Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Head and Neck Quiz: Questions Answers My Answer Correct?
Hochgeladen von
api-2462598170 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
40 Ansichten6 SeitenThe EAM is part of which bone? the nasolacrimal duct drains fluid into which structure? the middle meningeal and the recurrent branch of the mandibular nerve traverse which foramina in the posterior fossa?
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe EAM is part of which bone? the nasolacrimal duct drains fluid into which structure? the middle meningeal and the recurrent branch of the mandibular nerve traverse which foramina in the posterior fossa?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
40 Ansichten6 SeitenHead and Neck Quiz: Questions Answers My Answer Correct?
Hochgeladen von
api-246259817The EAM is part of which bone? the nasolacrimal duct drains fluid into which structure? the middle meningeal and the recurrent branch of the mandibular nerve traverse which foramina in the posterior fossa?
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
Head and Neck Quiz
Questions Answers My Answer Correct?
Name the three
divisions of the
trigeminal nerve
Opthalmic (V1)
Maxillary (V2)
Mandibular (V3)
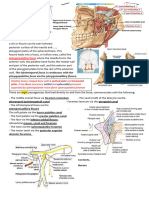
The EAM is part of
which bone?
Temporal
Name the major
cutaneous branches
of V1
External nasal,
infratrochlear,
lacrimal, supra-
orbital, supra-
trochlear
Name the major
cutaneous branches
of V2
Infra-orbital,
zygomaticofacial,
zygomaticotemporal
Name the major
cutaneous branches
of V3
Auriculo-temporal,
buccal, mental
Where does the
facial artery cross
the border of the
mandible?
Anterior border of
masseter
What cartilage forms
the nostrils?
Alar cartilage
The lacrimal
canaliculus drains
fluid into which
structure?
Lacrimal sac
Name the
transparent outer
coating of the
anterior aspect of
the eyeball
Cornea
Name the white
posterior portion of
the outer coat of the
eyeball
Sclera
What is an
inflammation of a
small sebaceous
gland around an
eyelash known as?
A stye
Where does the
nasolacrimal duct
Inferior meatus
drain into
What bony
prominence serves
as the insertion for
the occipitalis and
the trapezius
muscle?
External occipital
protuberance
Through what
foramina in the
posterior fossa do
cranial nerves 7 and
8 exit?
Nerves 9,10 and 11?
Nerve 12
7+8 internal
acoustic meatus
9,10 and 11 jugular
foramen
12 hypoglossal
canal
The middle
meningeal and the
recurrent branch of
the mandibular
nerve traverse
which foramen
Foramen spinosum
What artery supplies
the dura mater and
many of the skull
bones?
Middle meningeal
What CSF containing
space lining the
brain acts as a shock
absorber?
Sub-arachnoid space
What is the largest
cistern in the skull?
Cisterna magna
Name the projection
of the ethmoid bone
that acts as the
anterior attachment
of the falx cerebri
Crista galli
The superior orbital
fissure transmits
what structures?
CN 3,4,V1+6,
superior ophthalmic
vein, orbital branch
of middle meningeal
artery.
The optic nerve and
ophthalmic artery
enter the orbit
through which
opening?
Optic canal
The foramen ovale
transmits what
important nerve and
Mandibular nerve
(V3) and accessory
meningeal artery
vessel
What structures run
across the foramen
lacerum?
Internal carotid a.
Name the inclining
bony surface
anterior to the
foramen magnum
Clivus
What cranial sinus
drains blood from
the transverse
sinus?
Superior petrosal
sinus
What structures
traverse the
cavernous sinus?
Internal carotid
artery, CN 3,4, V1,V2
and 6
Name the tough ring
serving as the origin
of the four rectal
muscles
Anulus tendinosus
The ophthalmic
nerve V1 gives off
what branches in the
orbit
Frontal nerve,
lacrimal nerve,
nasociliary nerve
Oculomotor nerve
innervates what
muscles?
Inferior oblique,
levator palpebrae
superioris, superior,
middle and inferior
recti
The optic nerve
contains an artery in
its centre, what is it?
The central artery of
the retina
Name the four
refractive layers in
the eye through
which light passes
Cornea,
Aqueous humor,
Lens,
Vitreous humor
What is the name of
the retinal region
where the optic
nerve enters the
eyeball
Optic disc (blind
spot)
Name the middle
vascular layer of the
eye
Choroid
Name the area of the
retina responsible
for the highest visual
Fovea Centralis
acuity (only cones)
Which two neck
muscles have two
bellies separated by
an intertendon?
Digastric and
omohyoid
Five large nerves
emerge along the
posterior border of
the
sternocleidomastoid.
Name them
Accessory (11)
Great auricular
Lesser occipital
Supraclavicular
Transverse Cervical
What nerve
descends vertically
across the surface of
the anterior scalene
on its way to the
thorax?
Phrenic
What cartilage forms
the adams apple?
Thyroid cartilage
What are the
boundaries of the
muscular triangle of
the neck
Midline of the neck,
Sternocleidomastoid,
superior belly of
omohyoid
What are the
boundaries of the
carotid triangle
Posterior belly of the
digastric muscle,
sternocleidomastoid,
superior belly of the
omohyoid
What is the
innervation of the
strap muscles?
Ansa cervicalis
What nerve
innervates the
cricothyroid muscle?
External laryngeal
Name the 6
branches of the
external carotid
artery
Superior thyroid,
Ascending
Pharyngeal, Lingual,
Facial, Occipital,
Posterior auricular,
Maxillary, Superficial
temporal
What cranial nerve
innervates the
carotid body and
sinus
Glossopharyngeal
What two nerves
innervate the
digastric muscle?
Anterior belly V3
Posterior belly - 7
Which nerve
innervates all
laryngeal muscles
except cricothyroid?
Recurrent Laryngeal
The spinal accessory
nerve innervates
which two muscles?
Sternocleidomastoid
and trapezius
What muscles
extend from the
inferior surface of
the mandible to the
hyoid bone?
Geniohyoid and
mylohyoid
The prevertebral
fascia encloses what
structures?
Vertebral column
and its muscles
What bone forms the
inferior portion of
the nasal septum?
Vomer
What nerve artery
and vein pass
through the parotid
gland?
Facial nerve,
External carotid
artery,
Retromandibular
vein
The mouth opens in
a hinge-like motion
through what joint?
Temporomandibular
joint
Name the small
delicate nerve that
joins the lingual
nerve high in the
infratemporal fossa
Chorda tympani
What fascial layers
form the walls of the
retropharyngeal
space?
Buccopharyngeal
Prevertebral
Name the ligament
that holds the dens
within the atlas
Transverse ligament
What ligaments limit
side to side
movement of the
head?
Alar ligament
What is the motor
innervation of the
tongue?
Hypoglossal nerve
What structure
separates the
oropharynx and
larynx?
Epiglottis
Name the four sets
of sinuses
Ethmoidal, Frontal,
Maxillary,
Sphenoidal
What muscle
elevates during
swallowing?
Levator palate
Name the anterior
and then posterior
attachment of the
vocal ligaments
Thyroid cartilage,
Arytenoid Cartilage
Name the 3 ossicles Malleus, incus,
stapes
The stapes vibrates
which membrane?
Oval window
On what bone does
the tensor tympani
insert?
Malleus
What nerve provides
sensation to the
anterior 2/3 of the
tongue
Lingual
The constrictor
muscles of the
pharynx are
innervated by which
nerve?
Vagus
What ligament
forms the false vocal
chords?
Vestibular ligaments
What nerve provides
sensory innervation
to the larynx above
the level of the vocal
chords?
Internal laryngeal
Name the four layers
of the pharyngeal
wall (superficial to
deep)
Buccopharyngeal
fascia, Muscular
layer, Fibrous
pharyngobasilar
fascia, Mucous layer
Which tonsils form
waldeyers ring?
(From superior to
inferior mouth)
1 pharyngeal tonsil
(AKA Adenoids
when swollen), 2
tubal tonsils, 2
palatine tonsils, 1
lingual tonsil
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- אני משתף איתך את 'OMF injuries (traumas) answers'Dokument119 Seitenאני משתף איתך את 'OMF injuries (traumas) answers'Shany SchwarzwaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Branchial ArchesDokument49 SeitenBranchial ArchesSherin ThomasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Human Function AnatomyDokument8 SeitenHuman Function AnatomyaishbiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Essay Solution On Space in The SkullDokument21 SeitenEssay Solution On Space in The SkullEmmanuel IshiomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital AnatomyDokument45 SeitenOrbital AnatomyDevdutta NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pterygd and OrbitDokument10 SeitenPterygd and OrbitAmbg GhalyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain StemDokument6 SeitenBrain StemOjambo FlaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mnemonic SDokument8 SeitenMnemonic Smueen hashmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaDokument62 SeitenAnatomi Penginderaan: Ahmad Azwar Habibi Lab Anatomi FK UIN Syarif Hidayatullah JakartaIin Widya Sari SiregarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions AnswersDokument3 SeitenLower Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions Answersapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Axial Skeleton ScriptDokument4 SeitenAxial Skeleton ScriptMichaelVincentLimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final CapDokument38 SeitenFinal CapEliza ToteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy 2Dokument2 SeitenAnatomy 2Brian RamosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedDokument88 SeitenLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial NervesDokument137 SeitenAnatomy Orbit Nasalcavity Sinuses Cranial Nervesalhader libraryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Craneo Sobotta PDFDokument111 SeitenCraneo Sobotta PDFMaria Teresa AlvaradoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Muscles, Nerves, and Blood Vessels in The Human EyeDokument2 SeitenMuscles, Nerves, and Blood Vessels in The Human EyeHerman SitohangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves: Anatomy and FunctionsDokument54 SeitenCranial Nerves: Anatomy and FunctionsFatima Kh SalahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Block 3 Review Slides-PART 01 (2 Files Merged)Dokument222 SeitenBlock 3 Review Slides-PART 01 (2 Files Merged)spitzmark2030Noch keine Bewertungen
- GRDA Intro Head&NeckDokument18 SeitenGRDA Intro Head&NeckKingNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid Anatomy NotesDokument15 SeitenFirst Aid Anatomy NotessethrbNoch keine Bewertungen
- (9-2) THT - KL Anatomi 2020Dokument88 Seiten(9-2) THT - KL Anatomi 2020ayurhrdiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- THE HUMAN SKELETONDokument24 SeitenTHE HUMAN SKELETONIza ShaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves: Study Online atDokument4 SeitenCranial Nerves: Study Online atRami AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Presentation ScriptDokument2 SeitenAnatomy Presentation ScriptMikey ZhitnitskyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervus Cranialis Dan Basis Cranii: Praktikum Anatomi IIDokument42 SeitenNervus Cranialis Dan Basis Cranii: Praktikum Anatomi IIRahayu OktalianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves: Dede GunawanDokument46 SeitenCranial Nerves: Dede GunawanmohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Orbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityDokument45 SeitenOrbital and Ocular Anatomy: Abdulrahman Al-Muammar, MD, FRCSC King Saud UniversityAriyanie NurtaniaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osta Lecture 4 Notes Online ENGLISH Base of Skull and BrainDokument36 SeitenOsta Lecture 4 Notes Online ENGLISH Base of Skull and BrainslyfoxkittyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions AnswersDokument5 SeitenUpper Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions Answersapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Cervical Plexus: Spinal NervesDokument4 SeitenThe Cervical Plexus: Spinal Nervesxxyume0% (1)
- Head, Neck, Limbs OINADokument17 SeitenHead, Neck, Limbs OINAFrancis HenaresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Major Arteries and Veins Map with Nerve RoutesDokument8 SeitenMajor Arteries and Veins Map with Nerve RoutesMuhammad Usman FastNUNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial Nerves: Anatomy and FunctionsDokument7 SeitenCranial Nerves: Anatomy and FunctionsCristina A RodriguezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Openings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedDokument19 SeitenOpenings in The Skull Bone of The Skull Structures TransmittedMacy Peralta100% (1)
- Trigeminal NerveDokument2 SeitenTrigeminal NerveVanshika JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of NoseDokument8 SeitenAnatomy of Noserizgah jawas100% (1)
- Cns LectureDokument10 SeitenCns Lectureferg jeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial CavityDokument94 SeitenCranial CavityShashank Tripathi100% (1)
- Development of The Head and Neck: Pharyngeal Apparatus: DR Odetola A. A. Edo University, IyamhoDokument68 SeitenDevelopment of The Head and Neck: Pharyngeal Apparatus: DR Odetola A. A. Edo University, IyamhomatthewNoch keine Bewertungen
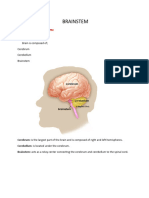
- BRAINSTEMDokument17 SeitenBRAINSTEMaroosadilbar27Noch keine Bewertungen
- W1-1 Review of Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear and Nose and Other Important Face and Neck Structures - LectureDokument126 SeitenW1-1 Review of Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear and Nose and Other Important Face and Neck Structures - LectureDhandepatil PavanKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Classification and Emergence of Cranial NervesDokument10 SeitenFunctional Classification and Emergence of Cranial NervesObansa JohnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Olfactory nerve ( 2024)Dokument40 SeitenOlfactory nerve ( 2024)doctormdali7889Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 AnatomyDokument14 SeitenLecture 3 AnatomyZA IDNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Mnemonics Memory HacksDokument7 SeitenMedical Mnemonics Memory HacksHaseebUl haqNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial and Peripheral Nerves - MartinDokument108 SeitenCranial and Peripheral Nerves - MartinTherese Jane Tirador100% (1)
- Cranial Nerves V, Ix, X, XiDokument89 SeitenCranial Nerves V, Ix, X, XiUloko Christopher100% (1)
- Auditory Pathway PDFDokument35 SeitenAuditory Pathway PDFJohnson JayarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy and Physiology EditedDokument5 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology EditedAya BantuasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7 Anatomy First YearDokument8 SeitenLecture 7 Anatomy First Yearspo9equtabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nerves of The OrbitDokument6 SeitenNerves of The OrbitAshifa SahiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Early Embryology Week OneDokument14 SeitenEarly Embryology Week OnelukesqueNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Orbit and Eye: Anatomy and FunctionsDokument12 SeitenThe Orbit and Eye: Anatomy and FunctionsOjambo FlaviaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide - Anterior Triangle of NeckDokument3 SeitenStudy Guide - Anterior Triangle of Neckravi guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Head and NeckDokument63 SeitenHead and Neckbayenn100% (1)
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide to the Voice Box and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsVon EverandA Simple Guide to the Voice Box and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 6: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 6: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Upper Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions AnswersDokument5 SeitenUpper Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions Answersapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 8: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 8: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lower Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions AnswersDokument3 SeitenLower Limb Anatomy Quiz: Questions Answersapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 7Dokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 7api-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument1 SeiteUntitledapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 6: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 6: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet Wednesday 6: 1. What Are The Three Parts of The Uterus?Dokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet Wednesday 6: 1. What Are The Three Parts of The Uterus?api-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hi If Information On Potassium Levels Is Also Available Then You Should Use This in Your Calculation As Well. MarinaDokument1 SeiteHi If Information On Potassium Levels Is Also Available Then You Should Use This in Your Calculation As Well. Marinaapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument1 SeiteUntitledapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet Wednesday 5: CSIM Questions Are in BlueDokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet Wednesday 5: CSIM Questions Are in Blueapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 5: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument2 SeitenYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 5: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Intro To Mic/ PPDDokument4 SeitenIntro To Mic/ PPDapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument3 SeitenUntitledapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To FCDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To FCapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Shoulder Anatomy SummaryDokument4 SeitenShoulder Anatomy Summaryapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?Dokument14 SeitenHow Do The Kidneys Control Things?: Why Do We Need To Maintain It?api-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 2: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 2: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 4: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 4: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 3: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 3: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet Wednesday 3: CSIM Questions Are in BlueDokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet Wednesday 3: CSIM Questions Are in Blueapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet Wednesday 3: CSIM Questions Are in BlueDokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet Wednesday 3: CSIM Questions Are in Blueapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet Wednesday 2: What Are The Different Categories of Differentiation of Malignant Neoplasms?Dokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet Wednesday 2: What Are The Different Categories of Differentiation of Malignant Neoplasms?api-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument1 SeiteUntitledapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet 1 AnswersDokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet 1 Answersapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- UntitledDokument1 SeiteUntitledapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet 1 AnswersDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet 1 Answersapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 2 Worksheet Wednesday 1: CSIM Questions Are in BlueDokument1 SeiteYear 2 Worksheet Wednesday 1: CSIM Questions Are in Blueapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- Year 1 Worksheet Wednesday 1: CVRR Questions Are in RedDokument1 SeiteYear 1 Worksheet Wednesday 1: CVRR Questions Are in Redapi-246259817Noch keine Bewertungen
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDokument13 SeitenNew Microsoft Word DocumentdinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chest Breath Vs Belly BreathDokument8 SeitenChest Breath Vs Belly BreathsetankabiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7D Hifu HF700Dokument49 Seiten7D Hifu HF700Jonathan AvilesNoch keine Bewertungen
- NIKE-The Program DefenceDokument20 SeitenNIKE-The Program DefenceCharlotteEngNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gas Exchange in the Lungs - How Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are TransferredDokument15 SeitenGas Exchange in the Lungs - How Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide are TransferredThe Deep Sea IdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Article PDF Neeraj Madan Nidhi Kathuria 49Dokument3 SeitenArticle PDF Neeraj Madan Nidhi Kathuria 49evieramawati_4536812Noch keine Bewertungen
- Muscle Tone PhysiologyDokument5 SeitenMuscle Tone PhysiologyfatimaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reviewer Science For Grade 9 StudentsDokument29 SeitenReviewer Science For Grade 9 StudentsevanescentNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryDokument13 Seiten1.1 Surface Anatomy and Surface Landmarks For Thoracic SurgeryResidentes CirugíaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3 Diagnosis of Acute Groin Injuries A Prospective Study of 110 Athletes 3757147577Dokument9 Seiten3 Diagnosis of Acute Groin Injuries A Prospective Study of 110 Athletes 3757147577César ArveláezNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQs & EMQ For DOHNSDokument162 SeitenMCQs & EMQ For DOHNSyasino0% (1)
- Levers of Body and Angle of Pull: Saba LatifDokument26 SeitenLevers of Body and Angle of Pull: Saba LatifSaba Latif100% (1)
- 10,11-Arterial Blood Pressure & Its Regulation Team441Dokument51 Seiten10,11-Arterial Blood Pressure & Its Regulation Team441saran kNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stocker and Dehner's Pediatric PathologyDokument2.196 SeitenStocker and Dehner's Pediatric PathologyJose SirittNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Cavity, Tongue, and Mandibular ReconstructionsDokument39 SeitenOral Cavity, Tongue, and Mandibular ReconstructionsAlfadzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintaining Mobility Through ROM ExercisesDokument16 SeitenMaintaining Mobility Through ROM ExercisesAttila Tamas100% (1)
- Hip ExaminationDokument43 SeitenHip ExaminationJayakrishnu tjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Back RubDokument18 SeitenBack RubJehan EnokNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy of The Eye PDFDokument15 SeitenAnatomy of The Eye PDFPaolo Naguit0% (1)
- Tom Skin-Sparing Approach To Treatemen of NSTI 2016Dokument14 SeitenTom Skin-Sparing Approach To Treatemen of NSTI 2016Sadaf Raisa KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 107 Rotator Cuff Exercises - Zach CalhoonDokument136 Seiten107 Rotator Cuff Exercises - Zach CalhoonSam Gregory100% (2)
- Thyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportDokument5 SeitenThyroid Hormone Synthesis, Secretion, and TransportAnonymous UTUWFODCEYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gorilla WorkoutDokument4 SeitenGorilla WorkoutKishoreVancheeshwaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Spinal Schwannoma Case ReportDokument17 SeitenPediatric Spinal Schwannoma Case ReportrakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial NervesDokument90 SeitenCranial NervesGaVee AgranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skeletal Muscle Cells and Muscle Fiber FasciclesDokument9 SeitenSkeletal Muscle Cells and Muscle Fiber Fasciclesjessa prendol100% (1)
- Anatomy Physio ExamDokument2 SeitenAnatomy Physio ExamJecxter BedañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12-Week Full Body Workout SplitDokument4 Seiten12-Week Full Body Workout SplitDakota SheppardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sample Patient Initial EvaluationDokument8 SeitenSample Patient Initial EvaluationYang TubioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rowing Machine: By: Josephin Starrett & Patricia GalvanDokument8 SeitenRowing Machine: By: Josephin Starrett & Patricia Galvanfuentes_patNoch keine Bewertungen