Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chemical Equation Formulas Balanceing Chemical Equation Periodic Table
Hochgeladen von
Nidhi SisodiaOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chemical Equation Formulas Balanceing Chemical Equation Periodic Table
Hochgeladen von
Nidhi SisodiaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
Test-1
group-1
Chemical formulas,equations and periodic table
1. The results of three halogen displacement experiments are shown.
The table shows the results.
What are halogens X, Y and Z?
X
Y
A
Br
Cl
B
I
Br
C
Br
Cl
D
I
Cl
Z
I
Cl
I
Br
2. In which process is a catalyst not used?
A The Blast furnace for the manufacture of iron.
B The Contact process for the manufacture of sulphuric acid.
C The Haber process for the manufacture of ammonia.
D The manufacture of margarine from unsaturated vegetable oils.
3. The diagrams show the arrangements of the electrons of four elements.
9. Which atom has the same electronic configuration as the strontium
ion?
A calcium
B krypton
C rubidium
D selenium
10. Rubidium is in Group I of the Periodic Table.
What are properties of rubidium chloride?
formula
Approximate
Solubility in water
melting point /oC
A
RbCl
70
insoluble
B
RbCl
700
soluble
C
RbCl2
70
soluble
D
RbCl2
700
insoluble
11. Rubidium, Rb, is an element in Group I of the Periodic Table.
Which statement about rubidium is correct?
A It reacts slowly with water.
B It forms an insoluble hydroxide.
C It is liberated at the cathode during the electrolysis of an aqueous
solution of its chloride.
D It forms a sulphate, Rb2SO4.
12. The element sulphur, S, is in Group VI of the Periodic Table.
Which formula is incorrect?
A S2
B S2O3
C SO42 D SO3
13. The table shows some of the properties of four elements.
Which element is most likely to be a transition metal?
A
B
C
D
Which two elements are metals?
A 1 and 2 B 1 and 3 C 2 and 4 D 3 and 4
4. Use the Periodic Table to decide which element has all four of the
properties shown.
_ high melting point
_ variable oxidation states
_ good electrical conductivity
_ forms coloured compounds
A caesium, Cs B cobalt, Co C iodine, I D strontium, Sr
5. Which statement about catalysts is correct?
A Catalysts are used in industry to reduce energy costs.
B Catalysts are used up during a reaction.
C Iron is used as a catalyst in the Contact Process.
D Transition metals do not make good catalysts.
6. Element X is a solid at room temperature. It needs one electron per
atom to gain the electronic structure of a noble gas. It is the least reactive
element in its group. What is the element X?
A At
B Cs
CF
D Li
7. A lump of element X can be cut by a knife. During its reaction with water
X floats and melts. What is X?
A calcium
B copper
C magnesium
D potassium
8. Elements X and Y are in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
X is a liquid at room temperature. Y is a solid at room temperature.
1 Atoms of Y have more protons than atoms of X.
2 Molecules of Y have more atoms than molecules of X.
3 Y displaces X from aqueous solutions of X- ions.
Which statements are correct?
A 1 only B 2 only C 3 only D 1, 2 and 3
melting point
/C
3550
1860
660
232
density
g / cm3
3.5
7.2
2.7
7.3
Electrical conductivity
poor
good
good
good
14. Which statement about the alkali metals is true?
A they form covalent bonds with Group VII elements
B they form oxides on reacting with water
C their melting points decrease on descending Group I
D their reactivities decrease on descending Group I
15. Which statement about the Periodic Table is correct?
A the melting point of the elements increases down Group I
B the reactivity of the elements increases down Group VII
C the reactivity of the elements decreases down Group I
D the colour of the elements becomes darker down Group VII
16. Which deduction about the element astatine, At, can be made from its
position in Group VII?
A It forms covalent compounds with sodium.
B It is displaced from aqueous potassium astatide, KAt, by chlorine.
C It is a gas.
D It is more reactive than iodine.
1
13
10
14
11
15
12
16
Test-1
group-1
B It lowers the activation energy of the reaction.
C It makes the reaction more exothermic.
D It prevents a reverse reaction from occurring.
17. Which gas is present in the light bulb?
25. Many properties of an element and its compounds can be predicted
from the position of the element in the Periodic Table.
What property could not be predicted in this way?
A the acidic or basic nature of its oxide
B the formula of its oxide
C the number of isotopes it has
D its metallic or non-metallic properties
26. In the Periodic Table, how many periods are needed to accommodate
the elements of atomic numbers 1-18?
A2
B3
C4
D8
A argon B krypton C nitrogen D oxygen
18. Which shows the correct catalyst for each industrial process?
manufacture
manufacture
manufacture
of sulphuric
of ammonia
of margarine
acid
A
nickel
iron
vanadium(V)
oxide
B
nickel
vanadium(V)
oxide
iron
C
vanadium(V)
oxide
iron
nickel
D
vanadium(V)
nickel
iron
oxide
19. X and Y are diatomic elements. X is less reactive than Y.
What are elements X and Y?
X
Y
A
bromine
iodine
B
iodine
bromine
C
potassium
sodium
D
sodium
potassium
20. Element Z has the following properties.
It has a high melting point.
Its presence can lower the activation energy for a reaction.
What type of element is Z?
A a halogen B an alkali metal C a noble gas D a transition metal
21. Two elements are in the same group of the Periodic Table.
Which property will be the same for both elements?
A the charge on their ions
B their electronic structure
C their melting point
D their reactivity with water or acids
22. The element with a proton number 12 has similar chemical properties
to the element with the proton number
A 2.
B 11.
C 13.
D 20.
23. The positions of four elements are shown on the outline of part of the
Periodic Table. Element X has a high melting point and is a good
conductor of electricity. It forms chlorides XCl2 and XCl3. Which element is
X?
27. Which pair of properties are both correct for a typical transition
element?
A
B
C
D
property 1
forms coloured compounds
high density
low melting point
low density
property 2
soluble in water
has variable oxidation states
can act as a catalyst
high melting point
28. Sodium, aluminium and sulphur are in the same period of the Periodic
Table. What trend in types of oxide occurs across this period?
left
right
A
acidic
amphoteric
basic
B
amphoteric
basic
acidic
C
basic
acidic
amphoteric
D
basic
amphoteric
acidic
29. Three elements X, Y and Z have consecutive, increasing proton
numbers. If element X is a noble gas, what will be the symbol for the ions
of element Z in its compounds?
A Z2
B Z+
C Z2+
D Z3+
17
21
25
18
22
26
19
23
27
20
24
28
29
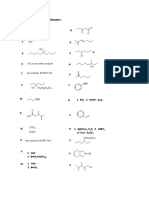
Q.1.Balance the following equations.
(5)
1.
____Fe2O3 + ____CO
_____Fe + ____CO2
2.
____NaOH + ____H2SO4
____Na2SO4 + ___H2O
3.
____Pb(NO3)2
4.
____MnO2 + _____HCl
5.
____Pb(NO3)2 + _____Na2SO4 ____PbSO4 + _____NaNO3
___PbO + ___NO2 + ____O2
____MnCl2 + ___Cl2 + ____H2O
Q.2.Write down the chemical formula of the following
24. Why is nickel used in the hydrogenation of alkenes?
A It increases the yield of products.
(5)
1.Sodium Carbonate
__________________
2.Silver Oxide
__________________
Test-1
3.Zinc Hydroxide
__________________
4.Calcium Sulfate
__________________
5.Aluminium Phosphate
__________________
group-1
Test-1
group-1
Q.1. The Periodic Table is arranged in groups.
(a) Rubidium, Rb, is in Group I of the Periodic Table. It reacts with water
according to the equation below.
2Rb(s) + 2H2O(l) 2RbOH(aq) + H2(g)
Predict what you would see when a small piece of rubidium is added to
cold water.
(b) Write two other differences between Mendeleevs original table and a
modern Periodic Table.
..
.................................................................................................
..
.................................................................................................[2]
(c) Find rubidium, Rb, in the Periodic Table provided on page 16.
Predict the reaction between rubidium and cold water.
Include observations and the chemical equation.
..
[3]
(b) Chlorine is in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
Chlorine, Cl2, reacts with aqueous sodium bromide.
(i) Predict what you would see in this reaction.
..
(ii) Write a balanced ionic equation for this reaction.
[2]
(c) Lithium reacts with fluorine to form lithium fluoride.
(i) Draw a dot and cross diagram to show the bonding in lithium fluoride.
You should show all the electrons.
.................................................................................................
.................................................................................................
.................................................................................................
.................................................................................................
.................................................................................................[3]
s05/q3
Q.3. Lithium is in Group I of the Periodic Table.
Lithium reacts with water to form lithium hydroxide and hydrogen.
(a) Describe what you would observe when a small piece of lithium is
dropped onto the surface of cold water.
.................................................................................................[2]
(b) Write the equation for the reaction between lithium and water.
................................................................................................. [1]
(c) When lithium reacts with water, lithium ions, Li+, are formed.
Li Li+ + e
Explain why the formation of a lithium ion from a lithium atom is an
example of oxidation.
(ii) Explain why lithium fluoride conducts electricity when molten but not as
a solid.
..
..
..
(iii) State one other physical property of lithium fluoride.
.[5]
Q.2. This question is about the Periodic Table.
The diagram below shows part of the original Periodic Table first published
by Mendeleev in 1869.
.................................................................................................[1]
(d) Rubidium, Rb, is another element in Group I.
Predict what you would observe when a small piece of rubidium is dropped
onto cold water.
.
................................................................................................
.................................................................................................[2]
s06/q6
Q.4. Chlorine is in Group VII of the Periodic Table.
Chlorine reacts with aqueous potassium iodide to form potassium chloride
and iodine.
(a) Describe what you would see when chlorine is added to aqueous
potassium iodide.
.................................................................................................
.................................................................................................[1]
(b) Write the equation for the reaction between chlorine and potassium
iodide.
................................................................................................. [1]
(c) When chlorine reacts with potassium iodide, iodine molecules are
formed.
2I I2 + 2e
Explain why the formation of an iodine molecule from iodide ions is an
example of oxidation.
The asterisks (*) show gaps in the table that Mendeleev deliberately left.
(a) Which group of elements in a modern Periodic Table is missing from
Mendeleevs Periodic Table?
.................................................................................................[1]
.................................................................................................[1]
Test-1
(d) Astatine is another element in Group VII. It is highly radioactive and so
is very difficult to study.
(i) Predict, with reasons, whether astatine will react with aqueous
potassium iodide.
..........................................................................................................[1]
(ii) Write the equation for the reaction between astatine and sodium.
group-1
Aqueous chlorine
aqueous potassium chloride
aqueous bromine
aqueous potassium bromide
aqueous iodine
aqueous potassium iodide
Your answer should include details of
which of the reagents you would use in each experiment,
a table showing the observations you would expect to see,
the equations for any reactions.
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................[1]
[Total: 5]
Q.5. This question is about the chemistry of the elements in Period 3 of the
Periodic Table.
(a) Compare the reactions of sodium and of magnesium with cold water. In
each case identify the products formed.
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
.......................................................................................................[3]
(b) Draw electronic structures, including the charges, of the ions present in
sodium oxide. Hence deduce the formula for sodium oxide.
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
[2]
(c) Write an equation for the formation of aluminium oxide from its
elements.
..........................................................................................................[1]
(d) Pure sand is silicon(IV) oxide. It has a giant molecular structure similar
to that of diamond. Suggest two physical properties of silicon(IV) oxide.
.......................................................................................................[7]
(b) Chlorine reacts with water to make a solution that can be used as a
bleach. The equation is shown below.
C2 + H2O HC + COH
Use oxidation numbers to show that chlorine is both oxidized and reduced
in this reaction.
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
........................................................................................................[3]
[Total:10 marks]
..........................................................................................................[2]
(e) Chlorine(VII) oxide, C2O7, has a simple molecular structure.
Suggest one physical and one chemical property of C2O7.
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................
........................................................................................................[2]
[Total: 10]
Q.6. Chlorine, bromine and iodine are elements in Group VII of the
Periodic
Table.
(b) Describe how you would carry out a series of experiments to
show the trend in reactivity of these three elements, using the
reagents shown below.
Q.7.Helium, neon, argon, krypton and xenon are noble gases.
(a) State a use for argon.
..........................................................................................................[1]
(b) Use ideas about electronic structure to explain why the noble gases
are unreactive.
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................[1]
(c) Complete the table to show the number of particles in two isotopes of
argon.
Test-1
isotope
36
18
Ar
40
18
Ar
number of
protons
number of
electrons
number of
neutrons
[2]
(d) Explain why potassium comes after argon in the Periodic Table even
though it has a relative atomic mass which is lower than that of argon.
.................................................................................................
.................................................................................................[1]
(e) Compounds of xenon with fluorine were first made in the 1960s.
Xenon reacts with fluorine at 400 C to form xenon tetrafluoride, XeF4.
Write a symbol equation for this reaction.
................................................................................................. [1]
(f) Balloons filled with helium, neon, argon and krypton were tied to a bar.
They were held horizontally at the same height and then released. The
position of three of the balloons 5 seconds after release is shown in the
diagram.
Predict the position of the balloon filled with krypton.
................................................................................................. [1]
Q.8. Germanium, Ge, is an element in Group IV of the Periodic Table.
Some of its chemistry resembles that of carbon.
(a) How many electrons does an atom of germanium have in its outer
shell?
..........................................................................................................[1]
(b) Germanium forms a range of saturated compounds with hydrogen.
These compounds resemble the alkanes.
(i) Predict the general molecular formula for these compounds.
..........................................................................................................[1]
(ii) Germanoethane, Ge2H6, has a similar structure to ethane.
Draw the full structural formula for germanoethane.
..........................................................................................................[1]
(iii) Hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium germanide, Mg2Ge, to form
germanomethane, GeH4, and magnesium chloride.
Write an equation for this reaction.
..........................................................................................................[1]
(c) Germanium(IV) oxide, GeO2, is an amphoteric oxide.
What do you understand by the term amphoteric?
..........................................................................................................
..........................................................................................................[1]
[Total: 5]
group-1
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Rearrangements and Reactive Intermediates Hilary Tem 2017: 1A Organic Chemistry Handout 1Dokument32 SeitenRearrangements and Reactive Intermediates Hilary Tem 2017: 1A Organic Chemistry Handout 1Nidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Bansal CHEMICAL - EQUILIBRIUMDokument32 SeitenBansal CHEMICAL - EQUILIBRIUMNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Theory of Solutions WorkbookDokument35 SeitenTheory of Solutions WorkbookNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Chess 5334 Problems PDFDokument1.105 SeitenChess 5334 Problems PDFNidhi Sisodia0% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Bansal CHEMICAL - CLASSIFICATIONDokument11 SeitenBansal CHEMICAL - CLASSIFICATIONNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equilibria (With Solution)Dokument49 SeitenEquilibria (With Solution)Nidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chess 5334 Problems PDFDokument1.105 SeitenChess 5334 Problems PDFNidhi Sisodia0% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Iit Jam Inorganic ChemistryDokument10 SeitenIit Jam Inorganic ChemistryNidhi Sisodia100% (1)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- 2010 Ionic Eqm MCQ PDFDokument15 Seiten2010 Ionic Eqm MCQ PDFNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Chem Equlbrm PDFDokument77 SeitenChem Equlbrm PDFNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- 2010 Chem Eqm MCQDokument14 Seiten2010 Chem Eqm MCQNidhi Sisodia0% (1)
- Elias Inorg Lec 5 PDFDokument14 SeitenElias Inorg Lec 5 PDFNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Problems On Manometer & BarometerDokument5 SeitenProblems On Manometer & BarometerNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis Final Review AnswersDokument4 SeitenSynthesis Final Review AnswersNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- JEEADV2017P1 SolutionsDokument14 SeitenJEEADV2017P1 SolutionsNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- 84 PSOC-Sample Chapter-For MarketingDokument28 Seiten84 PSOC-Sample Chapter-For MarketingNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Alcohols Problem Set 3 Answers:: 2 PyridineDokument1 SeiteAlcohols Problem Set 3 Answers:: 2 PyridineNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Exposure Camp Chemistry - Web UploadDokument2 SeitenExposure Camp Chemistry - Web UploadNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Bhayankar SawaalDokument6 SeitenBhayankar SawaalNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Nucleophilic Aromatic SubstitutionDokument5 SeitenNucleophilic Aromatic Substitutionnjwaghmare7392100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Gaseous Cengel AnswersDokument1 SeiteGaseous Cengel AnswersNidhi SisodiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic ChemistryDokument80 SeitenInorganic ChemistryRajeswari Raji100% (1)
- Question Bank Chemistry-Xii The Solid State CHAPTER - 1 (Weightage 4 Marks) Very Short Answer Type Questions (Of 1 Mark Each)Dokument63 SeitenQuestion Bank Chemistry-Xii The Solid State CHAPTER - 1 (Weightage 4 Marks) Very Short Answer Type Questions (Of 1 Mark Each)Shiv GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imp Questions 12-Chemistry 2022 (EM) - WingofeducationDokument17 SeitenImp Questions 12-Chemistry 2022 (EM) - WingofeducationVickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stakeholder Panel On Infant Formula & Adult Nutritionals (Spifan) & Adult Nutritionals (Spifan)Dokument27 SeitenStakeholder Panel On Infant Formula & Adult Nutritionals (Spifan) & Adult Nutritionals (Spifan)hongminh nguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steffan Conway - Transition Metals PPQsDokument7 SeitenSteffan Conway - Transition Metals PPQsSteffan ConwayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9701 w14 QP 43Dokument20 Seiten9701 w14 QP 43CindyVortexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Transition Metals (Co - II, Fe - IIDokument5 SeitenSynthesis of Transition Metals (Co - II, Fe - IIAHLBAIT TVNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics: Class: SZ1 JEE-ADV (2018-P1) MODEL Date: 17-07-21 Time: 3hrs WTA-03 Max - Marks: 180Dokument14 SeitenPhysics: Class: SZ1 JEE-ADV (2018-P1) MODEL Date: 17-07-21 Time: 3hrs WTA-03 Max - Marks: 180Ask NeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- 26 - ChemistryDokument19 Seiten26 - Chemistryrajeevtyagi41Noch keine Bewertungen
- Inorganic Chemistry: Periodic PropertiesDokument45 SeitenInorganic Chemistry: Periodic PropertiesMr. cool ChaturvediNoch keine Bewertungen
- D and F Block ElementsDokument6 SeitenD and F Block ElementsDipti MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electron Configuration and Periodicity - Paper 2Dokument30 SeitenElectron Configuration and Periodicity - Paper 2elenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 8 AP Chem - Organic and ComplexesDokument20 SeitenUnit 8 AP Chem - Organic and ComplexesMinnie InarapmasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDokument20 SeitenClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesELVIS BoradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 03Dokument28 SeitenChapter 03Marc ValentineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied ChemistryDokument4 SeitenApplied Chemistrynischal aryalNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHEMISTRY Question Paper 2017 All India Download in PDF SetDokument15 SeitenCHEMISTRY Question Paper 2017 All India Download in PDF SetAmit YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 9 Chemistry AssignmentDokument35 SeitenGroup 9 Chemistry AssignmentNatasha Kim Maria RamalhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Chemistry Form 4Dokument30 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Chemistry Form 4fakiah binti abdul khalid100% (2)
- D N F ElementsDokument21 SeitenD N F ElementsJatinChadhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry New Sample PaperDokument6 SeitenChemistry New Sample PaperSuvham Kumar SahooNoch keine Bewertungen
- The D and F Block Elements-Anil-HssliveDokument8 SeitenThe D and F Block Elements-Anil-HssliveRanit MukherjeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (II)Dokument3 SeitenLesson Plan: Lesson: D-Block Elements (II)MarcTnnNoch keine Bewertungen
- D - and F-Block Elements NotesDokument9 SeitenD - and F-Block Elements NotesDevapriya SUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Periodic Table Online Scavenger HuntDokument6 SeitenPeriodic Table Online Scavenger HuntAaya Alowaiyesh0% (1)
- Transition Metal ConfigurationsDokument3 SeitenTransition Metal ConfigurationsDaKing ZWNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Ions and Their Ligands LMDokument70 SeitenComplex Ions and Their Ligands LMMyra Joy B Montero0% (1)
- D-Block Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesDokument12 SeitenD-Block Chemistry: Answers To Worked ExamplesAhliaIkhwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry: Higher 2 (2017) (Syllabus 9647)Dokument45 SeitenChemistry: Higher 2 (2017) (Syllabus 9647)Ng Shu QingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classificationof Elements Q-AnsDokument11 SeitenClassificationof Elements Q-AnsSHAJIYA ANoch keine Bewertungen