Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
RPT Add MT f4 2013
Hochgeladen von
Naa Chu0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
28 Ansichten11 SeitenYEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013. Khairul farez binnahrawi SMK aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 1 Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes 1 Orientation A1 - functions 2 - 4 1. Understand the concept of relations 1. Represent a relation using a) Arrow diagrams b) Ordered pairs c) Graphs 1. Identify domain, codomain,object image
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Rpt Add Mt f4 2013 (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenYEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013. Khairul farez binnahrawi SMK aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 1 Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes 1 Orientation A1 - functions 2 - 4 1. Understand the concept of relations 1. Represent a relation using a) Arrow diagrams b) Ordered pairs c) Graphs 1. Identify domain, codomain,object image
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
28 Ansichten11 SeitenRPT Add MT f4 2013
Hochgeladen von
Naa ChuYEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013. Khairul farez binnahrawi SMK aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 1 Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes 1 Orientation A1 - functions 2 - 4 1. Understand the concept of relations 1. Represent a relation using a) Arrow diagrams b) Ordered pairs c) Graphs 1. Identify domain, codomain,object image
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 11
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 1
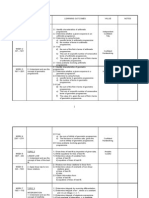
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
1 Orientation
A1 - FUNCTIONS
2 - 4
1. Understand the concept of relations 1.1 Represent a relation using
a) Arrow diagrams
b) Ordered pairs
c) Graphs
1.2 Identify domain, codomain,object image and range of a relation.
1.3 Classify a relation shown on a mapped diagrams as: one to one, many to
one, one to many or many to many relation.
2. Understand the concept of functions 2.1 Recognise functions as a special relation.
2.2 Express functions using function notation.
2.3 Determine domain, object, image and range of a function.
2.4 Determine image of a function given the object and vice versa.
3. Understand the concept of composite
functions.
3.1 Determine composition of two functions.
3.2 Determine image of composite functions given the object and vice versa.
3.3 Determine one of the functions in a given composite function given the
other related function.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 2
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
2 - 5
4. Understand the concept of inverse
fuctions.
4.1 Find object by inverse mapping given its image and function.
4.2 Determine inverse function using algebra.
4.3 Determine and state the condition for existence of an inverse function.
A2. LEARNING AREA: QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
6 - 7
1. Understand the concept of quadratic
equation and its roots.
1.1 Recognise quadratic equation and express it in general form.
1.2 Determine whether a given value is the root of a quadratic equation by
a) Substitution inspection.
1.3 Determine roots of a quadratic equation by trial and improvement method.
2. Understand the concept of quadratic
equations
2.1 Determine the roots of a quadratic equation by
a) factorisation;
b) completing the square
c) using the formula
2.2 Form a quadratic equation from given roots.
3. Understand and use the conditions for
quadratic equations to have
a) two different roots
b) two equal roots
no roots
3.1 Determine the types of roots of quadratic equations from the value of
ac 4 b
2
3.2 Solve problems involving ac 4 b
2
, in quadratic equations to
a) find an unknown value derive a relation
Week 7 Holidays for Chinese New Year
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 3
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
A3. LEARNING AREA: QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
8 - 9
1. Understand the concept of quadratic
functions and their graphs.
1.1 Recognise quadratic functions.
1.2 Plot quadratic functons graphs
a) based on given tabulated values
by tabulating values, based on given function.
1.3 Recognise shapes of graphs of quadratic functions.
1.4 Relate the position of quadratic functions graphs with types of roots for
0 ) x ( f
2. Find maximum and minimum values of
quadratic functions.
2.1 Determine the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function by completing
the square.
3. Sketch graphs of quadratic functions.
3.1 Sketch quadratic function graphs by determining the maximum or minimum point
and two other points.
4. Understand and use the concept of
quadratic inequalities.
4.1. Determine the ranges of values of x that satisfies quadratic inequalities.
Week 11 Test 1, 2013.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 4
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
A4 - LEARNING AREA: SIMULTANEOUS EQUATION
11-12
1. Solve simultaneous equations in two
unknowns one linear equation and one
non- linear equation.
1.1 Solve simultaneous equations using the substitution method.
1.2 Solve simultaneous equations involving the real life situations.
A5. LEARNING AREA: INDICES AND LOGARITHMS
13 - 15
1. Understand and use the concept of indices
and laws of indices to solve problems
1.1 Find the value of numbers given in the form of:
a) integer indices
b) fractional indices
1.2 Use law of indices to findthe values of numbers in index form that are
multiplied, divided or raised to a power.
1.3 Use laws of indices to simplify algebraic expressions
2. Understand and use the concept of
logarithms to solve problems
2.1 Express equation in index form and vice versa.
2.2 Find logarithm of a number.
2.3 Find logarithm of numbers by using laws of logarithms.
2.4 Simplify logarithmic expressions to the simplest form.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 5
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
13 - 15
3.Understand and use the change of base of
logarithm to solve the problems
3.1 Find the logarithm of a number by changing the base of the logarithm to a suitable
base.
3.2 Solve problems involving the change of base and laws of logarithm
4. Solve equations involving indices and
logarithms
4.1 Solve equations involving indices.
4.2 Solve equations involving logarithms.
G1. LEARNING AREA: COORDINATE GEOMETRY
16 - 18
1. Find distance between two points 1.1 Find distance between two points using formula.
2. Understand the concept of division of a line
segment
2.1 Find midpoint of two given points.
2.2 Find coordinates of a point that divides a line according to a given ratio m: n
3.Find areas of polygons.
3.1 Find area of a triangle based on the area of spesific geometrical shapes.
3.2 Find area of triangle y using formula
3.3 Find area of a quadrilateral using formula.
4. Understand and use the concept of equation
of a straight line
4.1 Determine the x intercept of a line.
4.2 Find the gradient of line that passes through two points.
4.3 Find the gradient of a straight line using
the x-intercept.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 6
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
16 - 18
4.4 Find the equation of a straight line given:
a) gradient and one point.
b) two points
c) x-intercept and y-intercept
4.5 Find the gradient and the intercepts of a straight line given the equation.
4.6 Change the equation of a straight line to the general form.
4.7 Find the point of intersection of two lines
5. Understand and use the concept of parallel
and perpendicular lines
5.1 Determine whether two staright lines are paralel when gradients of both lines
are known and vice versa.
5.2 Find the equation of a straight line that passes through a fixed point and parallel
to a given line
5.3 Detremine whether two straight lines are perpendicular lins are known and vice
versa.
5.4 Determine the equation of a straight line that passes through a fixed point and
perendicular to a given line.
5.5 Solve problems involving equations of a straight lines
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 7
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
16 - 18
6. Understand and use the concept of
equation of locus involving the distance
between two points
6.1 Find the equation of locus that satisfies the condition if:
a) The distance of a moving point from
a fixed point constant.
b)The ratio of the distances of a moving
point from two fixed points is constant
6.2 Solve problems involving loci.
Week 18 and 20 Mid Year Examination 2013.
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
S1.LEARNING AREA: STATISTICS
21 - 24
1. Understand and use the concept of
measures of central tendency to solve
problems.
1.1 Calculate mean of ungrouped data.
1.2 Determine mode of ungrouped data.
1.3. Determine median of ungrouped data.
1.4 Determine modal calss of grouped data
from the frequency distribution table.
1.5 Find mode from histogram.
1.6. Calculate mean of grouped data.
1.7 Calculate median of grouped data from the
cumulative frequency distribution table.
1.8 Estimate median of grouped data from an
ogive.
1.9 Determine the effects on mode, median,
and mean for a set of data when:
a) Each set of data is changed uniformly.
b) Extreme values exist.
c) Certain data is addedor removed.
1.10 Determine the most suitable measure
of central tendency for given data.
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
21 - 24 2. Understand and use the concept of 2.1 Find the range of ungrouped data.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 8
measures of dispersion to solve problems. 2.2 Find the interqurtile range of ungrouped data.
2.3 Find the range of grouped data.
2.4 Find the interquartile range of grouped data from the cumulative frequency
table.
2.5 Determine the interquartile range of grouped data from an ogive.
2.6 Determine the variance of
a) ungrouped data
b) grouped data.
2.7 Determine standard deviation of
a) ungrouped data
b) grouped data
2.8 Determine the effects on range, interquartile range variance and standard
deviation for a set of data when
a) each data is chaged uniformly
b) extreme values exist
c) certain data is added ir removed
2.9 Compare the measures of central tendency and dispersion between two sets
of data.
T1. LEARNING AREA: CIRCULAR MEASURES
25 - 26
1. Understand the concept of radian.
1.1 Convert measurements in radians to degrees and vice versa
2. Undestand and use the concept of length of
arc of a circle to solve problems
2.1 Determine:
a) length of arc
b) radius and
c) angle subtended at the centre of a circle
based on given information.
2.2 Find perimeter of segments of circles.
2.3 Solve problems involving length of arc.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 9
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
25 - 26
3. Understand the concept of area of sector of
a circle to solve problems.
3.1 Determine
a) area of sector
b) radius and
c) anle subtended at the centre of a circles
based on given information
3.2 Find area of segments of circle.
3.3 Solve problems involving area of sectors.
C1. LEARNING AREA: DIFFERENTIATION
27 - 30
1. Understand and use the concept of gradients
of curve and differentation.
1.1. Determine value of a function when its variable approaches a certain value.
1.2 Find gradient of a chord joining two points on a curve.
1.3 Find the first derivative of a function y=f(x) as gradient of tangent to its
graph.
1.4 Find the first derivative for polynomial using first principles.
1.5 Deduce the formula for first derivation of function y=f(x) by induction
2. Understand and use the concept of first
derivative of polynomial functions to solve
problems.
2.1 Determine first derivative of the function
n
ax y using formula.
2.2 Determine value of the first derivative of the function
n
ax y for a given
value x.
2.3 Determine first derivative of a function involving
a) addition or
b) subtraction of algebraic terms.
2.4 Determine first derivative of a product of two polynomials.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 10
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
27 - 30
2.5 Determine first derivative of a quotient of two polynomials.
2.6 Determine first derivative of composite function using chain rule.
2.7 Determine gradient of tangent at a point on a curve.
2.8 Determine equation of tangent at a point on a curve.
2.9 Determine equation of normal at a point on a curve
3. Understand and use the concept of
maximum and minimum values to solve
problems.
3.1 Determine coordinates of turning
points of a curve.
3.2 Determine whether a turning point is a maximum or minimum point.
3.3 Solve problems involving maximum and minimum values.
4. Understand and use the concept of rates of
change to solve problems.
4.1 Determine rates of change for related quantities.
5. Understand use the concept of small
changes and approximation to solve
problems.
5.1 Detemine small changes in quantities.
5.2 Determine approximate values using differentation.
6. Understand and use the concept of second
derivative to solve problems.
6.1 Determine second derivative of function y=f(x).
6.2 Determine whether a turning point is maximum or minimum point if a curve
using the second derivative.
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
AST1.LEARNING AREA: SOLUTION OF TRIANGLES
31 - 33
1. Understand and use the concept of sine rule
to solve problems.
1.1 Verify sine rule.
1.2 Use sine rule to find unknown sides or angles of triangle.
1.3 Find unknown sides and angles of a triangle in an ambiguous case.
1.4 Solve problems involving the sine rule.
YEARLY TEACHING PLAN FOR ADDITIONAL MATHEMATHICS FORM 4 2013.
Khairul Farez Bin Nahrawi | SMK Aminuddin Baki, Chemor 2013 11
2. Understand and use the concept of cosine
rule to solve problems.
2.1 Verify cosine rule.
2.2 Use cosine rule to find unknown sides or angles of a triangle.
2.3 Solve problems involving cosine rule.
2.4 Solve problems involving sine and cosine rules.
3.Understand and use the formula for area of
triangles to solve problems
3.1 Find area of triangles using formula
2
1
C sin ab or its equivalent.
3.2 Solve problems involving three-dimensional objects
INDEX NUMBER
34 - 36
1. Understand and use
the concept of
index number to
solve problems.
1.1 Calculate index number
1.2 Calculate price index
1.3 Find Q
0
or Q
1
given relevant information.
Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes
34 - 36
2. Understand and use the concept of
composite index to solve problems
2.1 Calculate composite index
2.2 Find index number or weightage given relevant information.
2.3 Solve problems involving index number and composite index.
Revision
Final Exam.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Slab DesignDokument96 SeitenSlab Designdilrangi100% (2)
- Adv Algebra Unit 3Dokument7 SeitenAdv Algebra Unit 3api-264152935Noch keine Bewertungen
- Further MathematicsDokument44 SeitenFurther MathematicsMohd Tirmizi100% (1)
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Madai WDT 178, 91209 KUNAK, SABAH. Mathematics Form 2 Yearly Lesson Plan 2012Dokument20 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Madai WDT 178, 91209 KUNAK, SABAH. Mathematics Form 2 Yearly Lesson Plan 2012Nik NabihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- CA-Clipper For DOS Version 5.3 Programming and Utilities GuideDokument718 SeitenCA-Clipper For DOS Version 5.3 Programming and Utilities GuideChris Harker91% (11)
- Acoustical Materials 2.0Dokument16 SeitenAcoustical Materials 2.0anuragNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seafloor Spreading TheoryDokument16 SeitenSeafloor Spreading TheoryMark Anthony Evangelista Cabrieto100% (1)
- 02 Minerals Library Basic Objects 5p1s4aDokument113 Seiten02 Minerals Library Basic Objects 5p1s4aman_y2k100% (1)
- Yearly Plan Mathematics T Sem 1 2015Dokument8 SeitenYearly Plan Mathematics T Sem 1 2015Tan Chin HuatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4Von EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Add MT F4 2012Dokument11 SeitenRPT Add MT F4 2012bolakampungNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPMP, Teaching PlanDokument14 SeitenGPMP, Teaching Planrosmawati_kadirNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2008 Form 5 Am Teaching SchemeDokument11 Seiten2008 Form 5 Am Teaching SchemeSujairi AmhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths f4Dokument11 Seiten2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths f4nurizwahrazak100% (1)
- Yearly Plan Add Math f4 2013Dokument17 SeitenYearly Plan Add Math f4 2013Ayu Lil'princessNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Add MT F5 2012Dokument20 SeitenRPT Add MT F5 2012Haswa ShazwatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Maths FORM 5 (Yearly Planning 2014)Dokument12 SeitenAdd Maths FORM 5 (Yearly Planning 2014)berusgigi1Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Add Math Form 4Dokument9 SeitenRPT Add Math Form 4Norhapidah Mohd SaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Kuadratic EkspressionDokument3 SeitenLesson Plan Kuadratic EkspressionKocheng Mie gorengNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itm402s Course OutlineDokument7 SeitenItm402s Course Outlinegwashilunga nuuyomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Form 4 2010Dokument21 SeitenYearly Plan Form 4 2010NurulAkmalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1Dokument9 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan KSSM Form 1cikguakmal78100% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2016Dokument12 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2016Mohd Sabri0% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Math F2Dokument13 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Math F2Yd MnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal: Outcome Based CurriculumDokument4 SeitenRajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal: Outcome Based Curriculumकिशोरी जूNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan FORM 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICSDokument2 SeitenYearly Plan FORM 4 ADDITIONAL MATHEMATICSchand_065Noch keine Bewertungen
- Course Syllabus in Mathematics IIDokument9 SeitenCourse Syllabus in Mathematics IIGena ClarishNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Math F4 2013Dokument34 SeitenRPT Math F4 2013ummuinsyirahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Math f3Dokument33 SeitenYearly Plan Math f3Faziyana Busu NollahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week/ Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Value NotesDokument9 SeitenWeek/ Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Value Notesaziahjamaluddin82Noch keine Bewertungen
- CO1 Quadratic Formula - LESSON PLANDokument4 SeitenCO1 Quadratic Formula - LESSON PLANJODALYN ODICTANoch keine Bewertungen
- College Mathematics OutlineDokument5 SeitenCollege Mathematics OutlineGary DunnNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMO 46 s2007 - Annex III Course Specification CerEngDokument56 SeitenCMO 46 s2007 - Annex III Course Specification CerEngJoshua Maverick BerameNoch keine Bewertungen
- SyllabusesDokument16 SeitenSyllabusesapi-230427224Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan 2014Dokument6 SeitenYearly Plan 2014shazeema74Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9 EXT Course Syllabus 2019 PDFDokument6 Seiten9 EXT Course Syllabus 2019 PDFandroid indiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterDokument3 SeitenSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterJimley CanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- g09 Gbs Mat g1Dokument217 Seiteng09 Gbs Mat g1Joieanne A. GarzoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 956 SP FurthermathDokument44 Seiten956 SP FurthermathDaniel Firdaus YusoffNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hsp-Add Math-F5Dokument28 SeitenHsp-Add Math-F5Azreen DaudNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 AprilDokument3 Seiten3 AprilTAN KUI GEK MoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- mpm1d Course OutlineDokument5 Seitenmpm1d Course Outlineapi-271045051Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form Four Additional Mathematics Yearly Plan 200Dokument10 SeitenForm Four Additional Mathematics Yearly Plan 200wilson tingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diana Curriculum AnalysisDokument14 SeitenDiana Curriculum Analysisapi-245618390Noch keine Bewertungen
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterDokument3 SeitenSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterJessie OlantigueNoch keine Bewertungen
- DLL Quadratic FormulaDokument3 SeitenDLL Quadratic Formulajennifer siarotNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics 4 N 1987Dokument18 SeitenMathematics 4 N 1987Tracy Treacher0% (1)
- Tingkatan 2 Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remark 1. Directed NumbersDokument8 SeitenTingkatan 2 Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remark 1. Directed NumbersMuhammad ElhamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Mathematics Scheme of Work Form 4 (2012)Dokument24 SeitenAdditional Mathematics Scheme of Work Form 4 (2012)Zabidah Awang100% (3)
- Course Outline BA301-2Dokument4 SeitenCourse Outline BA301-2drugs_182Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012Dokument12 SeitenSMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012norhasmizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bidor: Shceme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2012Dokument9 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bidor: Shceme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2012Zarina JusohNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4th Form Syllabus 16-17Dokument5 Seiten4th Form Syllabus 16-17RealGenius (Carl)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Addmathsf514Dokument12 SeitenYearly Lesson Addmathsf514SasiKalaRamayahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ima411s Course Outline 2023Dokument7 SeitenIma411s Course Outline 2023Wilma GoeiemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- COURSE GUIDE-college and Advanced AlgebraDokument6 SeitenCOURSE GUIDE-college and Advanced AlgebraShailanie Valle Rivera100% (1)
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Convent Bukit Nanas Kuala LumpurDokument26 SeitenSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Convent Bukit Nanas Kuala LumpurElfysia FredolinNoch keine Bewertungen
- MATH G8 I-Day 2Dokument4 SeitenMATH G8 I-Day 2Judith AbogadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Plan BDokument19 SeitenUnit Plan Bapi-309050107Noch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Algebra/Trigonometry: 2.1. Numbers, Number Systems and Number RelationshipsDokument5 SeitenAdvanced Algebra/Trigonometry: 2.1. Numbers, Number Systems and Number RelationshipsAustin ChiversNoch keine Bewertungen
- DAILY LESSON LOG OF M9AL-Ia-b-1 (Day Four)Dokument4 SeitenDAILY LESSON LOG OF M9AL-Ia-b-1 (Day Four)julito iliganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Honors Precalculus 2020-2021Dokument6 SeitenHonors Precalculus 2020-2021Jack HilbertNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Add Math F5Dokument23 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Add Math F5Lee Fhu SinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSTR in SeriesDokument3 SeitenCSTR in SeriesDhananjay KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flexible Perovskite Solar CellsDokument31 SeitenFlexible Perovskite Solar CellsPEDRO MIGUEL SOLORZANO PICONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5 Grade 10 FinalDokument9 SeitenModule 5 Grade 10 FinalSandy CarbonillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01Dokument43 SeitenRelayoperationprinciples 141126065914 Conversion Gate01kenlavie2Noch keine Bewertungen
- Eaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsDokument379 SeitenEaton Xeffect Industrial Switchgear Range Catalog Ca003002en en UsMAURIZIO MARININoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 4. Heat TransferDokument28 SeitenModule 4. Heat TransferBry RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camber For Construction StageDokument18 SeitenCamber For Construction StageOanh PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- HNBR Material TestDokument16 SeitenHNBR Material TestskyerfreeNoch keine Bewertungen
- ManageEngine Application Manager Best PracticesDokument12 SeitenManageEngine Application Manager Best PracticesNghiêm Sỹ Tâm PhươngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perawatan Pasien Dengan Gips Cast Skill LabDokument36 SeitenPerawatan Pasien Dengan Gips Cast Skill LabFadhilah putri fertyciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3.1 - Igneous RockDokument64 SeitenChapter 3.1 - Igneous Rockalvinllp83Noch keine Bewertungen
- RF Optimization Tips - TCH Block Rate Optimization Tips in Huawei GSMDokument4 SeitenRF Optimization Tips - TCH Block Rate Optimization Tips in Huawei GSMdolisieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1 - Spring2006: SolutionDokument31 SeitenAssignment 1 - Spring2006: SolutionMuhammad UmairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mazda 3Dokument5 SeitenMazda 3Jhony GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Lecture 2: Review of StatisticsDokument41 SeitenECON4150 - Introductory Econometrics Lecture 2: Review of StatisticsSaul DuranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics of Structure IIDokument3 SeitenMechanics of Structure IIvenkata369Noch keine Bewertungen
- Binomial Poisson Normal DistributionDokument9 SeitenBinomial Poisson Normal DistributionFahim MahmudNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAD-based Design of Three Phase Transformer and CoDokument13 SeitenCAD-based Design of Three Phase Transformer and CoM4gne7icNoch keine Bewertungen
- HKV-8 Valve Catalog SPLRDokument128 SeitenHKV-8 Valve Catalog SPLRCabrera RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mesh Based Multicast Routing ProtocolDokument10 SeitenMesh Based Multicast Routing ProtocolArul JothiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection and ShearDokument7 SeitenReflection and ShearsamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendix 1 - Using Avaya Site Administration (ASA)Dokument11 SeitenAppendix 1 - Using Avaya Site Administration (ASA)raghavNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICOM P12x-TechnicalDataSheetDokument28 SeitenMICOM P12x-TechnicalDataSheetSeba GonzálezNoch keine Bewertungen
- IB Lite 1 11 0 New FeaturesDokument11 SeitenIB Lite 1 11 0 New Featuresm.n.malasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bread and Pastry ProductionDokument9 SeitenBread and Pastry Productionwhite newgatesNoch keine Bewertungen