Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
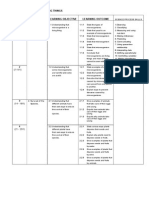
Investigating Living Things Year 5-Science: Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Vocabulary
Hochgeladen von
FadzliSufi0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten8 SeitenOriginaltitel
yearly plan y 5
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
15 Ansichten8 SeitenInvestigating Living Things Year 5-Science: Week Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Vocabulary
Hochgeladen von
FadzliSufiCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 8
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
1. INVESTIGATING LIVING THINGS Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
1. Microorganism
1,2
3/1-15/1
1.1 Understanding that
microorganism is a living
thing
state types of microorganisms.
state that yeast is an example of microorganism.
state that microorganism breathes.
state that microorganism grows.
state that microorganism moves.
conclude that microorganisms are living things and
most of them cannot be seen with naked eyes.
yeast- ragi
harmful- berbahaya
magnifying glass- kanta
pembesar
uses- kegunaan
sprinkling merenjis
3
17/1-21/1
1.2 Understanding that some
microorganisms are
harmful and some are
useful.
state examples of use of microorganisms.
state the harmful effects of microorganisms.
describe that diseases caused by microorganisms
can spread from one person to another.
explain ways to prevent diseases caused by
microorganisms.
contagious- berjangkit
quarantine diasingkan
measles- campak
chicken pox- cacar
stomach upset- sakit perut
cough- batuk
harm- kesan buruk
dengue denggi
sneezing bersin
flu - selsema
mumps beguk
conjunctivitis sakit mata
2. Survival of The Species
4
24/1-28/1
2.1 Understanding that
different animals have
their own ways to ensure
the survival of their
species.
give examples of animals that take care of their
eggs and young.
explain how animals take care of their eggs and
young.
explain why animals take care of their eggs and
young.
kemandirian
adapt- menyesuaikan
take care- menjaga
protect- melindungi
young anak
slimy berlendir
pouch kantong
herd kumpulan yang besar
disturbed- diganggu
plenty banyak
attack- menyerang
hide menyembunyikan
ensure- memastikan
feed memberi makan
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
1. INVESTIGATING LIVING THINGS Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
2. Survival of The Species
5
31/1 -4/2
2.2 Understanding that
different plants have their
own ways to ensure the
survival of their species
state various ways plants disperse their seeds and
fruits.
explain why plants need to disperse seeds or fruits.
give examples of plant that disperse seeds and
fruits by water.
give examples of plant that disperse seeds and
fruits bywind.
give examples of plant that disperse seeds and
fruits by animals.
give examples of plant that disperse seeds by
explosive mechanism.
relate characteristics of seeds and fruits to the ways
they are dispersed
various pelbagai
waxy berlilin
husk sabut
shell tempurung
disperse pencaran
edible boleh dimakan
flame of the forest
semarak api
chestnut buah berangan
balsam keembung
ocra kacang bendi
love grasskemuncup
6
7/2-11/2
2.3 Realising the importance
of survival of the species
predict what will happen if some species of animals
or plants do not survive.
extinction kepupusan
shortage kekurangan
3. Food Chain and Food Web
7
14/2-18/2
3.1 Understanding food
chains
identify animals and the food they eat.
classify animals into herbivore, carnivore and
omnivore.
construct food chain.
identify producer.
identify consumer.
8
21/2-25/2
3.2 Synthesizing food chains
to construct food web.
construct a food web
construct food webs of different habitats.
predict what will happen if there is a change in
population of a certain species in a food web.
explain what will happen to certain species of
animals if they eat only one type of food.
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
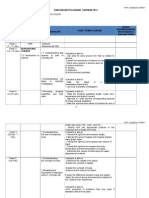
%. INVESTIGATING &O'(E AN) ENE'GY Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
1. Energy
9
28/2-4/3
1.1 Understanding the
uses of energy
explain why energy is needed.
give exampleswhere and when energy is used.
state various sources of energy.
sources- sumber
energy- tenaga
bounce-melantun
fuel-bahan api
boil-mendidih
10
7/3-11/3
UJIAN BULANAN PERTAMA
14/3-20/3 CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 1
11,12
21/3-1/4
1.2 Understanding that energy
can be transformed from
one form to another
state the various forms of energy.
state that energy can be transformed.
give examples of appliances that make use of
energy transformation.
transform-berubah
principle-prinsip
whistle- wisel
appliances - peralatan
13
4/4-8/4
1.3 Understanding renewable
and nonrenewable energy
state what renewable energy is.
state what nonrenewable energy is.
list renewable energy resources.
list non-renewable energy resources.
explain why we need to use energy wisely.
explain why renewable energy is better than non-
renewable energy.
give examples on how to save energy.
practise saving energy.
renewable energy-tenaga
diperbaharui
non-renewable energytenaga
yang tidak dapat
diperbaharui
replenished
digantikan
used up- habis digunakan
coal- arang batu
charcoal- arang kayu
wisely-secara bijaksana
biomass-biojisim
2. Elecriciy
14
11/4-15/4
2.1 Knowing the sources of
electricity
state the sources of electricity. dry cell- sel kering
hydroelectric power kuasa
hidro elektrik
15,16
18/4-29/4
2.2 Understanding a series
circuit and a parallel circuit
identify the symbols of various components in a
simple electric circuit.
draw circuit diagrams.
identify the difference in the arrangement of bulbs in
series and parallel circuits.
build a series circuit.
build a parallel circuit.
compare the brightness of the bulbs in a series and
a parallel circuit.
compare the effect on the bulbs when various
series circuit-litar bersiri
parellel circuit litar selari
brightness- kecerahan
arrangement-susunan
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
switches in a series and a parallel circuit are off.
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
%. INVESTIGATING &O'(E AN) ENE'GY Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
2. Elecriciy
17
2/5-6/5
2.3 Understanding the safety
precautions to be taken
when handling electrical
appliances
describe the danger of mishandlingelectrical
appliances.
explain the safety precautions to be taken when
using electrical appliances.
3. !igh
18,19
9/5-20/5
3.1 Understanding that light
travels in a straight line
state that light travels in a straight line.
give examples to verify that lighttravels in a straight
line.
describe how shadow is formed.
design a fair test to find out what cause the size of a
shadow to change by deciding what to keep the
same, what to change and what to observe.
design a fair test to find out what factors cause the
shape of a shadow to change by deciding what to
keep the same, what to change and what to
observe.
beam- alur cahaya
travel- bergerak
opaque legap
20
23/5-27/5
3.2 Understanding that light
can be reflected
state that light can be reflected.
draw ray diagrams to show reflection of light.
give examples of uses of reflection of light in
everyday life.
reflection- pembalikan
sharp bend- selekoh tajam
ray diagram- gambarajah sinar
21
31/5-3/6
UJIAN PEPERIKSAAN PERTENGAHAN TAHUN 2010
4/6-19/6 CUTI PERTENGAHAN TAHUN 2010
". #ea
22
21/6-25/6
4.1 Understanding that
temperature is an indicator
of degree of hotness
state that when a substance gains heat it will
become warmer
state that when a substance loses heat it will
become cooler.
measure temperature using the correct technique.
state the metric unit for temperature.
state that temperature of an object or material
increases as it gains heat.
state that temperature of an object or material
decreases as it loses heat.
conclude that the temperature is an indicator to
measure hotness.
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
%. INVESTIGATING &O'(E AN) ENE'GY Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
". #ea
23
28/6-2/7
4.2 Understanding the effects
of heat on matter.
state that matter expands when heated.
state that matter contracts when cooled.
give examples of the application of the principle of
expansion and contraction in everyday life.
dent kemek
expand-mengembang
contract-mengecut
snap - putus
*. INVESTIGATING +ATE'IALS Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
1. Saes of Maer
24,25
5/7-16/7
1.1 Understanding that matter
exist in the form of solid,
liquid or gas.
classify objects and materials into three states of
matter.
state the properties of solid.
state the properties of liquid.
state that some liquids flow faster than others.
state the properties of gas.
solid pepejal
liquid cecair
gas gas
water vapour wap air
evaporation penyejatan
condensation kondensasi
water cycle kitar air
interchangeable boleh
saling bertukar
syringe - picagari
26
19/7-23/7
1.2 Understanding that matter
can change from one state
to another
state that water can change its state. evaporation-penyejatan
condensation-kondensasi
freezing-pembekuan
melting peleburan
27
26/7-30/7
1.3 Understanding the water
cycle
describe how clouds are formed.
describe how rain is formed.
explain how water is circulated in the environment.
explain the importance of water cycle.
cloud awan
water cycle
kitaran air
28
2/8-6/8
1.4 Appreciating the
importance of water
resources
give reasons why we need to keep our water
resources clean.
describe ways to keep our water resources clean.
2. $cid and $l%ali
29, 30
9/8-20/8
2.1 Understanding the
properties of acidic,
alkaline and neutral
substances.
identify acidic, alkaline and neutral substances
using litmus paper
identify the taste of acidic and alkaline food.
conclude the properties of acidic alkaline and
neutral substances.
litmus paper kertas litmus
sour masam bitter pahit
neutral neutral acidic keasidan
alkaline-kealkalian property-sifat
31
23/8-27/8
UJIAN BULANAN KEDUA
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
,. INVESTIGATING THE EA'TH AN) THE -NIVE'SE Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
1. Consellaion
32
30/8-3/9
1.1 Understanding the
constellation
state what constellation is.
identifyconstellations.
state the importanceof constellations.
constellation - buruj
Orion - Belantik
Scorpion - Skorpio
Big Dipper - Biduk
Southern Cross Pari
pattern corak
direction arah
season - musim
4/9-12/9 CUTI PERTENGAHAN PENGGAL 2
2. The Earh& The Moon and The Sun
33
13/9-17/9
2.1 Understanding the
movements of the Earth,
the Moon and the Sun
state that the Earth rotates on its axis.
state that the Earth rotates and at the same time
moves round the Sun.
state that the Moon rotates on its axis.
state that the Moon rotates and at the same time
moves round the Earth.
state that the Moon and the Earth move round the
Sun at the same time.
describe the changes in length and position of the
shadow throughout the day.
conclude that the Earth rotates on its axis from west
to east.
rotate berputar
sundial jam matahari
axis - paksi
west barat
east timur
movement pergerakan
position kedudukan
throughout sepanjang
shadow bayang-bayang
34
20/9-24/9
2.2 Understanding the
occurrence of day and
night.
state that it is day time for the part of the Earth
facing the Sun.
state it is night time for the part of the Earth facing
away from the Sun.
explain that day and night occur due to the rotation
of the earth on its axis.
illuminating menyuluh
facing menghadap
rotating globe glob yang
berputar
day siang
night malam
occurrencekejadian
35
27/9-1/10
2.3 Understanding the phases
of the Moon
state that the Moon does not emit light.
explain that the Moon appears bright when it
reflects sunlight.
describe the phasesof the Moon.
new moon anak bulan
crescent - bulan sabit
half moon -bulan separa
full moon bulan purnama
reflect - memantulkan
phase - fasa
lunar calendar Takwim
Qamari
emit - memancarkan
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
SK PPR LEMBAH SUBANG
5. INVESTIGATING TE(HNOLOGY Year 5-Science
WEEK Learning Objectives Learning Otc!"es V!cab#ar$
1. Srengh and Sabiliy
36
4/10-8/10
1.1 Knowing the shapes of
objects in structures.
state the shapes of objects.
identify shapes in structure.
shape bentuk
cube - kubus
cuboid - kuboid
sphere - sfera
cone - kon
cylinder - silinder
pyramid - piramid
hemisphere - hemisfera
structure - struktur
37,38
11/10-
22/10
1.2 Understanding the
strength and stability of a
structure.
identify shapes of objects that are stable.
identify the factors that affect stability of objects.
explain how base area affects stability.
explain how height affects stability.
identify the factors that affect the strength of a
structure.
design a model that is strong and stable.
strength kekuatan /
kekukuhan
stability kestabilan
base area luas tapak
affect - mempengaruhi
stand at ease senang diri
stand at attention -
bersedia
39
23/8-27/8
PEPERIKSAAN AKHIR TAHUN 2010
40 PEMULANGAN DAN PENGAGIHAN BUKU TEKS
41 PERSEDIAAN KELAS UNTUK TAHUN 2011
42 PENGURUSAN KELAS
20/11-2/1 CUTI AKHIR TAHUN
IZZAT HIDAYAH SCIENCE YEARLY PLAN YEAR 5
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Science Yearly Plan Year Five 2006Dokument13 SeitenScience Yearly Plan Year Five 2006Hikeri HarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science Yr5 - 2011Dokument9 SeitenRPT Science Yr5 - 2011Mohd HamedanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterDokument10 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5 2 0 10 First SemesterRaffie MuksinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan Year Five 2006Dokument10 SeitenScience Yearly Plan Year Five 2006Ayu SumaiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year Planner (f1) LatestDokument13 SeitenYear Planner (f1) LatestNor ShakeelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument9 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Annie GoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Tahunan Sains Tahun 5Som Mai EmaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SN Y5Dokument8 SeitenRPT SN Y5vargan_ramoNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science FRM 2Dokument12 SeitenRPT Science FRM 2reanizaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT: Science Form 2Dokument12 SeitenRPT: Science Form 2Emmy MasturaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Dokument8 SeitenScience Yearly Lesson Plan: Year 5Muhammad FarisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument8 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science Form 1ssukgantiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ranc Tahunan Sns TH 5Dokument11 SeitenRanc Tahunan Sns TH 5Marhaini MasngutNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan For Year ThreeDokument11 SeitenScience Yearly Plan For Year Threefarizal_scribdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Choo Li MingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work Science Year 5Dokument4 SeitenScheme of Work Science Year 5murniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Penyelarasan RPT Sains T4 Zt91gdDokument14 SeitenPenyelarasan RPT Sains T4 Zt91gdMohammad FadzliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1adleenshazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomeDokument8 SeitenTheme: Investigating Living Things Learning Area Learning Objective Learning OutcomewmpejonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 3Dokument12 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 3Awang Bakhtiar Awang SeriNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT SN THN5Dokument10 SeitenRPT SN THN5Jhoster YulongNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science FRM 1Dokument9 SeitenRPT Science FRM 1Maslen DadeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Form 1 EditedDokument15 SeitenYearly Plan Form 1 EditedDianasalmie AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Dokument127 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 4Satia KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science f1 Lesson Plan Lates 09tDokument26 SeitenScience f1 Lesson Plan Lates 09tSahrulRashidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Nur Hayati YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Noralizah IsmadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Year 5-Yearly PlanDokument12 SeitenScience Year 5-Yearly PlanThevagi GovindasamyNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT: Science Form 3Dokument14 SeitenRPT: Science Form 3Hajar Norasyikin Abu BakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsDokument24 SeitenOrientation Programme For Form 1 StudentsVictor ManivelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science F1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan 2014: RPT: Science F1Lydia HuangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan For Year TwoDokument11 SeitenScience Yearly Plan For Year TwoAziz AljaffariNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Form 2Dokument8 SeitenRPT Form 2Aidatul Shima IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Sains Ting. 1Dokument10 SeitenRPT Sains Ting. 1Norzaliatun RamliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Mahfuzah AzmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Pelajaran Tahunan: RPT: Science Form 1300664Noch keine Bewertungen
- Scheme of Work 2012 Science Form 2Dokument11 SeitenScheme of Work 2012 Science Form 2salmiza_sabliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Bio Form 4Dokument50 SeitenRancangan Pengajaran Tahunan Bio Form 4Cik NanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strenght and StabilityDokument11 SeitenStrenght and StabilityAyu SumaiyahNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT: Science Form 3Dokument14 SeitenRPT: Science Form 3Safwan AzizulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 4Dokument140 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 4shahar289Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3rd Grade Ubd Stage 1 2 ExampleDokument4 Seiten3rd Grade Ubd Stage 1 2 Exampleapi-194916439Noch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science FRM 3Dokument14 SeitenRPT Science FRM 3Ashlan AdamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1 2015Dokument6 SeitenYearly Lesson Plan Science Form 1 2015Muhd Mustaffa Kamal AbidinNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science Year 6Dokument9 SeitenRPT Science Year 6Firdaus RipinNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science FRM 4Dokument16 SeitenRPT Science FRM 4Siraj Ul-Akmal YusriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Yearly Plan y 3Dokument20 SeitenScience Yearly Plan y 3Alice TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan For Science Year 3: Theme: Learning About Living ThingsDokument13 SeitenYearly Plan For Science Year 3: Theme: Learning About Living ThingsMuhammad Azrieen SamsudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rancangan Tahun 6 - Sem 1Dokument9 SeitenRancangan Tahun 6 - Sem 1Mismah Binti Tassa YanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yearly Plan Science Year 5Dokument5 SeitenYearly Plan Science Year 5wawa2006Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marina International School: Science Scheme of WorkDokument13 SeitenMarina International School: Science Scheme of WorkMariama KanyiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science 4Dokument26 SeitenScience 4Mazlan SamatNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT: Science Year 6Dokument9 SeitenRPT: Science Year 6Teratak MayaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curriculum Map 2013-2014Dokument18 SeitenCurriculum Map 2013-2014api-233653042Noch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 6 Science Budget of Work 1st To 4thDokument4 SeitenGrade 6 Science Budget of Work 1st To 4thKristine Barredo100% (5)
- Ecosystem EcologyDokument36 SeitenEcosystem EcologyDemar LyleNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science Form 3 2011Dokument14 SeitenRPT Science Form 3 2011So HannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RPT Science f2Dokument26 SeitenRPT Science f2Aldrich Malaga Gregory MNoch keine Bewertungen
- Card Answer Dates Ruling Planet ConstellationDokument3 SeitenCard Answer Dates Ruling Planet ConstellationKendra KoehlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 - Angular Kinematics - PER Wiki105205 PDFDokument7 SeitenModule 1 - Angular Kinematics - PER Wiki105205 PDFronald salapareNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary Notes - Topic 8 Astrophysics - Edexcel Physics IGCSEDokument3 SeitenSummary Notes - Topic 8 Astrophysics - Edexcel Physics IGCSEXiaoxu MaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BĐS of HavardDokument30 SeitenBĐS of HavardChân Hoàn DịchNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brigitte Kienle - Lenormand Combi PDFDokument13 SeitenBrigitte Kienle - Lenormand Combi PDFgleicyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Idol of SaturnDokument6 SeitenThe Idol of SaturnDAVIDNSBENNETTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ec6004 Unit 1 Satellite Orbits NotesDokument24 SeitenEc6004 Unit 1 Satellite Orbits NotesKottai eswariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nakshatras in Jyotish IDokument727 SeitenNakshatras in Jyotish IANANTHPADMANABHAN89% (9)
- Four Step TheoryDokument3 SeitenFour Step Theoryanand_kpmNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asimov Published StoriesDokument33 SeitenAsimov Published StoriesDeniFarelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Progressed Moon in Declination CyclesDokument5 SeitenProgressed Moon in Declination CyclesDositheus SethNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Lesson Plan For ScienceDokument3 SeitenSample Lesson Plan For ScienceAlyn Mondrano Alonzo100% (2)
- AGU Ref Shelf 1 - Global Earth Physics A Handbook of Physical Constants - T. AhrensDokument381 SeitenAGU Ref Shelf 1 - Global Earth Physics A Handbook of Physical Constants - T. AhrensLiza Dorothi100% (1)
- 2012Dokument37 Seiten2012Mehul JaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Wick: The Magazine of Hartwick College - Fall 2010Dokument48 SeitenThe Wick: The Magazine of Hartwick College - Fall 2010Stephanie BrunettaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geodesy Exam Reviewer (Besavilla)Dokument59 SeitenGeodesy Exam Reviewer (Besavilla)Pa A Ao100% (6)
- Sirian Attunements and Activations From Sirius: What Is A Sirian Attunement?Dokument8 SeitenSirian Attunements and Activations From Sirius: What Is A Sirian Attunement?Dina LazarosNoch keine Bewertungen
- No Mans Sky Game Guide GAME GUIDE PDFDokument56 SeitenNo Mans Sky Game Guide GAME GUIDE PDFFlora JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Encyclopaedia Britannica Fourteenth Edition (1937), Volume 8, Pages 751-755 ETHER (In Physics) PDFDokument17 SeitenEncyclopaedia Britannica Fourteenth Edition (1937), Volume 8, Pages 751-755 ETHER (In Physics) PDFPUNISHMENT POSSENoch keine Bewertungen
- Semper Et Al 2008Dokument13 SeitenSemper Et Al 2008hectorbazan75Noch keine Bewertungen
- TrigonometryDokument101 SeitenTrigonometryMarilyn LiconoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toilet Paper Solar System PDFDokument3 SeitenToilet Paper Solar System PDFShellz RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Delia Schwartz-Perlov and Alexander Vilenkin - Measures For A Transdimensional MultiverseDokument30 SeitenDelia Schwartz-Perlov and Alexander Vilenkin - Measures For A Transdimensional MultiverseDex30KMNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ejemplo Revolucion Solar PDFDokument19 SeitenEjemplo Revolucion Solar PDFrobertosayasNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Walk of The Hundred Fountains of Villa D Este - I. . P. . H. . Guillermo Calvo Soriano, 33rdDokument61 SeitenThe Walk of The Hundred Fountains of Villa D Este - I. . P. . H. . Guillermo Calvo Soriano, 33rdsupremo7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gravitation (XII) Eng WADokument16 SeitenGravitation (XII) Eng WAPrashantcool1999Noch keine Bewertungen
- DTL Elzevir PresentationDokument89 SeitenDTL Elzevir PresentationDr. Frank E. BloklandNoch keine Bewertungen
- September 21 (Test 3)Dokument11 SeitenSeptember 21 (Test 3)Karun SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultima Cumaei Venit Iam Carminis AetasDokument21 SeitenUltima Cumaei Venit Iam Carminis AetasMalKukura100% (1)
- A2 42 GravitationDokument45 SeitenA2 42 GravitationJeffreyNoch keine Bewertungen