Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
How Does Email Work
Hochgeladen von
api-2544013390 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
69 Ansichten2 SeitenOriginaltitel
how does email work
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
69 Ansichten2 SeitenHow Does Email Work
Hochgeladen von
api-254401339Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 2
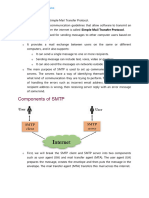
How it works
Packets- it is a network that breaks up a specific e-mail message into parts of a
certain size in bytes. Each packet carries information that will help get it to its
desired destination, whether that is regional or world-wide.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP):
TCP- is responsible for verifying the data from each client and ensuring that it is
correct. Its possible for data to be lost but T! adds support to detect errors and or
lost data.
IP- forwards each packet based on a four byte destination address or as we would
call it, the I! number. I! operates on "gateway machines# which then send data
from department to organization to region and then all around the world.
How Does E-Mail Work?
Sending Mail
When you send an email youre connected to the Internet service provider's mail
server. our messa!e will "e "roken up into smaller parts #packets$ and this way it
can travel more %uickly &rom server to server. 'nce your messa!e reaches its
destination it is then reassem"led.
Sorting the Mail
In the same way that postal mail is sorted &irst "y (I) code* e-mail messa!es are
sorted "y domain. +or the e-mail address feedback@allbusiness.com* &or e,ample* the
domain is the allbusiness.com portion. -he domain identi&ies where the messa!e
needs to !o.
Each domain name maps to a uni%ue We" address* called an Internet )rotocol #I)$
address* which is a strin! o& num"ers "y which each server is identi&ied* the same way
a street address identi&ies a physical location. -hese relationships are stored in the
Domain .ame /e!istry. When the e-mail server receives a messa!e* it looks at the
domain and checks the re!istry to determine what I) address to send the messa!e to.
'nce it determines the proper destination* the e-mail messa!e is sent on its way.
Delivering the Mail
Dependin! on where the destination server is* the ori!inal e-mail server may not
actually make the &inal hando&&0 in &act* it is likely that the messa!e will travel
"etween several trans&er points "e&ore reachin! its &inal destination. Each 1hop1
identi&ies the domain* and passes the messa!e to another trans&er point. -his process is
repeated 2 the messa!e !ettin! closer and closer to its destination 2 until the correct
server is reached. 3sernames are like post o&&ice "o, num"ers* and passwords act like
keys that open the correct "o,. 'nce a messa!e reaches the appropriate domain
server* it's channeled into the ri!ht e-mail account and stored until the user lo!s in and
checks &or mail. In other words* this is how the feedback@allbusiness.com address is
di&&erentiated &rom the service@allbusiness.com address.
When the recipient tells his or her e-mail pro!ram* like Microso&t 'utlook* to check
&or new mail* the e-mail pro!ram connects to the e-mail server* looks in the user's
mail"o,* and retrieves any mail that's waitin!. -he messa!e's 4ourney is complete 2
and all this may have taken place in 4ust a matter o& seconds.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Load Balancing in Oracle RAC 11GR2Dokument3 SeitenLoad Balancing in Oracle RAC 11GR2angeldn06Noch keine Bewertungen
- Alcatel ScirbdDokument3 SeitenAlcatel ScirbdNovery BriantonoNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Email WorkDokument2 SeitenHow Does Email Workapi-254400423Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Email WorkDokument2 SeitenHow Does Email Workapi-256171856Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is A Mail ServerDokument2 SeitenWhat Is A Mail ServerAnonymous s3TzBvwS1Noch keine Bewertungen
- How Does Email WorkDokument2 SeitenHow Does Email Workapi-254400175Noch keine Bewertungen
- Internetworking Systems 603 Assignment 1: SK MD Saif Iqbal ID No. 14542703Dokument4 SeitenInternetworking Systems 603 Assignment 1: SK MD Saif Iqbal ID No. 14542703saif1509Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Question ArDokument10 SeitenThe Question Arhwx8nckbnqNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Mailforensics 161124053030Dokument22 SeitenE Mailforensics 161124053030gadisa gemechuNoch keine Bewertungen
- ICF-9-week-1-2 - Q2Dokument13 SeitenICF-9-week-1-2 - Q2Anna May BuitizonNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Email Works PDFDokument10 SeitenHow Email Works PDFKavya AmmuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Partially Qualified AddressesDokument5 SeitenPartially Qualified AddressesLovekesh BhagatNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Email WorksDokument12 SeitenHow Email WorksRaju SrujanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Purp Com FinalsDokument10 SeitenPurp Com FinalsRaW sTaRNoch keine Bewertungen
- DC 6 PDFDokument8 SeitenDC 6 PDFZain Alabeeden AlarejiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Email HackingDokument96 SeitenEmail HackingGhanshyam SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol What Is SMTP?Dokument6 SeitenSMTP - Simple Mail Transfer Protocol What Is SMTP?haziq raoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding TCP/IP: PC Network AdvisorDokument6 SeitenUnderstanding TCP/IP: PC Network AdvisormiladNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Mail TutorialDokument7 SeitenE Mail TutorialMani KandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- DNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Dokument13 SeitenDNS (Domain Name Service) - TCP and Udp 53: The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)Suraj Singh RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT221 T Project Template - 1444Dokument9 SeitenIT221 T Project Template - 1444Rr rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reading Organizer Answer Key: Name - DateDokument8 SeitenReading Organizer Answer Key: Name - DateSosukeAizenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question 1. What Is An Aws Availability Zone?: AnswerDokument13 SeitenQuestion 1. What Is An Aws Availability Zone?: Answerlkfdsn fdksljflksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Who Owns Global Email System ? Who Sets Email Standards? Who Maintain The Servers? Why Tiqqed ?Dokument9 SeitenWho Owns Global Email System ? Who Sets Email Standards? Who Maintain The Servers? Why Tiqqed ?api-249833795Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mail ServicesDokument40 SeitenMail Servicesk3112724Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Assignment1Dokument46 SeitenCisco Assignment1Dave HartNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications:Electronic Mail (SMTP, Pop, Imap, Mime) : Presented By-Tarun Lall Badrinath Sai Kumar PraveenDokument28 SeitenApplications:Electronic Mail (SMTP, Pop, Imap, Mime) : Presented By-Tarun Lall Badrinath Sai Kumar PraveenkdhanamjayNoch keine Bewertungen
- U5 SMTP Pop ImapDokument35 SeitenU5 SMTP Pop ImapDr.W.Regis Anne - PSGCTNoch keine Bewertungen
- Switched Networks.: Bytes IP AddressDokument12 SeitenSwitched Networks.: Bytes IP AddressTejas SalunkheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Casestudy 3rdIA Mail ArchitectureDokument8 SeitenCasestudy 3rdIA Mail ArchitectureARYA MURALI ECE-2020-24Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Is E Mail?Dokument7 SeitenWhat Is E Mail?Gaurav KulshreshthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practical-1 Email Investigation and IP Tracing: HistoryDokument8 SeitenPractical-1 Email Investigation and IP Tracing: Historydashrath singhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connection Oriented and Connectionless ServicesDokument4 SeitenConnection Oriented and Connectionless ServicesSomnath SinhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is E-Mail?Dokument15 SeitenWhat Is E-Mail?uoksajith_639482650Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Ironport and Exchange 2016Dokument10 SeitenCisco Ironport and Exchange 2016shan1512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 5 Client - Server Model & Network SecurityDokument18 SeitenUnit 5 Client - Server Model & Network Securityall thinks waseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Internet Tools: E-Mail, FTP and TelnetDokument24 SeitenUnit 2 Internet Tools: E-Mail, FTP and TelnetsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Email SecurityDokument9 SeitenSmart Email Securityash_527100% (1)
- UntitledDokument7 SeitenUntitledyeabsera muluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Case StudyDokument10 SeitenComputer Network Case StudyAlan ANoch keine Bewertungen
- Comenzi Linux 2017 EmailDokument6 SeitenComenzi Linux 2017 EmailGabriel AvasiloaeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- E Commerce 3Dokument35 SeitenE Commerce 3premaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MailflowArchitecture ExchangeServerDokument8 SeitenMailflowArchitecture ExchangeServerSaravana KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch2 - Communication and Internet TechnologiesDokument17 SeitenCh2 - Communication and Internet TechnologiesNayu OumiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anarchist Cookbook 2004Dokument12 SeitenAnarchist Cookbook 2004Jagmohan JagguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Addressing NotesDokument5 SeitenInternet Addressing Notestornado2307Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 32 - P2Dokument8 SeitenUnit 32 - P2tahiroheroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Email 2021Dokument3 SeitenEmail 2021MthiSolutionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Telnet: "TELNET Is A General-Purpose Client/server Application Program."Dokument3 SeitenTelnet: "TELNET Is A General-Purpose Client/server Application Program."devendra yadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer:: Browser Add-Ons and ExtensionsDokument5 SeitenAnswer:: Browser Add-Ons and ExtensionsLexy Ira CapaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.4 Electronic Mail in The InternetDokument4 Seiten4.4 Electronic Mail in The Internetsampath998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 2 TCP IpDokument6 SeitenLec 2 TCP IpAli TehreemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internet Operation 2010Dokument8 SeitenInternet Operation 2010dukeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3-Way HandshakeDokument3 Seiten3-Way Handshakem4_prashanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frequently Asked Questions About Hacking and ComputersDokument8 SeitenFrequently Asked Questions About Hacking and Computersravirawat15Noch keine Bewertungen
- SMTPDokument4 SeitenSMTPshenoykunaltanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 11 Electronic Mail OverviewDokument44 SeitenLecture 11 Electronic Mail OverviewDJEFOUO FOUODJI ANGE MAGLOIRE100% (1)
- Computer Networks UNIT 5Dokument21 SeitenComputer Networks UNIT 5thefamousbro123Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Structure of The InternetDokument14 SeitenThe Structure of The InternetAnshulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisVon EverandHacking Network Protocols: Unlocking the Secrets of Network Protocol AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Can’t SEND Email When Away or Abroad? Here’s How 2!Von EverandCan’t SEND Email When Away or Abroad? Here’s How 2!Bewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Evaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsVon EverandEvaluation of Some SMTP Testing, Email Verification, Header Analysis, SSL Checkers, Email Delivery, Email Forwarding and WordPress Email ToolsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Refining Your Internet Search 1Dokument2 SeitenRefining Your Internet Search 1api-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Katie Elliott Newpaper Article DoneDokument2 SeitenKatie Elliott Newpaper Article Doneapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- My Weekend Power PointDokument4 SeitenMy Weekend Power Pointapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- The History of ComputersbetterDokument9 SeitenThe History of Computersbetterapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Qsales 2Dokument1 SeiteQsales 2api-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- RainDokument1 SeiteRainapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- CamperlandDokument1 SeiteCamperlandapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Flyer For Simcoe PartyDokument1 SeiteFlyer For Simcoe Partyapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Buisness EssayDokument8 SeitenBuisness Essayapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Katie Elliott Business LetterDokument1 SeiteKatie Elliott Business Letterapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Elliott Honsco Kennels NewletterDokument1 SeiteElliott Honsco Kennels Newletterapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- All About MeDokument9 SeitenAll About Meapi-254401339Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 10 ExamDokument10 SeitenChapter 10 ExamOngHongTeckNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEEE 802.11 StandardDokument20 SeitenIEEE 802.11 StandarddtygjqdbNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flex ConnectDokument26 SeitenFlex ConnectPadilla Dan JesusNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Review On Industrial Training in Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokument7 SeitenA Review On Industrial Training in Electronics and Communication EngineeringGovardhan NavanandiNoch keine Bewertungen
- IwconfigDokument2 SeitenIwconfigdamionNoch keine Bewertungen
- NLB Core Technology OverviewDokument56 SeitenNLB Core Technology Overviewsanjeev_prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Loon Seminar ReportDokument14 SeitenProject Loon Seminar ReportRajdeep Dodia92% (13)
- SRSP 521 DTT PDFDokument23 SeitenSRSP 521 DTT PDFGodwin Anthony GravadorNoch keine Bewertungen
- AP Discovery of WLCDokument2 SeitenAP Discovery of WLCLucija Fioretti100% (1)
- Cisco 3750 Switch Etherchanel Configuration GuideDokument24 SeitenCisco 3750 Switch Etherchanel Configuration Guidejames opioNoch keine Bewertungen
- SCM - Analog Modulation For 21 Century Digital Content: Cover StoryDokument5 SeitenSCM - Analog Modulation For 21 Century Digital Content: Cover StoryNeeraj RajputNoch keine Bewertungen
- Decentralized 6G Business Models: April 2019Dokument3 SeitenDecentralized 6G Business Models: April 2019Lawyer GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS IS Routing Protocol Part 1 Cheatsheet Network WalksDokument1 SeiteIS IS Routing Protocol Part 1 Cheatsheet Network Walkssridhar reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PRTG Report 2101 - A. Disponibilidad (Ping) - Created 2021-06-02 09-54-16 (2021-05-01 00-00 - 2021-05-31 00-00) UTCDokument2 SeitenPRTG Report 2101 - A. Disponibilidad (Ping) - Created 2021-06-02 09-54-16 (2021-05-01 00-00 - 2021-05-31 00-00) UTCSander SanchezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thin-AP&AC200 Quick Configuration Guide - v1.0Dokument15 SeitenThin-AP&AC200 Quick Configuration Guide - v1.0abdirahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Command Cheat SheetDokument33 SeitenCCNA Command Cheat SheetLumin Han100% (1)
- Mellanox MLNX-OS User Manual For VPI Rev 5.3Dokument1.719 SeitenMellanox MLNX-OS User Manual For VPI Rev 5.3Bart KusNoch keine Bewertungen
- NH BrochuresDokument16 SeitenNH BrochuresKoushik DuttaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Message Service (SMS) Call Flow On RoamingDokument3 SeitenShort Message Service (SMS) Call Flow On RoamingSudharsan Sundar100% (4)
- Netsim: Network Simulation and Emulation SoftwareDokument16 SeitenNetsim: Network Simulation and Emulation SoftwaretamernadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- HP 7700 Access Point Series - 3COM Wireless 7760 11A B G POE AP - SpecificationsDokument4 SeitenHP 7700 Access Point Series - 3COM Wireless 7760 11A B G POE AP - Specificationsedgar7venNoch keine Bewertungen
- Net-Net 4000 S-CX6.3.0 MIB Reference GuideDokument114 SeitenNet-Net 4000 S-CX6.3.0 MIB Reference GuidesuicidemanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Activity: Topology DiagramDokument4 Seiten7.6.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challenge Activity: Topology DiagramAdo PabsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jdsu Ant 5Dokument15 SeitenJdsu Ant 5jalmeida88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Packet DumpDokument2 SeitenPacket Dumpravi.krid1284Noch keine Bewertungen
- 02 575 722 075 DNA A211 I - UserManualDokument103 Seiten02 575 722 075 DNA A211 I - UserManualAditya Guru0% (1)