Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Sps 2013 Traditional Topology Model PDF
Hochgeladen von
davidlam01090 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
52 Ansichten1 SeiteThe query processing component in SharePoint 2013 offloads much of the CPU and disk load from SQL Server. The query role can be combined with the web server role on a server only if there are enough resources. The traditional three-tier roles of a SharePoint farmcan be deployed on a single server for evaluation or development, or on many servers.
Originalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
sps_2013_traditional_topology_model.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThe query processing component in SharePoint 2013 offloads much of the CPU and disk load from SQL Server. The query role can be combined with the web server role on a server only if there are enough resources. The traditional three-tier roles of a SharePoint farmcan be deployed on a single server for evaluation or development, or on many servers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
52 Ansichten1 SeiteSps 2013 Traditional Topology Model PDF
Hochgeladen von
davidlam0109The query processing component in SharePoint 2013 offloads much of the CPU and disk load from SQL Server. The query role can be combined with the web server role on a server only if there are enough resources. The traditional three-tier roles of a SharePoint farmcan be deployed on a single server for evaluation or development, or on many servers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
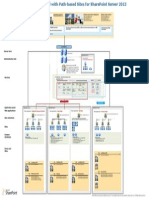
Overview
Topology design principles
Traditional Topologies for SharePoint 2013
Important: The query processing component in SharePoint 2013 offloads much of the CPU and
disk load fromSQL Server. The footprint and performance requirements for SQL Server in
SharePoint 2013 are lower than the previous product version. As a result of this architecture
improvement, the query processing component requires more local resources than previous
versions. The query role can be combined with the web server role on a server only if there are
enough resources. Running both of these roles on a single virtual machine requires a 6-8-core
VMand a physical host that runs Windows Server 2012. A 4-core VMdoes not provide enough
resources for both the query processing component and the Web server role.
Topology concepts for SharePoint 2013
The traditional three-tier roles of a Microsoft
SharePoint 2013 farmcan be deployed on a single
server for evaluation or development, or on many
servers. The three-tier roles include:
Web server role Fast, light-weight server which
responds to user requests for web pages. All web
servers in a farmare mirrors of each other and are
load balanced.
Application server role Provides the service
features of SharePoint products and technologies.
An application server often provides all or a subset
of service features. Multiple redundant application
servers can be load balanced.
Database server role Stores content and service
data. All databases can be assigned to one
database server. Or databases can be spread
across multiple servers. All databases can be
clustered or mirrored for failover protection.
In a small farm, server roles can be combined on one
or two servers. For example, web server and
application server roles can be combined on a single
server or on two or more servers to achieve
redundancy.
Service Applications
Service applications are services that are shared across
sites within a farm (for example, Search and Excel
Services). Some service applications can be shared
across multiple farms.
Service applications are deployed to the application
server tier. Some services include multiple
components, and deployment of these components
requires planning.
Limited deployments are typically used for product
evaluation, development and testing, or for environments
that have limited numbers of users and dont require
fault-tolerance.
This farmillustrates a fully fault-tolerant, virtual environment that includes Office Web Apps Server VMs and a plan for
scaling out databases. This diagramalso calls out all search application roles.
Example topologies
Limited deployments (1-2 servers) Medium farm with Office Web Apps Server and articulated search roles
2013 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. To send feedback about this documentation, please write to us at ITSPdocs@microsoft.com.
For example:
The Search service application includes multiple
application components and multiple databases.
The User Profile service application includes
multiple databases.
Each service application is associated with at least
one service on the Services on Server page in Central
Administration.
Services on the Server
The Services on Server page in Central Administration
lists services that are started or stopped on specific
servers in the farm:
Some of these services are associated with service
applications. After you deploy service applications
to the farm, go to the Services on Server page and
ensure that the associated services are started on
the appropriate servers.
Some of these services are not associated with
service applications.
After you plan the farm topology, see Plan services on
server in the TechNet library to plan the mapping of
services to server applications. Note: To deploy
search components to servers, you use the Search
service application pages in Central Administration
instead of the Services on Server page.
Virtual Topologies
This model provides examples of virtualized
topologies. Virtualized topologies depend on the
capacity of physical hosts, desired ratio or virtual
machines to hosts, and the underlying virtualization
technology.
Database server
In a small farmenvironment, all databases can
be deployed to a single server. In larger
environments, group databases by roles and deploy
these to multiple database servers.
In many farms, all services will run on two
identically configured application servers for
redundancy.
The Search service application automatically
configures the necessary services on application
servers. Using the Services on Server page is
not necessary.
After deployment, look for services that
consume a disproportionate amount of
resources and consider placing these services
on dedicated hardware.
Application server roles
Use the Services on Server page in Central Administration to
assign services to specific application servers.
Hosts web pages, Web services, and Web Parts
that are necessary to process requests served
by the farm.
Directs requests to the appropriate application
servers.
In dedicated services farms, this role is not
necessary because web servers at remote farms
contact application servers directly.
Development Environments
Mimic a three-tier environment by using virtualization.
One-server farm
Evaluation or <100 users
All roles on one
server, including
SQL Server
Host A
Web Server
All Application Server
Roles
Database Server
Two-tier farm
Up to 10,000 users
All Web and
application
server roles
Databases
Host F
All SharePoint Databases
Host E
All SharePoint Databases
Crawl DB
Query Processing
Crawl
Host D
Application Server
Application Server All other
Application Server Roles
Replica
Query Processing
Crawl
Host C
Application Server
Application Server All other
Application Server Roles
Index Partition 0 Replica
SQL Server installed and configured to support SQL clustering, mirroring, or AlwaysOn
across both of the hosts.
Windows Server 2008 R2
Load Balancer
Office Web Apps Server VMs can share the same host as a SharePoint Web or
application server. If more than one Office Web Apps Server VM is included in the
architecture, add a load balancer or configure Application Request Routing in IIS.
The index is stored across replicas.
Each replica for a given index
partition contains the same data. The
data within index replicas is stored in
the file system on the server.
The rest of the search components:
Crawl, Search Admin, Content
Processing Component, Analytics
Processing Component.
Scale out the database layer by first
separating content DBs from services
DBs. The Config DB can share a server
with the content DBs.
Host A
Web
Server
Office
Web
Apps
Server
Host A
Web
Server
Office
Web
Apps
Server
Search Databases
Link DB
Analytics DB
Crawl DB
Admin DB
All other Services DB
Crawl DB
Config DB
Mediumfarmarchitectures can be multi-purpose or optimized for specific purposes.
Medium-size farms are fully fault-tolerant. Some environments might require more web
servers. Factor 10,000 users per web server as a starting point.
Medium farm architectures (6+ servers)
Eight-server physical farmoptimized
for search
Query processing
components and index
components
All Databases
Web Servers
Application servers
running all service
application roles
Six-server physical farm Six-server virtualized farm
Windows Server 2008 R2
Host A
Web Server
Host B
Dedicated
Web Server
for Crawling
Web Server Web Server
Host C
All other
Application
Server Roles
Host D
All other
Application
Server Roles
Query and
Index
Query and
Index
Host E
All
Databases
Host F
All
Databases
SQL Server installed and configured to support SQL clustering,
mirroring, or AlwaysOn. AlwaysOn requires SQL Server 2012.
Small farm architectures serve a larger number of users and scale out based on how heavily services are used. Not all small farms are fault-tolerant.
Small multipurpose farms (3-4 servers)
Smallest fault-tolerant farm utilizing virtualization
All farmserver roles virtualized and distributed across two or four host servers (depending
on the operating system) to provide fault tolerance using the minimum number of servers.
Four-server physical farms
Add a dedicated application server for
environments with moderate service usage.
Three-server virtualized farm
Use virtualization to maximize the potential
of a smaller number of servers.
Two web servers are predicted to serve
10,000-20,000 users.
Host A
All
Application
Server Roles
Host A
All
Application
Server Roles
Web Server Web Server
Request Management does not apply to Office Web Apps Server.
Request Manager runs within SharePoint under SPRequestModule
and responds to HTTP requests only.
To configure Request Manager:
Start the Request Management service on desired web servers.
Configure rules by using Windows PowerShell.
Load Balancer
Web servers
All databases
Application servers
running all other
service application
roles
Query processing
components and
index components
Office Web
Apps Server
farm
Request Management runs
on all web servers in a farm
when in integrated mode
Server Roles
Web server
Smallest fault-tolerant farm
The smallest fully redundant physical farm
incorporates six servers two for each tier.
User requests are automatically load-balanced
across the web servers and application servers
are utilized equally.
For SharePoint 2013, the query processing
component replaces the query role of previous
versions. The query processing component
requires more resources and is not
recommended for web servers unless these are
sized appropriately.
Use SQL Server clustering, mirroring, or
AlwaysOn for the database servers. AlwaysOn
requires SQL Server 2012.
Application servers
running all service
application roles
All databases
Web servers
A search-optimized farm separates the query
processing component and index component
to dedicated application servers. The remainder
of the search components and all other
application roles remain on two all-purpose
application servers.
If crawling is producing more traffic on web
servers than user requests, you can dedicate
one or more web servers for crawling. We
recommend this in environments that crawl
large amounts of data. In SharePoint 2013, it is
not necessary or recommended to configure
affinity for these servers on the load balancer.
Search optimized farm
Web servers
Dedicated
web server
for crawling
All databases
Application servers
running all other
service application
roles
Dedicated application servers
for the query processing
component and the index
component
The distributed cache feature is enabled by
default and the Distributed Cache service is
automatically started on all web and application
servers in a farm. Distributed cache improves
performance by:
Caching social data, such as news feeds.
Caching authentication tokens.
In very large environments distributed cache can
be offloaded to dedicated servers.
Distributed cache
Web servers
All databases
Application servers
running all other
service application
roles
Distributed cache is started
on all Web and application
servers by default.
Query processing
components and index
components
High availability For environments above 1,000 users, two
servers utilizing SQL Server clustering, mirroring, or AlwaysOn
is recommended. AlwaysOn requires SQL Server 2012.
All SharePoint Databases
If fault-tolerance of services is more important than user
performance, configure the farm with redundant
application servers instead of redundant Web servers.
Web/Query server
Application Server
All SharePoint Databases
Application Servers
All SharePoint Databases
Web server
Office Web Apps Server is a separate server product
that can:
Serve multiple SharePoint Server farms for
viewing and editing.
View files from Exchange Server, Microsoft Lync.
Integrate with URL-accessible file servers.
By separating Office Web Apps fromthe SharePoint
farm, servers can be updated more frequently and
scale and performance can be managed
independent of the SharePoint environment. Office
Web Apps Server can be used with all versions of
SharePoint 2013. The Office Web Apps Server
architecture does not include a database.
Office Web Apps Server
Web servers
All databases
Application servers
running all other
service application
roles
Query processing
components and
index components
Office Web
Apps Server
farm
Request Management is a feature that gives SharePoint farms control over
incoming requests and how these are routed. Routing rules are prioritized and
apply logic to determine the nature of requests and to apply the most
appropriate response, such as the following types of actions:
Route requests to web servers that have good health characteristics.
Identify and block known bad requests .
Route requests of specific types (such as search) to specific servers in the farm.
Request management does not replace the role of a load balancer and it is not
enabled by default.
The Request Management component can run in integrated mode on chosen
web servers in a farm. Alternatively, the Request Management component can
run on dedicated servers that are not part of the SharePoint farm.
Integrated mode Request Management runs on the web servers you
choose in a farm. This mode is appropriate for most environments (shown
below).
Dedicated mode Servers in a separate Request Management farmsit
between the hardware load balancer and one or more SharePoint farms. This
mode is appropriate for large-scale environments. With this configuration,
Request Management can serve several SharePoint farms. A Request
Management farmcan be scaled independently based on utilization (not
shown).
Request management and load balancing
Two redundant
database servers
Legend for
database icons
Single database
server
Virtualizing with Windows Server 2008 R2 versus Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012 allows a greater number of resources to be allocated to each virtual machine, and thus allows running a
SharePoint farmwith fewer virtual machines than Windows Server 2008 R2. Due to the virtual architectures that are possible, this
topology model indicates which operating system a virtual topology is designed for.
Windows Server 2008 R2
Host C
All
Databases
Host A
All
Application
Server Roles
Host B
All
Application
Server Roles
Web Server Web Server
SQL Server installed and configured to support SQL
clustering, mirroring, or AlwaysOn. AlwaysOn requires
SQL Server 2012.
Host D
All
Databases
Windows Server 2012
SQL Server installed and configured to support SQL
clustering, mirroring, or AlwaysOn. AlwaysOn requires
SQL Server 2012.
Host A
All
Application
Server Roles
Host B
All
Application
Server Roles
Web Server Web Server
All
Databases
All
Databases
All SharePoint
Databases
Web Servers
Application servers
running all service
application roles
Scaling farms with server groups and storage groups
Sever groups
The recommendation for scaling out a farmis to group services or databases that have
similar performance characteristics onto dedicated servers and then scale out the
servers as a group.
These topology examples group service applications and related components (for
example, databases) into several different logical groupings that can be used as a
starting point. In large environments, the specific groups that evolve for a farmdepend
on the specific demands for each service.
Note: Server groups is a planning concept. This termand concept is not found in Central
Administration.
Scaling out large-size farms
The recommendation for scaling out a large farmis to group service applications, services, or databases that have similar performance characteristics onto dedicated servers and then scale out the
servers as a group. The following topology illustrates a practical example of this concept. The text beloweach group of servers (red text) lists one possible way to build server groups.
As illustrated, the farmon the right is designed to crawl 10 million items (~800 GB of
data). The correlation between items and volume of data will vary depending on the
types of data that are crawled. It is important to understand the characteristics of the
data within the environment. Above 40 million items, consider a dedicated search farm.
The following table provides starting-point numbers for search components based on
number of items.
For more information and examples on scaling search farms, see the following model:
Example Search Architectures for Enterprise Search.
Scaling out search
ANALYTICS
PROCCESING
COMPONENTS
Starting-point numbers for search components based on number of items*
NUMBER
OF ITEMS
General
Guidance
10 million
10-40 million
100 million
INDEX
COMPONENTS
ANDPARTITIONS
QUERY PROCESSING
COMPONENTS
CONTENT
PROCCESING
COMPONENTS
CRAWLERS CRAWL
DATABASES
ANALYTICS REPORTING
DATABASE
SEARCH ADMNISTRATION
COMPONENT
Add 1 index
partition per 10
million items
2 components
1 partition
8 components
4 partitions
20 components
10 partition
Use 2 query processing
components for redundancy.
Above 80 million items, increase
to 4.
2
2
4
2
4
6
2
2
6
LINK
DATABASE
Add 1 crawl
database per 20
million items
1
2
5
Add 1 crawl
database per 60
million items
1
1
2
Add one analytics reporting database for
each 500K unique items viewed each day
or every 10-20M total items
Variable
Variable
Variable
Use 2 search administration components for
redundancy, for all farm sizes
2
2
2
2
2
2
* This guidance is intended for enterprise search within an organization. Guidance for Internet sites is provided in a different document.
Scaling out medium-size farms
Scale out medium-size farms based on the workload. This illustrated mediumserver farmis
scaled to host sites with large amounts of content. Scale the web servers and content
database servers as needed for growth. Scale out all other servers based on the utilization of
other service applications and services within the farmand the volume of content the farm
will host.
Web
Servers
Application
Servers
Database
Servers
Web server group 1
Web servers for all incoming
requests
Dedicated web server(s) for
crawling and administration
Web server group 2
Application server group 1 Application server group 2
Query and index servers All other search components
Application server group 3 Application server group 4
Servers for running sandboxed code All other services (use these servers
for the Central Admin site)
Database group 1 Database group 2 Database group 3
Content databases and configuration
database
All other SharePoint databases Search databases
When scaling out search, typically one index partition is spread across two servers or
VMs. In this configuration, a server or VM hosts only one index replica. Index replicas
for the same partition must run on separate physical hosts (whether virtualized or not)
to achieve fault tolerance. In SharePoint 2013, more index components are required
than query processing components.
Storage groups
Storage groups is a concept in which similar types of databases are grouped together and scaled out independent of the rest
of the databases based on need. All databases within a storage group are treated the same with backup procedures and
restore protocols. The best practice is to include the configuration database with the content database group.
Host B
Application Server - Index
Physical Host 3
Application Server - Index
Index Partition 0 Replica Replica
Application Server - Index Application Server - Index
Index Partition 1 Replica Replica
Physical Host 4
The number of users will affect the requirement for web
servers. Factor 10,000 users per web server as a starting
point. Adjust the number based on how heavily the servers
are utilized. Heavy use of client services will increase the
load on web servers.
Start with two application servers dedicated to the query
processing component and index partitions and place all other
service application components on a separate application
server. Based on utilization, consider either adding all-purpose
application servers that are configured similarly, or adding
application servers to dedicate resources to specific service
applications. For example, if performance data indicates that
Excel Services is using a disproportionate amount of
resources, offload this service to a dedicated server.
When scaling at the database layer, start separating
databases by role. First, separate the content databases
from the rest of the databases (as illustrated). Add database
servers based on the volume of content in your environment
and sizing targets for your organization.
Web servers
Dedicated
web server
for crawling
Database
Servers
Query processing
components and
index components
All other application server
components and services
Content databases All other SharePoint
databases
Medium farm with Office Web Apps Server and articulated search roles
If the cost of server hardware is a limiting factor (as opposed to the cost of licensing), four VMs can be
consolidated onto a single physical host given enough server resources.
Physical Host D
All SharePoint Databases
Physical Host C
All SharePoint Databases
Crawl DB
Application Server
Distribution Service
Application Server All
Application Server Roles
Application Server
Distribution Cache Service
SQL Server installed and configured to support SQL clustering, mirroring, or AlwaysOn
across both of the hosts.
Windows Server 2008 R2
Load Balancer
Physical Host A
Web
Server
Office
Web
Apps
Server
Physical Host B
Web
Server
Office
Web
Apps
Server
Up to four VMs can be combined onto one
physical host if the host has sufficient CPU
cores and RAM.
Dedicated application servers for the
distributed cache service are recommended
in environments that use social features, such
as social feeds and microblogging.
Combining all application server roles onto
one VM requires Windows Server 2012 which
allows a greater amount of resources to be
allocated to individual VMs.
Index Partition 0 Replica 1a Replica 1b
Application Server All
Application Server Roles
Crawl DB Crawl DB
Stretched farms for SharePoint 2013 are supported as of April 2013: Some enterprises have data centers
that are located in close proximity to one another, connected by high-bandwidth fiber optic links. When
this environment is available it is possible to configure the two data centers as a single farm. This
distributed farm topology is called a "stretched" farm. For stretched farm architecture to work as a
supported high availability solution the follow prerequisites must be met:
There is a highly consistent intra-farmlatency of <1ms, 99.9% of the time over a period of ten
minutes. (Intra-farmlatency is commonly defined as the latency between the front-end web servers
and the database servers.)
The bandwidth speed must be at least 1 gigabit per second.
To provide fault tolerance in a stretched farm, use the standard best practice guidance to configure
redundant service applications and databases.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mobile Device Management Guide v9 - 1Dokument217 SeitenMobile Device Management Guide v9 - 1davidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- APC Symmetra RMDokument64 SeitenAPC Symmetra RMdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Path Based Sites PDFDokument1 SeiteSps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Path Based Sites PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- TestLabGuide IntranetAndTeamSites EbookDokument41 SeitenTestLabGuide IntranetAndTeamSites EbookShashank VeerkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Server ChecklistsDokument2 SeitenServer Checklistsdavidlam0109100% (1)
- Neutral Density Calculation TableDokument1 SeiteNeutral Density Calculation Tabledavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Host Named Sites PDFDokument1 SeiteSps 2013 Design Sample Corporate Portal Host Named Sites PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Brocade - Trouble Shooting and Diagnostic GuideDokument146 SeitenBrocade - Trouble Shooting and Diagnostic GuideuthramNoch keine Bewertungen
- Configure and Environment For Apps SharePoint 2013Dokument20 SeitenConfigure and Environment For Apps SharePoint 2013davidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- SPC 2013 Bcs Hybrid Model PDFDokument1 SeiteSPC 2013 Bcs Hybrid Model PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sps 2013 Design Sample Extranet PDFDokument1 SeiteSps 2013 Design Sample Extranet PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Share Point 2013 On Premises SocialDokument1 SeiteShare Point 2013 On Premises Socialdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sps 2013 Streamlined Topology Model PDFDokument1 SeiteSps 2013 Streamlined Topology Model PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sps-2013-Enterprise Farm-Model PDFDokument1 SeiteSps-2013-Enterprise Farm-Model PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sharepoint 2013Dokument674 SeitenSharepoint 2013Euclides Pereira da Silva100% (2)
- Sps 2013 Architecture Overview PDFDokument1 SeiteSps 2013 Architecture Overview PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Svs Single Farm Sharepoint Services 2013 PDFDokument1 SeiteSvs Single Farm Sharepoint Services 2013 PDFdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sp2013 Upgrade Testing XDokument1 SeiteSp2013 Upgrade Testing XplanetsridharNoch keine Bewertungen
- SP2013 AuthenticationDokument1 SeiteSP2013 Authenticationdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Plan and Use The Distributed Cache ServiceDokument1 SeitePlan and Use The Distributed Cache Servicedavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sp2013 Upgrade ProcessDokument1 SeiteSp2013 Upgrade Processdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- SP 2013 Internet Sites Search ModelDokument1 SeiteSP 2013 Internet Sites Search Modeldavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Itpro 2013 DB PosterDokument1 SeiteItpro 2013 DB Posterdavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- SharePoint 2013 End UserDokument90 SeitenSharePoint 2013 End Userdavidlam0109100% (1)
- Oit2013 Model Sharepoint Search ArchitectureDokument1 SeiteOit2013 Model Sharepoint Search Architecturemully31Noch keine Bewertungen
- SP 2013 Enterprise Search ModelDokument1 SeiteSP 2013 Enterprise Search Modeldavidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Global Solutions SharePoint 2013Dokument1 SeiteGlobal Solutions SharePoint 2013davidlam0109Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multi Farm Sharepoint 2013Dokument1 SeiteMulti Farm Sharepoint 2013davidlam0109100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- How Search Engines WorkDokument18 SeitenHow Search Engines WorkEnglish Institute, Training and Grooming centerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Franz Thalmair Curating Medianetart 1Dokument160 SeitenFranz Thalmair Curating Medianetart 1'Leonard RentonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analytics Audit TemplateDokument110 SeitenAnalytics Audit TemplateBuk MarkzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Audit - WWW - Keepemquiet.com - 2021 07 31 - 17 20 00Dokument51 SeitenAudit - WWW - Keepemquiet.com - 2021 07 31 - 17 20 00Nikola NikolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intranet Search EngineDokument31 SeitenIntranet Search EngineTage NobinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Seo CourseDokument427 SeitenSeo CourseMarina ShilovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D SearchingDokument7 Seiten3D Searchingbhagya sri puvvadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- How a search engine works and the most popular optionsDokument3 SeitenHow a search engine works and the most popular optionshantu malamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code: X11182Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Paper Code: X11182Div DeepakNoch keine Bewertungen
- What is SEO & Types of SEO TechniquesDokument11 SeitenWhat is SEO & Types of SEO TechniquesAbhishek Mathur100% (1)
- Effect of Digital Marketing On The Buying Behaviour of The Customers..Dokument98 SeitenEffect of Digital Marketing On The Buying Behaviour of The Customers..deepak GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of Amharic Search Engine: January 2010Dokument9 SeitenDesign and Implementation of Amharic Search Engine: January 2010Henok NegesseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Moz The Beginners Guide To SEODokument54 SeitenMoz The Beginners Guide To SEOPlacement Cell TISS. SENoch keine Bewertungen
- Advanced SEO Interview Questions and AnswersDokument41 SeitenAdvanced SEO Interview Questions and AnswersNirav ThakkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS3308 Information Retrieval QuizDokument63 SeitenCS3308 Information Retrieval QuizMagarsa Bedasa50% (2)
- Web CrawlerDokument16 SeitenWeb Crawlersheoran30% (1)
- Bab #9 Customer Relationship ManagementDokument33 SeitenBab #9 Customer Relationship ManagementShifa Fauzia AfrianneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Web Crawler Assisted Web Page Cleaning For Web Data MiningDokument75 SeitenWeb Crawler Assisted Web Page Cleaning For Web Data Miningtheviper11Noch keine Bewertungen
- TEDAS: A Twitter-Based Event Detection and Analysis SystemDokument4 SeitenTEDAS: A Twitter-Based Event Detection and Analysis SystemYolanda NomokaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 SEO Quirk Textbook 5Dokument18 Seiten9 SEO Quirk Textbook 5studentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Storage and RetrievalDokument5 SeitenData Storage and RetrievalDahlia GamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Comparison of Existing Open-Source Tools For Web Crawling and Indexing of Free MusicDokument6 SeitenComparison of Existing Open-Source Tools For Web Crawling and Indexing of Free MusicJournal of TelecommunicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Reliablesoft - Net) SEO Basics Mini Course 2021Dokument35 Seiten(Reliablesoft - Net) SEO Basics Mini Course 2021Huỳnh Lê Quang ĐệNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS8080 Information Retrieval Techniques Reg 2017 Question BankDokument6 SeitenCS8080 Information Retrieval Techniques Reg 2017 Question BankProject 21-22Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cas Install GuideDokument30 SeitenCas Install GuideManikks ThiruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Itws ManualDokument98 SeitenItws Manualapi-291463406Noch keine Bewertungen
- Literature Review On On-Page & Off-Page SEO For Ranking PurposeDokument5 SeitenLiterature Review On On-Page & Off-Page SEO For Ranking PurposeUIJRT United International Journal for Research & TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mohr Et Al 2004Dokument15 SeitenMohr Et Al 2004neonfirexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importance of Similarity Measures in Effective Web Information RetrievalDokument5 SeitenImportance of Similarity Measures in Effective Web Information RetrievalEditor IJRITCCNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Use Search Engine Optimization Techniques ToDokument17 SeitenHow To Use Search Engine Optimization Techniques ToTháng NămNoch keine Bewertungen