Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Circular Motion2
Hochgeladen von
Rashid Azeem RafhaCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Circular Motion2
Hochgeladen von
Rashid Azeem RafhaCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CIRCULAR MOTION
- A type of motion exhibited by bodies
following a circular/curved path.
- Motion caused by centripetal force.
Related Terms:
Rotation motion about an internal axis
Revolution motion about an external axis
The earth revolves around the sun. It takes
earth a year to complete one revolution around
the sun.
To differentiate, for example:
The earth rotates on its own axis. This is the
reason why we are experiencing night and day.
Basic Rotational Quantities
The angular displacement is
defined by:
For a circular path it follows
that the angular velocity is
and the angular acceleration is
where the acceleration here is
the tangential acceleration.
Basic Rotational Quantities
Angular velocity
can be considered to
be a vector quantity,
with direction along
the axis of rotation in
the right-hand rule
sense.
Angular velocity
For an object rotating about an axis, every point on the
object has the same angular velocity. The tangential
velocity of any point is proportional to its distance from
the axis of rotation. Angular velocity has the units rad/s.
Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular
displacement and can be described by the relationship
1. What is the angular velocity in rad/s of the
second hand of a watch?
Sample Problem:
Answer: = 2rad / 60s = 0.10 rad/s
2. A bicycle travels 141 m along a circular track
of radius 15 m. What is the angular
displacement in radians of the bicycle from its
starting position?
Answer: = 141m / 15m = 9.4 rad
Centripetal Force
Any motion in a
curved path represents
accelerated motion, and
requires a force directed
toward the center of
curvature of the path.
This force is called the
centripetal force which
means "center seeking"
force.
where:
m = mass of the object
v = tangential velocity
r = radius of the curved
path
Centripetal Force
The straight line motion in the absence of the
constraining force (tension) is an example of
Newtons first law of motion.
Centripetal Acceleration
The centripetal acceleration can be derived for the
case of circular motion since the curved path at any point
can be extended to a circle.
Centripetal Acceleration
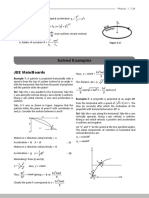
Problem 3:
A 200g object is tied to the end of a cord and
whirled in a horizontal circle of radius 1.20m at
a constant 3.0 rev/s. Assume that the cord is
horizontal, determine:
(a) the acceleration of the object; and
(b) the tension in the cord.
2 2
2
) / 6 )( 20 . 1 ( s rad m r
r
v
a
c
T [ ! ! !
Solution 3:
a. The object is not accelerating tangentially to
the circle but is undergoing a radial or
centripetal acceleration:
2
2
[ r
r
v
a
c
! !
2
/ 426 s a
c
!
where must be in rad/s, then, 3.0 rev/s = 6.0rad/s
b. To cause the acceleration found in (a), the
cord must pull on the 0.20 kg mass with a
centripetal force:
) / 426 )( 20 . 0 (
2
s m kg ma F
c c
! !
N F
c
85 !
This is the tension in the cord.
Centripetal force on banked highway
curve
The centripetal force is
proportional to the square
of the velocity, e.g.
doubling of speed will
require four times the
centripetal force to keep
the motion in a circle.
If centripetal force must
be provided by friction
alone on a curve, an
increase in speed could
lead to an unexpected skid
if friction is insufficient
Working Equations:
Since centripetal force is provided by friction
If F
f
= F
N
and F
N
= mg, then
The minimum speed required to make a turn
r
mv
F F
f c
2
! !
r
v
g
2
! Q
gr v Q !
Also, the equation of = tan, therefore:
r
v
g
2
) ( tan ! U
gr
v
2
1
tan
! U
where is the banking angle.
A car enters a horizontal, curved
roadbed of radius 50 m. The coefficient of
static friction between the tires and the
roadbed is 0.20. What is the maximum
speed with which the car can safely
negotiate the unbanked curve?
Problem 4:
) 50 )( 8 . 9 )( 20 . 0 ( ! ! gr v Q
Solution:
s v / 89 . 9 !
Determine the minimum angle at which a
roadbed should be banked so that a car
traveling at 20m/s can safely negotiate the
curve if the radius of the curve is 200m.
Problem 5:
Solution:
) 200 )( 8 . 9 (
) 20 (
tan tan
2
1
2
1
! !
gr
v
U
r ! 5 . 11 U
Motion in a Vertical Circle
Motion in a Vertical Circle
The motion of a mass on a string in a vertical
circle includes a number of mechanical concepts.
1. It must satisfy the constraints of centripetal
force to remain in a circle,
2. It must satisfy the demands of conservation
of energy as gravitational potential energy is
converted to kinetic energy when the mass
moves downward.
3. The velocity must increase as the mass
moves downward from the top of the circle,
subject to the constraints stated.
Motion in a Vertical Circle
Using the centrifugal force conditions, the
tension at the bottom can be related to the
tension at the top:
A 0.75-kg ball is attached to a 1.0-m rope and
whirled in a vertical circle. The rope will break
when the tension exceeds 450 N. What is the
maximum speed the ball can have at the bottom
of the circle without breaking the rope?
Problem 6:
Solution:
mg
r
v m
T
bottom
bottom
!
2
) (
? A
s m v / 24
75 . 0
) 1 ( ) 8 . 9 )( 75 . 0 ( ) 450 (
!
!
Circular Orbit
The force of gravity in keeping an object in
circular motion is an example of centripetal force.
Since it acts always perpendicular to the motion,
gravity does not do work on the orbiting object if it is
in a circular orbit.
What is the acceleration due to gravity at
an altitude of 1.00 10
6
m above the
earth's surface? (Note: the radius of the
earth is 6.38 10
6
m.)
Problem 7:
Solution:
2
6 6
6
2
) 10 38 . 6 10 1 (
10 38 . 6
) 8 . 9 (
!
x x
x
r
R
g g
planet
surface orbit
2
/ 32 . 7 s m g
orbit
!
Assignment:
1. In an amusement park ride, a small child
stands against the wall of a cylindrical
room that is then made to rotate. The
floor drops downward and the child
remains pinned against the wall. If the
radius of the device is 2.15 m and the
relevant coefficient of friction between
the child and the wall is 0.400, with what
minimum speed is the child moving if he
is to remain pinned against the wall?
2. An indoor track is to be designed such
that each end is a banked semi-circle with
a radius of 24 m. What should the
banking angle be for a person running at
speed v = 6.0 m/s?
3. Outdoor Activity in Motion
- tell your experience about motion in an
amusement park.
- include your picture in motion
- written output must be 1-2 pages only and
must be compiled by group (lab. group) in
a clear book
- deadline: before midterm exam
- other option: experience motion within
your vicinity
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Seekers Journey - GregTurekDokument100 SeitenA Seekers Journey - GregTurekseeker33Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Amitabha Ghosh-Origin of Inertia - Extended Mach's Principle and Cosmological Consequences-Apeiron (2000) PDFDokument161 SeitenAmitabha Ghosh-Origin of Inertia - Extended Mach's Principle and Cosmological Consequences-Apeiron (2000) PDFderaj1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Speed Velocity and AccelerationDokument73 SeitenSpeed Velocity and AccelerationArth LubayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astronomy - Chapter 18 TestDokument36 SeitenAstronomy - Chapter 18 TestJ. R. Silvey100% (2)
- 00b.types of MotionDokument4 Seiten00b.types of Motionaldy faleraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4Dokument23 Seiten4api-254547723Noch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Physics 1: Brwebberandchwbarnes Michaelmas Term 2008Dokument73 SeitenTheoretical Physics 1: Brwebberandchwbarnes Michaelmas Term 200821260paco61Noch keine Bewertungen
- Free Fall and Motion PDFDokument36 SeitenFree Fall and Motion PDFMark Francis HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- WudkaGR 7Dokument48 SeitenWudkaGR 7Pranalistia Tiara PutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDokument17 SeitenChapter 3 DynamicsTutor_KLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motion in A Plane: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedDokument10 SeitenMotion in A Plane: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedAnchitBansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basics of Biomechanics PDFDokument228 SeitenBasics of Biomechanics PDFVarun Kumar100% (1)
- Experiment 02: Objective ApparatusDokument7 SeitenExperiment 02: Objective ApparatusMuhammad HamzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rotational MechanicsDokument25 SeitenRotational MechanicsUjib DamianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Science Questions - Physics Velocity and AccelerationDokument5 SeitenPractice Science Questions - Physics Velocity and Acceleration김재명Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ygiel - Spacetime in The Perspective of The Theory of Quantum GravityDokument18 SeitenYgiel - Spacetime in The Perspective of The Theory of Quantum GravityCopernicus Center for Interdisciplinary StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flywheel ApparatusDokument15 SeitenFlywheel ApparatusFrank.JNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Relativity and Cosmology by GibbonsDokument64 SeitenGeneral Relativity and Cosmology by GibbonsSidhartha SamtaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temario OLUF 2018 EnglishDokument7 SeitenTemario OLUF 2018 EnglishMihyun KimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Special Relativity EbookDokument99 SeitenSpecial Relativity Ebookapi-18367735Noch keine Bewertungen
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4th Edition Knight Test Bank 1Dokument36 SeitenPhysics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4th Edition Knight Test Bank 1kimberlysheltonoagfzwcndy100% (26)
- UniverseDokument265 SeitenUniverseAmit UpadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
- ,, Understanding Work Energy - Power and EfficiencyDokument10 Seiten,, Understanding Work Energy - Power and EfficiencymynameiseyzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Black Hole Lectures (GR)Dokument39 SeitenBlack Hole Lectures (GR)সায়ন চক্রবর্তীNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 11 Physics 1st Unit Test 2021Dokument3 SeitenClass 11 Physics 1st Unit Test 2021Academics AITNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Circular Motion Tutorial SolutionsDokument6 Seiten06 Circular Motion Tutorial SolutionsMe4d SHiV23Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1Dokument7 Seiten1Argie AdduruNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions and SolutionsDokument47 SeitenQuestions and SolutionssonuvuceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 6 WSDokument34 SeitenChapter 6 WSsuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 37 RelativityDokument39 Seiten37 RelativityAdam100% (1)