Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Plan and Use The Distributed Cache Service
Hochgeladen von
davidlam0109Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Plan and Use The Distributed Cache Service
Hochgeladen von
davidlam0109Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
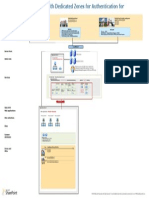
PLANNING AND USING THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE SERVICE
2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. To send feedback about this documentation, please write to us at ITSPDocs@microsoft.com.
Review the
capacity planning
guidance
Output = number of
servers, memory
requirements, and
topology
When using
Virtualization, do
not use dynamic
memory
If server has >= 320
GB of memory, plan
to reconfigure the
memory
The memory allocation for the Distributed
Cache services cache size must be less
than or equal to 16GB on each host, and
the memory allocation of the cache size
must be less than or equal to 40% of the
total memory on the server.
Proceed to install
Output = memory
related tasks to
include in overall
plan
Ensure all servers
running the Distributed
Cache service has the
same amount of
memory
Start
Step 1: Perform
capacity planning
Step 2: Plan your
Memory usage
and
configurations
The Distributed Cache service provides in-memory caching services to several features in SharePoint Server 2013. Some of the features that
use the Distributed Cache service include:
Newsfeeds
Authentication
OneNote client access
Security Trimming
Page load performance
These features use the Distributed Cache for quick data retrieval. The Distributed Cache service stores data in memory and does not have a
dependency on databases in SharePoint Server 2013. However, some SharePoint features may store data in both the Distributed Cache and
databases.
This model describes the planning process, installation steps, and configuration tasks to perform and to implement the Distributed Cache
service in your SharePoint Server 2013 farm. You must do this to ensure that the Distributed Cache service is healthy and supports dependent
services as required. Use this model together with other TechNet content to plan and implement your deployment of the Distributed Cache
service.
PLANNING FOR THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE SERVICE
Planning for the Distributed Cache service helps ensure that the Distributed Cache service remains healthy, and reduces potential issues
on dependent services. When planning for the Distributed Cache service, you should:
Perform capacity planning. When performing capacity planning, you will consider your workload and amount of usage to develop the
capacity recommendations in terms of number of servers, memory requirements, and topology.
Use the capacity planning results to plan which memory configuration works best for your server farm.
1
2
For more information on Capacity Planning Guidance, see 1
2 All servers running the Distributed Cache service must match exactly in terms of total memory specifications on all servers
in the cache cluster.
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=269567
3
3 During installation, 5% of server memory is automatically allocated to the Distributed Cache services cache size. The
maximum amount of memory that can be allocated to the Distributed Cache services cache size is 16GB per cache host in
the server farm. When installing the Distributed Cache service on a server with 320GB of memory, the default memory
assignment for the Distributed Cache services cache size is automatically set to 16GB. For servers with > 320GB of memory,
you must plan to reconfigure the memory allocation of the Distributed Cache services cache size.
4
4 If an administrator allocates more than 16GB of memory to the Distributed Cache services cache size, the server may
unexpectedly stop responding for more than 10 seconds. The recommended minimum total physical memory on the server
that runs the Distributed Cache service is 8GB (this is different from the cache size). If you are using a cache cluster with
more than 1 cache host, ensure the memory allocation for the Distributed Cache service's cache size on each cache host is
set to the same value.
When the Distributed Cache service runs on a server together with other services and the servers memory resources near 95%
utilization, the Distributed Cache will start throttling requests. This means that the Distributed Cache service will no longer accept read or
write requests until the server utilization reduces to approximately 70% utilization.
Consider the following best practices to manage the Distributed Cache service:
Do not run the following services on the same server running the Distributed Cache service: SQL Server, Project Server, Excel
Services and Search services.
Review SharePoint Server 2013's Health Rules for Distributed Cache service issues
Change a non-cache host to a cache host, or a cache host to a non-cache host
Add a new server to the cache cluster
INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE
SERVICE
When installing and configuring SharePoint Server 2013, an administrator must perform certain steps to ensure the Distributed Cache service
is installed and configured correctly.
MAINTAINING THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE
Administrators might need to perform required maintenance and operational tasks to manage their SharePoint Server 2013 deployment. The following flowcharts describe
how to perform some of these maintenance activities as it relates to maintaining the Distributed Cache service.
Start
Download and install the
Windows AppFabric package
on all servers. Use the
recommended cache roles
and the /gac switch
Stop
Installation of all pre-
requisites are complete.
Use the SharePoint Products Configuration Wizard,
psconfig.exe or PowerShell cmdlets without the
/skipRegisterAsDistributedCachehost parameter
Yes (default)
Use PSConfig.exe or PowerShell cmdlets
with the
/skipRegisterAsDistributedCachehost flag
on all servers that are not cache hosts.
No
Use PSConfig.exe or PowerShell cmdlets
without the
/skipRegisterAsDistributedCachehost
flag on all servers which are cache hosts.
Install SharePoint Server
2013
Install
pre-requisites
No
Install remaining pre-requisites
Continue with the
SharePoint Server
2013 configuration
Perform post reconfiguration
checks
ABOUT CACHE HOSTS AND CLUSTERS
ABOUT THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE SERVICE
A cache host is any server in the server farm that runs the Distributed Cache service. A cache cluster exists when one or more servers in the
farm run the Distributed Cache service.
The total cache size for the server farm is the sum of each cache hosts memory allocation for the cache size. The cache clusters cache
spans all cache hosts and saves data on each cache host. Data is not duplicated or copied on other cache hosts in the cache cluster. A
cache cluster cannot be configured for High Availability.
Legend
Are you using
the
pre-requisite
installer?
5
5 For more information on
pre-requisites, see
http://go.microsoft.com/
fwlink/p/?LinkId=269625
Run the Distributed
Cache on all servers
in the farm?
Legend
INCREASING AVAILABLE RESOURCES FOR THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE SERVICE
As your SharePoint Server 2013 farm grows, you might need to increase the resources that are available to the Distributed Cache service by adding another cache
host to the cache cluster. You can do this by either adding a new server to the farm (and the cache cluster), or changing a non-cache host to a cache host. After the
new cache host is added, SharePoint Server will start using and populating the Distributed Cache service with data on the newly added cache host automatically.
This may be a gradual process.
ADDING A NEWSERVER TO THE FARM AND THE CACHE CLUSTER
Start
Download and install the
Windows AppFabric package
on the new server. Use the
recommended cache roles
and the /gac switch
Installation of all pre-
requisites are complete.
Use the SharePoint Products
Configuration Wizard to add the new
server to the farm
Perform post reconfiguration checks
Install SharePoint Server
2013
Install
pre-requisites
Install
remaining
pre-requisites
Stop
6 For more information on pre-requisites, see
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/p/?LinkId=269625
Legend
6
CHANGING A NON-CACHE HOST TO A CACHE HOST
Start
Run the
Add-SPDistributedCacheServiceInstance
cmdlet on the cache host being added
Perform post reconfiguration checks
Stop
Use this procedure if you are adding a new server to the farm, and using it
as a cache host
Use this procedure if the server you want to use as a cache host is
already joined to your server farm.
Are you using
the pre-
requisite
installer?
CHANGING A CACHE HOST TO A NON-CACHE HOST
Use this procedure if you want to change a cache host into a non-cache host.
Start
Run the
Remove-SPDistributedCacheServiceInstance
cmdlet on the cache host you are changing to a
non-cache host
Perform post
reconfiguration checks
Stop
REPAIRING A CACHE HOST
During installation, configuration, or maintenance activities, the Distributed Cache service may enter a non-functioning state. Evidence of a malfunctioning
Distributed Cache service will appear in Health Rules in Central Administration or when users use features in SharePoint Server 2013 that rely on the Distributed
Cache. For example, the Newsfeed on a users My Site will start reporting errors. Use the following procedure to restore a non-functioning Distributed Cache
host.
Start
Run Add-
SPDistributedCacheServiceInstance to
reinstall and start the Distributed Cache
service on the cache host you are
repairing.
Run Get-SPServiceInstance
to list all services for all
servers in the server farm
Note the GUID from the ID
property of the Distributed
Cache service on the server
you are repairing.
Run the PowerShell code
below
Stop
The Get-SPServiceInstance cmdlet lists all services on all
servers in the server farm. Ensure you note the correct GUID
fromthe server you are trying to repair.
$s = get-spserviceinstance GUID
$s.delete()
where GUID is the GUID of the Distributed Cache service running
on the server being repaired.
RECONFIGURING THE MEMORY ALLOCATION
Use this procedure to adjust the cache size of the Distributed Cache service. Use this procedure during initial configuration of the Distributed Cache service, when
changes are made to the total memory on the server, or when a new cache host is added to the server farm. Note: A default of 10% of total memory is assigned to
the Distributed Cache service at installation time. You may want to increase this memory allocation depending on your requirements.
Start Stop
Run the Update-
SPDistributedCacheSize cmdlet on
any cache host
Restart the Distributed Cache
service on all cache hosts
from the Services on Server
page in Central
Administration
Stop the Distributed
Cache service on all cache
hosts from the Services
on Server page in Central
Administration
Other Caches which do not use the Distributed Cache service
Blob Cache. The Blob Cache is a disk-based cache that caches files such as images, JavaScript files, and so on. This cache exists
on each Web Front End server in the farm.
Output cache. The Output Cache is an ASP.NET feature that provides caching functionality. The Output Cache is used to store
frequently-accessed pages as a means of increasing the throughput of the system. On every Web Front End server in the farm, the
Output Cache stores the rendered output of an .aspx web page.
Cache Host Management
Legend
A
B
Yes
No
Yes
INSTALLATION STEPS FOR THE DISTRIBUTED CACHE SERVICE
When installing SharePoint Server 2013, include the steps in this procedure in your overall installation plan.
POST RECONFIGURATION CHECKS
When reconfiguring the Distributed Cache service, perform this procedure to ensure the Distributed Cache service is available.
Start Stop
Repair the cache
host
Stop
On the Services on
Server page in Central
Administration, is the
Distributed Cache
service started on all
cache hosts?
On the Services on
Server page in Central
Administration, is the
Distributed Cache
service started on all
cache hosts?
On all non-cache
hosts, is the
Distributed Cache
service listed on the
Services on Server
page in Central
Administration?
On all non-cache
hosts, is the
Distributed Cache
service listed on the
Services on Server
page in Central
Administration?
Yes Yes
No No
No No
Yes Yes
A
B
Cache Host A
Cache Host
Bs cache
size = 8GB
Cache Host B
Cache Host
As cache
size = 8GB
Server Farm
Cache clusters
cache size for the
entire farm =
16GB
+ =
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Server ChecklistsDokument2 SeitenServer Checklistsdavidlam0109100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Network Dna Network Documentation ChecklistDokument5 SeitenNetwork Dna Network Documentation Checklistdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- APC Symmetra RMDokument64 SeitenAPC Symmetra RMdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brocade - Trouble Shooting and Diagnostic GuideDokument146 SeitenBrocade - Trouble Shooting and Diagnostic GuideuthramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Extranet PDFDokument1 SeiteSps 2013 Design Sample Extranet PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- TestLabGuide IntranetAndTeamSites EbookDokument41 SeitenTestLabGuide IntranetAndTeamSites EbookShashank VeerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Sharepoint 2013Dokument32 SeitenExploring Sharepoint 2013davidlam0109100% (1)
- Subject Alternative Name CertificatesDokument65 SeitenSubject Alternative Name Certificatesdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Monthly Expenses: Income 1 Income 2 Extra Income Total MonthlyDokument1 SeiteMonthly Expenses: Income 1 Income 2 Extra Income Total Monthlydavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- HP Client Manager User GuideDokument57 SeitenHP Client Manager User Guidedavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- MT6570 Android ScatterDokument7 SeitenMT6570 Android ScatterВасилий ИвановNoch keine Bewertungen
- Auto Vba PDFDokument5 SeitenAuto Vba PDFretrueke1170Noch keine Bewertungen
- Hypercard 2Dokument2 SeitenHypercard 2scriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Docker Certified Associate: Training DemoDokument21 SeitenDocker Certified Associate: Training Demoravindramca43382Noch keine Bewertungen
- ShipRight FDA Level 2 FAQDokument11 SeitenShipRight FDA Level 2 FAQnkoreisha7752Noch keine Bewertungen
- Opic: Servlets, XML & AjaxDokument86 SeitenOpic: Servlets, XML & AjaxSE02 Purvesh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- XnView User ManualDokument57 SeitenXnView User ManualAngieNoch keine Bewertungen
- License Plate Recognition Using Training ToolboxDokument13 SeitenLicense Plate Recognition Using Training ToolboxNguyễn Trinh Lan AnhNoch keine Bewertungen
- WCF Rest XML PostDokument3 SeitenWCF Rest XML PostRajesh SamanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Installing Win 7 From PendriveDokument82 SeitenInstalling Win 7 From PendriveOrendro KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps For Programming LPC2129Dokument2 SeitenSteps For Programming LPC2129Koratala HarshaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multicast Impelementations Case Study PDFDokument5 SeitenMulticast Impelementations Case Study PDFOmer GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vmware Validated Design 62 SDDC Architecture Design Vi Workload DomainDokument166 SeitenVmware Validated Design 62 SDDC Architecture Design Vi Workload DomainSarah AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Questions & Answers PDFDokument45 SeitenComputer Questions & Answers PDFSwity SalviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cache Memory and Cache Mapping (Kashavi)Dokument14 SeitenCache Memory and Cache Mapping (Kashavi)Varun BajlotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blackmagic Switchers SDKDokument637 SeitenBlackmagic Switchers SDKyukiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vsphere Esxi 802 Installation Setup GuideDokument268 SeitenVsphere Esxi 802 Installation Setup Guideadam suydamNoch keine Bewertungen
- PS Pulse Connect Secure Software Dates MilestonesDokument3 SeitenPS Pulse Connect Secure Software Dates MilestonesMohamed AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- BTS GT-1 E01 WDokument17 SeitenBTS GT-1 E01 WLugrinderNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Enable Telnet Client in Windows 11 and Server 2022 - Petri IT KnowledgebaseDokument14 SeitenHow To Enable Telnet Client in Windows 11 and Server 2022 - Petri IT KnowledgebasepushpalataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor Exit Exam Reviewer: B. CMC - Complement Carry C. CLD - Clear Direction FlagDokument20 SeitenMicroprocessor Exit Exam Reviewer: B. CMC - Complement Carry C. CLD - Clear Direction Flagpclr07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Configuring Remote Access VPN Via ASDM - Posted - 1!15!09Dokument45 SeitenConfiguring Remote Access VPN Via ASDM - Posted - 1!15!09Mauro GuañoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Event Id - 18Dokument2 SeitenEvent Id - 18Mihai SorescuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Call Manager CUCM RTMTDokument338 SeitenCisco Call Manager CUCM RTMTBinh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced Format Technology - HGSTDokument7 SeitenAdvanced Format Technology - HGSTdrhollywood2001Noch keine Bewertungen
- TMS320C6748 DSP BOARD Package ContentDokument22 SeitenTMS320C6748 DSP BOARD Package ContentPrangya PradhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shihab Saadi ResumeDokument1 SeiteShihab Saadi ResumeMd. Nazmus ShakibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oracle® Database Patch 22191349 - Oracle Grid Infrastructure Patch Set Update 12.1.0.2Dokument7 SeitenOracle® Database Patch 22191349 - Oracle Grid Infrastructure Patch Set Update 12.1.0.2Nageswara DanikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operate A Personal Computer PDFDokument56 SeitenOperate A Personal Computer PDFEdgar G. Dela Rosa0% (1)
- Homogeneous System Copy Using OnlineDokument5 SeitenHomogeneous System Copy Using OnlineasimalampNoch keine Bewertungen