Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Mycology
Hochgeladen von
ibti100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
164 Ansichten9 SeitenMedically important Fungi, AUA class notes Micro
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMedically important Fungi, AUA class notes Micro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
164 Ansichten9 SeitenMycology
Hochgeladen von
ibtiMedically important Fungi, AUA class notes Micro
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 9
Mycology Fungi
- Eukaryotic may be unicellular, multicellular, branching filaments
o Cell wall: Chitin/mannan/glucan
o Cell membranes: Sterol ergosterol
- Reproduce: asexually through spores and buds
- Infect Immunocompromised people
1. Yeast (Cryptococcus & Candida)
- Unicellular, reproduce by budding
o Buds (blastoconidia) elongate to form Pseudohyphae (Hyphae with constrictions at
each septum
o Hyphae: multicellular, filamentous cellular units of molds and mushrooms
aseptate no cross walls, irregular width and branching patterns
sepatate cross walls with regular width and branching pattern
Mycelium Branched, MULTIcellular mass of hyphae
- Reproduction: Asexual spores = conidia and sporangiospores
o Macroconidia & Microconidia
o Arthropsores: Arthroconidia (rectangular) - Coccidioides immitis
o Chlamydospores: round thick walled spores (Candida albicans)
o Blastospores: UNDETACHED buds of yeast (Pseudohyphae Candida )
o Sporangiospores: (produced internally sporangium)
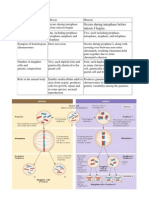
- Fungal dimorphism
o Exist as hyphal or yeasts (temperature depedent COLD=MOLD)
o Sporothrix schenkii
o Histoplasma capsulatum
o Blastomyces dermatidis
o Coccidioides immitis
o Paracoccidioides brazilliensis
- Pathogenesis
o Endogenous or acquired from environment
o Colonization pathogenic (when immunocompromised)
o Inhalation/inoculation of environmental conidia accidentally
Immunocompromised individuals at risk
o Adherence: Mannoproteins bind fibronectin
o Invasion: enzymes & temperature
Protease & elastase
o Injury: Mycotoxins (fungal toxin) & Delayed Hypersensitivity
- Immunity
o Host resistance: epithelial turnover, fatty acid content, ph of skin, normal flora, cilia &
macrophages
o Professional macrophages (neutrophils, macrophages, dendritic cells)
o Complement system (MBL, alternative)
o Risk factors: Neutropenia, depressed TH1 response, disruption of normal flora,
disruption of physical/chemical/physiological barriers
o Yeast killed by neutrophils (lysosomal enzymes)
Resist killing by inhibiting oxidative killing or phagosome- lysosomal fusion
- Adaptive immunity
o T-cell mediated responses (CMI)
T helper/killer
o Activation of macrophages (cytokines)
o Host response granuloma
o Activation of T-cell mediated immune results in delayed type hypersensitivity to fungal
antigens
o Opsonizing antibodies (anticapsular) yeast infections (encapsulated yeast
Cryptococcus neoformans, Candida albicans
Antifungal Agents
- Most infections are self-limiting exceptions; systemic mycoses
- Cytoplasmic membrane
o Polyenes bind ergosterol fight systemic & opportunistic mycoses
Amphotericin B - IV
Nystatin Thrush
o AZOLE derivatives Inhibit ergosterol synthesis (bind P450 enzymes) Systemic &
Opportunistic mycoses
Miconazole (topical), Ketoconazole etc.
o Allylamines inhibit ergosterol synthesis (squalene epoxidase) Systemic/topical
for Dermatophytes
Terbinafine
Naftifine topical
- Nucleic acid synthesis
o Nucleoside analog inhibits DNA & RNA synthesis Cryptococcus
o Flucytosine fluorouracil acts as an antimetabolite Candida
- Cell wall synthesis
o Echinocandins inhibits glucan synthesis Candida & Aspergillus
Caspofungin & Micafungin
- Others
o Grisans inhibits fungal mitosis (microtubules) Cutaneous mycoses (who dont
respond to topical antifungals)
Deposition in nails
Griseofluvin
o Potassium iodide therapeutic sporotrichosis
Mycoses Fungal infections
- Superficial: keratinised outermost layers of the skin hair and nails
- Cutaneous: keratinised layer of epidermis & deeper layers of skin, hair and nails
- Subcutaneous: dermis, subcutaneous tissues, muscles and fascia
- Systemic: disseminated infections
- Opportunistic: immunocompromised patients (chemotheraphy & HIV)
Superficial Mycoses
- NO IMMUNE RESPONSE
- Pityriasis versicolor
o Infective agent: Malassezia furfur (liophilic yeast)
o Systemic disease: associated with intralipid therapy (near sebaceous glands)
o Normal flora at risk patients (AIDS & transplant patients)
o Effects dry, scaly, pigmented lesions on torso arms & abdomen (Tinea Versicolor)
o Microscopic appearance Spaghetti & meat balls
o Treat with topical miconazole or selenium sulfide
Cutaneous Mycoses
- Elicit cellular immune response causing inflamed outward spreading lesions
- Dermatomycoses (Candida infections)
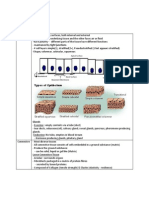
- Dermatophytoses dermatophytes
o Fungi infecting skin/nails/hair (ring worm or Tinea)
o Trichophyton hair, skin & nails
o Microsporum skin & hair
o Epidermophyton skin & nails
o Favic chandelier like fungus morphology
o Clinical clues macular lesion w scaly margin, circular patches on skin, patches of
alopecia, discoloured and brittle nails
o Human Human transfer via shed hyphae into breaks in skin
Through sharing clothes/towels/hair brushes etc (gym showers)
Animals and soil (geophilic)
Highly inflammatory Zoophilic
Little inflammation anthropophilic (human transfer)
a. Tinea capitis T. tonsurans & zoophilic species
i. Ring like erythematous lesion on scalp (alopecia)
b. Tinea barbae Zoophilic species & inflammatory
i. Vesiculopustular eruptions with alopecia in the beard/mustache area
c. Tinea pedis athletes foot
i. Itchy peeling erythematous lesions between toes/soles & feet
d. Tinea corporis - glabrous skin (non-keratinized skin)
e. Tinea cruris jock itch
i. T. rubrum/ E. floccosum erythematous lesion in the groin area
f. Onychomycoses; Tinea unguium
i. T. rubrum thickened friable & discoloured nails + subungual debris
accumulation (proximal in AIDS/distal in rest)
- Pathogenesis & Virulence factors
o Skin lesions in contact with shed hyphae from an infected person
o Keratophillic infections skin, nails & hair
o Secrete Kertinase digests keratin
o People with defects in Cell Mediated immunity at risk for chronic/disseminated
dermatophyte infections
- Microscopy KOH dissolves keratin while leaving the fungus untouched
o Sepatate hyphae seen from scrapings
o Microsporum can be seen fluorescence under woods light
o Culture Saburauds agar shows moldy growth
o Microscopic Microsporum (spindle shaped) Trichophyton rubrum (tear drop shape)
Epidermophyton (paddle shaped)
- Treatment: topical azoles (miconazole)
o Oral fluconazole/terbinafine
Subcutaneous Mycoses
- Melanin containing dematacious fungi present in soil and decaying vegetation
- Entry inoculation/breaks in skin (cuts/stabs/contaminated thorn) NO HUMAN to HUMAN
transmission
- Infections limited to subcutaneous tissues, lymphatic vessels & contiguous tissues
- Sporotrichosis (Rose Gardners disease)
o Dimorphic (cigar yeast at 37 & rosette mold at 25) Sporothrix schenkii
o Clinically manifestation nodules, ulcers at the site of inoculation and draining
lymphatic chain
o Lesions can appear weeks to months after inoculation
Enlargement of papule ulceration open sore
o Draining lymph nodes thicken + nodular
Pustular nodules develop along the draining lymphatic route
o Melanin inhibits neutrophils ** inoculation through rose thorns & sphagnum moss
o Treat with Potassium Iodide (orally)/Itraconazole or Amphotericin B
Geographic Mycoses
1. Endemic diseases dimorphic & transmitted by inhalation of spores that germinate in lungs
2. Important systemic mycoses
a. Histoplasmosis - Mississippi river valley (MI& OH)
i. Bat feces, soil contaminated with bird droppings
ii. Yeast in macrophages
b. Blastomycosis North/Central & Southeastern US
i. Decaying vegetation, soil contaminated with beaver excretions
ii. Yeast in tissues (broad based buds)
c. Coccidiodomycosis Southwestern United States (California/Arizona/NM)
i. Desert sand
d. Paracoccidioidomycosis
3. Present as minor & self-limiting pulmonary infections in healthy individuals while as severe
pulmonary complications leading to granulomas in immunocompromised individuals
4. Histoplasmosis
a. Dimorphic yeast in macrophages endemic to the Mississippi valley (MI&OH)
b. Present in Bat feces & soil contaminated with bird droppings
c. Asymptomatic in healthy individuals with Chronic pulmonary disease (pneumonia) in
immunocompromised
d. Inhalation of aerosolised molds (macroconidia) conversion into yeast in alveolar
macrophages multiplication and formation of granuloma
e. Survive phago-lysosome by increasing pH dissemination of RES
f. Continued growth calcified nodes (can be activated later when
immunocompromised)
g. Formation of a granuloma APC presents fungi to CD4+ cell TNF activates monocytes
to macrophages secretion of IFN-gamma (CD4+) causes monocyte differentiation and
formation of a giant cell granuloma
h. Manifestation
i. Asymptomatic to self-limiting fever/cough healthy adults
ii. Chronic secondary infections fever/cough for weeks, chills, malaise &
residual nodule **resembles TB
iii. Immunocompromised patients dermatosis (painless ulcers) on mucous
membranes hepatospleenomegaly
iv. CXR hilar/mediastinal lymphadenopathy
i. Lab id
i. Microscopic examination of specimen (sputum/bone marrow/LN biopsy)
ii. Look for; yeast within macrophages, dimorphism (culture), antibodies by
immunodiffusion/complement fixation, ELISA & DNA hybirdization
j. Treat with Itraconazole
5. Blastomycosis Blastomyces dermatitidis
a. Yeast phase in tissues extracellular in tissues
b. Symptomatic in 50% of infected individuals
i. Chest pain, sputum production & fever
ii. Can mimic TB or lung cancer
iii. Dissemination lesion on exposed skin/bone/Gentiourinary system/Prostate &
CNS
c. Lab id: microscopy of specimen (demonstrate Broad Based Budding yeast) in KOH
d. Treat with Itraconazole & Amphotericin B
6. Coccidiomycosis coccidioides immitis
a. Large distinction spherule (tissues) inhalation of ARTHROSPORES (rectangular)
b. Growth in desert (sandy alkaline soil with high salinity)
c. Spores germinate in lungs
i. Spherules secrete protease
ii. 40% chance of pulmonary disease formation
iii. Valey fever, cough/chest pain other flu like symptoms
iv. CXR hilar adenopathy
v. Disseminated disease meningitis/arthritis/skin lesions (erythema nodosum)
**multiple organ involvement
d. Lab id
i. Microscopy of sputum Arthropsores
ii. Tissue by KOH spherules
iii. Eosinophilia present!
e. Treat with Itraconazole
7. Paracoccidioidomycosis paracoccididides brasiliensis
a. Chronic pneumonia (similar to histo & coccidioides)
b. Estrogen inhibits conversion of spores to yeast
c. Infection more common in males
d. Lab id Pilot wheel, yeast with multiple buds
Opportunistic mycoses
- Predisposing factors antimicrobial therapy, corticosteroid therapy, organ transplants,
chemotheraphy immunocompromised states***
- Candida albicans
o Oval, yeast like budding Pseudohyphae (elongated bud) - with constrictions (NO
parallel walls & septa)
o Normally colonizes mucous membranes of the GI tract increased growth during
suppression of immune system
o Pathogenesis phenotypic switching (yeast to hyphal)
Invade tissue with true hyphae; germ tube (Hwp1)
Adhesins able to bind human cells & ECM
Complement receptor like surface molecules resist phagocytosis
Secrete proteinases/Phospholipases digest epithelial cells/keratin/collagen
Form biofilms on plastics/medical devices (catheters &IV lines)
o Transmission endogenous & exogenous
Species Tropicalis/paralopsis/glabrata/krusei
o Manifestation
Mucocutaneous candidiasis (Thrush) creamy curd/ cottage cheese like patches
on the mucosa
Appears on tongue/palate & oesophagus vaginal thrush on mucosa (itching
and burning)
Newborn bottle fed infants & AIDS patients
Oesophagitis AIDS, prolonged antibiotic therapy
Vulvovaginal candidiasis yeast vaginitis (AIDS/diabetics/antibiotic therapy)
Cutaneous candidiasis rash around moist folds of skin
Chronic Mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMCC) skin and mucous membranes
(TH1 cell deficient)
UTI catheters
Disseminated candidiasis multi-organ involvement (immunocompromised
patients)
Candidemia (septicemia/fungemia)
Endocarditis IV drug abusers, indwelling catheters, prosthetic valves
o Diagnosis
Stain G+ oval budding cells PAS/ KOH/ Gomorri methanamine silver
Culture saburauds medium or smooth creamy pasty colonies
Conformation Germ tube test
o Treatment - -Azoles **Drug resistance seen with C.albicans
- Cryptococcus neoformans
o Monomorphic yeast GXM capsule
o Soil contaminated with bird droppings & vegetation (decaying)
o Transmitted through aerosolized yeast cells from environment soil and roosting sites
o At risk patients AIDS, organ transplant, corticosteroids and immunsupressed
o Diagnosis
negative staining (india ink demonstrate capsule)
Mucicarmine stain in tissues
o Pathogenesis
Virulence GXM capsule/ Melanin production inhibits oxidative killing/
Melanin/urease/laccase
Spread via blood able to cross BBB converts catecholamines to melanin
Neutrophilic and granulomatous response TH1 response to capsule (weak
antigen)
o Manifestation
Meningitis (most common cause of meningitis in AIDS pts)
Subacute to chronic, head ache that worsens over weeks, fever, irritability &
dizziness
Can also present as Pulmonary infection (pneumonia) mucoid suptum
Cutaneous skin and bone lesions in disseminated cryptococcocis
o Lab ID
Detect Cryptococcal antigen in CSF/sputum by LATEX AGGLUTINATION
Demonstrate capsule with India ink
Culture Saburauds for confirmation
o Treat with Oral fluconazole or Amph B/Flucytosin
- Aspergillus species
o Morphology form mycelium (spetae hyphae) dichotomous growth
Airborne spores (conidia) inhalation
Fluffly, pigmented growth on agar
o Pathogenesis
Invasive filamentous hyphae germinate in lung alveoli & invade lung tissues
blood vessels
Secrete proteases, phospholipases, & elastases
Impaired cell mediated immunity due to underlying cause corticosteroid
therapy, cytotoxic drug therapy, neutropenia & immunocompromised diseases
Pulmonary macrophages first line defense against conidia
Hyphae are killed by neutrophils (secrete reactive oxygen intermediates kill
the organism)
Angioinvasive fungus tissue infarction, hemorrhages and necrosis
o Manifestation
Allergic reaction (Farmers lung) allergies or invasive infections
Nasal obstruction/facial pain
Allergic Broncho-pulmonary aspergilliosis
Aspergilloma colonization of preformed pulmonary cavities and paranasal
cavities with fungal balls, no invasion. Recurrent hemoptysis.
Invasive pulmonary aspergilliosis similar to pre-existing pulmonary disease like
TB, with dissemination to other organs in patients with haematological
malignancies, and immunosuppressive states
o LAB ID
Aspergillus antigen detection (galactomannan) by ELISA for invasive infection
Tissue biopsy, lung aspiration and bronchi-alveolar lavage demonstrations
of spetate, dichotomous hyphae by PAS/GMS
Culture for confirmation
Fungal DNA by PCR
o Treat with Itraconazole Amp B
- Zygoycetes (Zygomycosis/Mucormycosis/Phycomycosis)
o Rhizopus, Mucor and Absidia nonseptate filamentous fungi
o Airborne spores found in environment (soil/strawberries/moist bread)
o Tissue ribbon like non septate hyphae with branches
o Manifestation
Rhinocerebral zygomycosis head ache, paranasal swelling, mental lethargy,
blood tinged exudate, orbital cellulitis, cranial nerve palsy
Seen in pts with diabetic ketoacidosis, haematological malignancies
Penetrate mucosa of the nose/paranasal sinus spread to orbit, hard palate =
form ulcerative lesions
Progress through tissue, nerves, blood vessels, facial planes to the base of the
brain
o Lab Id
KOH with calcofluor white stain (necrotic tissue), H&E, GMS (biopsy)
Broad, ribbon like, non septate hyphae (branching)
o Treat debridement of necrotic tissue
Aggressive treatment with amph B
CONTROL DIABETES
- Pneumocystis jiroveci cyst/hat shaped
o Interstitial pneumonia in immunocompromised persons (AIDS) host with T
lymphocyte deficiency & CD4+ count <200 cells/mm
o Obligate extracellular fungal pathogen of humans
o Grows over surfactant layer of alveolar epithelium
o Cytoplasmic membrane ergosterol
o Pathogenesis
Primarily in AIDS patients severely malnourished premature infants
Kills type 1 pneumocystes excess replication of type II
MSG (major surface glycoprotein) helps attach to host fibronectin surfactant
Inflammation of alveoli, decreased gas exchange (exudate),
o Manifestation
Pneumocystis pneumonia interstitial pneumonia
Non-productive cough, fever, progressive dysnea, tachypnea, cyanosis, hypoxia
CXR diffuse interstitial infiltrates spread out from hilum
Radiographs ground glass appearance
o Lab Id
Cant be cultured diagnose based on microscopic examination
Lung tissue biopsy or bronchial washings (BAL)
Stains
H&E - Foamy, honey comb appearance
GMS silver stained cysts in center spaces
Toluidine blue O stain
Giemsa stain, calcofluor stain, fluorescent antibody stain, PCR
o Treat trimethoprim & sulfamethoxazole, pentamidine
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Medically Important FungihandoutDokument55 SeitenMedically Important FungihandoutHervis FantiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical MycologyDokument14 SeitenMedical Mycologyhawkar omerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cutaneous Mycoses GuideDokument55 SeitenCutaneous Mycoses GuideAlpana Laisom100% (2)
- Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisVon EverandPathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention of LeishmaniasisMukesh SamantNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycology NotesDokument9 SeitenMycology NotesIya Corpus100% (1)
- Exercise 11 - Microscopic Morphology of Fungal CultureDokument82 SeitenExercise 11 - Microscopic Morphology of Fungal CultureChristine Nazareno100% (8)
- Forensic MicrobiologyVon EverandForensic MicrobiologyDavid O. CarterNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Diverse Faces of Bacillus CereusVon EverandThe Diverse Faces of Bacillus CereusVincenzo SaviniNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Mycology 2006-07Dokument47 SeitenGeneral Mycology 2006-07api-3699361100% (5)
- Proceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964Von EverandProceedings of the First International Congress of Parasitology: Roma, 21-26 September 1964Augusto CorradettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Medical MycologyDokument25 SeitenIntroduction To Medical MycologyMohamed100% (4)
- Pathology, Vector Studies, and CultureVon EverandPathology, Vector Studies, and CultureJulius P. KreierBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Organization and Practice in Tuberculosis BacteriologyVon EverandOrganization and Practice in Tuberculosis BacteriologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic Bacteriology: Clinical and Laboratory PracticeVon EverandAnaerobic Bacteriology: Clinical and Laboratory PracticeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycobacteria: Institute of Medical Laboratory Sciences MonographsVon EverandMycobacteria: Institute of Medical Laboratory Sciences MonographsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycoses: Mallare - Morales - QuibalDokument67 SeitenMycoses: Mallare - Morales - QuibalBianca MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nanomycotoxicology: Treating Mycotoxins in the Nano WayVon EverandNanomycotoxicology: Treating Mycotoxins in the Nano WayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MycologyDokument129 SeitenMycologyPriyanka Rajput100% (4)
- Parasitology - Lec - FinalDokument69 SeitenParasitology - Lec - FinalJannah Monaliza BambaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mycology Lab1tableDokument6 SeitenMycology Lab1tableapi-3700579100% (1)
- Deepshikha Chhetri Msc. FSNDokument50 SeitenDeepshikha Chhetri Msc. FSNDaiane SantanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology Slides MediaDokument34 SeitenMicrobiology Slides MediaTarek ElnagdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cytology and Cell PhysiologyVon EverandCytology and Cell PhysiologyGeoffrey BourneNoch keine Bewertungen
- SaprophytesDokument40 SeitenSaprophytesRami Aldalistar100% (1)
- Pathogenesis of Viral InfectionsDokument13 SeitenPathogenesis of Viral InfectionsCitoy BastianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anaerobic Bacteria: Dept. of Microbiology Medical Faculty, Padjadjaran UniversityDokument52 SeitenAnaerobic Bacteria: Dept. of Microbiology Medical Faculty, Padjadjaran UniversitySabrina Indri WardaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical MycologyDokument1 SeiteMedical MycologyHairul AnuarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Taxonomic Guide to Infectious Diseases: Understanding the Biologic Classes of Pathogenic OrganismsVon EverandTaxonomic Guide to Infectious Diseases: Understanding the Biologic Classes of Pathogenic OrganismsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Bacterial ClassificationDokument7 SeitenBacterial ClassificationAsimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Campylobacter: Features, Detection, and Prevention of Foodborne DiseaseVon EverandCampylobacter: Features, Detection, and Prevention of Foodborne DiseaseGünter KleinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesVon EverandPractical Manual for Detection of Parasites in Feces, Blood and Urine SamplesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Malaria: Immunology and ImmunizationVon EverandMalaria: Immunology and ImmunizationJulius P. KreierNoch keine Bewertungen
- MycologyDokument68 SeitenMycologyaalipuriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laboratory Handbook of Medical MycologyVon EverandLaboratory Handbook of Medical MycologyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Developing Costimulatory Molecules for Immunotherapy of DiseasesVon EverandDeveloping Costimulatory Molecules for Immunotherapy of DiseasesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation and Identification of FungiDokument9 SeitenIsolation and Identification of FungiSuseela SudhakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- MYCOLOGY PAST UHS SEQS SOLVEDDokument4 SeitenMYCOLOGY PAST UHS SEQS SOLVEDFiaz medicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MycologyDokument66 SeitenIntroduction To MycologyHerlinaNababanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Medical Parasitology Prepared By: Geraldine P. PulidoDokument26 SeitenIntroduction To Medical Parasitology Prepared By: Geraldine P. PulidoMark Reynie Renz SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rickettsia Coxiella: Prof. Khalifa Sifaw GhengheshDokument20 SeitenRickettsia Coxiella: Prof. Khalifa Sifaw GhengheshKhalifa Sifaw GhengheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Representative Questions on Fungal Lectures and LabsDokument8 SeitenRepresentative Questions on Fungal Lectures and LabsYousefM.R.AlmassriNoch keine Bewertungen
- (OS 217 - IDS) LEC 04 Diagnostic MycologyDokument6 Seiten(OS 217 - IDS) LEC 04 Diagnostic MycologyErtyWitalayaL.ToruanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Protozoology and Parasitology Key ConceptsDokument60 SeitenApplied Protozoology and Parasitology Key ConceptsIL Mago50% (2)
- General MycologyDokument28 SeitenGeneral MycologyShimelis Teshome AyalnehNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology textbook and reference guide comparisonDokument2 SeitenMicrobiology textbook and reference guide comparisonIbrahimFikryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pseudomonas BasicsDokument32 SeitenPseudomonas Basicstummalapalli venkateswara raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Mycology BasicsDokument46 SeitenMedical Mycology Basicstummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Mycotic InfectionDokument22 SeitenMycotic InfectionDevanshi Kulkarni100% (1)
- Mycology Lab1Dokument4 SeitenMycology Lab1api-3700579100% (5)
- Gram Positive BacilliDokument6 SeitenGram Positive BacilliSteve ShirmpNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification, General Characteristics of Parasites and Medically Important ParasitesDokument30 SeitenClassification, General Characteristics of Parasites and Medically Important ParasitesSteph AsideNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Medically Important MycosesDokument8 SeitenThe Medically Important MycosesNatasha JeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mini 4 StuffDokument26 SeitenMini 4 StuffibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sickle Cell PresentationDokument11 SeitenSickle Cell PresentationibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hibah's Notes - Exam 4Dokument31 SeitenHibah's Notes - Exam 4ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- End of Life Care - PresentationDokument5 SeitenEnd of Life Care - PresentationibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MitosisDokument1 SeiteMitosisibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 NotesDokument6 SeitenUnit 3 NotesibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MeiosisDokument2 SeitenMeiosisibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mendel's LawsDokument2 SeitenMendel's LawsibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Notes - Bio1Dokument6 SeitenUnit 3 Notes - Bio1ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SDokument1 SeiteSibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mitosis Vs MeiosisDokument2 SeitenMitosis Vs MeiosisibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Cell Is A Preface To The Procedure, Through More Mitotic DivisionsDokument2 SeitenThis Cell Is A Preface To The Procedure, Through More Mitotic DivisionsibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen 2Dokument9 SeitenGen 2ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- War Crimes PosterDokument1 SeiteWar Crimes PosteribtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Animal OrganizationDokument10 SeitenBasic Animal OrganizationibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trial - 2Dokument1 SeiteTrial - 2ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ProfitDokument1 SeiteProfitibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gen 1Dokument10 SeitenGen 1ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Free The Childrennew2Dokument9 SeitenFree The Childrennew2ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Phyics - ExperimentDokument1 SeitePhyics - ExperimentibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TrialDokument1 SeiteTrialibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Original & March Stock Values: Ibthaj KhiljiDokument4 SeitenOriginal & March Stock Values: Ibthaj KhiljiibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment Results: CentimetersDokument3 SeitenExperiment Results: CentimetersibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hate Crimes Against Hispanics in UDokument1 SeiteHate Crimes Against Hispanics in UibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Careers 12Dokument1 SeiteCareers 12ibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Swim MeetDokument2 SeitenSwim MeetibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Track ProgressDokument1 SeiteTrack ProgressibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- PayrollDokument1 SeitePayrollibtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Net ProviderDokument2 SeitenNet ProvideribtiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isolation of Microsporum Canis From The Hair Coat of Pet Dogs and Cats Belonging To Owners Diagnosed With M. Canis Tinea Corporis (Pages 327-331)Dokument5 SeitenIsolation of Microsporum Canis From The Hair Coat of Pet Dogs and Cats Belonging To Owners Diagnosed With M. Canis Tinea Corporis (Pages 327-331)jenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Articulo Cientifico Derivado Del FenilpropanoDokument23 SeitenArticulo Cientifico Derivado Del FenilpropanoKaren GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tinea Cruris Abq JournalDokument3 SeitenTinea Cruris Abq JournalGustiandari FidhyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tinea IncognitoDokument3 SeitenTinea IncognitoAan Sii DiademsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gupta Ak Et Al Fungal Skin Infections PDFDokument17 SeitenGupta Ak Et Al Fungal Skin Infections PDFValeria BeltranNoch keine Bewertungen
- ClinDermatolRev133-5811533 160835Dokument9 SeitenClinDermatolRev133-5811533 160835rehanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Palmoplantar Pustulosis. Power Point NewwwDokument17 SeitenPalmoplantar Pustulosis. Power Point NewwwIna TahirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Insights From Veterinary MedicineDokument290 SeitenInsights From Veterinary Medicinenorma paulina carcausto lipaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungal Nail Disease (Onychomycosis) Challenges and SolutionsDokument6 SeitenFungal Nail Disease (Onychomycosis) Challenges and SolutionsRatih Anindita Rahajeng RipyonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microbiology TablesDokument19 SeitenMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intertrigo and Secondary Skin InfectionsDokument5 SeitenIntertrigo and Secondary Skin Infectionskhalizamaulina100% (1)
- Topical Efinaconazole: A Sequential Combination Therapy With Oral Terbinafine For Refractory Tinea UnguiumDokument4 SeitenTopical Efinaconazole: A Sequential Combination Therapy With Oral Terbinafine For Refractory Tinea UnguiumMini LaksmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungal Infections of The Skin: Dr. M. DissanayakeDokument52 SeitenFungal Infections of The Skin: Dr. M. Dissanayakev_vijayakanth7656100% (1)
- Systemic Mycoses: Cold Mold Heat YeastDokument4 SeitenSystemic Mycoses: Cold Mold Heat YeastHanunNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER I and IIDokument9 SeitenCHAPTER I and IICharish MedidasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Superficial Mycoses: Paramasari D PHD Darukutni DRDokument50 SeitenSuperficial Mycoses: Paramasari D PHD Darukutni DRSheilla ElfiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Claw Diseases in Dogs and CatsDokument6 SeitenClaw Diseases in Dogs and CatsAndrea VargaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fungal Infections of The Skin: by Bekele T. (BSC, MSC) 1Dokument109 SeitenFungal Infections of The Skin: by Bekele T. (BSC, MSC) 1desuloveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tinea CorporisDokument7 SeitenTinea CorporisAziza Ulfie WijayaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of Antidermatophytic Activity of Piper Betle, Allamanda Cathertica and Their Combination: An in Vitro and in Vivo StudyDokument8 SeitenEvaluation of Antidermatophytic Activity of Piper Betle, Allamanda Cathertica and Their Combination: An in Vitro and in Vivo Studyfrez_kingdomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Atlas of Canine and Feline Dermatology (VetBooks - Ir)Dokument514 SeitenClinical Atlas of Canine and Feline Dermatology (VetBooks - Ir)Evelyn Louise C. M. BNoch keine Bewertungen
- General:: Previous Lecture Next LectureDokument12 SeitenGeneral:: Previous Lecture Next LectureKutaibaa AkraaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research ArticleDokument4 SeitenResearch ArticleBharathi RagavanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infestation: ScabiesDokument16 SeitenInfestation: ScabiesBrix ValdrizNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 - Tinea Corporis An Updated ReviewDokument12 Seiten2020 - Tinea Corporis An Updated ReviewYunita SariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 Comparative Study of 2% Sertaconazole Solution and Cream Formulation in Patients With Tinea Corporis...Dokument9 Seiten7 Comparative Study of 2% Sertaconazole Solution and Cream Formulation in Patients With Tinea Corporis...Gepe AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphology and Ultrastructure Aspects in Species Belongs To Trichophyton Genus Using Light and Scanning Electron Microscopy C. V. Mihali, A. Buruiana, Violeta Turcus, Aurelia Covaci, A. ArdeleanDokument6 SeitenMorphology and Ultrastructure Aspects in Species Belongs To Trichophyton Genus Using Light and Scanning Electron Microscopy C. V. Mihali, A. Buruiana, Violeta Turcus, Aurelia Covaci, A. ArdeleanMitha Dwi MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Mycology: Fungal Diseases and Cutaneous MycosesDokument54 SeitenMedical Mycology: Fungal Diseases and Cutaneous MycosessuwarnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itrafungol PrezentareDokument20 SeitenItrafungol PrezentaredCpoPPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical MycologyDokument94 SeitenMedical MycologyNozomiNoch keine Bewertungen