Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Stirrer Batch Reactor
Hochgeladen von
Cik Tiem Ngagiman0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
257 Ansichten4 Seitenadvantages and disadvantages of stirred batch reactor
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenadvantages and disadvantages of stirred batch reactor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
257 Ansichten4 SeitenStirrer Batch Reactor
Hochgeladen von
Cik Tiem Ngagimanadvantages and disadvantages of stirred batch reactor
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 4
[ASSIGNMENT OF CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING] December 21, 2013
STIRRER BATCH REACTOR (SBR):
In the stirred-batch reactor, the catalyst is dispersed as slurry. Although this reactor
has better contact between the catalyst and the fluid than either the differential or integral
reactor, it has a sampling problem.
Samples of fluid are usually passed though cyclones or withdrawn through filters or
screen to separate the catalyst and fluid, thereby stopping the reaction. However, slow
quenching of the reaction in the cyclone or plugging of the filter sampling system by the
catalyst particles is a constant concern, thus making the rating in the sampling category
only fair.
Since the system is well-mixed, its isothermally is good. There is good contact
between the catalyst and reactants and the contact time is known since the catalyst and
reactants are fed at the same time. However, if the catalyst decays, the activity and
selectivity will vary during the course of data collection. This reactor is useful for substrate
solution of high viscosity and for immobilized enzymes with relatively low activity.
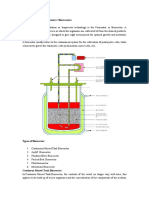
THE FIGURES OF STIRRED BATCH REACTOR:
[ASSIGNMENT OF CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING] December 21, 2013
APPLICATION OF STIRRED BATCH REACTOR:
For this reactor, some application has been present in all factories. The examples
application that used this kind of reactor is such as quit diverse, covering both waste water
treatment, food industry, polymerization, process involving microorganism and paper
industry.
1. COAGULATION AND FLOCCULATION:
The coagulation-flocculation method is used for removal of solid particles from
waste water. Coagulation is the destabilization of colloidal particles by adding some
chemical. While flocculation is where the aggregation and compacting of
coagulated particles are takes place and formed into large assemblages called floc
particles. For the coagulation, it required raid mixing that can be gain from stirred
batch reactor.
2. POLYMERIZATION:
The term of polymerization is referring to the process of bonding monomer
molecules to form polymer molecules. A homopolymer is formed when identical
monomers are bonded together while copolymer is formed from two different
monomers. But the types of polymerization method are varying with the impeller
that used in the stirred batch reactor.
3. FERMENTATION:
Fermentation involves the utilization of microorganism to convert substances into
another. Common microorganisms are bacteria, yeast and molds. Fermentation can
be performed with or without oxygen present, the process is therefore said to be
aerobic or an aerobic respectively. Thus, the process is takes place in the stirred
batch reactor that used to mixed and to disperse oxygen into the slurry, suspended
microorganisms, enhance heat transfer and blend the content of the fermenter.
4. FOOD INDUSTRY:
In the production of soft drink and fruit juices, mixing is needed in blending and
storage of syrups and pulp. Sweetening of drinks is usually done by adding syrup
[ASSIGNMENT OF CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING] December 21, 2013
and consisting of dissolved sugar. Thus, efficient fluid motion, provided by an axial
impeller is necessary to maintain temperature uniformly to avoid colour variations.
The power level depends on the viscosity and concentration of the syrup. Agitation
is also applied for uniform suspension of pulp in fruit juices.
ADVANTAGES OF STIRRED BATCH REACTOR:
1. High conversions per unit volume for one pass.
2. Flexibility of operation same reactor can produce one product one time and a
different product the next.
3. Easy to clean.
4. Versatility. A single vessel can carry out a sequence of different operations without
the need to break containment. This is particularly useful when processing toxic or
highly potent compounds.
DISADVANTAGES OF STIRRED VATCH REACTOR:
1. High operating cost.
2. Product quality more variable than with continuous operation.
3. If use high agitator loads, it can cause shaft stability problem.
4. Inlet temperature of the heat transfer fluid which can oscillate over a wide
temperature range to cause hot or cold spots at the jacket inlet points.
LIMITATION OF STIRRED BATCH REACTOR:
1. Use smaller flowing system with high speed agitators to create higher mixing rates
and it can overcome shaft stability problems.
2. The uses of heating and cooling jackets in order to removed or add the heat to the
reactor contents and maintain to the desired temperature.
[ASSIGNMENT OF CHEMICAL REACTION ENGINEERING] December 21, 2013
3. The temperature in the single jacket design is regulated to control heating or
cooling. But in the large vessels, it takes many minutes to adjust the temperature
and it cause sluggish temperature control.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Fermenter DesignDokument31 SeitenFermenter DesignV0% (1)
- 2.5 Bioreactor Design 1Dokument31 Seiten2.5 Bioreactor Design 1Astra BeckettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Chemical ReactorsDokument7 SeitenTypes of Chemical ReactorsLyka BalmesNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOPIC 5 - Types of BioreactorDokument35 SeitenTOPIC 5 - Types of BioreactorfadhilahmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Figure 1: Labelled Diagram of Batch Stirred-Tank ReactorDokument4 SeitenFigure 1: Labelled Diagram of Batch Stirred-Tank Reactorfareeha saeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Bioreactors ExplainedDokument23 SeitenTypes of Bioreactors ExplainedSundar SkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Differences in Polymer ReactorsDokument3 SeitenDifferences in Polymer ReactorsMarvin ParasNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5243 Heterogeneous Catalysis1Dokument7 Seiten5243 Heterogeneous Catalysis1Mohit PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Title of Experiment: BKF2741 Chemical Reaction Engineering Laboratory IDokument4 Seiten1.0 Title of Experiment: BKF2741 Chemical Reaction Engineering Laboratory IAs Eleyana100% (2)
- Reactors1 33Dokument2 SeitenReactors1 33Mourad kharbachNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Fermenters and Control SystemsDokument8 SeitenTypes of Fermenters and Control Systemsgopinadh reyyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 07 Batch ReactorDokument4 SeitenModule 07 Batch ReactorFarah -HNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bulk Chemical Mixing and Reactor Design OverviewDokument9 SeitenBulk Chemical Mixing and Reactor Design OverviewAbhishek KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Types of Fermentors and BioreactorsDokument16 SeitenDifferent Types of Fermentors and BioreactorsJaison JeevanandamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palding, Justine Grace M. Operations and Applications of General Types of Reactors 1. Batch ReactorDokument3 SeitenPalding, Justine Grace M. Operations and Applications of General Types of Reactors 1. Batch ReactorAngelica Joyce BenitoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fermenter and Its Features 1Dokument14 SeitenFermenter and Its Features 1Akhil Suresh (Synthite Biotech)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Study and Improvement in Operations of Chemical Plant: Guide: Shri. Mahesh DhawalikarDokument68 SeitenStudy and Improvement in Operations of Chemical Plant: Guide: Shri. Mahesh DhawalikarPrathamesh NaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Batch Reactor: Ancheta, Nicole Ann KDokument4 SeitenI. Batch Reactor: Ancheta, Nicole Ann KNicole Ann KimmayongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch ReactorDokument4 SeitenBatch ReactorFoo Xiao BingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 and 2 Lecture, رابع بوليمرات - د.زينبDokument30 Seiten1 and 2 Lecture, رابع بوليمرات - د.زينبMr. nobodyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bubble Column Fermenter/BioreactorDokument9 SeitenBubble Column Fermenter/BioreactorLouellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction & FundamentalDokument4 SeitenIntroduction & FundamentalsugieebakiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BIOREACTOR DESIGNDokument9 SeitenBIOREACTOR DESIGNVignesh KNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Experiment Batch ReactorDokument2 SeitenTutorial Experiment Batch Reactorkhaito K5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of A New Three Dimensional Network Co Polymer and Studying The Ability of Drug Delivery SystemDokument7 SeitenSynthesis of A New Three Dimensional Network Co Polymer and Studying The Ability of Drug Delivery SystemNadherdaman AlshamaryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Encyclopedia of Chemical Engineering Bioreactors: FermentersDokument13 SeitenVisual Encyclopedia of Chemical Engineering Bioreactors: FermentersVanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of FermenterDokument24 SeitenTypes of FermenterANJALI100% (2)
- UASB DesignDokument17 SeitenUASB DesignQuốc TuyênNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of ReactorsDokument16 SeitenTypes of Reactorsmunding21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micro ReactorDokument7 SeitenMicro Reactorrr1819Noch keine Bewertungen
- Micro ReactorDokument7 SeitenMicro ReactorMaxwell Quezada FelizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module-2 NotesDokument41 SeitenModule-2 NotessanemsinoritaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactor Design LessonDokument10 SeitenReactor Design LessonKrystel Monica ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regeneration of 3Å Molecular Sieves, Conventional vs. Microwave HeatingDokument7 SeitenRegeneration of 3Å Molecular Sieves, Conventional vs. Microwave Heating12ka42barNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waste in ReactorsDokument4 SeitenWaste in ReactorsjamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design For A High Temperature Shift ConverterDokument43 SeitenDesign For A High Temperature Shift ConverterAaron GyamfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packed Bed ReactorDokument6 SeitenPacked Bed ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman89% (9)
- Bioreactor: ECH 3201 Biochemical EngineeringDokument26 SeitenBioreactor: ECH 3201 Biochemical EngineeringWazif ZakwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch ReactorDokument3 SeitenBatch ReactorNicole Ann KimmayongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Desain Reaktor IsomerisasiDokument7 SeitenDesain Reaktor IsomerisasiIka Y. RachmawatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flow ChemistryDokument6 SeitenFlow Chemistryrr1819Noch keine Bewertungen
- Packed Bed Reactors LectureDokument14 SeitenPacked Bed Reactors LectureRobinson ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Reactor DesignDokument10 SeitenReactor DesignKrystel Monica ManaloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wastewater Treatment Lab TestDokument8 SeitenWastewater Treatment Lab TesthuyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Mechanical Agitation On The Production of Cellulases by Trichoderma Reesei RUT - 30 in A Draft - Tube Airlift BioreactorDokument9 SeitenEffect of Mechanical Agitation On The Production of Cellulases by Trichoderma Reesei RUT - 30 in A Draft - Tube Airlift BioreactormariaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PURPOSE OF AGITATION VESSELSDokument5 SeitenPURPOSE OF AGITATION VESSELSMAHAD ZahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purpose of Agitation VesselDokument5 SeitenPurpose of Agitation VesselMAHAD ZahidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hysys Project of Chemical Reaction Engineering: Prepared By: Mahmoud Mohamed ID: 141761Dokument9 SeitenHysys Project of Chemical Reaction Engineering: Prepared By: Mahmoud Mohamed ID: 141761Mahmoud HendawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Batch Reactor Design and PerformanceDokument16 SeitenBatch Reactor Design and Performancechisom100% (1)
- 2 Chemical Reactor To Reactor Safety PDFDokument41 Seiten2 Chemical Reactor To Reactor Safety PDFV DhinakaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Algae SimplifiedDokument21 SeitenLab Algae SimplifiedImran AzmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Product and Process Design: Dr. Aprilina Purbasari, ST, MTDokument32 SeitenChemical Product and Process Design: Dr. Aprilina Purbasari, ST, MTnurfadilla raufNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reaction Mini ProjekDokument5 SeitenReaction Mini ProjekMeck LotfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top bioprocessing techniques for separating insoluble biomoleculesDokument7 SeitenTop bioprocessing techniques for separating insoluble biomoleculesChemical Engg Evensem2021Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1-S2.0-S0255270196041682-Main Westerterp PDFDokument11 Seiten1-S2.0-S0255270196041682-Main Westerterp PDFnicocarraraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6aerobic Fludised Bed BioreactorDokument5 Seiten6aerobic Fludised Bed Bioreactorsneha raphelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Enzyme ReactorsDokument36 SeitenEnzyme ReactorsSanjay Kumar0% (1)
- Rheology of Dispersions: Principles and ApplicationsVon EverandRheology of Dispersions: Principles and ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsVon EverandAdvances in Biofeedstocks and Biofuels, Volume 2: Production Technologies for BiofuelsLalit Kumar SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. I Introduction to New Classifications of Polymeric Systems and New Concepts in ChemistryVon EverandNew Frontiers in Sciences, Engineering and the Arts: Vol. I Introduction to New Classifications of Polymeric Systems and New Concepts in ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Intellectual PropertyDokument6 Seiten7 Intellectual PropertyCik Tiem NgagimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulation Using PFR (Aspen Plus)Dokument10 SeitenSimulation Using PFR (Aspen Plus)Cik Tiem NgagimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Packed Bed ReactorDokument6 SeitenPacked Bed ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman89% (9)
- L9-Tubular Flow ReactorDokument20 SeitenL9-Tubular Flow ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman82% (11)
- Social Networking Problems Among Uitm Shah Alam StudentsDokument21 SeitenSocial Networking Problems Among Uitm Shah Alam StudentsCik Tiem Ngagiman100% (1)
- Differential ReactorDokument3 SeitenDifferential ReactorCik Tiem Ngagiman100% (1)
- Uv-Vis NoteDokument14 SeitenUv-Vis NoteCik Tiem NgagimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpDokument19 SeitenFluid Lab 2 - Bernoulli ExpCik Tiem Ngagiman89% (65)
- CSTR 40 LDokument28 SeitenCSTR 40 LCik Tiem Ngagiman50% (2)
- Flow of Water by Notch and WeirsDokument15 SeitenFlow of Water by Notch and WeirsCik Tiem Ngagiman93% (29)
- Perfect Gas ExpansionDokument35 SeitenPerfect Gas ExpansionCik Tiem Ngagiman63% (8)
- Determination of Concentration of ChromiumDokument26 SeitenDetermination of Concentration of ChromiumCik Tiem Ngagiman70% (10)
- Soap and DetergentDokument24 SeitenSoap and DetergentCik Tiem Ngagiman80% (10)
- PumpDokument18 SeitenPumpCik Tiem NgagimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expressive Matter Vendor FaqDokument14 SeitenExpressive Matter Vendor FaqRobert LedermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Learning: Bilal KhanDokument26 SeitenMachine Learning: Bilal KhanBilal KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Brunswick CDS - 2020-2021Dokument31 SeitenNew Brunswick CDS - 2020-2021sonukakandhe007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Empowerment Technology Reviewer: First SemesterDokument5 SeitenEmpowerment Technology Reviewer: First SemesterNinayD.MatubisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Oscilloscope BasicsDokument29 SeitenUnderstanding Oscilloscope BasicsRidima AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microsoft Word 2000 IntroductionDokument72 SeitenMicrosoft Word 2000 IntroductionYsmech SalazarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capacity PlanningDokument19 SeitenCapacity PlanningfarjadarshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health Education and Health PromotionDokument4 SeitenHealth Education and Health PromotionRamela Mae SalvatierraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feasibility StudyDokument47 SeitenFeasibility StudyCyril Fragata100% (1)
- Give Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishDokument12 SeitenGive Five Examples Each of Nature Having Reflection Symmetry and Radial Symmetry Reflection Symmetry Radial Symmetry Butterfly StarfishANNA MARY GINTORONoch keine Bewertungen
- Victron MultiPlus 48 1200-13-16 Datasheet enDokument1 SeiteVictron MultiPlus 48 1200-13-16 Datasheet enBAHJARI AMINENoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul-Document Control Training - Agus F - 12 Juli 2023 Rev1Dokument34 SeitenModul-Document Control Training - Agus F - 12 Juli 2023 Rev1vanesaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ryerson EthicsDokument20 SeitenRyerson EthicssinghbabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paradigm Shift Essay 2Dokument17 SeitenParadigm Shift Essay 2api-607732716Noch keine Bewertungen
- Obligations and Contracts Bar Questions and Answers PhilippinesDokument3 SeitenObligations and Contracts Bar Questions and Answers PhilippinesPearl Aude33% (3)
- NameDokument5 SeitenNameMaine DagoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2002, Vol.86, Issues 4, Hospital MedicineDokument221 Seiten2002, Vol.86, Issues 4, Hospital MedicineFaisal H RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold Forging Process TutorialDokument28 SeitenCold Forging Process TutorialpanyamnrNoch keine Bewertungen
- A General Guide To Camera Trapping Large Mammals in Tropical Rainforests With Particula PDFDokument37 SeitenA General Guide To Camera Trapping Large Mammals in Tropical Rainforests With Particula PDFDiego JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vidura College Marketing AnalysisDokument24 SeitenVidura College Marketing Analysiskingcoconut kingcoconutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of Quality Gurus Deming, Juran, Crosby, Imai, Feigenbaum & Their ContributionsDokument11 SeitenOverview of Quality Gurus Deming, Juran, Crosby, Imai, Feigenbaum & Their ContributionsVenkatesh RadhakrishnanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.4 Avogadro's Hypothesis+ Equivalent MassesDokument12 Seiten2.4 Avogadro's Hypothesis+ Equivalent MassesSantosh MandalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsDokument602 SeitenYanmar America publication listing for engine parts, service, and operation manualsEnrique Murgia50% (2)
- Desert Power India 2050Dokument231 SeitenDesert Power India 2050suraj jhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control SystemsDokument269 SeitenControl SystemsAntonis SiderisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyDokument4 SeitenAssessing Gross Efficiency and Propelling Efficiency in Swimming Paola Zamparo Department of Neurological Sciences, Faculty of Exercise and Sport Sciences, University of Verona, Verona, ItalyVijay KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- SiBRAIN For PIC PIC18F57Q43 SchematicDokument1 SeiteSiBRAIN For PIC PIC18F57Q43 Schematicivanfco11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Development of Rsto-01 For Designing The Asphalt Pavements in Usa and Compare With Aashto 1993Dokument14 SeitenDevelopment of Rsto-01 For Designing The Asphalt Pavements in Usa and Compare With Aashto 1993pghasaeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Your Inquiry EPALISPM Euro PalletsDokument3 SeitenYour Inquiry EPALISPM Euro PalletsChristopher EvansNoch keine Bewertungen
- VEGA MX CMP12HP Data SheetDokument2 SeitenVEGA MX CMP12HP Data SheetLuis Diaz ArroyoNoch keine Bewertungen