Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Question 2 Fundamentals
Hochgeladen von
Jess Fernandez BorgaOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Question 2 Fundamentals
Hochgeladen von
Jess Fernandez BorgaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The absence of breathing is referred to as:
a. apnea
b. eupnea
c. bradypnea
d. tachypnea
Reference: Apnea is referred to as the absence of breathing. Breathing that is normal in rate and depth is called eupnea.
Abnormally slow respirations are referred to as bradypnea. Abnormally fast respirations are called tachypnea.
If taking a patient's pulse for the first time, when obtaining baseline data, or if the pulse is irregular, count for:
a. a full minute
b. 30 seconds
c. 15 seconds and multiply by 4
d. 2 minutes
Reference: In assessing a peripheral pulse, count for 15 seconds and multiply by 4. If taking a patient's pulse for the first
time, when obtaining baseline data, or if the pulse is irregular, count for a full minute.
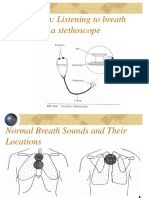
Gurgling sounds heard as air passes through moist secretions in the respiratory tract:
a. bubbling
b. stridor
c. stertor
d. wheeze
Reference: Bubbling - gurgling sounds heard as air passes through moist secretions in the respiratory tract. Stridor - a
shrill, harsh sound heard during inspiration with laryngeal obstruction. Stertor - snoring or sonorous respiration, usually
due to a partial obstruction of the upper airway. Wheeze - continuous, high-pitched musical squeak or whistling sound
occurring on expiration and sometimes on inspiration when air moves through a narrowed or partially obstructed
airway.
A wave of blood created by contraction of the left ventricle of the heart:
a. pulse
b. cardiac output
c. blood pressure
d. murmur
Reference: The pulse is a wave of blood created by contraction of the left ventricle of the heart. This wave represents
the stroke volume output and the amount of blood that enters the arteries with each ventricular contraction.
Underexpansion of the lungs characterized by shallow respirations:
a. Hypoventilation
b. Tachypnea
c. Bradypnea
d. Hyperventilation
Reference: Hypoventilation is the underexpansion of the lungs characterized by shallow respirations.
Measured in degrees, this vital sign reflects the balance between the heat produced and the heat lost from the body:
a. Body temperature
b. Core temperature
c. Surface temperature
d. Basal body temperature
Reference: Body temperature reflects the balance between the heat produced and the heat lost from the body. Core
and surface temperatures are two kinds of body temperature. Core temperature (relatively constant) is the temperature
of the deep tissues of the body, such as the abdominal and pelvic cavities. Surface temperature (rises and falls in
response to the environment) is the temperature of the skin, the subcutaneous tissue and fat. Basal body temperature is
the lowest temperature attained by the body during rest (usually during sleep).
Overexpansion of the lungs characterized by rapid and deep breaths:
a. Hyperventilation
b. Hypoventilation
c. Tachypnea
d. Bradypnea
Reference: Hyperventilation is overexpansion of the lungs characterized by rapid and deep breaths. Hypoventilation is
the underexpansion of the lungs characterized by shallow respirations. Tachypnea - quick, shallow breaths. Bradypnea -
abnormally slow breathing.
A shrill, harsh sound heard during inspiration with laryngeal obstruction:
a. stridor
b. stertor
c. wheeze
d. bubbling
Reference: Stridor - a shrill, harsh sound heard during inspiration with laryngeal obstruction. Stertor - snoring or
sonorous respiration, usually due to a partial obstruction of the upper airway. Wheeze - continuous, high-pitched
musical squeak or whistling sound occurring on expiration and sometimes on inspiration when air moves through a
narrowed or partially obstructed airway. Bubbling - gurgling sounds heard as air passes through moist secretions in the
respiratory tract.
A pulse with an irregular rhythm that may consist of random, irregular beats or a predictable pattern of irregular beats:
a. dysrhythmia
b. tachycardia
c. bradycardia
d. fibrillation
Reference: Dysrhythmia (also known as arrhythmia) is a pulse with an irregular rhythm. An electrocardiogram is
necessary to define the dysrhythmia further.
A blood pressure that is persistently above normal is called:
a. hypertension
b. hypotension
c. primary hypertension
d. secondary hypertension
Reference: Hypertension is a blood pressure that is persistently above normal. Hypotension is a blood pressure below
normal. An elevated blood pressure of unknown cause is called primary hypertension. An elevated blood pressure of
known cause is called secondary hypertension.
The average blood pressure of a healthy adult is:
a. 120/80 mm Hg
b. 130/70 mm Hg
c. 110/60 mm Hg
d. 140/90 mm Hg
Reference: The average blood pressure of a healthy adult is 120/80 mm Hg.
If a patient's usual blood pressure is 170/100 mm Hg, and it drops to 120/80 mm Hg post surgery, it must be:
a. reported to the physician immediately
b. monitored continually every hour
c. plotted in the chart and assessed again in 15 minutes
d. reported to the nurse on the next shift
Reference: Blood pressure can vary among individuals and it is important for nurses to know the baseline blood pressure
of patients. If a patient's usual blood pressure is 170/100 mm Hg, and it drops to 120/80 mm Hg post surgery, it must be
reported to the physician immediately.
The body usually has a small amount of warm air adjacent to it that rises and is replaced by cooler air. The dispersion of
heat by air currents is called:
a. Convection
b. Conduction
c. Radiation
d. Vaporization
Reference: Convection is the dispersion of heat by air currents. Conduction is the transfer of heat from one molecule
when in comes in contact to a molecule of lower temperature. Radiation is the transfer of heat from the surface of one
object to the surface of another without contact between the two objects. Vaporization is continuous evaporation of
moisture from the respiratory tract and from the mucosa of the mouth and from the skin.
This pulse site is usually used to measure blood pressure:
a. brachial
b. carotid
c. apical
d. popliteal
Reference: The brachial pulse site is used to measure blood pressure. The carotid is used in cases of cardiac arrest and to
determine circulation to the brain. The apical pulse is routinely used for infants and children up to 3 years of age, to
determine discrepancies with radial pulse and in conjunction with some medications. The popliteal pulse site is used to
determine circulation to the lower leg.
The interchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the circulating blood and the cells of the body tissues
(throughout the body):
a. internal respiration
b. external respiration
c. inhalation
d. expiration
Reference: Internal respiration is the interchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the circulating blood and the
cells of the body tissues. External respiration is the interchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli of the
lungs and the pulmonary blood. Inhalation or inspiration refers to the intake of air into the lungs. Exhalation or
expiration refers to breathing out or the movement of gases from the lungs to the atmosphere.
The pressure exerted by the blood as it flows through the arteries:
a. arterial blood pressure
b. systolic pressure
c. diastolic pressure
d. pulse pressure
Reference: Arterial blood pressure is a measure of the pressure exerted by the blood as it flows through the arteries.
Systolic pressure is the pressure of the blood as a result of contraction of the ventricles. Diastolic pressure is the
measure of the pressure when the ventricles are at rest. Pulse pressure is the difference the systolic and diastolic
pressure.
Abnormally slow respirations are referred to as:
a. bradypnea
b. tachypnea
c. apnea
d. eupnea
Reference: Abnormally slow respirations are referred to as bradypnea. Abnormally fast respirations are called
tachypnea. Apnea is referred to as the absence of breathing. Breathing that is normal in rate and depth is called eupnea.
During assessment of respiration, an inhalation and an exhalation count as how many respiration?
a. 1 b. 2
c. 3 d. 4
Reference: An inhalation and an exhalation count as one respiration.
Continuous, high-pitched musical squeak or whistling sound occurring on expiration and sometimes on inspiration when
air moves through a narrowed or partially obstructed airway:
a. wheeze
b. bubbling
c. stridor
d. stertor
Reference: Wheeze - continuous, high-pitched musical squeak or whistling sound occurring on expiration and sometimes
on inspiration when air moves through a narrowed or partially obstructed airway. Bubbling - gurgling sounds heard as air
passes through moist secretions in the respiratory tract. Stridor - a shrill, harsh sound heard during inspiration with
laryngeal obstruction. Stertor - snoring or sonorous respiration, usually due to a partial obstruction of the upper airway.
The ability to breathe only in upright sitting or standing positions is called:
a. Orthopnea
b. Dyspnea
c. Cheyne-Stokes breathing
d. Apnea
Reference: Orthopnea is the ability to breathe only in upright sitting or standing positions. Dyspnea is difficult and
labored breathing. Cheyne-Stokes breathing is the rhythmic waxing and waning of respirations, from very deep to very
shallow breathing and temporary apnea. Apnea is the cessation of breathing.
Abnormally fast respirations are called:
a. tachypnea
b. apnea
c. eupnea
d. bradypnea
Reference: Abnormally fast respirations are called tachypnea. Apnea is referred to as the absence of breathing.
Breathing that is normal in rate and depth is called eupnea. Abnormally slow respirations are referred to as bradypnea.
Heat loss from the body through continuous evaporation of moisture from the respiratory tract and from the mucosa of
the mouth and from the skin:
a. Vaporization
b. Convection
c. Conduction
d. Radiation
Reference: Vaporization is continuous evaporation of moisture from the respiratory tract and from the mucosa of the
mouth and from the skin. Convection is the dispersion of heat by air currents. Conduction is the transfer of heat from
one molecule when in comes in contact to a molecule of lower temperature. Radiation is the transfer of heat from the
surface of one object to the surface of another without contact between the two objects.
Breathing that is normal in rate and depth:
a. eupnea
b. bradypnea
c. tachypnea
d. apnea
Reference: Breathing that is normal in rate and depth is called eupnea. Abnormally slow respirations are referred to as
bradypnea. Abnormally fast respirations are called tachypnea and apnea is absence of breathing.
The interchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli of the lungs and the pulmonary blood:
a. external respiration b. internal respiration
c. inhalation d. expiration
Reference: External respiration is the interchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the alveoli of the lungs and the
pulmonary blood. Internal respiration is the interchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the circulating blood
and the cells of the body tissues. Inhalation or inspiration refers to the intake of air into the lungs. Exhalation or
expiration refers to breathing out or the movement of gases from the lungs to the atmosphere.
A pulse oximeter is a noninvasive device that measures a patient's arterial blood oxygen saturation (SaO2). What
percent of SaO2 reading is considered life threatening?
a. 100%
b. 95%
c. 80%
d. 60%
You answered "60%".
This is the correct answer.
Reference: Normal SaO2 is 95% to 100%. An SaO2 below 70% is life threatening.
Question 26
Snoring or sonorous respiration, usually due to a partial obstruction of the upper airway:
a. stertor
b. wheeze
c. bubbling
d. stridor
You answered "stertor".
This is the correct answer.
Reference: Stertor - snoring or sonorous respiration, usually due to a partial obstruction of the upper airway. Wheeze -
continuous, high-pitched musical squeak or whistling sound occurring on expiration and sometimes on inspiration when
air moves through a narrowed or partially obstructed airway. Bubbling - gurgling sounds heard as air passes through
moist secretions in the respiratory tract. Stridor - a shrill, harsh sound heard during inspiration with laryngeal
obstruction.
Question 27
The vital or cardinal signs are:
a. body temperature, pulse, respirations, blood pressure
b. body temperature, pulse, blood pressure, basal metabolic rate
c. core temperature, surface temperature, pulse, blood pressure
d. body temperature, pulse, blood pressure, ventilation
You answered "body temperature, pulse, respirations, blood pressure".
This is the correct answer.
Reference: The vital or cardinal signs are body temperature, pulse, respirations and blood pressure. Pulse oximetry is
also commonly measured as a traditional vital sign.
Question 28
The transfer of heat from one molecule when in comes in contact to a molecule of lower temperature is called:
a. Conduction
b. Radiation
c. Convection
d. Vaporization
You answered "Convection".
This is not the correct answer.
The correct answer is: "Conduction"
Reference: Conduction is the transfer of heat from one molecule when in comes in contact to a molecule of lower
temperature. Radiation is the transfer of heat from the surface of one object to the surface of another without contact
between the two objects. Convection is the dispersion of heat by air currents. Vaporization is continuous evaporation of
moisture from the respiratory tract and from the mucosa of the mouth and from the skin.
Question 29
The following are the times to assess vital signs except for:
a. When a patient doesn't have a change in health status or doesn't report any symptoms
b. On admission of patient to obtain baseline vital signs data
c. Before and after the patient undergoes surgery or any invasive procedure
d. Before and after any nursing intervention that could affect the patient's vital signs
You answered "When a patient doesn't have a change in health status or doesn't report any symptoms".
This is the correct answer.
Reference: Vital signs are assessed when a patient has a change in health status or reports symptoms such as chest pain
or feeling warm/hot.
Question 30
The transfer of heat from the surface of one object to the surface of another without contact between the two objects is
called:
a. Radiation
b. Conduction
c. Convection
d. Vaporization
You answered "Radiation".
This is the correct answer.
Reference: Radiation is the transfer of heat from the surface of one object to the surface of another without contact
between the two objects. Conduction is the transfer of heat from one molecule when in comes in contact to a molecule
of lower temperature. Convection is the dispersion of heat by air currents. Vaporization is continuous evaporation of
moisture from the respiratory tract and from the mucosa of the mouth and from the skin.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Basic Clinical SkillsDokument6 SeitenBasic Clinical SkillsBlake KamminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oxygenation 1Dokument155 SeitenOxygenation 1Khatlen BagaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- NCM 101 Vital Signs PPT BSN 1a Group 1Dokument138 SeitenNCM 101 Vital Signs PPT BSN 1a Group 1Brian Anthony100% (1)
- Clinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 7th Edition Jardins Test BankDokument6 SeitenClinical Manifestations and Assessment of Respiratory Disease 7th Edition Jardins Test BankBrookeStarksdgao93% (15)
- Cardio Practical 1Dokument6 SeitenCardio Practical 1roshanleung11Noch keine Bewertungen
- MVS Pulmonary AuscultationDokument8 SeitenMVS Pulmonary Auscultationvashini9151Noch keine Bewertungen
- Repiratory Emergencies McqsDokument14 SeitenRepiratory Emergencies McqsMohamed MansourNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terminologies FNDokument3 SeitenTerminologies FNMonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terms RespiDokument5 SeitenTerms RespiDiane Kate Tobias MagnoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDokument27 SeitenPemeriksaan ThoraxYaasinta ArlaesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6 - Breath SoundsDokument31 Seiten6 - Breath SoundsggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation 6th Edition by CairoDokument24 SeitenTest Bank For Pilbeams Mechanical Ventilation 6th Edition by Cairojenniferhoustonmjcfngpbow100% (38)
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDokument27 SeitenPemeriksaan ThoraxSubchanPrasetyoNoch keine Bewertungen
- VentillatorDokument106 SeitenVentillatordeepaseira2205Noch keine Bewertungen
- RespirationDokument29 SeitenRespirationbemina jaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auscultation: Listening To Breath Sounds With A StethoscopeDokument12 SeitenAuscultation: Listening To Breath Sounds With A Stethoscopeajaykumar soddalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessmentpulmonary 151014090912 Lva1 App6892Dokument63 SeitenAssessmentpulmonary 151014090912 Lva1 App6892sasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Signs and SymptomsDokument11 SeitenRespiratory Signs and SymptomsChristiany Racho SalduaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Restrictive Lung DiseasesDokument31 SeitenRestrictive Lung DiseasesAnn FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respi SystemDokument6 SeitenRespi SystemKalichandren ArumugamNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Respiratory System (Intro)Dokument75 SeitenThe Respiratory System (Intro)Krestel Saligumba PalanogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thoracic Injuries 1Dokument32 SeitenThoracic Injuries 1awais mpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory ExaminationDokument19 SeitenRespiratory ExaminationMohini33% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan - Impaired Gas ExchangeDokument3 SeitenNursing Care Plan - Impaired Gas ExchangeYum C86% (65)
- Chapter 27: Alterations of Pulmonary Function Power-Kean Et Al: Huether and Mccance'S Understanding Pathophysiology, Second Canadian EditionDokument13 SeitenChapter 27: Alterations of Pulmonary Function Power-Kean Et Al: Huether and Mccance'S Understanding Pathophysiology, Second Canadian EditionmonicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan ThoraxDokument36 SeitenPemeriksaan ThoraxVaiz AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thorax and Lung - LectureDokument60 SeitenThorax and Lung - LectureТаншолпан ШохбутоваNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pemeriksaan Thorax: Coass Interna RSI Sultan Agung SemarangDokument59 SeitenPemeriksaan Thorax: Coass Interna RSI Sultan Agung SemarangImada KhoironiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDokument6 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemMonica VelascoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lungs and ThoraxDokument9 SeitenLungs and ThoraxMaria Mika Ella RetizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OxygenationDokument16 SeitenOxygenationMandy Jamero100% (1)
- Assessment of Respiratory SystemDokument18 SeitenAssessment of Respiratory SystemIbi Yulia Setyani100% (1)
- IPPADokument4 SeitenIPPAIsaac KipchumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assessment of Respiratory System PDFDokument41 SeitenAssessment of Respiratory System PDFsarhang talebaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory ExaminationDokument8 SeitenRespiratory ExaminationAbdullahi Mo'allin MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- MedSurg Ch30-31Dokument8 SeitenMedSurg Ch30-31Vanessa Da Cruz100% (1)
- Respiratory PhysiologyDokument9 SeitenRespiratory PhysiologyBrent TorresNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaDokument81 SeitenDR Amsalu Bekele Ass - Professor of Medicine Head of Chest Unit Department of Internal Medicine Addis Ababa University, School of Medicine Addis Ababa, EthiopiaBethelhem BirhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Symptoms and Signs in Respiratory SystemDokument31 SeitenSymptoms and Signs in Respiratory SystemAbdilahi Hassan-YTANoch keine Bewertungen
- Tidal Volume Residual Volume Vital Capacity Total Lung CapacityDokument3 SeitenTidal Volume Residual Volume Vital Capacity Total Lung CapacityZachary T HallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsDokument4 SeitenRespiratory System Assessment: Other SystemsChetan KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory System-Review PathoDokument100 SeitenRespiratory System-Review PathoSadiePartington-RiopelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 3&4 - Pulmonary PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenLec 3&4 - Pulmonary PhysiologyDana KostNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 RespDokument81 Seiten3 RespashuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lungs and ThoracicDokument66 SeitenLungs and ThoracicJoyce Jacobe0% (1)
- Respiration, - Characteristics N Factors Affecting RespirationDokument2 SeitenRespiration, - Characteristics N Factors Affecting RespirationShalabh JoharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lung ExaminationDokument14 SeitenLung Examinationსალომე მუმლაძე “Slay” TMANoch keine Bewertungen
- Care For A Client With Respiratory Disorders 2Dokument105 SeitenCare For A Client With Respiratory Disorders 2moncalshareen3Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Respiratory System PDFDokument21 SeitenThe Respiratory System PDFhechi_zeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory DisordersDokument17 SeitenRespiratory DisordersBrandi Worley100% (2)
- Breath Sounds: ConsiderationsDokument10 SeitenBreath Sounds: ConsiderationsKarl RobleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examination of The Chest and LungsDokument5 SeitenExamination of The Chest and Lungsteena12aNoch keine Bewertungen
- OxygenationDokument56 SeitenOxygenationHerald Clarence M. AmbayecNoch keine Bewertungen
- RespiratoryDokument3 SeitenRespiratoryKyla SanjuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Causes and Possible Prevention of Asthma and AllergiesVon EverandCauses and Possible Prevention of Asthma and AllergiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandPleural Effusion, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyVon EverandRespiratory gymnastics (Translated): Purification - Health - Strength - EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyspnea, (Breathlessness) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsVon EverandDyspnea, (Breathlessness) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Practice I-AnswerDokument9 SeitenNursing Practice I-AnswerJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample QuestionnaireDokument10 SeitenSample QuestionnaireJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsDokument110 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsJerome F. Adorable, RN92% (76)
- Sample QuestionareDokument4 SeitenSample QuestionareJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsDokument17 SeitenPractice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsPaul Christian P. Santos, RN94% (87)
- Medical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsDokument110 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsJerome F. Adorable, RN92% (76)
- Nursing Board Exam Review Questions in Emergency Part 6/20Dokument15 SeitenNursing Board Exam Review Questions in Emergency Part 6/20Tyron Rigor Silos100% (5)
- Neat People VsDokument4 SeitenNeat People VsJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regencia Cva PathoDokument11 SeitenRegencia Cva PathoJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- TleDokument8 SeitenTleJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Principal Religions of Asia AreDokument2 SeitenThe Principal Religions of Asia AreJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nursing Care PlanDokument7 SeitenNursing Care PlanJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hyperparathyroidism: Diabetes Incipidus Lab Test and DiagnosticDokument3 SeitenHyperparathyroidism: Diabetes Incipidus Lab Test and DiagnosticJess Fernandez BorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- De Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Dokument11 SeitenDe Thi Chon Hoc Sinh Gioi Cap Tinh Mon Tieng Anh Lop 12 So GD DT Thanh Hoa Nam Hoc 2015 2016Thuy LinggNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3Dokument128 SeitenCpar Characteristics and Functions Week 3christianwood0117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Low Speed Aerators PDFDokument13 SeitenLow Speed Aerators PDFDgk RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Camless EnginesDokument4 SeitenCamless EnginesKavya M BhatNoch keine Bewertungen
- Priest, Graham - The Logic of The Catuskoti (2010)Dokument31 SeitenPriest, Graham - The Logic of The Catuskoti (2010)Alan Ruiz100% (1)
- Mathematics - Mathematics of Magic - A Study in Probability, Statistics, Strategy and Game Theory XDokument32 SeitenMathematics - Mathematics of Magic - A Study in Probability, Statistics, Strategy and Game Theory XHarish HandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algorithms For Automatic Modulation Recognition of Communication Signals-Asoke K, Nandi, E.E AzzouzDokument6 SeitenAlgorithms For Automatic Modulation Recognition of Communication Signals-Asoke K, Nandi, E.E AzzouzGONGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Additional Article Information: Keywords: Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cribriform Pattern, Parotid GlandDokument7 SeitenAdditional Article Information: Keywords: Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma, Cribriform Pattern, Parotid GlandRizal TabootiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nescom Test For AM (Electrical) ImpDokument5 SeitenNescom Test For AM (Electrical) Impشاہد یونسNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extract The .Msi FilesDokument2 SeitenExtract The .Msi FilesvladimirNoch keine Bewertungen
- EngHub How To Break HabitsDokument13 SeitenEngHub How To Break HabitsViktoria NovikovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Great Muslim Scientist - Imam Jaffer Sadiq (ADokument78 SeitenThe Great Muslim Scientist - Imam Jaffer Sadiq (ASalman Book Centre100% (2)
- Bubble Test Direct Pressure InserviceDokument3 SeitenBubble Test Direct Pressure InserviceEdAlmNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Reason: B. FlowsDokument4 SeitenThe Reason: B. FlowsAryanti UrsullahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ST3 ManualDokument48 SeitenST3 ManualRon FosterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gastroesophagea L of Reflux Disease (GERD)Dokument34 SeitenGastroesophagea L of Reflux Disease (GERD)Alyda Choirunnissa SudiratnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic RegionDokument30 SeitenNewsletter 1-2021 Nordic-Baltic Regionapi-206643591100% (1)
- Working Capital Management 2012 of HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LTD.Dokument98 SeitenWorking Capital Management 2012 of HINDALCO INDUSTRIES LTD.Pratyush Dubey100% (1)
- RN42Dokument26 SeitenRN42tenminute1000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Green Dot ExtractDokument25 SeitenGreen Dot ExtractAllen & UnwinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9881 enDokument345 Seiten9881 enSaid BenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rights of Parents in IslamDokument11 SeitenRights of Parents in Islamstoneage989100% (2)
- Lab Manual Switchgear and Protection SapDokument46 SeitenLab Manual Switchgear and Protection SapYash MaheshwariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Music 9 Q3 Mod4 Musical Elements of Given Romantic Period PiecesDokument19 SeitenMusic 9 Q3 Mod4 Musical Elements of Given Romantic Period PiecesFinn Daniel Omayao100% (1)
- Manual de Operacion y MantenimientoDokument236 SeitenManual de Operacion y MantenimientoalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jpedal ManualDokument20 SeitenJpedal ManualDamián DávilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dessler HRM12e PPT 01Dokument30 SeitenDessler HRM12e PPT 01harryjohnlyallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cultural Sensitivity BPIDokument25 SeitenCultural Sensitivity BPIEmmel Solaiman AkmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Password Cracking Part 1Dokument8 SeitenIntroduction To Password Cracking Part 1Tibyan MuhammedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Existentialism in LiteratureDokument2 SeitenExistentialism in LiteratureGirlhappy Romy100% (1)