Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Week 5
Hochgeladen von
rafiqueuddin93Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Week 5
Hochgeladen von
rafiqueuddin93Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Week 5 - How Computers Work
Magnetic Disk
Magnetic Disk is usually referred as a hard disk and short for HD or HDD. The hard drive is
the computer's main storage media device. Its purpose is to permanently store all data on the
computer.
The hard drive consists of one or more hard drive platters inside of air sealed casing. Platter is one or
more aluminium glass or ceramic disk coated in a magnetic media which is inside a hard drive. The
platters permanently store the computer's data. The platters begin to rotate when a computers
power is turned on. The rate of rotations per minute (RPM) varies depending upon the hard drives
model, 7200 RPM is most common in modern hard drives. As the disk platters rotate, the read/write
head accesses information on one of the platters helping to store and retrieve the data from
the platter. Data is stored in tracks, sectors, and cylinders on each platter.
Most computer hard drives are placed in an internal drive bay located at the front of a computer. A
hard drive is connected to the motherboard via an ATA, SCSI, or a SATA and power cable.
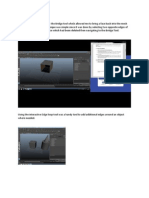
This is an image of inside of a hard drive for a desktop and laptop
Disk Capacity
Solid State Disk SSD
A solid-state drive (SSD is also known as electronic disk which is also a data storage
device using integrated circuit A SSD contains no actual "disk" of any kind or motors to "drive" the
disks. Electronic interfaces is used by SSD technology which is compatible with
traditional block input/output (I/O)hard disk drives. SATA Express are one of the new
interfaces created to catch up with the speed of SSD technology.
HDDs (Hard Disk Drive) run electromechanical magnetic disks however SSDs have no moving
mechanical components. Compared to HDDs which use electromechanical disks, SSDs are generally
more resistant to physical shock. SDDs also run silently, have lower access time and less latency
(time interval between the stimulation and response.
Comparison
A solid state drive ( SSD) can significantly speed up a computers performance, than upgrading to a
faster processor (CPU) . Although hard disk drives (HDD) are cheaper to buy and has higher storage
capacity, SSD disks are considerably expensive and generally available in 64 GB to 256 GB
configurations.
Below I have constructed a comparison chart showing how HDDs and SSDs differentiate between
each other.
Attribute Hard Disk Drive Solid State Drive
Speed
HDD has higher latency, longer
read/write times, and supports fewer
IOPs (input output operations per
second) compared to SSD.
SSD has lower latency, faster
read/writes, and supports more
IOPs (input output operations
per second) compared to HDD.
Heat, Electricity, Noise Hard disk drives utilize higher electricity
to rotate the platters which generate
heat and noise.
SSDs has no platters, instead
SSDs operate using a integrated
electronic circuit. Which means
less power is used and no heat
or noise is generated.
Defragmentation The performance of HDD drives
reduces because of the fragmentation
hence HDDs needs to be periodically
defragmented.
The performance of SSD drive is
not affected by fragmentation
as a result there is no need for
defragmentation.
Components HDD contains moving parts called
platters which is a motor driven spindle
holding flat circular disks with a
magnetic material. Magnetic heads are
positioned on top of the platters to
read and write the data.
Since SSD is essentially a
memory chip moving parts is
not required. The memory chip
consists of interconnected and
integrated circuits (ICs) with an
interface connector. There are
three basic components in
which are the controller, cache
and capacitor.
Weight HDDs are significintly heavier than SSD
drives.
because SSD drives do not have
the rotating disks (platters),
spindle and motor, SSDs are
much lighter than HDD drives
Vibration The moving parts of HDDs increases the
chance of crashes and damage because
of the vibration.
SSD drives can hold up to
2000Hz of vibration which is
more than HDD can withhold .
RAID
RAID is an collection of hard drives connected together. RAID is setup in ways to helps protect or
speed up the performance of a computer's disk storage. RAID is mainly used on servers and high
performance computers.
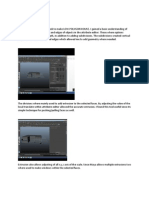
This a Drobo which uses RAID technology. It is a external storage hardware device which connects to
computers using numerous connections such as USB, Firewire, eSATA and iSCSI. The Dobo hardware
enables users to connect up to four or eight SATA hard drives depending upon four or eight ports.
RAID uses the following techniques:
Spanning and Software Striping
Splitting and writing information across to multiple physical disk drives. (RAID 0)
Mirroring
Duplicates data from one disk drive to another.
Duplexing
Duplicates the disk drive as well as the disk controller.
Deferred
As the disk drive becomes available, data is cached in cache memory then writes to the hard
drive
Hot Swapping
Failed disk drives can be replaced and data can be placed back onto the disk drive while the
remainder of the system is in operation
Hot Sparing
Disk drive can automatically be initialized into the array when another fails.
Spindle Synchronization
RAID 0
Minimum of 2 drives is needed for software stripping and Block Incorporation. Data is sucessfully
written to each drive. Each block then goes to the next available drive although the data which
distributed across the array drives. This is known as stripping. With data requests, stripping
provides faster operation and chances of a drive getting overloaded is dropped.
Because no redundancy is provided, the volume of any single drive can increase. If a single drive fails
the system will go down. RAID 0 is the fastest and most efficient array type however it has no
tolerance to faults.
Stripe set without parity
file blocks spread over a number of disks
Improved performance no fault tolerance
Duplex system transferring information.
RAID 1
Minimum of 2 drives is required for Disk Mirroring and Duplexing. The drives are used in pairs and all
data is written identically to both drives.
By connected to its own interface controller each drive can have two parts. In RAID 1 if one drive
fails, the system will not go down because the other drive will continue to operate.
This means two drives will be used for the equivalent of one drives storage capacity. The
performance cannot be improved at this level however if no more than two drives need to be used
then RAID 1 is the only choice for fault tolerance
Disk mirroring
Data written to two disks
Fault tolerance but no performance gain
Duplexing has two controllers
RAID 0+1, 0/1 or 10
Striped set mirrored
RAID 2- 4
RAID 2 deals with data striping and bit interleave. Data is written across each drive one bit at a time
with success. A separate drive records Checksum data (error detection scheme accompanied by a
numeric value) although this method is very slow for disk writing.
RAID 3
RAID 3 is similar to RAID 2 which also consists of data striping with bit interleave and parity
checking but more reliable. Data striping is done across the drives with very high data transfer
rates one byte at a time. Usually 4 or 5 drives are used with one drive dedicated to storing
parity information.
RAID 3 uses the parity drive to reconstruct failed drive content. Failure of a single drive can be
counter balanced. Since the parity drive is accessed on every write operation, the writing of
data is slower thereby failure of two drives or more can be a problem.
RAID 3 can be used in data intensive or single users. The speed of data transfer can be
increased by accessing long sequential records however RAID 3 requires synchronized spindle
drives to prevent performance being degraded with short records. Overlapping of multiple
I/O (input/output) operations is not allowed in RAID 3.
RAID 4
RAID 4 involves block interleave data striping with parity checking. A single parity drive and
block data striping is used like in RAID 0. An individual drive reads a block of data however the
other drives of RAID 4 function individually. A failure of the controller will cause sudden
damage to data. Multiple simultaneous write operations is not supportive which is the big
disadvantage over RAID-5
RAID 5
RAID 5 comprises block interleave and data striping with distributed check data on all drives. Parity
information is distributed across all drives. As the number of disks increases, RAID 5 efficiency is
increased too.
A failed drive on "the fly can be rebuilt by hot spares. RAID 5 is the best choice in multiuser
environments. A minimum of three but generally five drives are required for RAID-5 arrays.
Striped set with parity
As 4 but parity spread over different disk
Magnetic Tape backup
A magnetic tape is coated in magnetically thin piece plastic wrapped around wheels which stores
data.
External Disk Systems
Fibre channels have high speed and low latency with full duplex data communications scheme which
is optimized to carry large blocks of data. Fibre channels are capable of supporting up to more than
1Gbits a second.
Compact Disk
CD (compact disc) is a flat round storage mechanism which is read by a laser in a CD-ROM that was
James Russell invented this mechanism . The first CD was manufactured at a Philips factory in
Germany on August 17 1982.72 minutes of music or 650 MB of data can be held in a standard CD .
700 MB of data is contained in an 80 minute CD which is also commonly used to store data.
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/c/compactd.htm
A single spiral track divided into blocks
Blocks addressed by minute:second:block
Laser light reflected of land / pit
Can hold up to about 800 MB of data.
Transfer speed dependent on spin speed
(single speed rate approx. 150KB/s).
Random access time dependent on how fast head can be moved to appropriate part of
track.
CD-ROM Format
Digital Vesatile Disc
DVD is short for Digital Versatile Disc or Digital Video Disc. A DVD or DVD-ROM is the same size of a
standard Compact Disc which is also capable of storing large amounts of data on one disc.
Upon introduction to DVD drives in 1997, they were commonly used for storing and viewing movies
and other data. A DVD drive and a DVD player are required to play a DVD on a computer. A software
program which supports MPEG4 or dedicated software made for a specific DVD player is also
required to play and control a DVD disc.
Data Storage Capacity:
A single DVD disc is capable of holding numerous capacities. I have stated a listing of the
different types of DVD's and its total capacity.
Single sided, single layer disc are the most common DVD's capable of holding up 4.7 GB of
data.
A single sided, double layer disc is capable of holding between 8.5 to 8.7 GB of data.
A double sided, single layer disc is capable of holding up to 9.4 GB.
Double sided, double layer disc is capable of holding up to 17.08 GB.
How DVD and CD differentiate?
Although a DVD and CD disk are the same physically in diameter and width. Both discs have
one side with a label and the other side blank which the laser reads. Double sided DVD disks
can read from both sides. DVD technology stores significantly greater volume of data than a
CD
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/d/dvd.htm
Multilayer design and smaller pits mean a DVD can hold more data than a CD.
Capacity
hold about 17GB
48x CD-ROM mode
24x in DVD mode (base speed = 1.26MBytes/sec)
DVD-R and DVD-RAM
hold about 2.6GB per side. 4x
4.7 GB total
DVD-RW & DVD+RW
+RW has superior RW performance (2.4x) but can not write DVD-R which has
greatest compatibility
Blu-Ray Disc
BD or BD-ROM is short for Blu-ray Dis which is an optical disc cooperatively developed by thirteen
electronics and PC companies such as Dell, Hitachi, Hewlett Packard and LG. The Blu-ray was first
introduced in the 2006 CES (Consumer Electronic Show) on January 4, 2006. CES is a convention
held around the world allowing manufacturers and developers to talk about their latest electronic
devices, gadgets, and ideas. Blu-ray is capable of storing up to 25 GB of data on a single layer disc
and 50 GB on a dual layer disc.
Blu-ray discs are also the same size as a standard CD.
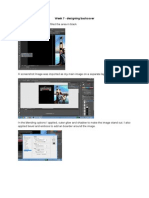
This is a picture of a blue laser on Blu-ray disc players.
Same size as CD/DVD
Uses Blue/Violet laser rather than red
25GB per Layer
Can be dual layer
Up to 12x (1x is 4.5MBps)
References
Computerhope.com. 2014. What is hard drive?. [online] Available at:
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/h/harddriv.htm [Accessed: 27 Mar 2014].
Computerhope.com. 2014. What is platter?. [online] Available at:
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/p/platter.htm [Accessed: 27 Mar 2014].
Wikipedia. 2014. Solid-state drive. [online] Available at: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solid-
state_drive [Accessed: 28 Mar 2014].
Diffen.com. 2014. HDD vs SSD - Difference and Comparison | Diffen. [online] Available at:
http://www.diffen.com/difference/HDD_vs_SSD [Accessed: 30 Mar 2014].
Computerhope.com. 2014. What is RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks)?. [online] Available
at: http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/r/raid.htm [Accessed: 1 Apr 2014].
Computerhope.com. 2014. What is fibre channel?. [online] Available at:
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/f/fibrecha.htm [Accessed: 4 Apr 2014].
Computerhope.com. 2014. What is DVD (Digital Versatile Disc)?. [online] Available at:
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/d/dvd.htm [Accessed: 5 Apr 2014].
Black, R. 2014. What the heck is a Blu-Ray Home Theatre System?. [online] Available at:
http://www.bigbrownboxblog.com.au/av-talk/what-the-heck-is-a-blu-ray-home-theatre-system-
and-how-can-it-immerse-you-in-the-action [Accessed: 5 Apr 2014].
Computerhope.com. 2014. What is BD (Blu-ray Disc)?. [online] Available at:
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/b/bd.htm [Accessed: 5 Apr 2014].
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Managing e BusinessDokument3 SeitenManaging e BusinessNeelesh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Evaluation AnimationDokument2 SeitenEvaluation Animationrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12 NewDokument8 SeitenWeek 12 Newrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week6 Model CompleteDokument10 SeitenWeek6 Model Completerafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4Dokument4 SeitenWeek 4rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 9Dokument2 SeitenWeek 9rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2Dokument4 SeitenWeek 2rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8Dokument5 SeitenWeek 8rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 11Dokument2 SeitenWeek 11rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10Dokument1 SeiteWeek 10rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- For The Texturing Part of My Model I Decided To Assign The Ocean Shader Material For The Two LinesDokument20 SeitenFor The Texturing Part of My Model I Decided To Assign The Ocean Shader Material For The Two Linesrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week4 ModelsDokument8 SeitenWeek4 Modelsrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week5 ModelsDokument13 SeitenWeek5 Modelsrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1Dokument2 SeitenWeek 1rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 3Dokument2 SeitenWeek 3rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12 ContinuedDokument2 SeitenWeek 12 Continuedrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12 ConclusionDokument4 SeitenWeek 12 Conclusionrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 12 - Intro Text Animation ScreenshotsDokument15 SeitenWeek 12 - Intro Text Animation Screenshotsrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4Dokument2 SeitenWeek 4rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 11 - Continued Editing, Started Creating My Logo Using Adobe Illustrator CS6Dokument3 SeitenWeek 11 - Continued Editing, Started Creating My Logo Using Adobe Illustrator CS6rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 10 - Promo Video, Logo ScreenshotsDokument3 SeitenWeek 10 - Promo Video, Logo Screenshotsrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 6Dokument5 SeitenWeek 6rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 9Dokument2 SeitenWeek 9rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1Dokument1 SeiteWeek 1rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 8Dokument10 SeitenWeek 8rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 4Dokument2 SeitenWeek 4rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Digital HomeDokument10 SeitenThe Digital Homerafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 7Dokument3 SeitenWeek 7rafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Week 2 - Grid Ideas TableDokument4 SeitenWeek 2 - Grid Ideas Tablerafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- SpreadsheetDokument5 SeitenSpreadsheetrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Installation of Domain ServerDokument8 SeitenInstallation of Domain Serverrafiqueuddin93Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bored Piling Method Statement - Planning Engineer EstDokument8 SeitenBored Piling Method Statement - Planning Engineer EstboomiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pawai Dam MVRWSS Project Progress in PannaDokument4 SeitenPawai Dam MVRWSS Project Progress in PannaWater Supply Project PannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshooting Kerberos ErrorsDokument65 SeitenTroubleshooting Kerberos ErrorsmakukoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Manual 8 1Dokument6 SeitenLab Manual 8 1sureshgurujiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus - Mobile App Development Using FlutterDokument5 SeitenSyllabus - Mobile App Development Using FlutterSagar KojuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network and Control ConsiderationDokument14 SeitenNetwork and Control ConsiderationIndika WithanachchiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quotation - Supply and Installation For Roller Shutter - SKBDokument2 SeitenQuotation - Supply and Installation For Roller Shutter - SKBCC Cost AdvisoryNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMW E34 EtmDokument701 SeitenBMW E34 EtmKoos Spindler50% (4)
- 04 JMS For Replace DoorDokument2 Seiten04 JMS For Replace DoorMohd KhaidirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iso 21905-HRSGDokument106 SeitenIso 21905-HRSGadepp8642100% (1)
- Root BlueStacks Beta & Gain R/W Access in Under 10 StepsDokument3 SeitenRoot BlueStacks Beta & Gain R/W Access in Under 10 StepsSiddharth GoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- WP DeltaV SPI Integr PDFDokument14 SeitenWP DeltaV SPI Integr PDFJoão FranciscoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Growatt 50 - 60KWDokument2 SeitenGrowatt 50 - 60KWmk gandhiNoch keine Bewertungen
- FPGA Applications in SpaceDokument5 SeitenFPGA Applications in SpacePiyush JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Operating Systems: Programme Elective - IIDokument66 SeitenReal Time Operating Systems: Programme Elective - IIDr D S Naga Malleswara RaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual: Training - Debugger BasicsDokument164 SeitenManual: Training - Debugger BasicsSaagar KarandeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Beyond A+.oDokument307 SeitenBeyond A+.oalexmyatooNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIM OF THE EXPERIMENT:-Binary To Decimal, Gray Code Apparatus RequiredDokument8 SeitenAIM OF THE EXPERIMENT:-Binary To Decimal, Gray Code Apparatus RequiredSai KaneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Design and Sign OffDokument43 SeitenPhysical Design and Sign OffAgnathavasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Java Source Code EditorDokument45 SeitenJava Source Code EditorKush BhargavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Xenta 511Dokument86 SeitenXenta 511Lucky Karunia Setyawan PratamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual de Servicio Escaner Scanelite 5400Dokument34 SeitenManual de Servicio Escaner Scanelite 5400erizo999Noch keine Bewertungen
- Training and Placement Cell AbstractDokument5 SeitenTraining and Placement Cell AbstractTelika Ramu100% (1)
- Trafo Test ReportDokument30 SeitenTrafo Test Reportksenthil090% (1)
- ZOOMLION QY25V Truck Crane Technical SpecificationsDokument15 SeitenZOOMLION QY25V Truck Crane Technical SpecificationsLi ZhangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure, detect and amplify signals with bridges and op-ampsDokument2 SeitenMeasure, detect and amplify signals with bridges and op-ampsRajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- KSG 50-70 Vertical - User and Service ManualDokument38 SeitenKSG 50-70 Vertical - User and Service ManualRomuald Eric TefongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experimental Performance RubricsDokument3 SeitenExperimental Performance RubricsAhmed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tomorrow I LL Learn PHP Global Variables. This Is A Bad Command: Del C: .Dokument5 SeitenTomorrow I LL Learn PHP Global Variables. This Is A Bad Command: Del C: .harsh bathlqNoch keine Bewertungen