Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Final Exam Questions #3 - Refraction
Hochgeladen von
anonslu2012Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Final Exam Questions #3 - Refraction
Hochgeladen von
anonslu2012Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
DivisionofTechnicalEducationandManagementStudies
AppliedEngineeringScience ESC103
PassExamQuestion Spring2009
Refraction
Fall2002
a) A Light is incident on an equilateral crown glass prism at
a 45.0
o
angle to one face. Calculate the angle which light
emerges from the opposite face.
Assume that n
glass
=1.52.
b) If the space to the right prism is filled with oil of
refractive index 1.6, what angle would the ray leave the glass/oil interface?
c) What angle of incidence would cause the ray to be total internally refracted
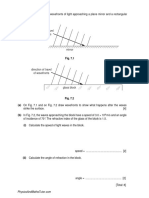
Summer2003
The diagram to the right shows a ray of light striking the
surface of oil at an angle of incidence of 65
o
. The light
passes through oil and then through a slab of glass fixed at
an angle of 45
o
to the horizontal.
a) Given that the refractive index of oil is 1.4 and that
of glass is 1.55, determine the path of the light
takes as it emerges through the glass.
b) What incident angle would cause the ray to just be totally internally reflected?
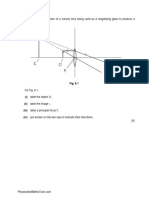
Spring2005
Figure shows a prism being used as a colour separator.
An incident beam containing a combination of red and
blue light is incident on face AB of the separator as
shown. Calculate the following:
(i) The incident angle
blue
that would cause the blue
light to strike the face AC at the critical angle.
(ii) The incident angle
red
that would cause the red light to strike the face AC at the critical
angle.
(iii) State the range of incident angle
blue
that would cause the blue light to be always
totally internal reflected when it strikes face AC.
(iv) State the range of incident angle
red
that would cause the red light to be always totally
internal reflected when it strikes face AC.
(v) Hence find that range of angle that would cause the blue light and the red light to
become separated.
Fall2006
The diagram shows a ray light entering the surface of oil at an unknown angle of incidence
o
.
The light passes through the oil, strikes and enters the glass and is just totally internally
reflected at the glass/air boundary.
a. Calculate the critical at the glass air boundary.
b. Determine the path the light takes as it passes
through the different media stating clearly the
incident angle .
c. If the area below the glass was occupied by
water, determine the path the light would take
with an incident angle of 45
o
Refractive index of Oil n
oil
= 1.43
Refractive index of Glass n
glass
= 1.65
Refractive index of water n
water
= 1.55
Colour Wavelength Refractive index
Red light
red
680 nanometers
n
red
1.500
Blue light
blue
480 nanometers
n
blue
1.520
Fall2004
Fig 2 shows a corner of a rectangular piece of glass ABC. If a
ray of light strikes the glass on side AB enters the glass,
calculate the minimum angle of incidence that would cause
the ray to be totally internally reflected at surface BC.
The refractive index of the glass n
g
= 4/3
Fall2006
a) A penny resting head up on a glass block 2.5cm thick when viewed from above
produces an image 3.25 cm below the top surface of the glass block. Which side of the
penny will be visible in the image and what is the refractive index of the glass?
b) The diagram shows a glass rod partially immersed in a
liquid of refractive index 1.24. If the glass rod has a
refractive index of 1.66 and a ray of light traveling
vertically downwards strikes the glass at an angle of
incident of 40o. Calculate the following:
i) The angle at which the incident ray will
eventually enter the liquid.
ii) What angle of incidence will cause the ray to be
just totally internally reflected at the glass liquid
boundary? What can you say about the angle
that will cause total internal refraction?
Spring2008
The figure shows an inverted glass prism on which one
side has oil and the other water.
a) Determine the path a ray of light would take if
it was incident at an angle of 60
o
to the oil.
b) Calculate what incident angle would cause the
ray to be totally internally refracted at the
glass/water face?
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Refraction WorksheetDokument8 SeitenRefraction WorksheetKennan PhilipNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction Physics SATDokument3 SeitenRefraction Physics SATAyman ElAshmawyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Questions Set1-OpticsDokument5 SeitenRevision Questions Set1-OpticsWilberforce JakiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Refraction at Plane SurfacesDokument7 SeitenClass 10 Refraction at Plane Surfacesfreya screepNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light ExerciseDokument29 SeitenLight Exercisemaatla monkgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- HW14-Light - 1 (学生版) - 021527Dokument14 SeitenHW14-Light - 1 (学生版) - 021527Jun WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.2 Refraction and 5.3 Total Internal Reflection (Exercise)Dokument2 Seiten5.2 Refraction and 5.3 Total Internal Reflection (Exercise)mydadawalfn50% (2)
- 5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionDokument51 Seiten5.3 QUICK REVISION Total Internal ReflectionAnna Latifah CammryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection: Name: GR: 10 IGCSEDokument3 SeitenReflection: Name: GR: 10 IGCSEshivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light 5 QPDokument8 SeitenLight 5 QP985wtz8rcjNoch keine Bewertungen
- WS Physics 312 E L20Dokument2 SeitenWS Physics 312 E L20Eira SethiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2.2 Refraction 00-10Dokument12 Seiten3.2.2 Refraction 00-10Murray PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Are The Two Laws of Reflection Also Valid For Curved SurfacesDokument2 SeitenAre The Two Laws of Reflection Also Valid For Curved SurfacessajalgiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch-13 LightDokument6 Seitench-13 LightSonica SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Refraction 1Dokument23 SeitenLight Refraction 1psnarayanan99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Total Internal Reflection of LightDokument21 SeitenUnderstanding Total Internal Reflection of LightSiti Arbaiyah AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE Physics Optics ExerciseDokument1 SeiteIGCSE Physics Optics ExerciseJenkins TsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewerDokument14 SeitenReviewerHeidi de LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection and Refraction AnsDokument8 SeitenReflection and Refraction Anssjk4763dNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPTICS. Term 2Dokument20 SeitenOPTICS. Term 2kabir ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction and ReflectionDokument7 SeitenRefraction and ReflectionAndrew EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction Through Glassslab1Dokument3 SeitenRefraction Through Glassslab1RikuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics II Problems PDFDokument1 SeitePhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reflection and RefractionDokument1 SeiteReflection and RefractionAnderson KandaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light NotesDokument31 SeitenLight Notesamandaangela0067Noch keine Bewertungen
- 7refractive IndexansDokument7 Seiten7refractive IndexansyongshengngNoch keine Bewertungen
- (48251) 9. H Refraction of Light QuestionsDokument8 Seiten(48251) 9. H Refraction of Light Questionsmuhammadmauz800Noch keine Bewertungen
- 12 - LightDokument25 Seiten12 - LightEdgardo LeysaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light PDF of Practice QuestionsDokument24 SeitenLight PDF of Practice Questionsyuvrajchourasia786Noch keine Bewertungen
- 32.5 Light Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPDokument9 Seiten32.5 Light Cie - Igcse - Physics - Ext Theory QPLiliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Optics Practice Problems-2012!05!07Dokument24 SeitenGeometric Optics Practice Problems-2012!05!07AravindhNoch keine Bewertungen
- IGCSE 33 LightWavesDokument36 SeitenIGCSE 33 LightWavesAhmed MawahibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 12Dokument20 SeitenClass 12Pritha KhannaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Virtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce ADokument11 SeitenVirtual Image.: 1 (A) Fig. 8.1 Is A Ray Diagram of A Convex Lens Being Used As A Magnifying Glass To Produce AahmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light 2 QPDokument11 SeitenLight 2 QPgambixo3005Noch keine Bewertungen
- Light 7 QPDokument8 SeitenLight 7 QPHabibullah AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light 7 QP - 240314 - 053508Dokument9 SeitenLight 7 QP - 240314 - 053508diyanooooooorNoch keine Bewertungen
- G10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Dokument12 SeitenG10 - Chapter Test 6 Ans - Ch.10 - 10 Nov 23Urmila GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Geometric Optics Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDokument23 SeitenGeometric Optics Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsMohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 20 - Reflection and Refraction of Light: CommentsDokument14 SeitenChapter 20 - Reflection and Refraction of Light: CommentsSalwa Mahbub0% (1)
- Total Internal ReflectionDokument18 SeitenTotal Internal ReflectionshivamNoch keine Bewertungen
- S.5 Phy P2 Eot 1 2003 Revision Past PapersDokument3 SeitenS.5 Phy P2 Eot 1 2003 Revision Past Paperskinene richardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 5.3 LightDokument10 SeitenLesson 5.3 LightRais RahimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refraction at Plane SurfacesDokument2 SeitenRefraction at Plane SurfacesVenu GopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review Sheet 2426 Final ExamDokument19 SeitenReview Sheet 2426 Final ExamperezromNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wolfson Eup3 Ch30 Test BankDokument8 SeitenWolfson Eup3 Ch30 Test BankifghelpdeskNoch keine Bewertungen
- Light Revision Class 10Dokument34 SeitenLight Revision Class 10karun.senthil.kumar.25Noch keine Bewertungen
- Light NsejsDokument3 SeitenLight NsejsGarvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class Xii Test 1 Ray OpticsDokument1 SeiteClass Xii Test 1 Ray OpticsAcademics AITNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.2.1 Refraction 91-01Dokument16 Seiten3.2.1 Refraction 91-01Murray PhysicsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eu1c3 by Adel KhamisDokument26 SeitenEu1c3 by Adel KhamisAdel Khamis50% (2)
- Tutorial Sheet 1Dokument3 SeitenTutorial Sheet 1EDENINoch keine Bewertungen
- Year 10 Light PractiseDokument5 SeitenYear 10 Light Practiseqaz xswNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3.2.3 Refraction at A Plane SurfaceDokument70 Seiten3.3.2.3 Refraction at A Plane Surfacesara patwardhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- PHY 2B Geometric Optics QuestionsDokument4 SeitenPHY 2B Geometric Optics Questionsvolfan555Noch keine Bewertungen
- Questio 1Dokument2 SeitenQuestio 1Ankit GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opticks: Or, A Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of LightVon EverandOpticks: Or, A Treatise of the Reflections, Refractions, Inflections, and Colours of LightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #11 - Doppler's EffectDokument2 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #11 - Doppler's Effectanonslu2012100% (1)
- Final Exam Questions #10 - Waves in StringsDokument2 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #10 - Waves in Stringsanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thevenizing A CircuitDokument1 SeiteThevenizing A Circuitanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #9 - SoundDokument5 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #9 - Soundanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #8 - SHMDokument3 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #8 - SHManonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #7 - EMWDokument3 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #7 - EMWanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #6 - InterferenceDokument2 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #6 - Interferenceanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #5 - Optical InstrumentsDokument2 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #5 - Optical Instrumentsanonslu2012100% (1)
- Final Exam Questions #4 - LensDokument4 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #4 - Lensanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #2 - Spherical MirrorsDokument2 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #2 - Spherical Mirrorsanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Questions #1 - Plain MirrorsDokument3 SeitenFinal Exam Questions #1 - Plain Mirrorsanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- ESC103 Final Exam Dec 2011 Sir Arthur Lewis Community CollegeDokument7 SeitenESC103 Final Exam Dec 2011 Sir Arthur Lewis Community Collegeanonslu2012Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rid and Clean Safety DataDokument1 SeiteRid and Clean Safety DataElizabeth GraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grope Assignment 1Dokument5 SeitenGrope Assignment 1SELAM ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Branding Assignment KurkureDokument14 SeitenBranding Assignment KurkureAkriti Jaiswal0% (1)
- GooseberriesDokument10 SeitenGooseberriesmoobin.jolfaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jewish Standard, September 16, 2016Dokument72 SeitenJewish Standard, September 16, 2016New Jersey Jewish StandardNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Skylane Pilot's CompanionDokument221 SeitenThe Skylane Pilot's CompanionItayefrat100% (6)
- 1b SPC PL Metomotyl 10 MG Chew Tab Final CleanDokument16 Seiten1b SPC PL Metomotyl 10 MG Chew Tab Final CleanPhuong Anh BuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book Review On PandeymoniumDokument2 SeitenBook Review On PandeymoniumJanhavi ThakkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Notice: Constable (Driver) - Male in Delhi Police Examination, 2022Dokument50 SeitenNotice: Constable (Driver) - Male in Delhi Police Examination, 2022intzar aliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Walt Whitman Video Worksheet. CompletedDokument1 SeiteWalt Whitman Video Worksheet. CompletedelizabethannelangehennigNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cct4-1causal Learning PDFDokument48 SeitenCct4-1causal Learning PDFsgonzalez_638672wNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dragon Ball AbrigedDokument8 SeitenDragon Ball AbrigedAlexander SusmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)Dokument11 SeitenFoucault, M.-Experience-Book (Trombadori Interview)YashinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hellwalker: "What Terrors Do You Think I Have Not Already Seen?"Dokument2 SeitenHellwalker: "What Terrors Do You Think I Have Not Already Seen?"mpotatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat Hydo 10wDokument4 SeitenCat Hydo 10wWilbort Encomenderos RuizNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm D1895 17Dokument4 SeitenAstm D1895 17Sonia Goncalves100% (1)
- Basics of An Model United Competition, Aippm, All India Political Parties' Meet, Mun Hrishkesh JaiswalDokument7 SeitenBasics of An Model United Competition, Aippm, All India Political Parties' Meet, Mun Hrishkesh JaiswalHRISHIKESH PRAKASH JAISWAL100% (1)
- 4Q 4 Embedded SystemsDokument3 Seiten4Q 4 Embedded SystemsJoyce HechanovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damodaram Sanjivayya National Law University VisakhapatnamDokument6 SeitenDamodaram Sanjivayya National Law University VisakhapatnamSuvedhya ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- (IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesDokument51 Seiten(IME) (Starfinder) (Acc) Wildstorm IndustriesFilipe Galiza79% (14)
- Journal Entry EnrepDokument37 SeitenJournal Entry Enreptherese lamelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPSS 415 Feb90Dokument7 SeitenOPSS 415 Feb90Muhammad UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seangio Vs ReyesDokument2 SeitenSeangio Vs Reyespja_14Noch keine Bewertungen
- LBST 2102 Final EssayDokument9 SeitenLBST 2102 Final Essayapi-318174977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Contact Numbers of Head Office: Managing DirectorDokument6 SeitenContact Numbers of Head Office: Managing DirectorRatneshNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5g-core-guide-building-a-new-world Переход от лте к 5г английскийDokument13 Seiten5g-core-guide-building-a-new-world Переход от лте к 5г английскийmashaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohak Meaning in Urdu - Google SearchDokument1 SeiteMohak Meaning in Urdu - Google SearchShaheryar AsgharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Karak Rules - EN - Print PDFDokument8 SeitenKarak Rules - EN - Print PDFWesley TeixeiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- VIII and IXDokument56 SeitenVIII and IXTinn ApNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Future of Psychology Practice and Science PDFDokument15 SeitenThe Future of Psychology Practice and Science PDFPaulo César MesaNoch keine Bewertungen