Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Lecture 15 - Transport in Humans
Hochgeladen von
Dulshan JayCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Lecture 15 - Transport in Humans
Hochgeladen von
Dulshan JayCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
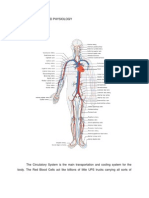
TRANSPORT IN HUMANS
The human transport system is a system of tubes with a pump and valves to ensure one
way blood flow !e need a transport system to deliver o"y#en$ nutrients and other
substan%es to all our body %ells$ and ta&e away waste produ%ts from them
The o"y#enated blood 'hi#h in o"y#en$ red in %olor( %omes to the heart from the lun#s in
the pulmonary vein) the heart pumps it to the aorta 'an artery( to the rest of the body The
deo"y#enated blood returns to the heart from the body in the vena %ava 'a vein($ the heart
pumps is to the lun#s to #et rid of the %arbon dio"ide
Oxygenated Blood* Red %olor$ hi#h o"y#en low +arbon dio"ide
Deoxygenated Blood* ,lue %olor$ low o"y#en hi#h +arbon dio"ide
-id you noti%e that durin# one %ir%ulation$ the blood went throu#h the heart twi%e$ this is
why we %all it double %ir%ulation
!hen the blood is flowin# away from the heart$ it has a very hi#h pressure$ when it is
flowin# towards the heart it has a lower pressure
The Blood
The blood is a fluid %onsistin# of several types of %ells floatin# in a li.uid %alled plasma
Red Blood Cells
These are one of the smallest %ells in your body$ they are round with a dent in the middle$ we %all this shape
a ,i%on%ave dis%
The fun%tion of the red blood %ells is to transport o"y#en from the lun#s to the body %ells A red protein
%alled Haemo#lobin$ when the blood rea%hes the lun#s$ o"y#en diffuses from the alveoli to the red blood
%ells and %ombines with haemo#lobin formin# an unstable %ompound %alled o"yhaemo#lobin !hen the
blood rea%hes the body %ells$ the o"yhaemo#lobin is easily split into o"y#en and haemo#lobin a#ain$ the
o"y#en diffuses throu#h the blood plasma to the %ells
Red blood %ells are fully adapted to their fun%tion by the followin# %hara%teristi%s*
/ ,i%on%ave dis% shape #ives it lar#e surfa%e area to %arry more o"y#en
haemo#lobin to %ombine with o"y#en
0 No nu%leus that ta&es up spa%e
White Blood Cells
!hite blood %ells are one of the substan%es floatin# in the blood plasma They are
%ompletely different in fun%tion than red blood %ells !hite blood %ells are part of the
Immune System$ they play a bi# role in prote%tin# the body by &illin# ba%teria whi%h
%ause disease$ also &nown as patho#ens !hite blood %ells %an be distin#uished from red
blood %ells easily be%ause they are mu%h bi##er$ with a nu%leus$ and present in fewer
amounts
Types Of White Blood Cells:
Phagocytes:
They &ill ba%teria by en#ulfin# them$ ta&in# them in the %ell then &ill them by di#estin#
them usin# en1ymes$ this pro%ess is %alled pha#o%ytosis
Most white blood %ells are the pha#o%yte type
Lymphocytes:
Unli&e pha#o%ytes$ lympho%ytes have a lar#e nu%leus They are produ%ed in the lymph
nodes 'in the lymphati% system( 2ympho%ytes &ill ba%teria by se%retin# antibodies and
antito"ins whi%h &ill the patho#ens dire%tly or ma&e them easier to &ill 3a%h patho#en
%ould be &illed by a %ertain type of antibody
The Platelets
Platelets are tiny %ell fra#ments that prevent bleedin# when the s&in is %ut$ and stops
ba%teria from enterin# our systems throu#h the wound This wor&s by blood %lottin#$
when the s&in is %ut$ some rea%tions ta&e pla%e that results in platelets produ%in# a
protein$ this protein will %han#e the fibrino#en 'another soluble protein in the plasma( to
insoluble fibrin The fibrin forms lon# fibres that %lot to#ether blo%&in# the %ut$ thus
preventin# any bleedin#$ this is %alled blood %lottin#
Blood Plasma
This ma&es up most of the blood It is mostly water with some substan%es dissolved in it$
these in%lude %arbon dio"ide$ hormones$ food nutrients$ urea and other waste produ%ts
The blood plasma transports substan%es from one pla%e to another
Functions of the blood
/ Transportation of R,+4s$ !,+4s$ o"y#en$ food nutrients$ hormones$ and waste
produ%ts
0 -efen%e a#ainst disease$ by white blood %ells pha#o%ytosis and produ%tion of
antibodies
5 Supplyin# %ells with #lu%ose to respire and &eep a %onstant temperature
6
Blood essels !ascula" #ystem$
There are a number tubes %arryin# blood away from and to the heart and other or#ans
The main types are Arteries$ 7eins and +apillaries
%"te"ies
Their fun%tion is to transport blood away from the heart to the lun#s or other body
or#ans
The blood in the arteries always has a hi#h pressure The heart pumps the blood .ui%&ly
into the arteries$ resultin# in the pressure$ ea%h time the ventri%le of the heart %ontra%ts$
the pressure in arteries in%rease$ when the ventri%le rela"es$ the pressure falls The lumen
of arteries is also very narrow$ addin# to the pressure
The stru%ture is simple$ beside the narrow lumen$ the arteries have a stron# thi%& wall to
withstand the pressure Their walls are also elasti% and stret%hable
B"ief desc"iption of cha"acte"istics of a"te"ies:
Transportin# blood away from the heart
Always in a hi#h pressure
Stron# but stret%hable walls
Narrow lumen
eins
Their fun%tion is to transport blood to the heart from the body
The veins always have a low blood pressure be%ause by the time the blood with hi#h
pressure rea%hes the veins$ it loses most of the pressure This means that blood flows very
slowly in veins$ to help this$ veins lie between mus%les so that the blood is s.uee1ed
when the mus%les %ontra%t
They have a simple stru%ture ,e%ause they have a low pressure$ they don4t need stron#$
thi%& walls li&e the artery$ instead they have thin less elasti% walls Their lumen is mu%h
wider too 7eins have a uni.ue feature$ that is valves ,e%ause blood in veins flows
slowly with a low pressure$ there is a ris& of a ba%&flow$ spe%ially in veins that move
blood upwards a#ainst #ravity$ li&e the ones in the le# The valves ensure that the blood is
always flowin# in the dire%tion of the heart !hen the mus%les s.uee1e the blood$ the
valves are open the let blood throu#h$ when mus%les rela"$ valves %lose to prevent a
ba%&flow
B"ief desc"iption of cha"acte"istics of &eins:
They %arry blood to the heart
Always in a low pressure
Thin less elasti% walls
!ide lumen
7alves present
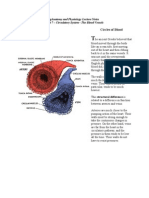
Blood Capilla"ies
,lood %apillaries are the smallest blood vessels in our systems Their fun%tion is to #et
blood from the arteries as %lose as possible to the tissues in order to e"%han#e materials
with the %ells$ and to lin& arteries with veins
!hen arteries %ome near an or#an or a tissue$ it divides into arterioles$ these arterioles
divide more into several blood %apillaries that #o throu#h the tissue$ this is when the
e"%han#e of o"y#en and food nutrients with %arbon dio"ide and waste produ%ts su%h as
urea ta&e pla%e by diffusion
,lood %apillaries are very well adapted to their 8obs They are one %ell thi%& to redu%e the
diffusion distan%e of materials for faster diffusion They also have pores in their walls
between the %ells$ to allow the plasma to #et out of the blood and be%ome tissue fluid
The 'ea"t
The heart is a pumpin# or#an that is responsible for the movement of blood around the
body The fun%tion of the heart is to #ive the blood a push$ &eepin# it flowin# around the
body all the time That is why the heart is %onstantly wor&in#$ if it stops for a minute$ the
other or#ans will not re%eive any o"y#en or nutrients$ thus the body fails and the person
dies The heart is lo%ated in the %hest$ the thoria% %avity between both lun#s
#t"uctu"e:
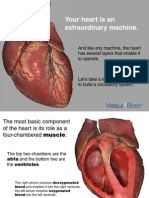
The heart is hollow$ it has 6 %hambers Two of them are atria and two are ventri%les One
of ea%h of these on ea%h side !hen loo&in# at the dia#ram of a heart$ noti%e that your
ri#ht is the left side of the heart$ and your left is the heart4s ri#ht$ as if you are loo&in# at
your own heart on a mirror
The sides of the heart are separated by a wall %alled septum 3a%h side %ontains an atrium
'at the top( and a ventri%le 'at the bottom($ there is a valve between the atrium and the
ventri%le in ea%h side$ it is %alled bi%uspid valve in the left side and tri%uspid valve in the
ri#ht side There are several blood vessels asso%iated with the heart$ these are*
The Pulmona"y &ein$ it transports o"y#enated blood from the lun#s to the ri#ht atrium
The %o"ta$ whi%h is the bi##est artery in the body$ it transports o"y#enated blood from
the heart to the rest of the body
The ena Ca&a$ the bi##est vein in the body$ it transports deo"y#enated blood from the
whole body to the heart
The pulmona"y a"te"y$ it transports deo"y#enated blood from the heart to the lun#s
Note that blood vessels enterin# the heart are veins$ and the ones leavin# the heart are
arteries The left side of the heart always %ontains o"y#enated blood be%ause it re%eives
blood fresh from the lun#s and pumps it to the body$ the ri#ht side always %ontains
deo"y#enated blood be%ause it re%eives is from the body 9ou %an memorise this by the
word 2OR-*
2eft O"y#enated : Ri#ht -eo"y#enated
The heart re%eives blood from the lun#s at the left atrium and pumps it to the body from
the left ventri%le$ then it re%eives it a#ain from the body at the ri#ht atrium and pumps it
to the lun#s from the ri#ht ventri%le The red shows o"y#enated blood and the blue shows
deo"y#enated blood
Noti%e that the walls around the left ventri%le are mu%h thi%&er than the ones in the ri#ht
ventri%le The reason for this is that be%ause the left ventri%le pumps blood to the whole
body$ so blood will travel a lon# distan%e$ so it needs lots of mus%les to %ontra%t and
pump the blood more stron#ly
However$ the ri#ht ventri%le pumps blood the lun#s whi%h are very %lose to heart$ the
blood does not need to be pumped very stron#ly
(echanism of the hea"t:
!hen the heart is bein# filled with blood 'whether from the body or the lun#s($ this is
%alled the diastole !hen the heart is pumpin# the blood out of it 'whether to the body or
to the lun#s($ it is %alled the systole
-urin# diastole$ the heart is #ettin# filled with blood$ the blood enters the atria first$ the
atria %ontra%t to for%e blood into the ventri%les$ both tri%uspid and bi%uspid valves are
open to allow blood into the ventri%les and the semilunar valves are shut On%e the
ventri%les #et filled with blood$ it is systole$ the bi%uspid and tri%uspid valves #et shut and
semilunar valves are open$ the ventri%les %ontra%t stron#ly for%in# the blood into the
Aorta or pulmonary artery
-urin# diastole the semilunar valves are shut to &eep the blood out of the arteries -urin#
systole the tri%uspid and bi%uspid valves are %losed$ to prevent blood from flowin# ba%&
into the atria when it is pumped The tri%uspid and bi%uspid valves are &ept fi"ed by
fibres %alled tendons$ they prevent the valves from openin# in the opposite dire%tion$
allowin# ba%&flow
The tendons also %ontrol the openin# and %losin# of the %uspid valves$ when the tendons
are loose$ the valves are open !hen the tendons are ti#htened the valves %lose
-iastole Systole
7entri%les* Rela" +ontra%t
Atria* +ontra%t Rela"
+uspid 7alves* Open +lose
Tendons* 2oose Ti#htened
Semilunar 7alves* +lose Open
If you listen to your heartbeat$ you will hear two sounds$ one low and one hi#h These are
results of the systole and diastole They are the sounds of the %ardia% valves openin# and
shuttin#
Co"ona"y 'ea"t Disease !C'D$
The heart$ li&e any other or#an$ needs a supply of blood %ontainin# o"y#en and nutrients
In fa%t$ the heart needs a hi#her amount of blood supply than any other or#an be%ause it is
wor&in# all the time$ and %ontains a lot of mus%les The %oronary arteries are those whi%h
supply the heart tissues with blood$ they bran%h from the aorta +H- develops when
%holesterol layers build on the walls of the %oronary arteries$ partially blo%&in# the path
of blood$ thus this tissue of the heart is not supplied with o"y#en nor nutrients$ so it stops
wor&in# properly If it is not treated at this a#e$ a blood %lot may form near the partially
blo%&ed area$ %ompletely blo%&in# the artery$ when this happens$ the blood %annot
fun%tion anymore$ a heart atta%& o%%urs$ whi%h is e"tremely fatal
The %auses of +H- are mostly in the diet A diet with lots of fats$ in%reases the %han%e of
%holesterol buildin# up on the walls of the artery$ %ausin# +H-$ Same thin# with salts
Smo&in# also in%reases the rate of fat deposition It was also said that +auses Of +H-
are*
-iet full of fats in%reases the fats level in blood
-iet full of salts$ salts %an be deposited in the artery leadin# to +H-$ same as fats
or %holesterol
Smo&in#$ %arbon mono"ides in%reases fat deposition
Stress is also said to %ontribute to +H- by raisin# blood pressure
2a%& of e"er%ise$ re#ular wor&outs improve the blood flow wearin# layers of fats
or salts deposited on the walls of arteries away
So to prote%t yourself from +H- you need to avoid diets full of fats and salts$ avoid
smo&in#$ try to be less stressed out$ and e"er%ise re#ularly
Tissue ;luid And 2ymph
Tissue fluid is a fluid surroundin# the %ells of a tissue It supplies them with all their
needs of o"y#en and nutrients$ and ta&es away all their waste produ%ts in%ludin# %arbon
dio"ide Tissue fluid plays a very bi# role in substan%e e"%han#e between blood and %ells
Plasma from the blood %apillaries move to the tissue throu#h #aps in the walls They
be%ome tissue fluid They e"%han#e their %ontent of o"y#en and nutrients with the %ells
and ta&e %arbon dio"ide and waste produ%ts At the end of the %apillary bed$ the tissue
fluid lea&s ba%& into the blood$ and be%omes plasma a#ain$ but not all of it A little of it is
absorbed by the lymphati% vessel and be%omes lymph The lymphati% vessel ta&es the
lymph to the blood stream by se%retin# them in a vein near the heart$ %alled sub%lavian
vein The lymph in the lymphati% vessels are moved alon# by the s.uee1e of mus%les
a#ainst the vessel$ 8ust li&e some veins
The lymphati% system plays a bi# role in the prote%tion a#ainst disease It produ%es the
white blood %ells lympho%ytes !hi%h &ill any %ell with a different anti#ens than the ones
in your body %ells So if ba%teria #et into your body$ your lympho%ytes .ui%&ly re%o#nise
them as forei#ners and will divide and &ill them
2ympho%ytes are %onsidered a problem when it %omes to or#ans transplant ;or e"ample
if someone 're%ipient( with renal failure re%eives a &idney from another person 'the
donor($ the %ells of the &idney will have different anti#ens than the other %ells in the
patient4s body The lympho%ytes will %onsider the %ells of the &idney an enemy and start
atta%&in# it$ this is %alled tissue re8e%tion Or#an transplant is perfe%t in one %ase$ this is
when the donor and the re%ipient are identi%al twins$ be%ause the anti#ens of their %ells
perfe%tly mat%h In other %ases the re%ipient is #iven immunosuppressant dru#s to
a%tually wea&en their immune system to prevent tissue re8e%tion
B"ief #umma"y Of Functions Of The Lymphatic #ystem:
/ Produ%tion of white blood %ells lympho%ytes
0 Transport of di#ested fats from villi to blood stream
5 Transport of lymph from the tissue fluids to the blood stream at the sub%lavian
vein
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionVon EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Vascular System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideVon EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (3)
- Circulatorysys PP White BackgroundDokument70 SeitenCirculatorysys PP White Backgroundapi-246864303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsDokument10 SeitenAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood VesselsIssac LauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dokumen - Tips Grade 9 Science ReviewerDokument2 SeitenDokumen - Tips Grade 9 Science ReviewerShang AbellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory SystemDokument2 SeitenThe Circulatory Systemapi-251796752Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bio 336 Test #2Dokument28 SeitenBio 336 Test #2edgarthendoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pulmonary - Critical Care Associates of East Texas: Signs and SymptomsDokument12 SeitenPulmonary - Critical Care Associates of East Texas: Signs and SymptomsanggiehardiyantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 170 Anatomy Circulatory SystemDokument26 Seiten170 Anatomy Circulatory SystemGenevieve MerroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood Vessels-1Dokument10 SeitenAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood Vessels-1hungerfighterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System - Lecture IIDokument5 SeitenCardiovascular System - Lecture IIpragantraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transport in Animals o Level2018Dokument12 SeitenTransport in Animals o Level2018MuneebNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System: What Is The Job of The Circulatory System?Dokument19 SeitenCirculatory System: What Is The Job of The Circulatory System?SuaidahRahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heart ValvesDokument16 SeitenHeart ValvesReyhan FarandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osmoza Ne KapilareDokument9 SeitenOsmoza Ne KapilareEdisa CaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory SystemDokument51 SeitenThe Circulatory SystemMohammed ahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Nature of The Feast - Blood, Feeding and Sex in Vampire: The MasqueradeDokument8 SeitenThe Nature of The Feast - Blood, Feeding and Sex in Vampire: The MasqueradeGnomeMadeIonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Portal VeinDokument7 SeitenPortal VeinAsher Eby VargeeseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular System: Edison Vincent A. Olegario, RN, LPTDokument25 SeitenCardiovascular System: Edison Vincent A. Olegario, RN, LPTEdison OlegarioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory MechanismDokument8 SeitenCirculatory MechanismGresia FalentinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arterial SystemDokument3 SeitenArterial SystemRabi SyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument25 SeitenCirculatory SystemamirehmoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Circulatory SystemDokument10 SeitenThe Circulatory SystemRezki RasyakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument3 SeitenCirculatory SystemtadashiiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 1Dokument19 SeitenBiology 1Keerthana KeerthanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument26 SeitenCirculatory SystemJeus BatadlanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Lymphatic System H. S. MayersonDokument14 SeitenThe Lymphatic System H. S. MayersonGio Galanti100% (1)
- VB Circulatory StructuresDokument14 SeitenVB Circulatory StructuresSamara EmerichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arterial Supply, Orbit: Synonyms and Related Keywords: Arterial System, Orbital VascularDokument9 SeitenArterial Supply, Orbit: Synonyms and Related Keywords: Arterial System, Orbital VascularMagdalena PranataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and SssDokument9 SeitenAnatomy and SssAia JavierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System in MammalsDokument8 SeitenCirculatory System in MammalsObiora Ekene HilaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 125 Introduction To Cardiovascular PhysiologyDokument8 Seiten125 Introduction To Cardiovascular PhysiologydramaysinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation in Plants and AnimalsDokument7 SeitenTransportation in Plants and AnimalsDivyansh JhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Fluids and CirculationDokument10 SeitenBody Fluids and CirculationArjun ChristopherNoch keine Bewertungen
- Body Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Study Notes: BloodDokument7 SeitenBody Fluids and Circulation Class 11 Study Notes: BloodTUSHAR DASHNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology - Circulatory System Notes 1Dokument13 SeitenBiology - Circulatory System Notes 1archit.kulkarni7756Noch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System NotesDokument10 SeitenCirculatory System Notesadriann strakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blood and Circulation LECTUREDokument24 SeitenBlood and Circulation LECTUREshasagailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transportation Notes Class 10thDokument10 SeitenTransportation Notes Class 10thKrishna SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulation + Composition of Blood + Vertebrate Heart + Invertebrate Heart + Blood VesselsDokument121 SeitenCirculation + Composition of Blood + Vertebrate Heart + Invertebrate Heart + Blood VesselsReina RamirezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular and Circulatory SystemDokument29 SeitenCardiovascular and Circulatory SystemfayeleechaiyapornkulNoch keine Bewertungen
- CirculationDokument3 SeitenCirculationAIKA BAYANoch keine Bewertungen
- Note On Pressure Flow and ResistanceDokument43 SeitenNote On Pressure Flow and ResistanceSilver FestusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument7 SeitenCirculatory SystemWisdom DzombeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cardiovascular SystemDokument39 SeitenCardiovascular SystemdumbledoreaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Biology Transport in Humans SummaryDokument63 SeitenIGCSE Biology Transport in Humans SummaryClarissa Muliawan100% (1)
- Circulatory System Vascular TissueDokument8 SeitenCirculatory System Vascular TissueDrSachin SrivastavaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 10Dokument16 SeitenBiology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 10Nik Husna100% (2)
- Human BloodDokument3 SeitenHuman BloodAshrul Anwar MukhashenNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Peripheral Vascular System Summary ScriptDokument5 SeitenThe Peripheral Vascular System Summary ScriptJi CaratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument37 SeitenCirculatory SystemKathleen DuenasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEDokument55 SeitenCirculatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEAjay N. SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFDokument8 SeitenClass 10 Biology Chapter 7 Revision Notes PDFNayla Masroor 9BNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Dokument10 SeitenStudy Materials: Vedantu Innovations Pvt. Ltd. Score High With A Personal Teacher, Learn LIVE Online!Nikhil BhalothiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Competitive Exams: Heart: ExamraceDokument3 SeitenCompetitive Exams: Heart: Examraceathira vijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CardioDokument6 SeitenCardioBrian John DivinagraciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScienceDokument7 SeitenScienceRiza V. MacagalingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument60 SeitenCirculatory SystemraymontesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circulatory SystemDokument1 SeiteCirculatory Systemandrzej36Noch keine Bewertungen
- Energetics Revision Exam QuestionsDokument13 SeitenEnergetics Revision Exam QuestionsDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Circles CollageDokument1 SeiteCircles CollageDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2determining Water Potential of Potatoes StudentsDokument2 Seiten2determining Water Potential of Potatoes StudentsDulshan Jay100% (1)
- Unit C Enzyme InhibitorsDokument9 SeitenUnit C Enzyme InhibitorsDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations On The Photoelectric EffectDokument3 SeitenCalculations On The Photoelectric EffectChanchal LalwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planner 2014Dokument12 SeitenPlanner 2014Muhamad Ezrin IshakNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.1 - Energetics IIDokument3 Seiten4.1 - Energetics IInouran94Noch keine Bewertungen
- 99ebook Com-5090 Y13 SyDokument40 Seiten99ebook Com-5090 Y13 SyDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Timetable SheetDokument2 SeitenTest Timetable SheetDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoviesDokument1 SeiteMoviesDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Edexcel Chemistry AS UNIT 2 2011 QPDokument24 SeitenEdexcel Chemistry AS UNIT 2 2011 QPGhaleb W. MihyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- We'll Be Counting StarsDokument1 SeiteWe'll Be Counting StarsDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- We'll Be Counting StarsDokument1 SeiteWe'll Be Counting StarsDulshan JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Icu Masterclass - Inotropes and Vasopressors: Christopher R. Tainter, MDDokument78 SeitenIcu Masterclass - Inotropes and Vasopressors: Christopher R. Tainter, MDHhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- P. J. Butler, J. D. Metcalfe (Auth.), Dr. Trevor J. Shuttleworth (Eds.) - Physiology of Elasmobranch Fishes (1988, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg)Dokument328 SeitenP. J. Butler, J. D. Metcalfe (Auth.), Dr. Trevor J. Shuttleworth (Eds.) - Physiology of Elasmobranch Fishes (1988, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg)Karina SjNoch keine Bewertungen
- MURMURS - NotespaediaDokument8 SeitenMURMURS - NotespaediaZenithNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 - Physiology MCQ of CardiovascularDokument18 Seiten9 - Physiology MCQ of CardiovascularMuhammad Javed GabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- LessonplanDokument3 SeitenLessonplan=paul=Noch keine Bewertungen
- NBME FORM 26-AnswersDokument52 SeitenNBME FORM 26-Answersmed student50% (8)
- 3 Cardiology HemodynamicsDokument90 Seiten3 Cardiology HemodynamicsPravallika ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDF Class 11 Body Fluids Circulation BiologyDokument92 SeitenPDF Class 11 Body Fluids Circulation BiologyNiharika SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respi and CVS MCQsDokument2 SeitenRespi and CVS MCQsnikita jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- SSI 8000 SpecificationsDokument20 SeitenSSI 8000 SpecificationsMindaugas DaugelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Koran Pasien PJT LT4 2 Feb 2023Dokument9 SeitenKoran Pasien PJT LT4 2 Feb 2023maspul lamuruprintNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgDokument38 SeitenGroup 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgTimothy John Bautista100% (2)
- Indian Heart Journal: Original ArticleDokument5 SeitenIndian Heart Journal: Original ArticleRendi KurniawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Diseases PDFDokument8 SeitenPathophysiology of Congenital Heart Diseases PDFdramitjainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 4927329208029413644 PDFDokument578 Seiten1 4927329208029413644 PDFWaseem UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ajay, S FundasDokument145 SeitenAjay, S FundasAjayModgil100% (1)
- ST Emlyns Critical Appraisal 2019Dokument327 SeitenST Emlyns Critical Appraisal 2019ibeardsell1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Heart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure) FINALDokument6 SeitenHeart Failure (Congestive Heart Failure) FINALKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2017 - Diretrizes CMD (European Society of Veterinary Cardiology)Dokument11 Seiten2017 - Diretrizes CMD (European Society of Veterinary Cardiology)Flávia PinheiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 13 ActivityDokument4 SeitenCH 13 Activityash vldnbrNoch keine Bewertungen
- PREECLAMPSIADokument60 SeitenPREECLAMPSIAMary Grace MasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Monitoreo Hemodinamico Funcional PinskyDokument23 SeitenMonitoreo Hemodinamico Funcional PinskyJuan CarrascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1 Activities PDFDokument49 SeitenTopic 1 Activities PDFDeepan ChakkaravarthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid and Fundamentals of Clinical Practice: Zg6Tbhey H04D3RjclceDokument48 SeitenFirst Aid and Fundamentals of Clinical Practice: Zg6Tbhey H04D3RjclceGoran MaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- As SNAB Revision NotesDokument49 SeitenAs SNAB Revision NotesXneo KMeng 茗茗 ~Noch keine Bewertungen
- RRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRDokument2 SeitenRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRSaginesh MkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Physiology Cardiovascular System Heart MCQ Exam PDFDokument30 SeitenAnatomy Physiology Cardiovascular System Heart MCQ Exam PDFZIA QURESHINoch keine Bewertungen
- WatermelonDokument27 SeitenWatermelonSunny Mae T PuigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Left Ventricular VentingDokument3 SeitenLeft Ventricular VentingVAD CoordinatorNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Cardiac Cycle & Heart SoundsDokument32 Seiten5 Cardiac Cycle & Heart SoundsDisha SuvarnaNoch keine Bewertungen