Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Technical Writing Characteristics Requirements Aspects Principles
Hochgeladen von
John Mark0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
406 Ansichten2 Seitentechnical writing
Originaltitel
Technical Writing Chapter 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldentechnical writing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
406 Ansichten2 SeitenTechnical Writing Characteristics Requirements Aspects Principles
Hochgeladen von
John Marktechnical writing
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
Chapter 1
NATURE AND REQUIREMENTS OF TECHNICAL WRITING
Questions:
1. Define technical writing and discuss its characteristics
2. Distinguish technical writing in terms of the following criteria
Purpose
Subject Matter
Readers
3. Identify what people in the technical professions are required to write
4. Recognize the aspects of technical writing
5. Discuss the basic principles of good technical writing
Answers:
1. Technical writing is communication the primary aim of which is to convey a particular
piece of information for a particular purpose to a particular reader or group of readers.
And its characteristics are Objective, clear and accurate, concise and unemotional in its
presentation of facts, descriptions of mechanisms, descriptions of process,
classifications and interpretation.
2.
2.1 Purpose of Technical Writing
First, it gives information that leads to the accomplishment of specific tasks and in
the making of needed decision
Second, technical writing analyzes events and their implications, the failure of
certain systems are educational, socio-economic, political, etc. and the needed
changes.
Third, technical writing persuades and influences decision by showing how a
business or an industry succeeds because of just and fair treatment of labor, how an
agency like the NAPOCOR can improve the energy situation and save money, and
how the educational system can be improved through the implement of the
recommendations of the Educational Commission to Survey Philippine Education
(EDCOM).
2.2 Subject Matter Of Technical Writing
The content of technical writing is objective information that is accurately and
clearly presented. Technical readers need to know exactly what the piece of writing
means. It tells the reader exactly what to do, How to do it, and under what
conditions to do it.
Technical writing records data in business, science, engineering, industry and in all
the formal aspects of professional areas. It presents factual data, statistics and
measurable elements.
2.3 Readers of Technical Writing
The readers may be specific individuals or a general group with common interests.
In both groups, they are reading for particular purposes. They may be expects in the
field or in a related or another field. They may be managers, supervisors,
secretaries, engineers, scientists, sociologists, psychologists, technicians and they
come from any discipline of professional area.
3. Type of Writing Required in the Technical Professions
Some of the materials that people in the technical professions write consist of reports of
various sorts, memoranda, proposals, professional papers to be read or included in a
magazine or book, technical bulletins, manuals, handouts and even books. And also they
acquire experience, more and more often they may be asked to make recommendations
about decisions or make the decision themselves. Letters from customers of the company
have to be answered. Annual reports are a common writing assignments. Progress and final
reports are required for certain objects.
4. Basic Aspects of Technical Writing
- Technical writing may be subdivided into two parts, or aspects:
1. The Final products such as reports and letters, usually the specific material presented
2. The skills that are made use of in the preparation of the final product.
Final products or specific technical materials usually written:
a. Various kinds of written reports
b. Oral reports
c. Business letters
d. Articles for technical journals or books
e. Abstracts
f. Instruction manual
g. Graphic aids
h. Handbooks
i. Brochures
j. Specifications
k. Memoranda
l. Proposals
The following skills are important in technical writing:
a. Special techniques of technical writing, the most important of which are definitions,
descriptions of mechanisms, descriptions of processes, classification and interpretation.
b. Style
c. Introductions, transitions and conclusions
d. Outlines for organizations
e. The layout, or format of reports
6. Basic Principles of Good Technical Writing
a. The writer of a report must have a specific readers or group readers in mind
b. He must decide what the specific purpose of his report is and make sure that every part
of his report contributes to that purpose
c. He must use specific, single, concrete words and familiar language that cannot be
misinterpreted
d. The writer must check every part of his report to see whether he has followed the
principles of first, Telling the reader what he is going to tell them; second, telling them;
and third, telling them what he told them.
e. He must make his report very presentable in format. The layout must conform to
standard forms of writing.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Technical Writing Prelim ModuleDokument6 SeitenTechnical Writing Prelim ModuleKarl John Jay ValderamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nature of Technical WritingDokument2 SeitenNature of Technical WritingNaps ShaeneNoch keine Bewertungen
- The School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas City: College of Education Colegio de La Purisima ConcepcionDokument22 SeitenThe School of The Archdiocese of Capiz Roxas City: College of Education Colegio de La Purisima ConcepcionMergel Javillo100% (1)
- Lesson 1Dokument14 SeitenLesson 1Dolly Lyn ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Learn Technical Writing SkillsDokument10 SeitenLearn Technical Writing SkillsjoshuaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Technical Writing SkillsDokument17 SeitenImportance of Technical Writing SkillsJoenel DucayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20th Century Modern PeriodDokument10 Seiten20th Century Modern PeriodOussama HarizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Rousing Technical ReportsDokument24 SeitenWriting Rousing Technical ReportsBianca Petalio67% (3)
- Teaching and Assessment of The MacroskillsDokument7 SeitenTeaching and Assessment of The MacroskillsDarcknyPusodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Characteristics of Technical WritingDokument2 SeitenCharacteristics of Technical Writingwaqarali78692100% (1)
- LESSON 3 Writing Effective Business CorrespondenceDokument4 SeitenLESSON 3 Writing Effective Business CorrespondenceDiamante MhayaleneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lit 313 - Survey of Afro Asian LiteratureDokument9 SeitenLit 313 - Survey of Afro Asian LiteratureKyla RamiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Techniques in Technical WritingDokument26 SeitenBasic Techniques in Technical WritingCecillia Evan50% (4)
- 12 Strategies For: Teaching Literature in The 21st CenturyDokument8 Seiten12 Strategies For: Teaching Literature in The 21st CenturyJosethNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Instructional Design of A Coursebook Is As It Is Because of What It Has To DoDokument55 SeitenThe Instructional Design of A Coursebook Is As It Is Because of What It Has To Doanon_409285199100% (2)
- 01 Characteristics of Effective Technical WritingDokument1 Seite01 Characteristics of Effective Technical WritingReggie PalaganasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing MemorandaDokument18 SeitenWriting MemorandaBianca PetalioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual in The Teaching and Assessment of Literature Studies (ENG 358)Dokument17 SeitenManual in The Teaching and Assessment of Literature Studies (ENG 358)Armina Guiamalon100% (1)
- Human Development Meaning Concepts ApproachesDokument3 SeitenHuman Development Meaning Concepts ApproachesroseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan in English 8: 7:40 A.M. - 8:40 A.MDokument1 SeiteLesson Plan in English 8: 7:40 A.M. - 8:40 A.MEJ Escobillo0% (1)
- Technical Writing SyllabusDokument6 SeitenTechnical Writing Syllabusapi-194241825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Genre of PoetryDokument5 SeitenGenre of PoetryRoger RanigoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Republic of The Philippines West Prime Horizon Institute, Inc. Course Syllabus in Language and Education ResearchDokument11 SeitenRepublic of The Philippines West Prime Horizon Institute, Inc. Course Syllabus in Language and Education ResearchJessaMae AlbaracinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus On Philippine LiteratureDokument6 SeitenSyllabus On Philippine LiteratureArche Udtohan Gaudel100% (1)
- Chapter 1: Understanding The Nature of Technical WritingDokument3 SeitenChapter 1: Understanding The Nature of Technical WritingRaquel LimboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tech Writing Module 2Dokument19 SeitenTech Writing Module 2Elizabeth VelosoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Remedial Instruction in EnglishDokument18 SeitenRemedial Instruction in EnglishEd-Jay Ropero100% (1)
- Week Topic Subtopic Language Focus Indicator Activity Materials AssessmentDokument8 SeitenWeek Topic Subtopic Language Focus Indicator Activity Materials AssessmentnouvaleeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Afro Asian LiteratureDokument4 SeitenAfro Asian LiteratureRoxane Rivera100% (1)
- Eng 14 Afro Asian Literature PDFDokument5 SeitenEng 14 Afro Asian Literature PDFEzio AuditoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Testing LiteratureDokument6 SeitenTesting LiteratureRussNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teaching and Assessment of Grammar Activity JustineDokument2 SeitenTeaching and Assessment of Grammar Activity JustineJustine Palma100% (1)
- City College Course Outline for Children's LiteratureDokument3 SeitenCity College Course Outline for Children's LiteratureAlexandria Calixihan100% (1)
- Synopsis of Afro-Asian LiteratureDokument57 SeitenSynopsis of Afro-Asian Literatureمہنور مہتاب100% (2)
- 5 Assessment of GrammarDokument6 Seiten5 Assessment of GrammarEdisson Jan Esteban100% (1)
- Writing A Critique PaperDokument20 SeitenWriting A Critique PaperKurt Leonard AlbaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Components of Technical Writing VS Essays: Lecturer: Zeenatullah " Sail "Dokument14 SeitenComponents of Technical Writing VS Essays: Lecturer: Zeenatullah " Sail "Shabeer Maheer100% (1)
- Syllabus in Lit 2 Mythology and Folklore VisionDokument6 SeitenSyllabus in Lit 2 Mythology and Folklore VisionCarmie Lactaotao DasallaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Literary Criticism ApproachesDokument6 SeitenLiterary Criticism ApproachesJojie BatoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- v. Special Techniques of Technical CommunicationDokument25 Seitenv. Special Techniques of Technical CommunicationAnna DerNoch keine Bewertungen
- MECHANICS and PROCESS OF SPEAKINGDokument8 SeitenMECHANICS and PROCESS OF SPEAKINGongcojessamarie0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Macroskills SyllabusDokument14 SeitenMacroskills SyllabusHarold LuceroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Developing Materials For SpeakingDokument29 SeitenDeveloping Materials For SpeakingKristine OgatisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Technical Writing ModuleDokument4 SeitenTechnical Writing ModuleNicky Cardenas100% (3)
- Lexico GrammarDokument42 SeitenLexico GrammarSabarlah DirikuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication For Academic PurposesDokument18 SeitenCommunication For Academic PurposesMax100% (1)
- Teaching & Assessment of The Macro SkillsDokument16 SeitenTeaching & Assessment of The Macro SkillsKrystel Mary SungaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldersgate College Teaching and Assessment of Literature Studies College of Arts, Sciences and Education Junelyn G. Villar, LPTDokument12 SeitenAldersgate College Teaching and Assessment of Literature Studies College of Arts, Sciences and Education Junelyn G. Villar, LPTJunelyn GapuzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speech Theater Arts Unit1Dokument7 SeitenSpeech Theater Arts Unit1Billy De Guzman UsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 ESP GenesisDokument25 Seiten02 ESP GenesisAlvin Gacer0% (1)
- Survey of Philippine LiteratureDokument82 SeitenSurvey of Philippine LiteratureEdnylyn Joyce Capa100% (2)
- "Of Studies" by Francis BaconDokument18 Seiten"Of Studies" by Francis BaconRo AnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elt 214 Week 6-7 Ulo B SimDokument12 SeitenElt 214 Week 6-7 Ulo B SimELLEN JANE BARASOLIANoch keine Bewertungen
- The Functions of Speech Communication AreDokument4 SeitenThe Functions of Speech Communication AreOcy Tojon0% (1)
- English K-12 Curriculum FrameworkDokument5 SeitenEnglish K-12 Curriculum FrameworkRENATO JR. RARUGALNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gendered Language DifferencesDokument9 SeitenGendered Language DifferencesMichelle BautistaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 (Materials Adaptation)Dokument13 SeitenUnit 3 (Materials Adaptation)Alvin DulinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Technical WritingDokument22 SeitenUnderstanding Technical WritingMark David Francisco100% (1)
- College Teaching Studies in Methods of Teaching in the CollegeVon EverandCollege Teaching Studies in Methods of Teaching in the CollegeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intro to Technical WritingDokument4 SeitenIntro to Technical WritingCarlo Mabini BayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Southwestern University: Application FormDokument1 SeiteSouthwestern University: Application FormThiody Hope LimosneroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gap Between Theory and Practice in The NursingDokument7 SeitenGap Between Theory and Practice in The NursingMark Jefferson LunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Leadership Compass ActivityDokument5 SeitenLeadership Compass ActivityPsiho LoguseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Business and Technology SyllabusDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To Business and Technology Syllabusapi-558398592Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bagus Kevin Raspati Join Ms. Nabella's Class On Edmodo: SubtitleDokument38 SeitenBagus Kevin Raspati Join Ms. Nabella's Class On Edmodo: SubtitleYahahah WahyuuNoch keine Bewertungen
- HISTORY of Abnormal PsychologyDokument12 SeitenHISTORY of Abnormal PsychologyDaisy AllenNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3RD Quarter Numeracy TestDokument4 Seiten3RD Quarter Numeracy TestJennyfer TangkibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection Paper (GMRC)Dokument7 SeitenReflection Paper (GMRC)Jesica Brizak OrbanejaNoch keine Bewertungen
- JEE Mains & Advanced 2022-DifferenceDokument3 SeitenJEE Mains & Advanced 2022-DifferenceEzhil MukilNoch keine Bewertungen
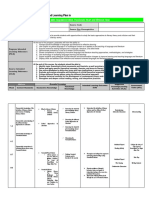
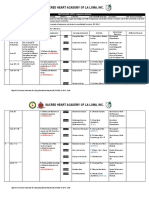
- Curriculum Map Grade 10 2019 2020Dokument15 SeitenCurriculum Map Grade 10 2019 2020Sacred Heart Academy of La Loma100% (1)
- An ESP Course Design For Airport Information Desk StaffDokument23 SeitenAn ESP Course Design For Airport Information Desk StaffAnonymous WCvomEEfNoch keine Bewertungen
- MED 1101 - Descriptive Anatomy I - 2015Dokument8 SeitenMED 1101 - Descriptive Anatomy I - 2015Sanjay VeerasammyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Education System of IndiaDokument14 SeitenEducation System of IndiaCaraxu James Ballesteros AmbrosioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vocabulary and grammar practice with prefixes, verbs and adjectivesDokument3 SeitenVocabulary and grammar practice with prefixes, verbs and adjectivesRosa MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edu 693 Portfolio Project Iain Fotheringham Section 3Dokument46 SeitenEdu 693 Portfolio Project Iain Fotheringham Section 3api-302484142Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aldharizma - An Analysis of 101 Activities For Teaching Creativity and Problem Solving by Arthur BDokument13 SeitenAldharizma - An Analysis of 101 Activities For Teaching Creativity and Problem Solving by Arthur BInd17 KhairunnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduling and Load BalancingDokument11 SeitenScheduling and Load BalancingSubburam SivakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 10 - Q3 - W6 - D2Dokument2 SeitenScience 10 - Q3 - W6 - D2zenaida a academiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BVOC - Syllabus Semmester I To VI - Final - 1Dokument47 SeitenBVOC - Syllabus Semmester I To VI - Final - 1Vikash. VNoch keine Bewertungen
- ListDokument5 SeitenListmyjoyonline.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Occupation Description AlphabeticalDokument24 SeitenOccupation Description AlphabeticalOvidiu CiobanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Affairs ReportDokument17 SeitenStudent Affairs ReportCalu MorgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ingles Evau Sept20Dokument4 SeitenIngles Evau Sept20Inés AlmenarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Department of Education - Division of PalawanDokument27 SeitenDepartment of Education - Division of PalawanJasmen Garnado EnojasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phase Diagram of Water Andcarbon DioxideDokument17 SeitenPhase Diagram of Water Andcarbon Dioxideraiyi shionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Number 1Dokument5 SeitenAssignment Number 1Ren HarryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychological Impact of COVID-19 in Grade 12 HUMSSDokument18 SeitenPsychological Impact of COVID-19 in Grade 12 HUMSSPsyche AnithaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Political SocialisationDokument6 SeitenPolitical SocialisationDivyank SurumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Emotional Intelligence and Affective Events in Nurse Edu - 2017 - Nurse EducatioDokument7 SeitenEmotional Intelligence and Affective Events in Nurse Edu - 2017 - Nurse EducatioarbhNoch keine Bewertungen
- I'll Be Back: Elementary IIDokument16 SeitenI'll Be Back: Elementary IIMIGUEL SANTIAGO SAAVEDRA DAZANoch keine Bewertungen