Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Spring Final Review - KEY
Hochgeladen von
Vrinda Dhongle0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten6 SeitenTotal mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of an object is conserved. Find the total mechanical energy at the beginning and that!ill be the total at the end. ". # hot air balloon is hovering in the air!hen it drops a $% &g food package to some lost golfers. #t the end of the 6hock.ave roller coaster ride the 7%%%1kg train of cars is slo!ed from a speed of +% m-s
Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenTotal mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of an object is conserved. Find the total mechanical energy at the beginning and that!ill be the total at the end. ". # hot air balloon is hovering in the air!hen it drops a $% &g food package to some lost golfers. #t the end of the 6hock.ave roller coaster ride the 7%%%1kg train of cars is slo!ed from a speed of +% m-s
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten6 SeitenSpring Final Review - KEY
Hochgeladen von
Vrinda DhongleTotal mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of an object is conserved. Find the total mechanical energy at the beginning and that!ill be the total at the end. ". # hot air balloon is hovering in the air!hen it drops a $% &g food package to some lost golfers. #t the end of the 6hock.ave roller coaster ride the 7%%%1kg train of cars is slo!ed from a speed of +% m-s
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
Name ___________________________ Period _____
Physics: Second Semester Final Exam Review
Conservation of Energy
KEY CONCEP: The total mechanical energy (kinetic + potential) of an object is conserved. Find the total mechanical
energy at the beginning and that !ill be the total at the end.
". # hot air balloon is hovering in the air !hen it drops a $% &g food package to some lost golfers. 'f the package is dropped
from an altit(de of )%% m and air resistance can be neglected ho! fast is the package moving !hen it hits the gro(nd*
!""#$% m&s'
+. Tyler is sliding do!n a frictionless ") m tall hill. ,e starts at the top !ith a velocity of "%.% m-s. .hat is his velocity at the
bottom of the hill* !("#)* m&s'
KEY CONCEP: The !ork re/(ired to change the speed of an object is e/(al to the change in kinetic energy of the object.
That0s the .ork12nergy Theorem. .ork 3 Force 4 distance.
5. #t the end of the 6hock .ave roller coaster ride the 7%%%1kg train of cars (incl(des passengers) is slo!ed from a speed of
+% m-s to a speed of ) m-s over a distance of +% meters. 8etermine the braking force re/(ired to slo! the train of cars by this
amo(nt. !+%*,%$ N'
-oment.m and /m0.lse
KEY CONCEP: Total moment(m is conserved. Force 4 time 3 'mp(lse. 'mp(lse 3 9hange in :oment(m.
". # person on roller blades !ith a mass of ;% kg thro!s a ball !ith a mass of ") kg. The person thro!s the ball !ith a
speed of ).% m-s. .hat is the speed of the person after the ball is thro!n* !+(#$1 m&s'
+. # brake !ith a force of +% Ne!tons is applied for "% seconds to stop a +% kilogram model car moving at 5% meters per
second. .hat is the magnit(de of the imp(lse to stop the car* !,$$ N s'
5. # sticky ball that has a mass of 5 kg is thro!n !ith a velocity of <m-s at a stationary cart that has a mass of "% kg. 'f
the ball sticks to the side of the cart !hat is the moment(m of the t!o objects moving together* !(#)% m&s'
Name ___________________________ Period _____
Sim0le -achines
KEY CONCEP: .ork inp(t is the !ork done by the (ser of the machine. .ork o(tp(t is the !ork accomplished. The
!ork o(tp(t is al!ays less than the !ork inp(t.
". =o( are (sing a lever to lift the edge of a heavy rock in order to slide a roller (nder it. The rock !eighs ))%% N. =o( are
able to e4ert a force of $5% N and move the handle of the lever ".)% meters. The rock lifts a distance of %.%>%% meters.
#) .hat are the inp(t and o(tp(t !ork done* (2in 3 *4% 56 2o.t 3 4"* 5'
?) .hat is the mechanical advantage of the lever* !-7 3 (,#1"'
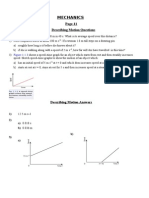
+. # !orker p(shes a )%.%1kg cylinder (p a frictionless incline at constant speed to a height of 51meters. # diagram of the
sit(ation is sho!n at right.
,o! m(ch !ork is done lifting the cylinder (p the 5.%m height* !(41(#% 5'
,o! m(ch force is re/(ired to p(sh the cylinder (p the incline* !,4%#,% N'
,o! m(ch force !o(ld be re/(ired to lift the cylinder !itho(t the ramp* !4"$#% N'
.hat is the mechanical advantage of the ramp* !,'
Circ.lar -otion
KEY CONCEP: @bjects tend to go in a straight line. 'f an object is moving in a circle there m(st be a centripetal force in
the direction of the center of the circle.
". .hich of the follo!ing statements are tr(e of an object moving in a circle at a constant speed* 'ncl(de all that apply.
a. The object e4periences a force !hich has a component directed parallel to the direction of motion.
b. 'nertia ca(ses objects to move in a circle.
c. ?eca(se the speed is constant the acceleration is Aero.
d. The acceleration and the net force vector are directed perpendic(lar to each other.
e. /f the net force acting .0on the o89ect is s.ddenly red.ced to :ero6 then the o89ect wo.ld s.ddenly de0art
from its circ.lar 0ath and travel tangent to the circle.
f. The acceleration of the object is directed tangent to the circle.
+. # race car travels aro(nd a flat horiAontal circ(lar track !ith a radi(s of )%.% meters. The mass of the race car is $%% kg.
The ma4im(m centripetal force the track can e4ert on the tires of the race car is +$%%N. .hat is the ma4im(m speed the
race car can go !itho(t sliding off the track* !(1#;, N'
5. # %.+%%1kg object is tied to the end of a cord and !hirled in a horiAontal circle of radi(s ".+% meters at a constant 5.%
revol(tions-second. Find the acceleration of the object and the tension in the cord. (,intB The tension in the cord is the so(rce
of the centripetal force.) !ac 3 4,*#;1 m&s
,
6 F 3 )%#,1 N'
Name ___________________________ Period _____
Electrostatics
". .hich of the follo!ing are tr(e of static charges* 9hoose all that apply.
a# <i=e charges re0el#
b. @pposite charges repel.
c# 7 0ositively charged o89ect has lost electrons#
d. # positively charged object has gained protons.
e. # negatively charged object has lost protons.
f# 7 negatively charged o89ect has gained electrons#
+. 'dentify the type of charge on objects #1? based on the electric field lines sho!n for each config(ration of charges. =o(r
choices in each case areB positive negative ne(tral.
# _____Positive____________ ? ______Negative________________
5. 'ndicate the final charge on the sphere in each scenario. =o(r choices are positive negative or ne(tral.
a. # positively charged balloon is to(ched to a ne(tral cond(cting sphere and then the balloon is removed. !Positive'
b. # positively1charged balloon is held near a ne(tral cond(cting sphere. The sphere is then to(ched on the opposite side.
!Negative'
c. # negatively1charged rod is held near a ne(tral cond(cting sphere. The sphere is to(ched on the opposite side. !Positive'
Name ___________________________ Period _____
Electric Circ.its
". Find the voltage drop and c(rrent thro(gh each resistor in the
diagram above.
+. Find the voltage drop and c(rrent thro(gh each resistor in the diagram above.
>eat
". 8efine cond(ction convection and radiation and give t!o e4amples of each.
a. cond(ction _______ransfer of heat via direct contact.___________ _______________
___________________________________________________________________________
b. convection ________ ransfer of heat via c.rrents !in fl.ids'# ____________________
___________________________________________________________________________
c.radiation___________ ransfer of heat via electromagnetic waves#________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
+. ,o! many grams of !ater !o(ld re/(ire +.+% 4 "%
$
jo(les of heat to raise its temperat(re from 5$.%C9 to "%%.%C9* The
specific heat of !ater is $."< D-gEC9. !1"#14g'
5. 'f +%%. grams of !ater is to be heated from +$.%C9 to "%%.%C9 to make a c(p of tea ho! m(ch heat m(st be added* The
specific heat of !ater is $."< D-gEC9 !*;%;* 5'
2aves 6 So.nd and <ight Practice F(estionsB
?
,@
3 4?
?
,$@
3 )?
?
($@
3 )?
?
($@
3 )?
/
,@
3 ,7
/
,$@
3 #47
/
($@
3 #)7
/
($@
3 #)7
?
,@
3 *?
?
4@
3 *?
?
*@
3 *?
?
($@
3 *?
/
,@
3 ;7
/
4@
3 (#%7
/
*@
3 (7
/
($@
3 #*7
Name ___________________________ Period _____
". 'f the particles of the medi(m are vibrating to and fro in the same direction of energy transport then the !ave is a ____
!ave.
a# longit.dinal b. so(nd c. standing d. transverse
+. .hen the particles of a medi(m are vibrating at right angles to the direction of energy transport then the !ave is a ____
!ave.
a. longit(dinal b. so(nd c. standing d# transverse
5. 'f the energy in a longit(dinal !ave travels from so(th to north the particles of the medi(m !o(ld be vibrating _____.
a. from north to so(th only 8# 8oth north and so.th
c. from east to !est only d. both east and !est
$. The main factor !hich affects the speed of a so(nd !ave is the ____.
a. amplit(de of the so(nd !ave b. intensity of the so(nd
c. lo(dness of the so(nd d# 0ro0erties of the medi.m
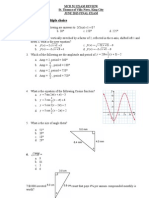
). .hat is the amplit(de of the !ave in the diagram belo!*
a# $#$; m. b. %.%$ m. c. %.%) m. d. %.%7 m.
7. The !avelength of the !ave in the diagram above is ____ m.
a. %.%5% b. %.%$% c. %.%7% d# $#$)$
;. .hy does so(nd diffract more than light does*
a. ?eca(se so(nd comes in many fre/(encies.
8# Aeca.se so.nd has a longer wavelength#
c. ?eca(se so(nd is a longit(dinal !ave.
d. ?eca(se so(nd has a greater amplit(de.
Name ___________________________ Period _____
<. ,o! many complete !aves are sho!n in the diagram above*
a. " b. + c. 5 d# (#%
>. # m(sical tone so(nded on a piano has a fre/(ency of $"% ,A and a !avelength of %.<% m. .hat is the speed of the so(nd
!ave*
a. ";% m-s c# ;;$ m&s
b. +$% m-s d. )>% m-s
"%. 'f yo( hear the pitch of a siren become lo!er yo( kno! that
a. neither yo( nor the siren is moving.
b. yo( are moving to!ard the siren or the siren is moving to!ard yo(.
c. yo( are moving a!ay from the siren or the siren is moving to!ard yo(.
d# the so.rce has 9.st 0assed yo. or it is accelerating away from yo.#
"". 8ra! a diagram to ill(strate each !ave phenomenonB
a. diffraction b. interference c. reflection
Aending of a wave addition & s.8traction of 8o.ncing of a wave off of a
aro.nd a 8arrier wave am0lit.des 8o.ndary or 8arrier
d. refraction e. resonance
Aending of a wave in forced vi8ration at an o89ects nat.ral freB.ency
a new medi.m#
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Mathematical Formula GuideDokument6 SeitenMathematical Formula Guidesayhigaurav07Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3. Technical Measurement and Vectors: Unit ConversionsDokument13 SeitenChapter 3. Technical Measurement and Vectors: Unit ConversionsJose De Jesus SuasteguiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Physics Concepts ExplainedTITLE Understanding Base Quantities and Derived Quantities in PhysicsTITLEGuide to Common Physics Quantities, Units and Measurement TechniquesDokument33 SeitenIntroduction To Physics Concepts ExplainedTITLE Understanding Base Quantities and Derived Quantities in PhysicsTITLEGuide to Common Physics Quantities, Units and Measurement TechniquesMNYNoch keine Bewertungen
- As11 Physics Solved 02 New Sol JVCDokument18 SeitenAs11 Physics Solved 02 New Sol JVCkishor0786Noch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding work, energy, power and efficiencyDokument9 SeitenUnderstanding work, energy, power and efficiencyLeong Mun FaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Expected Model Q.-2010Dokument9 SeitenExpected Model Q.-2010Vaibhav KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EENG350 Lecture Notes Ch4Dokument16 SeitenEENG350 Lecture Notes Ch4yasmin20Noch keine Bewertungen
- Structural Theory 1 (Part 2)Dokument11 SeitenStructural Theory 1 (Part 2)GinoOcampoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic CircuitsDokument18 SeitenMagnetic CircuitsNeedSolutionManualsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2: 1-D Kinematics: Velocity & Acceleration Hints & Answers. - Updated 9/6/11Dokument8 SeitenChapter 2: 1-D Kinematics: Velocity & Acceleration Hints & Answers. - Updated 9/6/11Jackie Swift FuntanillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Experiment 7: Uniform Circular Motion: PurposeDokument5 SeitenExperiment 7: Uniform Circular Motion: PurposeVince Rabin CandidatoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment #3B: Hydrometer AnalysisDokument5 SeitenLab Experiment #3B: Hydrometer AnalysishamiddinkomaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design of ShaftsDokument6 SeitenDesign of ShaftsamdevaNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Am Trying To Design A Bus Brace For A 3 Phase Busbar SyatemDokument9 SeitenI Am Trying To Design A Bus Brace For A 3 Phase Busbar SyatemSanjeewa HemaratneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vojislav Gligorijevic, Jovan Stepanovic, Vasilije Petrovic, Petar StojanovicDokument8 SeitenVojislav Gligorijevic, Jovan Stepanovic, Vasilije Petrovic, Petar StojanovicProf.dr Vojislav GligorijevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 1 Final ExamDokument7 SeitenPhysics 1 Final ExamRaul B. GironellaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rollercoaster Web Quest WorksheetDokument3 SeitenRollercoaster Web Quest WorksheetDaniel Toberman0% (1)
- Exam Review Word Sph4u1Dokument60 SeitenExam Review Word Sph4u1Johnny Jany100% (1)
- Continuous Comprehensive EvaluationDokument12 SeitenContinuous Comprehensive EvaluationsumikannuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Projectile Motion Study Guide Academic AnswersDokument5 SeitenProjectile Motion Study Guide Academic AnswersJennifer JiangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations GuideDokument28 SeitenSimple Harmonic Motion and Oscillations Guideshinichi_kesian6117Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 03Dokument6 SeitenChapter 03Ishtpreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Mechanics - Question BankDokument14 SeitenEngineering Mechanics - Question BankNishant B MayekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jhorne The Gas-O-Meter 050414Dokument12 SeitenJhorne The Gas-O-Meter 050414api-252669940Noch keine Bewertungen
- MrJacksonMaths Foundation Calculator Paper IDokument20 SeitenMrJacksonMaths Foundation Calculator Paper IRussell JacksonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab ManualDokument58 SeitenPhysics Lab ManualREDDYGAARI ABBAYINoch keine Bewertungen
- Emath and Amath FormulaDokument21 SeitenEmath and Amath FormulaveryveryhappyfeetNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matriculation Physics Electromagnetic InductionDokument96 SeitenMatriculation Physics Electromagnetic Inductioniki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering mechanics statics and dynamics conceptsDokument6 SeitenEngineering mechanics statics and dynamics conceptspvnandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab Report.Dokument23 SeitenPhysics Lab Report.Muhammad Sohag HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hardware Components and Sensors for Industrial AutomationDokument6 SeitenHardware Components and Sensors for Industrial AutomationJAIN2013Noch keine Bewertungen
- MrJacksonMaths Higher Non Calc Paper 1Dokument21 SeitenMrJacksonMaths Higher Non Calc Paper 1Russell Jackson100% (2)
- Two MarkDokument6 SeitenTwo MarkpvnandhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher GuideDokument20 SeitenChapter 1 Introduction To Physics Teacher GuideShu85Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics P3 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangDokument10 SeitenPhysics P3 SPM 2014 A Modul Melaka GemilangCikgu FaizalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tranophysintlab 2 ReportfinalDokument9 SeitenTranophysintlab 2 Reportfinalapi-249588785Noch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's Laws and Physics ProblemsDokument10 SeitenNewton's Laws and Physics ProblemsRonel ViolantaNoch keine Bewertungen
- UD 6 Mechanisms - Gears and Pulleys.Dokument10 SeitenUD 6 Mechanisms - Gears and Pulleys.Sergio Ruiz ArranzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applications of The Derivative Test NameDokument5 SeitenApplications of The Derivative Test NameAkhil RajNoch keine Bewertungen
- (Lecture 1) Translational MotionDokument16 Seiten(Lecture 1) Translational MotiondropgorgeousNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCR3U Exam Review 2013Dokument9 SeitenMCR3U Exam Review 2013Hari MenonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ithaca College Math Day Competition MARCH 31, 2008Dokument6 SeitenIthaca College Math Day Competition MARCH 31, 2008Prashant JainNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. Inversely As The Square ofDokument6 SeitenB. Inversely As The Square ofcielo_cetd367067% (3)
- Short CircuitDokument40 SeitenShort Circuitrajpre1213Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ch#4 Work and EnergyDokument16 SeitenCh#4 Work and Energysmart5733Noch keine Bewertungen
- As Unit 1 Student Book Question & AnswerDokument18 SeitenAs Unit 1 Student Book Question & Answernicky1213aNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kertas Soalan Ini Mengandungi 50 SoalanDokument27 SeitenKertas Soalan Ini Mengandungi 50 SoalanKhushdaveSandhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- INDIAN INSTITUTE OF REMOTE SENSING EDUSAT BASED COURSE ON RS, GIS AND GPS EXAMINATIONDokument10 SeitenINDIAN INSTITUTE OF REMOTE SENSING EDUSAT BASED COURSE ON RS, GIS AND GPS EXAMINATIONNitin MadeshiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1 (Introduction To Science)Dokument6 SeitenModule 1 (Introduction To Science)Ashley OliverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics 30 Lesson 1-8 Review: Key ConceptsDokument4 SeitenPhysics 30 Lesson 1-8 Review: Key Conceptsi5piritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Forced Vibrations With Negligible Damping: I-IntroductionDokument9 SeitenForced Vibrations With Negligible Damping: I-IntroductionNevil JohnsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roof Integrated Solar Parabolic Collectors Simulation AnalysisDokument6 SeitenRoof Integrated Solar Parabolic Collectors Simulation AnalysisTri Septian MarsahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Λύση του 5 Χ 5 Χ 5 κύβου του ΡούμπικDokument11 SeitenΛύση του 5 Χ 5 Χ 5 κύβου του ΡούμπικTheodore HaralabisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report On CutchDokument19 SeitenProject Report On CutchMeghal VadhvanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Constant Acceleration in Linear MotionDokument11 SeitenConstant Acceleration in Linear MotionAlvin CabalquintoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Workbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringVon EverandWorkbook to Accompany Physics for Students of Science and EngineeringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyVon EverandWatch and Clock Escapements A Complete Study in Theory and Practice of the Lever, Cylinder and Chronometer Escapements, Together with a Brief Account of the Origin and Evolution of the Escapement in HorologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsVon EverandMechanics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Singular Points of Complex Hypersurfaces (AM-61), Volume 61Von EverandSingular Points of Complex Hypersurfaces (AM-61), Volume 61Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ap10 Comp Sci A Scoring GuidelinesDokument11 SeitenAp10 Comp Sci A Scoring GuidelinesVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linked List PDFDokument1 SeiteLinked List PDFVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Linked List PDFDokument1 SeiteLinked List PDFVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAT 2 Subject TestsDokument334 SeitenSAT 2 Subject TestsJen Elendu100% (5)
- Walker3 Lecture Ch12Dokument34 SeitenWalker3 Lecture Ch12Vrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write A Killer Sat Essay in 25 MinutesDokument24 SeitenHow To Write A Killer Sat Essay in 25 Minutesstudents00767% (3)
- How To Write A Killer Sat Essay in 25 MinutesDokument24 SeitenHow To Write A Killer Sat Essay in 25 Minutesstudents00767% (3)
- Linked List PDFDokument1 SeiteLinked List PDFVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Super Teacher Worksheets - : Charleston, WV Indianapolis, INDokument1 SeiteSuper Teacher Worksheets - : Charleston, WV Indianapolis, INVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Facts and Formulas 0Dokument6 SeitenFacts and Formulas 0mamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily CRDokument1 SeiteDaily CRVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- DBQArticles of ConfederationDokument3 SeitenDBQArticles of ConfederationVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read The Following SAT Test Question and Then Click On A Button To Select Your AnswerDokument3 SeitenRead The Following SAT Test Question and Then Click On A Button To Select Your AnswerVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2005 DBQDokument3 Seiten2005 DBQVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- ReconstructionDokument6 SeitenReconstructionVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation Revealed in Document 1Dokument1 SeiteWeaknesses of the Articles of Confederation Revealed in Document 1Vrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iss Pyaar Ko Kya Naam Doon LyricsDokument1 SeiteIss Pyaar Ko Kya Naam Doon LyricsVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1: The BeginningsDokument20 SeitenChapter 1: The BeginningsVrinda Dhongle100% (2)
- America Scholar SummaryDokument2 SeitenAmerica Scholar SummaryVrinda Dhongle100% (2)
- Import Public Class Private Int Private Int Private New PublicDokument3 SeitenImport Public Class Private Int Private Int Private New PublicVrinda DhongleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand Out Fortran 77Dokument3 SeitenHand Out Fortran 77Dj XperiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Common Technical DocumentDokument19 SeitenCommon Technical DocumentrandatagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Bank NACPDokument12 SeitenQuestion Bank NACPManoj MathewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multimedia Commnication Unit 4 VTUDokument41 SeitenMultimedia Commnication Unit 4 VTUraghudathesh100% (1)
- Joaquin Marro, Ronald Dickman-Nonequilibrium Phase Transitions in Lattice Models (Collection Alea-Saclay - Monographs and Texts in Statistical Physics) (2005) PDFDokument343 SeitenJoaquin Marro, Ronald Dickman-Nonequilibrium Phase Transitions in Lattice Models (Collection Alea-Saclay - Monographs and Texts in Statistical Physics) (2005) PDFTainã LaíseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Application Guidelines Kinross Tasiast Graduate Program July 2017Dokument6 SeitenApplication Guidelines Kinross Tasiast Graduate Program July 2017Touil HoussemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sptve: Business Math 7Dokument10 SeitenSptve: Business Math 7KissieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oral Com ReviewerDokument20 SeitenOral Com ReviewerEd JayNoch keine Bewertungen
- MoleDokument3 SeitenMoleRosita CayananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trainee Progress ChartDokument3 SeitenTrainee Progress ChartClark LlameraNoch keine Bewertungen
- LMI - PID-Robust PID Controller Design Via LMI Approach - (Ge2002)Dokument11 SeitenLMI - PID-Robust PID Controller Design Via LMI Approach - (Ge2002)PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- NXD 8.0 English ManualDokument36 SeitenNXD 8.0 English ManualFrancis Mark Bugayong33% (3)
- Cad StandardDokument4 SeitenCad StandardTony MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 123456Dokument2 Seiten123456Dianna Tercino IINoch keine Bewertungen
- Remedial Training Assignment WorksheetDokument2 SeitenRemedial Training Assignment WorksheetElmer D. PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- SteeringSensor RevA7Dokument6 SeitenSteeringSensor RevA7eng_moh04Noch keine Bewertungen
- Math 110: Linear Algebra Homework #4: David ZywinaDokument9 SeitenMath 110: Linear Algebra Homework #4: David ZywinaCody SageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbohydrate Polymers: Sara R. Labafzadeh, Kashmira Vyavaharkar, Jari S. Kavakka, Alistair W.T. King, Ilkka KilpeläinenDokument7 SeitenCarbohydrate Polymers: Sara R. Labafzadeh, Kashmira Vyavaharkar, Jari S. Kavakka, Alistair W.T. King, Ilkka KilpeläinenAbiCorreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADE 5 - Pointers To Review GRADE 5 - Pointers To Review: Computer - 5 Computer - 5Dokument2 SeitenGRADE 5 - Pointers To Review GRADE 5 - Pointers To Review: Computer - 5 Computer - 5Leizle Ann BajadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Morphophonemic Analyis of Tiv Loan Words by Dyako Aondonguter LeoDokument13 SeitenMorphophonemic Analyis of Tiv Loan Words by Dyako Aondonguter LeoDyako LeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Discrete Math NotesDokument454 SeitenDiscrete Math NotesDevesh Agrawal0% (1)
- Psycho Analysis LacanDokument155 SeitenPsycho Analysis LacanVar Stephens19% (16)
- Cross Platform Migration of Oracle Application R12 On Solaris 10 To AIX 6.1Dokument2 SeitenCross Platform Migration of Oracle Application R12 On Solaris 10 To AIX 6.1sachinappsdbaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Juevenile Delinquency Caused by Broken HomesDokument2 SeitenJuevenile Delinquency Caused by Broken HomesJulienne ZabalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MillDokument4 SeitenMillDlorrej OllamNoch keine Bewertungen
- AdvancedDokument173 SeitenAdvancedHein SanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson Plan Guide: Tennessee State Standard(s)Dokument4 SeitenLesson Plan Guide: Tennessee State Standard(s)api-428458364Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mike Smith-DataGuard TuningDokument55 SeitenMike Smith-DataGuard TuningCésar Pérez AvilezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mindray BC-760 and BC-780 series hematology analyzer installation reportDokument9 SeitenMindray BC-760 and BC-780 series hematology analyzer installation reportAndi UkengNoch keine Bewertungen
- EAPP Teacher's Guide PDFDokument207 SeitenEAPP Teacher's Guide PDFMary Grace Sagun40% (5)