1 LecturenotesDokument53 SeitenEE1 LecturenotesVivek SuranaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3Dokument18 SeitenLec 3api-3721075Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3Dokument9 Seiten3AMITAV JENANoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics CH 2+3+4+8Dokument8 SeitenPhysics CH 2+3+4+8Kashif KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- GeneralPhysics1 12 Q2 Module3 Periodic-MotionDokument34 SeitenGeneralPhysics1 12 Q2 Module3 Periodic-MotionJoshua RaninNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter No. 10Dokument50 SeitenChapter No. 10Mazher ShahabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes - Topic 13 Oscillations - CAIE Physics A-LevelDokument6 SeitenNotes - Topic 13 Oscillations - CAIE Physics A-LevelKen OtooNoch keine Bewertungen
- APEAPCET2024 InstructionBooklet EngineeringDokument39 SeitenAPEAPCET2024 InstructionBooklet Engineeringmamilla balakrishna reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Ebook - Class 11 - Part 2Dokument209 SeitenPhysics Ebook - Class 11 - Part 2Haltz t00nNoch keine Bewertungen
- 312 Physics Eng Lesson13Dokument10 Seiten312 Physics Eng Lesson13Aero e3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathongo Question SHM Jee Main 2021 February ChapterwisePBnK5LFaRexKSKglmOS0Dokument6 SeitenMathongo Question SHM Jee Main 2021 February ChapterwisePBnK5LFaRexKSKglmOS0Neerada PrajothNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Capsule For ICAR Technician 2022 ExamDokument69 SeitenScience Capsule For ICAR Technician 2022 ExamAbhijit NathNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1902 Enthusiast Phase-I (A) Paper-2 (E) (JA)Dokument28 Seiten1902 Enthusiast Phase-I (A) Paper-2 (E) (JA)Lakshya vashishtNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Dokument64 SeitenModul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Herman_MLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oscillations: V V V V V VDokument6 SeitenOscillations: V V V V V VZeba SiddiquiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAPE Physics Unit I MarathonDokument26 SeitenCAPE Physics Unit I MarathonLeighton ThompsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diploma in Computer Engineering 2018Dokument174 SeitenDiploma in Computer Engineering 2018Bikash WagleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Doc04 Lab Manual ExperimentsDokument22 SeitenDoc04 Lab Manual ExperimentsNutthaphat ToopanichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pdf. AP Physics C Mechanics Comprehensive Equations GuideDokument7 SeitenPdf. AP Physics C Mechanics Comprehensive Equations GuideJohn McEnroeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Tutorial 10-Natural Vibrations-One Degree of Freedom-27p PDFDokument31 SeitenDynamics Tutorial 10-Natural Vibrations-One Degree of Freedom-27p PDFmanfredm6435Noch keine Bewertungen
- TERM 2 Important Questions of Class 11thDokument9 SeitenTERM 2 Important Questions of Class 11thAdityaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anschp 14Dokument17 SeitenAnschp 14pashelo001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2022 Spring AP Physics C FinalDokument25 Seiten2022 Spring AP Physics C FinalQiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ariosn A'level PhysicsDokument60 SeitenAriosn A'level PhysicsFELECIAN AMOSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mth401 Quiz 3 Finl TRM MonkeyDokument319 SeitenMth401 Quiz 3 Finl TRM Monkeysapen79344Noch keine Bewertungen
- PHYICSDokument116 SeitenPHYICSDebayan BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB10 - SimpleHarmonicMotion - 1Dokument3 SeitenLAB10 - SimpleHarmonicMotion - 1Lucy fNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE (ADV) 2015 SOLUTION Paper 1 PDFDokument28 SeitenJEE (ADV) 2015 SOLUTION Paper 1 PDFAakash KapoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dynamics Part 1Dokument109 SeitenDynamics Part 1Maricel Bulay-og0% (1)
- PHY1104 B Lab Report09Dokument15 SeitenPHY1104 B Lab Report09plshamburger17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ib SL Waves Exercize X2aDokument12 SeitenIb SL Waves Exercize X2abhuwan gargNoch keine Bewertungen