Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
GSM System
Hochgeladen von
jedossousOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GSM System
Hochgeladen von
jedossousCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
GSM System GSM System
Prof. S.-I. Sou
EE, NCKU EE, NCKU
Fall, 2008
1
Outlines
Introduction
GSM Architecture
Air Interface
Location Tracking and Call Setup Location Tracking and Call Setup
Mobility Management
Summary
2
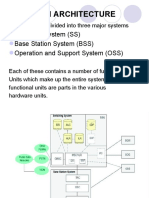
GSM Architecture GSM Architecture GSM Architecture GSM Architecture
3
GSM Architecture
MAP interface
4
Also called Mobile Terminal (MT)
The MS consists of two parts:
Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
Mobile Equipment (ME)
Mobile Station (MS)
5
A SIM contains subscriber-related information
A list of abbreviated and customized short dialing
numbers
Short message
SIM
Short message
Names of preferred Networks to provide service
Personal Identity Number (PIN) .
SIM information can be modified:
By the subscriber either by keypad or a PC using
an RS232 connection
By sending codes through short messages
(network operators)
6
Mobile Equipment (ME)
ME: non-customer-related hardware and
software specific to the radio interface
ME can not be used if no SIM is on the MS.
Except for emergency calls
The SIM-ME design supports portability: The SIM-ME design supports portability:
The MS is the property of the subscriber.
The SIM is the property of the service provider.
7
Base Station System (BSS)
The Base Station System (BSS) connects the
MS and NSS.
BSS contains
Base transceiver station (BTS)
Base station controller (BSC) Base station controller (BSC)
8
Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS)
Telephone switching functions
Subscriber profiles
Mobility management
Components in NSS:
NSS (1/2)
Components in NSS:
MSC: provide basic switching function
Gateway MSC (GMSC): route an incoming call
to an MSC by interrogating the HLR directly.
9
NSS (2/2)
Components in NSS (continuous):
HLR and VLR maintain the current location of
the MS.
Authentication Center (AuC) is used in the
security management.
Equipment Identity Register (EIR) is used for Equipment Identity Register (EIR) is used for
the registration of MS equipment.
10
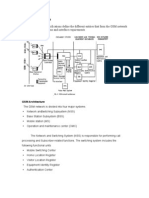
Mobility Databases
The hierarchical databases used in GSM.
The home location register (HLR) is a database
used for MS information management.
The visitor location register (VLR) is the
database of the service area visited by an MS.
MSC 1
HLR
VLR 1 VLR 2
MSC 2
11
Home Location Register (HLR)
An HLR record consists of 3 types of
information:
Mobile station information
IMSI (used by the MS to access the network)
MSISDN (the ISDN numberPhone Number
of the MS)
Location information
ISDN number of the VLR (where the MS resides)
ISDN number of the MSC (where the MS resides)
Service information
service subscription
service restrictions
supplementary services
12
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
The VLR information consists of three parts:
Mobile Station Information
IMSI
MSISDN
TMSI TMSI
Location Information
MSC Number
Location Area ID (LAI)
Service Information
A subset of the service Information stored in HLR
13
Registration
MS powers on.
By using FCCH and SCH to
synchronize with the BTS.
BS 2
BS 1
BS 3
From BCCH, the MS gets the
cell global identity (CGI).
MS registers with the MSC.
14
GSM Call Origination
15
GSM Call Termination
RACH(request signaling channel)
MS
BSS
PCH(page MS)
SDCCH(respond to paging)
SDCCH message exchanges for call setup
AGCH(assign signaling channel)
16
Location Tracking and Call Location Tracking and Call
Setup Setup Setup Setup
17
Location Area
Location area (LA) is the basic unit for location
tracking.
Location Area Identification (LAI)
MSC
MSC
MSC
LA 1
LA 2
LA 3
18
Key Terms
GSM uses some identifiers
Mobile system ISDN (MSISDN)
Mobile Station Roaming Number (MSRN)
International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI)
Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI)
International Mobile station Equipment Identity
(IMEI)
Location Area Identity (LAI)
Cell Global Identity (CAI)
19
MSISDN
Mobile System ISDN
MSISDN uses the same format as the ISDN
address (based on ITU-T Recommendation
E.164).
HLR uses MSISDN to provide routing
instructions to other components in order to instructions to other components in order to
reach the subscriber.
Country code
(CC)
National destination
code (NDC)
Subscriber
number (SN)
Total up to 15 digits
20
MSRN
Mobile Station Roaming Number
The routing address to route the call to the MS
through the visited MSC.
MSRN=CC+NDC+SN
21
IMSI
International Mobile Subscriber Identity
Each mobile unit is identified uniquely with an
IMSI.
IMSI includes the country, mobile network,
mobile subscriber.
Total up to 15 digits Total up to 15 digits
Mobile country
code (MCC)
Mobile network
code (MNC)
Mobile subscriber
identification code (MSIC)
3 digits 1- 2 digits Up to 10 digits
22
TMSI
Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identify
TMSI is an alias used in place of the IMSI.
This value is sent over the air interface in place
of the IMSI for purposes of security.
23
IMEI
International Mobile Station Equipment Identity
IMEI is assigned to the GSM at the factory.
When a GSM component passes conformance
and interoperability tests, it is given a TAC.
Up to 15 digits
Type approval
code (FAC)
Final assembly
code (FAC)
Serial number (MSIC)
3 digits 2 digits Up to 10 digits
Spare 1 digit
24
LAI
Location Area Identity
LAI identifies a location area (LA).
When an MS roams into another cell, if it is in the
same LAI, no information is exchanged.
Total up to 15 digits
Mobile country
code (MCC)
Mobile network
code (MNC)
Location area code (LAC)
3 digits 1-2 digits Up to 10 digits
25
CGI
Cell Global Identity
CGI = LAI + CI
= MCC + MNC + LAC + CI
CI : Cell Identity
26
Identifiers and Components
HLR VLR/MSC BSC BTS MS
MSISDN
MSRN
IMSI
TMSI
LAI
CGI
MSC
27
Cloud
Cloud
Cloud
Other
Switches
HLR
1
GMSC
VLR
1
1
1
2
2
The Mobile Call Termination
(Delivery) Procedure
MSISDN
MSRN MSRN
IMSI
MSISDN
IMSI
Cloud
Switches
3
MSC
Cloud
Cloud
Cloud
Other
Switches
3
3
MSISDN
PSTN
28
GSM Location Update GSM Location Update GSM Location Update GSM Location Update
29
MS Registration Process
HLR
3
5
HLR
location update
deregistration
VLR
IMSI
Old
VLR
New
VLR
1
4
2
TMSI
TMSI
MSs IMSI
new TMSI
IMSI
30
Periodically Registration
The MS periodically send registration
messages to the network.
The period is 6 minutes to 24 hours.
Periodic registration is useful for fault-tolerance
purposes. purposes.
31
Location Update Concept
Registration: the location update procedure
initiated by the MS:
Step 1. BS periodically broadcasts the LA
address.
Step 2. When an MS finds the LA of BS
different from the one stored in it memory, it
sends a registration message to the network.
Step 3. The location information is update.
32
GSM Basic Location Update
Procedure
In GSM, registration or location update occurs
when an MS moves from one LA to another.
Three cases of location update:
Case 1. Inter-LA Movement Case 1. Inter-LA Movement
Case 2. Inter-MSC Movement
Case 3. Inter-VLR Movement
33
Two LAs belong to the same MSC.
Four major steps:
Step 1. MS sends a location update request
message (MSBTSMSC) .
Parameters included: Previous LA, previous MSC
Inter-LA Movement (1/2)
Parameters included: Previous LA, previous MSC
and previous VLR.
IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) is
used to identify MS.
However, the MS identifies itself by the Temporary
Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI).
TMSI is used to avoid sending the IMSI on the
radio path.
TMSI is temporary identity is allocated to an MS
by the VLR at inter-VLR registration.
34
The Process continues:
Step 2. The MSC forwards the location update
request to the VLR by a TCAP message,
MAP_UPDATE_LOCATION_AREA.
Parameter includes: Address of the MSC, TMSI,
previous Location Area Identification (LAI), target
Inter-LA Movement (2/2)
previous Location Area Identification (LAI), target
LAI, Other related information
Steps 3 and 4.
Part I. The VLR find that both LA1 and LA2 belong
to the same MSC.
Part II. The VLR updates the LAI field of the MS.
Part III. The VLR replies an ACK to the MS
through the MSC.
35
Inter-MSC Registration
36
The two LAs belong to different MSCs of the same
VLR.
The process is:
Steps 1 and 2. MS sends a location update request
Inter-MSC Movement (1/2)
Steps 1 and 2. MS sends a location update request
message (MSBTSMSC) .
Step 3.
Part I. VLR1 finds that the LA1 and LA2 belong to
MSC1 and MSC2, respectively. Two MSCs are
connected to VLR1.
Part II. VLR1 updates the LAI and MSC fields of MS.
Part III. The VLR1 derives the HLR address of the
MS from the MSs IMSI.
37
The process continues:
Step 3.
Part IV. The VLR1 sends the
MAP_UPDATE_LOCATION to the HLR.
Parameter includes: IMSI, target MSC Address,
Inter-MSC Movement (2/2)
Parameter includes: IMSI, target MSC Address,
VLR Address, other related information
Step 4. HLR updates the MSC number field of
the MS. An acknowledgement is sent to VLR1.
Steps 5 and 6. The acknowledgement is
forwarded to the MS.
38
Inter-VLR Registration Message
Flow
39
Two LAs belong to MSCs connected to different
VLRs.
The process is:
Step 1. MS sends a location update request.
MSC2 sends MAP_UPDATE_LOCATION_AREA
Inter-VLR Movement (1/2)
MSC2 sends MAP_UPDATE_LOCATION_AREA
to VLR 2 with MSs TMSI.
Steps 2 and 3.
VLR2 does not have the record of MS.
VLR2 identifies the address the VLR1 and sends
MAP_SEND_IDENTIFICATION (with TMSI) to
VLR1.
VLR1 sends IMSI to VLR2.
40
The process continues:
Steps 4 and 5.
VLR2 creates a VLR record for the MS.
VLR2 sends a registration message to HLR.
HLR updates the record of the MS.
HLR sends an acknowledge back to VLR2.
Inter-VLR Movement (2/2)
HLR sends an acknowledge back to VLR2.
Step 6.
VLR2 generates a new TMSI and sends it to the
MS.
Steps 7 and 8.
The obsolete record of the MS in VLR1 is deleted.
41
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS)
A packet-switched protocol
GPRS radio link protocol
To guarantee fast call setup procedure and low-
bit error rate for data transfer between the MSs
GPRS
bit error rate for data transfer between the MSs
and the BSs
A new infrastructure is introduced to GPRS for
the packet services.
42
GPRS Architecture
MS
TAF
TE
MSC
PSTN
PSDN
ISDN
r adi o
i nt er f ace
SGSN GGSN
HLR
Signaling link
HLR : Home Location Register
VLR : Visitor Location Register
BSS : Base Station Subsystem
TAF : Terminal Adaption Function
TE : Terminal Equipment
BSS
PSTN : Public Switched Telephone Network
PSDN : Public Switched Data Network
MSC : Mobile Switching Center
SGSN : Serving GPRS Support Node
GGSN : Gateway GPRS Support Node
43
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mobility Management, Call Routing & SecurityDokument49 SeitenMobility Management, Call Routing & SecurityIslam BarakatNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriDokument137 SeitenGSM KT Session - MTN Iran PRS: Created By: Majid NaseriSaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-1 GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Dokument43 SeitenUnit-1 GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Gaha KuchrooNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Architecture: Gopal ReddyDokument36 SeitenGSM Architecture: Gopal ReddyRohan ChoudhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ArchitectureDokument36 SeitenGSM ArchitectureKashif AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Architecture: Alttc, GZBDokument45 SeitenGSM Architecture: Alttc, GZBSuresh MohapatraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM SystraDokument67 SeitenGSM SystraHi_Lev100% (1)
- GSM Mobility ManagementDokument35 SeitenGSM Mobility Managementgomzy_4560% (1)
- Lec 3 & 4 GSMNetArchitecture (Revised)Dokument63 SeitenLec 3 & 4 GSMNetArchitecture (Revised)Duy LeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)Dokument19 SeitenGSM Architecture: Switching System (SS) Base Station System (BSS) Operation and Support System (OSS)aimslifeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Priyanka Zep Infratech, Indore: Presented byDokument14 SeitenPriyanka Zep Infratech, Indore: Presented bypriyanka_741987Noch keine Bewertungen
- Protocals: Um InterfaceDokument7 SeitenProtocals: Um InterfaceRajashekar BhimanathiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- MOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICDokument89 SeitenMOBILINK - Trainnig Workshop For Optimization GSM BASICAli MurtazaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Mob MGMTDokument34 SeitenGSM Mob MGMTpratitkhareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless Cellular CommunicationDokument96 SeitenWireless Cellular CommunicationArjun P MNoch keine Bewertungen
- GB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-40Dokument40 SeitenGB Bt01 E1 1 GSM Basics-40Didier TangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliDokument66 SeitenGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM) : Asad AliMuhammadwaqasnaseemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gbo 001 E1 1 GSM Basic-40Dokument40 SeitenGbo 001 E1 1 GSM Basic-40Clive MangwiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM OverviewDokument81 SeitenGSM OverviewImran Khan100% (1)
- GSM System Introduction 1Dokument0 SeitenGSM System Introduction 1Shami TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ArchitectureDokument11 SeitenGSM ArchitectureHemangi Priya Devi DasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Architecture and InterfacesDokument25 SeitenGSM Architecture and InterfacesTelebeansNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Call FlowsDokument40 SeitenGSM Call FlowsNitin Jain100% (9)
- Basic Knowledge For CDMA SystemDokument42 SeitenBasic Knowledge For CDMA SystemSanjay GiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ArchitectureDokument18 SeitenGSM Architecture34Shreya ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For Mobile Communication: by Charu Mathur 090320Dokument25 SeitenGlobal System For Mobile Communication: by Charu Mathur 090320Charu MathurNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM and SS7 Overview: by Firoz AhmedDokument36 SeitenGSM and SS7 Overview: by Firoz AhmedAhmed FerozeNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Signaling and Protocols ArchitectureDokument180 SeitenGSM Signaling and Protocols ArchitectureMohammed Sa'dNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Network ArchitectureDokument72 SeitenGSM Network ArchitectureAkash Kumar100% (1)
- Wireless Network Security Issues and EvolutionDokument49 SeitenWireless Network Security Issues and EvolutionHaresh VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presented by Meenu Singh Supervised by Mr. Sunny Bhushan: Presentation On GSM NetworkDokument33 SeitenPresented by Meenu Singh Supervised by Mr. Sunny Bhushan: Presentation On GSM NetworkMeenu SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wireless WANs, GSM and Wi - MAXDokument18 SeitenWireless WANs, GSM and Wi - MAXNewNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM ArchitectureDokument8 SeitenGSM ArchitectureAbhishek PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Communication SystemsDokument136 SeitenMobile Communication SystemsJoseph JeremyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter VLR, MSCDokument17 SeitenInter VLR, MSCThanosNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM IntroductionDokument50 SeitenGSM IntroductionKausik RaychaudhuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Network Architecture ExplainedDokument14 SeitenGSM Network Architecture ExplainedNewNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM - An overview of the Global System for Mobile CommunicationsDokument44 SeitenGSM - An overview of the Global System for Mobile Communicationsvenkanna.rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Architecture: Project ReportDokument40 SeitenGSM Architecture: Project ReportaadafullNoch keine Bewertungen
- DT DocumentsDokument10 SeitenDT DocumentsSobaan ArshadNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM System Architecture: Mobile-Services Switching CenterDokument20 SeitenGSM System Architecture: Mobile-Services Switching Centerpg5555Noch keine Bewertungen
- The GSM Technology: Global System For Mobile CommunicationDokument31 SeitenThe GSM Technology: Global System For Mobile Communicationdips04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Interview Preparation - GSM Network Components & FunctionsDokument15 SeitenInterview Preparation - GSM Network Components & FunctionsAashish VigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument24 SeitenModule 2shreya harishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prepared By: Rady AbdelwahedDokument168 SeitenPrepared By: Rady AbdelwahedAmr Sunhawy50% (2)
- GSMDokument130 SeitenGSMhelpbgpNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSMDokument33 SeitenGSMHemangi Priya Devi DasiNoch keine Bewertungen
- GSM and Mobile Communication StandardsDokument33 SeitenGSM and Mobile Communication Standardsਗੁਰਪਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੂਰਾਪੁਰੀNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2G Network: Elecom EtworkDokument13 Seiten2G Network: Elecom Etworkpg5555Noch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Technology ExplainedDokument31 SeitenGSM Technology ExplainedMali198150% (2)
- GSM and SS7 OverviewDokument16 SeitenGSM and SS7 Overviewnkverma53Noch keine Bewertungen
- GSM Architecture FreeDokument20 SeitenGSM Architecture FreeTDMA2009Noch keine Bewertungen
- Présentation Sur GSMDokument60 SeitenPrésentation Sur GSMSarahHattanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Global System For Mobile Communication Technology PDFDokument41 SeitenGlobal System For Mobile Communication Technology PDFmalli gaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandVon EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNoch keine Bewertungen
- Communication Systems for the Mobile Information SocietyVon EverandCommunication Systems for the Mobile Information SocietyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationVon EverandMobile Network Optimization: A Guide for 2G and 3G Mobile Network OptimizationBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (3)
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update August 2020Dokument21 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update August 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update September 2020Dokument30 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update September 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update October 2020Dokument15 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update October 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update January 2020Dokument18 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update January 2020henry457Noch keine Bewertungen
- Actix Spotlight Desktop User GuideDokument263 SeitenActix Spotlight Desktop User GuidejedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update July 2020Dokument19 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update July 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update December 2020Dokument15 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update December 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update March 2020Dokument14 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update March 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReleaseNotes AnalyzerUpdate 2021 01 JanuaryDokument17 SeitenReleaseNotes AnalyzerUpdate 2021 01 JanuaryjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update November 2020Dokument26 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update November 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update February 2020Dokument15 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update February 2020henry457Noch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update April 2020Dokument25 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update April 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actix Diagnostic LogDokument4 SeitenActix Diagnostic LogjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actix Analyzer Getting Started GuideDokument72 SeitenActix Analyzer Getting Started GuidejedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Release Notes: Analyzer Update May 2020Dokument21 SeitenRelease Notes: Analyzer Update May 2020jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Report - Query - Result - 20200217143955468Dokument60 SeitenTraffic Report - Query - Result - 20200217143955468jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Actix Software Installation GuideDokument30 SeitenActix Software Installation GuidejedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atx InstDokument1 SeiteAtx InstjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurDokument30 Seiten3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurFaisal MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umts 850 L1Dokument15 SeitenUmts 850 L1jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Attach Data Server Connection: LTE ReportDokument3 SeitenAttach Data Server Connection: LTE ReportjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Umts 850 L2Dokument15 SeitenUmts 850 L2jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- License AgreementDokument1 SeiteLicense AgreementjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurDokument30 Seiten3G Wcdma: Aditya K. Jagannatham Indian Institute of Technology KanpurFaisal MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- PWM Solar Charge Contrller: RTC SeriesDokument1 SeitePWM Solar Charge Contrller: RTC SeriesjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result CarrierAggregatin 20200222 190657774Dokument279 SeitenResult CarrierAggregatin 20200222 190657774jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- EGS License Agreement 2012Dokument3 SeitenEGS License Agreement 2012jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Result CarrierAggregatin 20200222 190657774Dokument279 SeitenResult CarrierAggregatin 20200222 190657774jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Traffic Report - Query - Result - 20200217143955468Dokument60 SeitenTraffic Report - Query - Result - 20200217143955468jedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- Paper Final VersionDokument6 SeitenPaper Final VersionjedossousNoch keine Bewertungen
- BLDG TECH Juson Assignment Lecture 1Dokument23 SeitenBLDG TECH Juson Assignment Lecture 1Ma. Janelle GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gabi InfoDokument21 SeitenGabi Infoangel antoinette dagoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Predict CambodianDokument11 SeitenPredict CambodianMd Ibrahim KhalilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Servo LubesDokument2 SeitenServo LubesVignesh VickyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro810 Allen Bradley User ManualDokument120 SeitenMicro810 Allen Bradley User ManualStefano MontiNoch keine Bewertungen
- VPN Risk Report Cybersecurity InsidersDokument20 SeitenVPN Risk Report Cybersecurity InsidersMaria PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SheeshDokument31 SeitenSheeshfrancisco bonaNoch keine Bewertungen
- WBLFFDokument10 SeitenWBLFFMohd IzatNoch keine Bewertungen
- March 17, 2017 - Letter From Dave Brown and Megan McCarrin Re "Take Article Down" - IRISH ASSHOLES TODAY!Dokument459 SeitenMarch 17, 2017 - Letter From Dave Brown and Megan McCarrin Re "Take Article Down" - IRISH ASSHOLES TODAY!Stan J. CaterboneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examen 03 Aula - F PostgradoDokument5 SeitenExamen 03 Aula - F PostgradodiegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicroProcessadores ZelenovskyDokument186 SeitenMicroProcessadores ZelenovskyDavid SantosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Automotive Relay PDFDokument3 SeitenAutomotive Relay PDFSimon MclennanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The NF and BNF Charts from the Trading RoomDokument23 SeitenThe NF and BNF Charts from the Trading RoomSinghRaviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Sheet: Series CW SeriesDokument2 SeitenApplication Sheet: Series CW SerieskamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 FP Client AssessmentDokument54 SeitenModule 3 FP Client AssessmentJhunna TalanganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Return On Marketing InvestmentDokument16 SeitenReturn On Marketing Investmentraj_thanviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sales TAX FORMATDokument6 SeitenSales TAX FORMATMuhammad HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dof Omm Ss Skirting Sk-02Dokument8 SeitenDof Omm Ss Skirting Sk-02Ideal DesignerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Saturn Engine Compression Test GuideDokument7 SeitenSaturn Engine Compression Test GuideManuel IzquierdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2018: Internal Auditing: Theory & PrinciplesDokument39 SeitenTutorial Letter 101/3/2018: Internal Auditing: Theory & PrinciplesSAMANTHANoch keine Bewertungen
- Attaei PDFDokument83 SeitenAttaei PDFHandsomē KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample COBOL ProgramsDokument35 SeitenSample COBOL Programsrahul tejNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newman News January 2017 EditionDokument12 SeitenNewman News January 2017 EditionSonya MathesonNoch keine Bewertungen
- The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative DentistryDokument7 SeitenThe International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative DentistrytaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Derivatives and Foreign Currency: Concepts and Common TransactionsDokument28 SeitenDerivatives and Foreign Currency: Concepts and Common TransactionsElle PaizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Msme'S Premium Product Catalogue Book 2020: Craft CategoryDokument50 SeitenMsme'S Premium Product Catalogue Book 2020: Craft CategoryTomikoVanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Samsung Investor Presentation CE 2022 v1Dokument22 SeitenSamsung Investor Presentation CE 2022 v1Sagar chNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Servers ExplainedDokument15 SeitenWeb Servers ExplainedIman AJNoch keine Bewertungen
- Procurement of Railway Infrastructure Projects - ADokument15 SeitenProcurement of Railway Infrastructure Projects - ADan NanyumbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Main Purpose of Financial Planning AnDokument2 SeitenWhat Are The Main Purpose of Financial Planning AnHenry L BanaagNoch keine Bewertungen