Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Nigeria Situation Analysis: Achieving MDG Goals
Hochgeladen von
Chikezie OnwukweOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nigeria Situation Analysis: Achieving MDG Goals
Hochgeladen von
Chikezie OnwukweCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Nigeria
Situation Analysis
Impacts and costs
Estimated Impact in General Mortality and Incremental Cost
Mortality reduction MDG 4 & 5 Additional cost per
capita (US$)
Cost per live
saved (US$)
Number of childrens
live saved
Phase I (2007-2009) <5 year= 35.1% NNMR= 16.5%
MMR= 28.5%
10.85 1,770 442,695
Phase II (2010-2012) <5 year= 59.8% NNMR= 37.1%
MMR= 65.7%
19.05 2,605 840,228
Phase III (2013-2015) <5 year= 75.5% NMR= 54.1%
MMR= 85.0%
34.0 4,024 1,158,021
Estimated scal space and costing assumptions
Assumptions Scenario 1:
low case scenario
Scenario 2:
medium case scenario
Scenario 3:
high case scenario
Growth 6.8 % annual growth (-3.2% per capita) 6.8 % annual growth (-3.2% per capita 6.8 % annual growth; uctuates and sta-
bilizes at 8.3% annual (-3.2% per capita)
Domestic revenue 43.7 % of GDP in 2007, 42.6 in 2008
and 41.3 in 2009, then stable
43.7 % of GDP in 2007, 42.6 in 2008
and 41.3 in 2009, then stable
Increases by 3.0% to reach 56.1% by
2015
Budget support Increases to 8% of GDP Increases to 8% of GDP Increases to 8% of GDP
Allocation to health Stable at 5.8% of total budget Increases to 10% by 2015 Increases to 10% by 2015
Private Expenditures Increases by 1% Increases by 1% Increases by 5 %
Earmarked aid to
health
Doubles until 2015 (8% annual
increase)
Doubles until 2015 (8% annual
increase)
Doubles until 2015 (8% annual increase)
These additional estimates correspond to additional costs of 69%, 34% and 32% of the incremental public scal space for health by
2015 for the low, medium and high scal spaces respectively.
in the low case scenario it will be around $ 26.5 and will increase gradually to peak at $ 39 in 2016;
in the medium scenario it will be around $ 28.4 in 20 08 and will increase gradually to $ 80.4 in 2016;
in the high case scenario it will be around $ 29.2 in 2008 and will increase to $ 85.4 by 2016.
Basic indicators Health indicators
Total population: 140 millions inhab. Under-5 mortality rate : 195 per 1000 live births
Life expectancy at birth (years): 48 Infant mortality rate:100 per 1000 live births
GNI per capita (US$): 560 Neonatal mortality rate: 53 per 1000 live births
Population under 5: 20.1 millions inhab. New born low birth weight: 14%
Population growth rate : 3.2% Antenatal care coverage: 58%
Child marriage 1987-2005: 43% Maternal mortality ratio: 800 per 100,000 live births
Female as a % of males primary school, net: 89% Routine EPI vaccines nanced by government: 100%
About 1,000,000 Nigerian children die each year before their fth birthday
Annually an estimated 44,800 Nigerian women die from pregnancy related complications out of 5,600,000 pregnancies
Although many of these causes are preventable, the coverage and quality of health care services in Nigeria continue to fail women and
children. The key problems are both technical and operational.
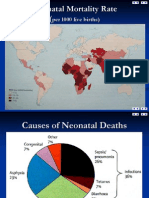
Major causes of under ve and maternal mortality
Malnutrition
56%
Malaria 25%
Diarrhoeal
disease 4%
Other 6%
Preterm birth 23%
Congenital 7%
Tetanus 10%
Sever
infection 23%
Birth
Asphyxia 26%
Neonatal 26%
Diarrhea 16%
Measles 6%
HIV 5%
Pneumonia 21%
Major causes of under five mortality
Neonatal causes
The Integrated Maternal Newborn and Child Health Strategy (IMNCH)
Strategy for National Coordination and Roll out to states and Local Government Areas
Partnership for Integrated Maternal, Newborn and Child Health Strategy
Monitoring and Evaluation of Maternal, Newborn and Child Health Strategy
Selected evidence-based interventions
Neonatal Malaria Pneumonia Diarrhea
Family
oriented
community
based
services
Clean delivery and
core care
Putting to breast
within 30 min of
delivery
Temperature
management
Use of ITN
by under-5
children
Antimalarial
treatment
Use drinking
water
Zinc for diarrhea
management
Oral rehydration
therapy
Exclusive breastfeeding for children 0-5 months
Supplementary & Therapeutic feeding for malnourished children
Population
oriented
outreach and
schedulable
services
Tetanus immunization
Prevention and
treatment of anaemia
in pregnancy
Antenatal care
ITN for under
ve through
EPI and ANC
Individually
oriented
clinical
services
Resuscitation of
asphyctic newborn
Management of
neonatal infections at
PHC level
Skilled delivery
ACT for
children
Antibiotics
for U5
pneumonia
Antibiotics for
diarrhoea
Strategy to achieve the MDGs
ACHIEVING THE MDGs IN
Harmonization for Health in Africa (HHA)
Kakemono prepared in close collaboration with CESAG - UNICEF
Anemia 11%
Obstructed Labor 11%
Major causes of maternal mortality
Eclampsia 5%
Complicated
abortion 11%
haemorrhage 23%
Malaria 11%
Other 11%
Puerperal infection 11%
About 74% of these occur in the 1st week of life mainly due to pregnancy and delivery related complications
Example of Evidence based
interventions will contribute to
reach adequate coverage.
Preventive infant & Child care
Baseline
Phase 1
Phase 2
Phase 3
100%
0%
20%
40%
60%
80%
Vaccines
in stock
Availability
nurses/
midwives
Access
to EPI
DPTI
Fully
imunized
1-2 yrs
Fully
imunized
at 1 yr
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Preclinical Behavioral Science and Social Sciences Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Von EverandPreclinical Behavioral Science and Social Sciences Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECG Questions for MRCP/MRCPI ExamsDokument52 SeitenECG Questions for MRCP/MRCPI ExamsHasan Mahmud100% (1)
- RMNCH+A Strategy Presentation: Goals, Challenges and InterventionsDokument65 SeitenRMNCH+A Strategy Presentation: Goals, Challenges and InterventionsSachin ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maurice Nicoll The Mark PDFDokument4 SeitenMaurice Nicoll The Mark PDFErwin KroonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vital StatisticsDokument35 SeitenVital StatisticsRadha100% (1)
- Bariatric GuidelinesDokument83 SeitenBariatric Guidelinessavvy_as_98100% (1)
- Sav 5446Dokument21 SeitenSav 5446Michael100% (2)
- Childhood Obesity: Causes and Consequences, Prevention and Management.Von EverandChildhood Obesity: Causes and Consequences, Prevention and Management.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 NCM 107 NewDokument44 SeitenModule 1 NCM 107 NewAmethystNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abra Valley College Vs AquinoDokument1 SeiteAbra Valley College Vs AquinoJoshua Cu SoonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Definitions and Pillars For Safemother HoodDokument39 SeitenDefinitions and Pillars For Safemother HoodMayom Mabuong50% (4)
- Definitions and Pillars For Safemother HoodDokument39 SeitenDefinitions and Pillars For Safemother HoodMayom Mabuong90% (29)
- POPDEV (Basic Concepts)Dokument64 SeitenPOPDEV (Basic Concepts)Paul Keene BonitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ContactsDokument10 SeitenContactsSana Pewekar0% (1)
- IMNCHDokument94 SeitenIMNCHAms BeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- LGT-9 Introduction To Child Health CareDokument26 SeitenLGT-9 Introduction To Child Health CareMazinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Health Epidemiology (Corrected)Dokument29 SeitenChild Health Epidemiology (Corrected)okwadha simionNoch keine Bewertungen
- FOPH - (Revision Class) Measure Pop Health Reprod and Assignment. (1-12-2023)Dokument61 SeitenFOPH - (Revision Class) Measure Pop Health Reprod and Assignment. (1-12-2023)Kamran SheikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDG Progress Towards MDG 4 and 5Dokument25 SeitenMDG Progress Towards MDG 4 and 5John Thiong'oNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efforts To Reduce MMR in 5 CountriesDokument11 SeitenEfforts To Reduce MMR in 5 CountriespitriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health-Related Issues and Challenges: Presented By: Joyce S. SalayoDokument51 SeitenHealth-Related Issues and Challenges: Presented By: Joyce S. SalayomackoypogiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knowledge About Neonatal Danger Signs and AssociatDokument8 SeitenKnowledge About Neonatal Danger Signs and AssociatLemi teshomeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Millennium Development GoalsDokument7 SeitenThe Millennium Development Goalsjug27Noch keine Bewertungen
- MNCH-FINAL._2023pptxDokument28 SeitenMNCH-FINAL._2023pptxpritaneionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mortality in Infancy and ChildhoodDokument12 SeitenMortality in Infancy and ChildhoodSamba SukanyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECON4410 Slide 7Dokument55 SeitenECON4410 Slide 7Farjad ImtiazNoch keine Bewertungen
- All-Cause Mortality and Malaria in African Children: Trends and ControversiesDokument32 SeitenAll-Cause Mortality and Malaria in African Children: Trends and ControversiesBesong MichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Community Case Management: BY:Nathifa Abdi H31/34946/2013 and Busaidy Swafiya H31/2369/2012Dokument37 SeitenCommunity Case Management: BY:Nathifa Abdi H31/34946/2013 and Busaidy Swafiya H31/2369/2012okwadha simionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reducing Perinatal and Neonatal MortalityDokument68 SeitenReducing Perinatal and Neonatal MortalityAndromedae Kartika100% (1)
- Advanced Maternal and Child Nursing: Latest Health StatisticsDokument10 SeitenAdvanced Maternal and Child Nursing: Latest Health StatisticssashimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Preterm Birth 2018Dokument5 SeitenWho Preterm Birth 2018Santi Ayu LestariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utilization of Antenatal Care Services by Urban Squatters of Kathmandu ValleyDokument6 SeitenUtilization of Antenatal Care Services by Urban Squatters of Kathmandu ValleyPramila PoudelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ayubi - Maternal Mortality Reduction in AfghanistanDokument21 SeitenAyubi - Maternal Mortality Reduction in AfghanistanDhaka2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.health IndicatorsDokument48 Seiten2.health IndicatorsMuhammad AsifNoch keine Bewertungen
- IndiaFactsheet PMTCTFactsheet 2010Dokument2 SeitenIndiaFactsheet PMTCTFactsheet 2010happyraamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health-Related Millennium Development GoalsDokument31 SeitenHealth-Related Millennium Development GoalsLiga LasmobaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reproductive & Child HealthDokument30 SeitenReproductive & Child HealthVeeresh IreniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maternal Health Program - Intro and Micronutrient SupplDokument55 SeitenMaternal Health Program - Intro and Micronutrient SupplBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Improving Mental HealthDokument11 SeitenImproving Mental HealthGeraldineMayNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSSM TyDokument22 SeitenCSSM TyDrPrachi PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Building MomentumDokument87 SeitenBuilding Momentumkfor774Noch keine Bewertungen
- Research Article: Estimating Maternal Mortality Level in Rural Northern Nigeria by The Sisterhood MethodDokument6 SeitenResearch Article: Estimating Maternal Mortality Level in Rural Northern Nigeria by The Sisterhood MethodFhasya Aditya PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Invest in Maternal and New Born in NepalDokument20 SeitenInvest in Maternal and New Born in NepalSeema GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap1 Presentation Bk2Dokument4 SeitenChap1 Presentation Bk2Geetha ManiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Child Survival StrategyDokument78 SeitenChild Survival Strategygeag20% (1)
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) Zuhrotul Eka Yulis ADokument43 SeitenIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) Zuhrotul Eka Yulis AShelly Dwi AnggrainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trends and Determinants of Maternal Mortality in Mizan-Tepi University Teaching and Bonga General Hospital From 2011 - 2015: A Case Control StudyDokument8 SeitenTrends and Determinants of Maternal Mortality in Mizan-Tepi University Teaching and Bonga General Hospital From 2011 - 2015: A Case Control StudyTegenne LegesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prof. Dr. Djaswadi Dasuki, MPH, Spog (K), PH.DDokument18 SeitenProf. Dr. Djaswadi Dasuki, MPH, Spog (K), PH.DFadhiah Nur ElvinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand - 2018 - Nyfl T - Strategies To Reduce Global Maternal MortalityDokument2 SeitenActa Obstet Gynecol Scand - 2018 - Nyfl T - Strategies To Reduce Global Maternal Mortalityadelbertha aprianaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DevelopmentDokument11 SeitenDevelopmentAizah EhsanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Epidemiology of The Leading Causes of MorbidityDokument22 SeitenClinical Epidemiology of The Leading Causes of MorbidityCLEMENTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relationship Between Mortality and Health Care Expenditure Sustainable Assessment of Health Care SystemDokument9 SeitenRelationship Between Mortality and Health Care Expenditure Sustainable Assessment of Health Care SystemANUJANoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Planning Fact Sheets MaldivesDokument6 SeitenFamily Planning Fact Sheets Maldivesabhilash k.bNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation On PRSP and MDG of BangladeshDokument33 SeitenPresentation On PRSP and MDG of BangladeshAbul Hasnat75% (4)
- CHAPTER ONE To FIVEDokument51 SeitenCHAPTER ONE To FIVEYARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Family Health Issues: Ap DR Tin Tin AyeDokument80 SeitenFamily Health Issues: Ap DR Tin Tin AyemdjohariNoch keine Bewertungen
- MY - PROJECT (1) Mai Kwai BroDokument39 SeitenMY - PROJECT (1) Mai Kwai BroAlameen kokoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics on Child Health Indicators and RatesDokument34 SeitenStatistics on Child Health Indicators and Ratescharan pooniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effective Interventions To Reduce Child Mortality and Undernutrition: The EvidenceDokument25 SeitenEffective Interventions To Reduce Child Mortality and Undernutrition: The EvidencegopscharanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDG 5Dokument19 SeitenMDG 5Ani 'cicieq' MargawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AssignmentDokument3 SeitenAssignmentPaul Nyakeh KandorNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ACSD AgendaDokument7 SeitenThe ACSD AgendaUNICEF UgandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final SDGs and MDGsDokument44 SeitenFinal SDGs and MDGsParas AzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Introduction To MCHDokument24 Seiten1.1 Introduction To MCHAYO NELSONNoch keine Bewertungen
- Group 06 DR Akhtar DR Nelofer DR Rehan DR SumaidaDokument34 SeitenGroup 06 DR Akhtar DR Nelofer DR Rehan DR Sumaidadr_hammadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Why Aren't There More Maternal Deaths? A Decomposition AnalysisDokument8 SeitenWhy Aren't There More Maternal Deaths? A Decomposition AnalysisFuturesGroup1Noch keine Bewertungen
- CDC Document Ebola Nigeria PDFDokument32 SeitenCDC Document Ebola Nigeria PDFChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viral Haem Fevers Nigeria PDFDokument60 SeitenViral Haem Fevers Nigeria PDFChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medicine As A BusinessDokument33 SeitenMedicine As A BusinessChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Arafah ReviewDokument21 SeitenArafah ReviewChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Dissertation FormatsDokument4 SeitenGuidelines For Dissertation FormatsChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Adrenal Insufficiency and Oncologic EmergenciesDokument12 SeitenAdrenal Insufficiency and Oncologic EmergenciesChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines For Dissertation FormatsDokument4 SeitenGuidelines For Dissertation FormatsChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDGs-SDGs2015 Toc PDFDokument10 SeitenMDGs-SDGs2015 Toc PDFChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- WHO-SEARO Snakebite Guidelines 2010Dokument162 SeitenWHO-SEARO Snakebite Guidelines 2010Galantry Ahmad AzhariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tiozzo HDL Subfractions and Carotid PlaqueDokument7 SeitenTiozzo HDL Subfractions and Carotid PlaqueChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mittendorf Giant InsulinomaDokument6 SeitenMittendorf Giant InsulinomaChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- HI76933 - Daily Meal Planning Guide - EnglishDokument5 SeitenHI76933 - Daily Meal Planning Guide - EnglishChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tests in EndocrinologyDokument1 SeiteTests in EndocrinologyChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nigeria PHC TextDokument86 SeitenNigeria PHC TextChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guias para El Diagnostico y Tratamiento de Acromegalia AACE 2011Dokument44 SeitenGuias para El Diagnostico y Tratamiento de Acromegalia AACE 2011Ricardo HemurNoch keine Bewertungen
- PSRDokument169 SeitenPSRvitogbadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vision for a Competent Civil ServiceDokument71 SeitenVision for a Competent Civil ServiceChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stephens Performance of Two New AlgorithmsDokument7 SeitenStephens Performance of Two New AlgorithmsChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gender Nigeria2012Dokument99 SeitenGender Nigeria2012Chikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kahaly Polyglandular Autoimmune SyndromesDokument10 SeitenKahaly Polyglandular Autoimmune SyndromesChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdulraheem Et Al PHC in NigeriaDokument9 SeitenAbdulraheem Et Al PHC in NigeriaChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hassan Doing A Pilot StudyDokument4 SeitenHassan Doing A Pilot StudyChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Guideines For The MGT of DsdsDokument73 SeitenClinical Guideines For The MGT of DsdsChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- Association Between Glycaemic Control and Erectile Dysfunction PDFDokument2 SeitenAssociation Between Glycaemic Control and Erectile Dysfunction PDFAlmira Shabrina SaraswatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Canadian Lipid Guidelines Update: FacultyDokument4 SeitenCanadian Lipid Guidelines Update: FacultyChikezie OnwukweNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRE EmtionDokument10 SeitenPRE EmtionYahya JanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Globalisation - Theories of Digital CommunicationDokument12 SeitenGlobalisation - Theories of Digital CommunicationDiya Patel-10SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Manual 36693 (Revision D, 5/2015) : PG Base AssembliesDokument10 SeitenProduct Manual 36693 (Revision D, 5/2015) : PG Base AssemblieslmarcheboutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Dokument14 SeitenOop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Hashir KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Death Without A SuccessorDokument2 SeitenDeath Without A Successorilmanman16Noch keine Bewertungen
- Case Analysis - Compania de Telefonos de ChileDokument4 SeitenCase Analysis - Compania de Telefonos de ChileSubrata BasakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sapkale Sandspit 2020Dokument5 SeitenSapkale Sandspit 2020jbs_geoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bar Exam 2016 Suggested Answers in Political LawDokument15 SeitenBar Exam 2016 Suggested Answers in Political LawYlnne Cahlion KiwalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tata Group's Global Expansion and Business StrategiesDokument23 SeitenTata Group's Global Expansion and Business Strategiesvgl tamizhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cib DC22692Dokument16 SeitenCib DC22692Ashutosh SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elementary School: Cash Disbursements RegisterDokument1 SeiteElementary School: Cash Disbursements RegisterRonilo DagumampanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Haryana Retial GarmentsDokument8 SeitenHaryana Retial Garmentssudesh.samastNoch keine Bewertungen
- Royal Enfield Market PositioningDokument7 SeitenRoyal Enfield Market PositioningApoorv Agrawal67% (3)
- Gattu Madhuri's Resume for ECE GraduateDokument4 SeitenGattu Madhuri's Resume for ECE Graduatedeepakk_alpineNoch keine Bewertungen
- Impact of Coronavirus On Livelihoods of RMG Workers in Urban DhakaDokument11 SeitenImpact of Coronavirus On Livelihoods of RMG Workers in Urban Dhakaanon_4822610110% (1)
- ABBBADokument151 SeitenABBBAJeremy MaraveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study - Soren ChemicalDokument3 SeitenCase Study - Soren ChemicalSallySakhvadzeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mayor Byron Brown's 2019 State of The City SpeechDokument19 SeitenMayor Byron Brown's 2019 State of The City SpeechMichael McAndrewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yi-Lai Berhad - COMPANY PROFILE - ProjectDokument4 SeitenYi-Lai Berhad - COMPANY PROFILE - ProjectTerry ChongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Meanwhile Elsewhere - Lizzie Le Blond.1pdfDokument1 SeiteMeanwhile Elsewhere - Lizzie Le Blond.1pdftheyomangamingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes On Lesson: Faculty Name Code Subject Name CodeDokument108 SeitenNotes On Lesson: Faculty Name Code Subject Name CodeJeba ChristoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Corporate Finance Canadian Canadian 8th Edition Ross Test Bank 1Dokument36 SeitenFundamentals of Corporate Finance Canadian Canadian 8th Edition Ross Test Bank 1jillhernandezqortfpmndz100% (22)
- Emperger's pioneering composite columnsDokument11 SeitenEmperger's pioneering composite columnsDishant PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- OBHR Case StudyDokument8 SeitenOBHR Case StudyYvonne TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Intro To Ozone LaundryDokument5 Seiten3 Intro To Ozone LaundrynavnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aptio ™ Text Setup Environment (TSE) User ManualDokument42 SeitenAptio ™ Text Setup Environment (TSE) User Manualdhirender karkiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BlueDokument18 SeitenBluekarishma nairNoch keine Bewertungen