Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
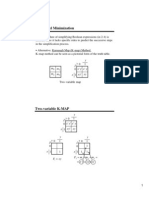
Kmap Logic Minimization Kmap Logic Minimization
Hochgeladen von
AshiqueHussain0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten27 Seitendigital system
Originaltitel
Lec06
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldendigital system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten27 SeitenKmap Logic Minimization Kmap Logic Minimization
Hochgeladen von
AshiqueHussaindigital system
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 27
CS221:DigitalDesign
KMapLogic Minimization KMap LogicMinimization
Dr.A.Sahu
Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. DeptofComp.Sc.&Engg.
IndianInstituteofTechnologyGuwahati
1
Outline Out e
SOP&POSImplementation
Boolean function: Representation Booleanfunction:Representation
SOM(SumofMinterms),Canonicalform
( ) SOP(SumofProduct)
Karnough mapsimplification
2,3,4variablekarnaugh map
Dontcarecondition
Algorithmforbettergrouping
Karnaugh map with >= 5 variable Karnaugh mapwith> 5variable
2
Implementation of SOP ImplementationofSOP
A SOP i
F(X,Y,Z) = XZ+YZ+XYZ
Any SOP expression can
be implemented using 2-
levelsof gates levels of gates
The 1
st
level consists of
ANDgates, andthe2
nd
AND gates, and the 2
level consists of a single
OR gate
Also called 2-level
Circuit
Implementation of POS ImplementationofPOS
F(X,Y,Z) = (X+Z)(Y+Z)(X+Y+Z)
Any POS expression can
be implemented using 2-
levelsof gates levels of gates
The 1
st
level consists of
OR gates andthe2
nd
OR gates, and the 2
level consists of a single
AND gate g
Also called 2-level
Circuit
I l t ti f SOP ImplementationofSOP
Consider F = AB + C(D+E)
This expression is NOT in the sum-of-products form
Use the identities/algebraic manipulation to convert to a
standardform(sumof products) asinF =AB +CD+CE standard form (sum of products), as in F = AB + CD + CE
Logic Diagrams:
A
F
D
C
B
F
C
B
A
E
C
E
D
3levelcircuit 2levelcircuit
Canonical Forms Canonical Forms
It is useful to specify Boolean s use u o spec y oo e
functions in a form that:
Allows comparison for equality Allows comparison for equality.
Has a correspondence to the truth tables
Canonical Forms in common usage:
Sumof Minterms (SOM) Sum of Minterms (SOM)
Product of Maxterms (POM)
Simplification: Theorem method Simplification:Theoremmethod
E = m(0,1,2,4,5)
+ + + + = m
0
+ m
1
+ m
2
+ m
4
+ m
5
= m
5
+ m
1
+ m
4
+ m
0
+ m
2
+ m
0
XYZ+XYZ+XYZ+XYZ+XYZ +XZY = XYZ+XYZ+XYZ+XYZ+XYZ +XZY
= (XY+XY)(Z+Z) + XYZ+ XZY
Y(X+X)(Z+Z) +XZ(Y+Y) = Y(X+X)(Z+Z) + XZ(Y+Y)
= Y + XZ
BothareinSOP
format:2level
Simplifiedone:Requireless
Gatesandfaster
2 Level 2Level
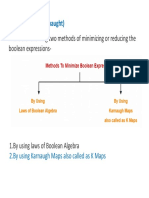
Simplification of Boolean Functions SimplificationofBooleanFunctions
An implementation of a Boolean Function AnimplementationofaBooleanFunction
requirestheuseoflogicgates.
A smaller number of gates with each gate Asmallernumberofgates,witheachgate
(otherthenInverter)havinglessnumberof
inputs may reduce the cost of the inputs,mayreducethecostofthe
implementation.
Th 2 h d f i lifi i f Thereare2methodsforsimplificationof
Booleanfunctions.
8
SimplificationofBooleanFunctions:
h d TwoMethods
Algebraic method by using Identities & Algebraicmethod byusingIdentities&
Theorem
Graphical method by using Karnaugh Map GraphicalmethodbyusingKarnaugh Map
method
TheKmapmethodiseasyandstraightforward. p y g
AKmapforafunctionofnvariablesconsistsof2
n
cells,and,
ineveryrowandcolumn,twoadjacentcells
shoulddifferinthevalueofonlyoneofthelogic
variables
9
variables.
Karnaugh Map Method Karnaugh MapMethod
A graphical method of simplifying logic Agraphicalmethodofsimplifyinglogic
equationsortruthtables.
Also called a K map AlsocalledaKmap
Theoreticallycanbeusedforanynumberof
i i bl b i ll li i d 5 6 inputvariables,butpracticallylimitedto5or6
variables.
Karnaugh Map Advantages Karnaugh MapAdvantages
Minimization can be done more Minimizationcanbedonemore
systematically
Muchsimplertofindminimumsolutions
Easiertoseewhatishappening(graphical)
Almostalwaysusedinsteadofboolean
minimization. minimization.
G C d GrayCodes
Graycodeisabinaryvalueencodinginwhich Gray code is a binary value encoding in which
adjacent values only differ by one bit
2bitGrayCode
00
01
11
10 10
TruthTableAdjacencies
These are adjacent in a gray code sense
A B F
0 0 1
- they differ by 1 bit
We can apply XY + XY = X
AB +AB =A(B+B) =A(1) =A
F=A
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 0
A B + A B A (B +B) A (1) A
1 1 0
A B F
0 0 0 Sameidea: AB +AB =B 0 0 0
0 1 1
1 0 0
1 1 1
F=B
Same idea: A B AB B
1 1 1
Key idea: Problem:
Physical adjacency in truth
Gray code adjacency allows use of
simplification theorems
y j y
table does not indicate gray
code adjacency
Karnaugh Map Method Karnaugh MapMethod
ThetruthtablevaluesareplacedintheK
map map.
AdjacentKmapsquaredifferinonlyone
variable both horizontally and vertically variablebothhorizontallyandvertically.
Thepatternfromtoptobottomandleftto
right must be in the form rightmustbeintheform
ASOPexpressioncanbeobtainedbyORing
all squares that contain a 1 allsquaresthatcontaina1.
AB,AB,AB,AB
00 01 11 01 00,01,11,01
Filling of Karnaugh Map FillingofKarnaugh Map
Whynot: AB,AB,AB,AB
00, 01, 10, 11 00,01,10,11
Onlytwoadjacentcanbegrouped
Group Reduce a variable: AB+AB=A(B+B)=A GroupReduceavariable:AB +AB=A(B +B)=A
AB AB AB AB AB,AB,AB,AB
00,01,11,01
All4Adjacentcanbegrouped
2Variable Karnaugh Map 2 VariableKarnaugh Map
A B F
0 0
A
B
0 1
0 0
0 1
1 0
A=0 B=0
A=1, B=0
0
1 0
1 1
A=0, B=0
A=1, B=1
1
A=0, B=1
Adifferent way to draw a truth table: by folding it A different way to draw a truth table: by folding it
Karnaugh Map Karnaugh Map
In a Kmap, physical adjacency does imply gray InaK map,physicaladjacencydoes implygray
codeadjacency
A A A
B
0 1
A
B
0 1
0
0 0
1
1 1
0
1 0
1
1 0
1
1 1
1
1 0
F=AB+AB=B F=AB+AB=A
2Variable Karnaugh Map 2 VariableKarnaugh Map
A B index F
A
0 0 0 1
A
B
0 1
0 1 1 1
1 0 2 0
B
0
1 0
1 0 2 0
1 1 3 0
1
1 0
2Variable Karnaugh Map 2 VariableKarnaugh Map
AA
B
0 1
A B index F
0 0 0 1
B
0
1 0
0 0 0 1
0 1 1 1
1
1 0
1 0 2 0
F = AB + AB = A
1 1 3 0
F = A B + A B = A
2Variable K Map: Grouping 2 VariableKMap:Grouping
A
B
0 1
A B index F
B
0
1 0
0 0 0 1
1
1 0
0 1 1 1
1 0 2 0
A = 0
F A
1 0 2 0
1 1 3 0
F=A
Another Example
A
AnotherExample
A B index F
B
0 1
A B index F
0 0 0 0
0
0 1
0 1 1 1
1 0 2 1
1
1 1
1 0 2 1
1 1 3 1
F = AB + AB + AB
(AB + AB) + (AB + AB) = (AB + AB) + (AB + AB)
= A + B
Another Example AnotherExample
AA
B
0 1
A B index F
B
0
0 1
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1
1
1 1
A 1
0 1 1 1
1 0 2 1
F = A + B
A=1
B=1
0
1 1 3 1
F=A+B
Yet Another Example YetAnotherExample
A
B
0 1
A B index F
0 0 0 1
B
0 1
0
1 1
0 1 1 1
1
1 1
1 0 2 1
1 1 3 1
F = 1
G f th t 1 b bi d Groups of more than two 1s can be combined
HALF ADDER: One bit adder HALFADDER:Onebitadder
X Y S C
0 0 0 0
x
x
0 0 0 0
0 1 1 0
1 0 1 0
Y
0 1
0
0 1
Y
0 1
0
0 0
1 1 0 1
0 1
1
1 0
0 0
1
0 1
X Y
S = AB + AB
C = AB
HalfAdder
S = A B + AB
= A XOR B
24
S C
KMap of three variable K Mapofthreevariable
A B C index F
0 0 0 0 1
BC
0 0 0 0 1
0 0 1 1 0
0 1 0 2 1
A BC BC BC BC
A 1 0 0 1
0 1 0 2 1
0 1 1 3 0
0 1 3 2
A 1
4
1
5
1
7
1
6
1 0 0 4 1
1 0 1 5 1
4 5 7 6
F= A + BC + BC
1 1 0 6 1
1 1 1 7 1
F= A+B C +BC
Groupof4
m(4,5,7,6)
Groupof2
m(2,6)
Groupof2
m(0,4)
F=m(0,2,4,5,6,7)
3VariableKarnaugh MapShowing
Minterm Locations
A
Note the order of
theB C variables:
A
BC
0 1
the B C variables:
0 0
0 1
00 m0 m4
01 m1 m5
0 1
1 1
1 0
ABC=101
01 m1 m5
11 m3 m7
10 m2 m6
ABC=010
Thanks
27
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To K-Maps: Boolean AdjacencyDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To K-Maps: Boolean AdjacencyJp FiniganNoch keine Bewertungen
- شرح مخطط كارنوفDokument65 Seitenشرح مخطط كارنوفzoherofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Lecture Logic Gates Boolean Algebra & KMDokument50 SeitenLecture Logic Gates Boolean Algebra & KMRiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Level Minimization1Dokument8 SeitenGate Level Minimization1Krista JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter3 DLDDokument58 SeitenChapter3 DLDShan E Shafiq MughalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DELD - Short Answer Questions and AnswersDokument23 SeitenDELD - Short Answer Questions and AnswersPasupuleti Venkata RamanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3.3Dokument30 SeitenUnit 3.3Marwa BarbouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chap 3 Combinational Logic CircuitsDokument98 SeitenChap 3 Combinational Logic Circuitsvinay.niranjan006Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Karnaugh MapDokument17 SeitenThe Karnaugh Mapthomas edisonNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 2 K MappingDokument31 SeitenUNIT 2 K MappingtoshgangwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- K MapDokument32 SeitenK MapHarshit SuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec4 AnnotatedDokument29 SeitenLec4 AnnotatedKarl VillaseñorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Simplification SlideDokument46 SeitenLogic Simplification Slideتوان ظاهيرو الدينNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument77 SeitenChapter 3HassnainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teknik Penyederhanaan: Karnaugh MapDokument22 SeitenTeknik Penyederhanaan: Karnaugh MapPengguna LinuxNoch keine Bewertungen
- Teknik Penyederhanaan: Karnaugh MapDokument22 SeitenTeknik Penyederhanaan: Karnaugh MapDimas KaruniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- K MapsDokument43 SeitenK Mapsprasanth naiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- MUCLecture 2022 6147264Dokument5 SeitenMUCLecture 2022 6147264Syed IrfanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2-4Dokument22 SeitenLecture 2-4contact.swati.4Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gate-Level Minimization: Karnaugh Maps POS Simplification Don't Care Conditions Nand and Nor Exclusive ORDokument77 SeitenGate-Level Minimization: Karnaugh Maps POS Simplification Don't Care Conditions Nand and Nor Exclusive ORahmad khanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Courses in Electrical Engineering: Digital Electronics Chapter Four: Karnaugh MappingDokument11 SeitenCourses in Electrical Engineering: Digital Electronics Chapter Four: Karnaugh MappingNGOUNENoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.deld Unit IDokument24 Seiten1.deld Unit Inandini pNoch keine Bewertungen
- KmapDokument84 SeitenKmapShubham JoshiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital System Design BTEC-302-18: Topic: K-MapDokument31 SeitenDigital System Design BTEC-302-18: Topic: K-Mapsonu sreekumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 - StudDokument49 SeitenChapter 8 - StudAshrafD.ZulkeflyNoch keine Bewertungen
- W-06-part2-LogicFuncRepresentation (K-Maps)Dokument40 SeitenW-06-part2-LogicFuncRepresentation (K-Maps)Eray GülerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wa0077Dokument2 SeitenWa0077Ndzebarah CarsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee177 Supplement 3Dokument14 SeitenEe177 Supplement 3stephen_562001Noch keine Bewertungen
- Review of Digital Design FundamentalsDokument75 SeitenReview of Digital Design FundamentalsKurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dwaraka Doss Goverdhan Doss Vaishnav College CHENNAI - 106: Fundamentals of Digitial ElectronicsDokument25 SeitenDwaraka Doss Goverdhan Doss Vaishnav College CHENNAI - 106: Fundamentals of Digitial ElectronicsRyuzz MalfoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karnaugh Map: Engr. Pablo B. Asi Engr. Leni A. Bulan Engr. Liza R. MaderazoDokument18 SeitenKarnaugh Map: Engr. Pablo B. Asi Engr. Leni A. Bulan Engr. Liza R. MaderazoDexter DoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gate Level Minimization-Method: Karnaugh MapDokument62 SeitenGate Level Minimization-Method: Karnaugh MapSirisha VamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Combinational Logic Circuits: Instructor: Afroza SultanaDokument25 SeitenCombinational Logic Circuits: Instructor: Afroza SultanaSamina TohfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebraic Methods For The Analysis and Synthesis of Logic CircuitsDokument100 SeitenAlgebraic Methods For The Analysis and Synthesis of Logic Circuitsbugaboo2323Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument41 SeitenChapter 3HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 6 Karnaugh Map ReviewDokument49 SeitenLec 6 Karnaugh Map ReviewCatherine IvanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 5: Karnaugh Maps: CS1104: Computer OrganisationDokument71 SeitenLecture 5: Karnaugh Maps: CS1104: Computer Organisationمحمود محمدNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Circuit ReportDokument31 SeitenLogic Circuit ReportK Aree D ElgadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homework 5Dokument4 SeitenHomework 5Ale Gomez100% (6)
- CSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems: Boolean Algebra M&K 2.3-2.5Dokument43 SeitenCSEE 3827: Fundamentals of Computer Systems: Boolean Algebra M&K 2.3-2.5Andrew KischNoch keine Bewertungen
- PLCDokument25 SeitenPLCsrgroups118Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7 PLC KarnaughDokument19 Seiten7 PLC KarnaughAhmad Reza AtefNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryDokument9 SeitenNotes and Formulae SPM Mathematics Form 1 - 3 Notes Solid GeometryJarnice Ling Yee ChingNoch keine Bewertungen
- BADASS Tutorial Karnaugh MapsDokument16 SeitenBADASS Tutorial Karnaugh MapsdjpsychoscientzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Che Ban-Calculus 2 - NVHDokument89 SeitenChe Ban-Calculus 2 - NVHTiến DũngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recurrences and Continued FractionsDokument73 SeitenRecurrences and Continued FractionsMaya RamyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Computer Unit I Part3 (2022)Dokument19 SeitenDigital Computer Unit I Part3 (2022)suhelkhan900500Noch keine Bewertungen
- BaiTap K Map v4Dokument15 SeitenBaiTap K Map v4Nguyễn Công Tuấn AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial KmapsDokument8 SeitenTutorial KmapsCalledo JLNoch keine Bewertungen
- K MapDokument19 SeitenK MapNoti GalNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsDokument9 SeitenSPM Notes & Formulae MathematicsPatrick PhuahNoch keine Bewertungen
- K MapDokument30 SeitenK MapJENATH223Noch keine Bewertungen
- K MapDokument30 SeitenK MapAnaliza NatividadNoch keine Bewertungen
- There Are Following Two Methods of Minimizing or Reducing The Boolean ExpressionsDokument10 SeitenThere Are Following Two Methods of Minimizing or Reducing The Boolean ExpressionsRaghavendra ShettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos QuestionsDokument6 SeitenCJC 2015 H2 J1 Math Promos QuestionsAlx0% (1)
- Logika Matematika 2004/2005: Circuit DigitalDokument4 SeitenLogika Matematika 2004/2005: Circuit DigitalskipjackkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Combinational Logic SystemsDokument36 SeitenUnit 2 Combinational Logic SystemsniranjanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PracticalDokument94 SeitenPracticalAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument97 SeitenUntitledAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 1Dokument51 SeitenBlock 1AshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 4 Sector Specific Issues and Policies: Major Development On Union State RelationsDokument121 SeitenBlock 4 Sector Specific Issues and Policies: Major Development On Union State RelationsAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cause and Counterfactual: Herbert A. SimonDokument19 SeitenCause and Counterfactual: Herbert A. SimonAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psych 1Dokument4 SeitenPsych 1AshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Recent Books (Continued) : W. G. Bickley A N D R. S. H. G. ThompsonDokument2 SeitenSome Recent Books (Continued) : W. G. Bickley A N D R. S. H. G. ThompsonAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lovejoy ConcubinesDokument23 SeitenLovejoy ConcubinesAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics of Measurement1Dokument12 SeitenMathematics of Measurement1AshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flux Linkage and Electromagnatic Induction L.V.BewleyDokument115 SeitenFlux Linkage and Electromagnatic Induction L.V.BewleyAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Event Field Algebra in Flat SpacetimeDokument5 SeitenEvent Field Algebra in Flat SpacetimeAshiqueHussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boolean Algebra Applications Reliability ExamplesDokument4 SeitenBoolean Algebra Applications Reliability ExamplesEmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tarea 2Dokument2 SeitenTarea 2Isai PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karnaugh Maps: Minimal Sum of Products (MSP)Dokument26 SeitenKarnaugh Maps: Minimal Sum of Products (MSP)GAMER JOWONoch keine Bewertungen
- Blender CrashDokument22 SeitenBlender CrashmusamikailgNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2-Boolean Algebra (5-16)Dokument12 SeitenChapter 2-Boolean Algebra (5-16)Khushi Y.SNoch keine Bewertungen
- DIGITAL AND LOGIC DESIGN-QUINE McCLUSKEY METHODDokument23 SeitenDIGITAL AND LOGIC DESIGN-QUINE McCLUSKEY METHODSchoolboy LTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Boolean AlgebraDokument23 SeitenIntroduction To Boolean Algebraraghuvanshbhagat6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Permutation Matrices Permutation MatricesDokument6 SeitenPermutation Matrices Permutation MatricesMiguel Sánchez ÁlvarezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles & ApplicationsDokument17 SeitenPrinciples & ApplicationsMahmud MusaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karnaugh Map: Engr. Pablo B. Asi Engr. Leni A. Bulan Engr. Liza R. MaderazoDokument18 SeitenKarnaugh Map: Engr. Pablo B. Asi Engr. Leni A. Bulan Engr. Liza R. MaderazoDexter DoteNoch keine Bewertungen
- (P Q) (P Q) : Truth Table For EXCLUSIVE OR Exclusive orDokument4 Seiten(P Q) (P Q) : Truth Table For EXCLUSIVE OR Exclusive orJunaid AkramNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Idea of A Boolean FunctionDokument16 SeitenThe Idea of A Boolean FunctionMaksud HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 6 Boolean FunctionsSOP - POSDokument17 SeitenModule 6 Boolean FunctionsSOP - POSnik occKNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit-2-Material-Notes-Duality laws-PDNF-PCNFDokument8 SeitenUnit-2-Material-Notes-Duality laws-PDNF-PCNFShreyash PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 Gate-Level MinimizationDokument48 SeitenChapter 3 Gate-Level MinimizationAbaid UllahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bits Pilani: Digital Systems (Combinational Circuit) Rktiwary ManoDokument39 SeitenBits Pilani: Digital Systems (Combinational Circuit) Rktiwary Manorktiwary256034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pragnya de 4Dokument5 SeitenPragnya de 4Pragnya RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karnaugh Maps MethodDokument124 SeitenKarnaugh Maps Methodkambala dhanushNoch keine Bewertungen
- NAND NOR ImplementationDokument3 SeitenNAND NOR Implementationsrisairampoly50% (2)
- SOP Dan POS FixDokument14 SeitenSOP Dan POS FixMuhammad ShofaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DigitalElectronics 1R1 141117 Scopy FinDokument57 SeitenDigitalElectronics 1R1 141117 Scopy FinShipra RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 03 - 04Dokument65 SeitenLecture 03 - 04infinitygaming.pakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class DiagramDokument1 SeiteClass DiagramAlhasan A. RayyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Write Two Set Level1 1Dokument2 SeitenWrite Two Set Level1 1Nicola NichelleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 15 More Connectives: Siti Mukaromah 0203519060 Khusus 2Dokument14 SeitenUnit 15 More Connectives: Siti Mukaromah 0203519060 Khusus 2Siti mukaromahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer:: Name: Yohanes Pratama Naibaho Student ID: 001201900101Dokument3 SeitenAnswer:: Name: Yohanes Pratama Naibaho Student ID: 001201900101Kelvin Putra UtamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 LogicDokument44 SeitenChapter 3 LogicdukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Solved Problems On K-MapDokument57 SeitenLecture Solved Problems On K-MapHugh100% (1)
- Week 6 - Module 5 Karnaugh MapsDokument12 SeitenWeek 6 - Module 5 Karnaugh MapsBen GwenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 9 Logic Gates SummaryDokument15 SeitenGrade 9 Logic Gates SummaryAbigel judith PeterNoch keine Bewertungen