Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Head and Face 2003
Hochgeladen von
Hamza KayssarCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Head and Face 2003
Hochgeladen von
Hamza KayssarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Head and Face
Head and Face
Laura Thurmond
Laura Thurmond
Amy Walker
Amy Walker
Ross Bailey
Ross Bailey
Dr. Joe
Dr. Joe
Milne
Milne
Facial, Eye and Dental
Facial, Eye and Dental
Trauma
Trauma
Cranial Vault
Cranial Vault
One frontal
One frontal
Two sphenoid
Two sphenoid
Two parietal
Two parietal
One occipital
One occipital
Also called the
Also called the
skull
skull
Strongest skull
Strongest skull
bone is the
bone is the
occipital and the
occipital and the
weakest is the
weakest is the
temporal
temporal
The skull reaches
The skull reaches
90% of its ultimate
90% of its ultimate
size by age 5
size by age 5
*Magee,67
*Magee,67
Facial Bones
Facial Bones
14 total facial
14 total facial
bones
bones
Most important
Most important
:
:
Maxilla
Maxilla
Mandible
Mandible
Nasal Bones
Nasal Bones
Palatine
Palatine
Lacrimal
Lacrimal
Zygomatic
Zygomatic
Ethmoid
Ethmoid
60% of the
60% of the
Ultimate size is
Ultimate size is
reached by age
reached by age
6
6
Zygomatic bone
Zygomatic bone
provides for the
provides for the
prominence of
prominence of
the cheek
the cheek
Cranial Vault and Facial Bones
Posterior View of the Cranial Vault
Facial Skull Cavities and
Facial Skull Cavities and
Sinuses
Sinuses
Cavities
Cavities
Orbital
Orbital
Nasal
Nasal
Oral
Oral
Sinuses
Sinuses
Frontal
Frontal
Ethmoid
Ethmoid
Maxillary
Maxillary
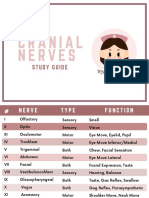
Cranial Nerves
Cranial Nerves
Olfactory Olfactory: smell : smell
Optic Optic: sight : sight
Oculomotor Oculomotor: eye muscles : eye muscles
Trochlear Trochlear: eye muscles : eye muscles
Trigeminal Trigeminal: facial sensation : facial sensation
Abducens Abducens: eye muscles : eye muscles
Facial Facial: facial movement : facial movement
Vestibulocochlear Vestibulocochlear: :
equilibrium and hearing equilibrium and hearing
Glossopharyngeal Glossopharyngeal: throat : throat
movement and sensation movement and sensation
Vagus Vagus: pharyngeal muscles : pharyngeal muscles
Accessory Accessory: turns head right : turns head right
and left and left
Hypoglossal Hypoglossal: tongue : tongue
movement movement
Cranial Vault and Facial
Cranial Vault and Facial
Muscles
Muscles
Cranial Vault
Cranial Vault
Frontalis
Frontalis
Temporalis
Temporalis
Occipitalis
Occipitalis
Facial
Facial
Orbicularis Oculi
Orbicularis Oculi
Orbicularis Oris
Orbicularis Oris
Zygomaticus Major
Zygomaticus Major
and Minor
and Minor
Masster
Masster
Depressor Anguli Oris
Depressor Anguli Oris
Buccinator
Buccinator
Anterior View: Cranial vault and
Facial Muscles
Lateral View: Cranial Vault and
Facial Muscles
Eye Anatomy
Eye Anatomy
Eyes
Our most important sensory organ
Foreign bodies in the eye
1. Non penetrating
May be washed out naturally with the tear
duct system, however, the upper lid may
need to be reversed and then the eye must
be Irrigated with sterile saline.
The cornea or conjunctiva may become
abraded or cut as a result of a foreign body
rubbing between the lid and the eye itself.
This type of wound is examined best under a uv
light with The surface of the eye stained with a
Fluor-I-Strip
[ sodium Fluorescein ]. This will indicate the
location and size of the Abrasions] is present. The
eye should be patched using a moist Sterile eye
patch and treated with optic antibiotics.
[ physician Required ].
The abrasion shows up as green, the dye penetrates
the abrasion and remains. It turns bright green
under UV light
Penetrating eye injuries
Never attempt to remove an object
that has penetrated the surface of
the cornea or conjunctiva and
especially any object that has
penetrated into the lens or posterior
chamber of the eye [ vitreous ]
This should be treated by covering
both eyes and transporting.
Contusions
Levator palpebrae contusion
This muscle elevates the upper lid
and can be contused when poked
or jabbed by a finger. Patching of
the eye and treating like a soft
tissue injury will usually result in
good results with 2-3 days.
Contusion of eye - patient was wearing glasses
Black Eye with associated laceration
Subconjunctival hematoma
While this condition is often very
noticeable, it is a condition that does
not require any care. It is caused by a
rupture of one of the small
superficial blood vessels.
Hyphemia - anterior chamber
contusion
This results from blunt trauma such as getting hit with a
ball or being stuck in the eye with a finger
Blood collects between the lens and the cornea. Visual
acuity may be reduced. This is a condition that can
become serious, and an ophthalmologist should always
be consulted. A secondary finding often associated with
this involves hypoglacoma in which the pressure in the
eye is reduced and this can lead to disruption of the
retina. Treatment involves bed rest.
Hemorrhage into the posterior
chamber
If there is considerable bleeding into the
globe, the eye may be tinted red with the
red reflex lost. This is when the eye shows
as red when examined with a light. This is
a serious injury and should be referred
quickly.
Hyphema Blood in the Anterior Chamber
Detached retina
The patient will report sights such as a
curtain fell over part of my eye and of
floaters, objects that come and go into the
field of vision. This condition should be
referred.
Retinal Detachment
Chemical burns to the eye
The only treatment that can be done is to wash
the eye and dilute the chemical. The patient
should then be referred to the ER and or
physician.It is important to know that
chemicals got into the eye. (product labels)
31,000 Eye Injuries in sport each year.
TABLE 1. 1998 Sports and Recreational Eye Injury Estimates by Age-Group and Percentage of Total
All Ages Under 5 Ages 5-14 Ages 15-24 Ages 25-64 65 and Older
Activity Est (%) Est (%) Est (%) Est (%) Est (%) Est (%)
Basketball 8,723 (22.2) 148 (0.4) 2,338 (5.9) 3,856 (9.8) 2,381 (6.1) 0 (0)
Water/pool sports 4,593 (11.7) 133 (0.3) 1,782 (4.5) 699 (1.8) 1,817 (4.6) 162 (0.4)
Baseball 4,029 (10.3) 182 (0.5) 2,195 (5.6) 823 (2.1) 829 2.1) 0 (0)
Racket sports* 2,767 (7.0) - (0) 1,000 (2.5) 926 (2.4) 822 (2.1) 19 (0)
Hockey** 1,614 (4.1) - (0) 515 (1.3) 628 (1.6) 471 (1.2) 0 (0)
Football 1,464 (3.7) - (0) 533 (1.4) 583 (1.5) 348 (0.9) 0 (0)
Soccer 1,325 (3.4) - (0) 741 (1.9) 378 (1.0) 206 0.5) 0 (0)
Ball sports*** 1,270 (3.2) 115 (0.3) 581 (1.5) 375 (1.0) 160 (1.0) 39 (0.1)
Golf 828 (2.1) 7 (0) 142 (0.4) 75 (0.2) 604 (1.5) 0 (0)
Combatives**** 448 (1.1) - (0) 56 (0.1) 82 (0.2) 310 (0.8) 0 (0)
Total selected sports 27,061 (68.9) 585 (1.5) 9,883 (25.1) 8,425 (21.4) 7,948 (20.2) 220 (0.6)
Other activities 12,236 (31.1) 596 (1.5) 4,273 (10.9) 2,932 (7.5) 4,190 (10.7) 245 (0.6)
Totals 39,297 (100.0) 1,181 (3.0) 14,156 (36.0) 11,357 (28.9) 12,138 (30.9) 465 (1.2)
*Includes racquetball, tennis, squash, paddleball, badminton, and handball
**Includes ice, field, street, and roller hockey
***Includes unspecified ball sports
****Includes boxing, martial arts, and wrestling
High Risk Sports for Eye Injury
Small, fast projectiles
Air rifle/BB gun
Paintball
Hard projectiles, fingers, "sticks," close contact
Baseball/softball/cricket
Basketball
Fencing
Field hockey
Ice hockey
Lacrosse, men's and women's
Squash/racquetball
Street hockey
Intentional injury
Boxing
Full-contact martial arts
Moderate Risk
Fishing
Football
Soccer/volleyball
Tennis/badminton
Water polo
Low Risk
Bicycling
Noncontact martial arts
Skiing
Swimming/diving/water skiing
Wrestling
Eye Safe
Gymnastics
Track and field*
http://www.physsportsmed.com/issues/2000/06_00/vinger.htm
Physician and Sports Medicine magazine article on
Facial Injuries.
Nasal fractures
Very little is done acutely
Ear, Nose, and Throat Physicians usually want the patient after some
of the swelling has subsided.
Acute cases can be splinted using a thermo plastic and moleskin or a
foam rubber. Full face protection is available from most orthotists.
Epistaxis or nasal bleeding should be controlled with ice and the use
of a nasal vasoconstrictor such as Neo Synephrine or Afrin.
Nasal Fracture
Jaw Fractures
Maxilla fractures
These may involve separation of the
palate and or may extend into the nasal
region.
Types of Jaw Fractures
Body 30%
Angle 25%
Condyle 15%
Symphysis 7%
Ramus 3%
Alvcolar 2%
Coronoid 1%
Mandibular fractures
This is the third most commonly fractured
bone in the face behind the nose and
zygomatic arch. They seldom occur as a
single fracture, they are most commonly
associated with at least two fracture sites and
it is not uncommon to have three fracture
sites and or an associated dislocation.
The most common symptom other than
pain is that of malocclusion. This is where
the teeth do not line up correctly due to the
loss of structural integrity of the lower jaw.
Bleeding in the mouth may be found, facial
distortion and pain with palpation or biting.
Fixation usually requires a wiring of the
teeth together for splinting any may
require an external bone plate to be
installed by the Oral Surgeon.
Disrupted Root on left, Malocclusion on the right.
Facial Fractures
Zygomatic Arch Fractures
This is a common facial bone to fracture when
hit in the face with a thrown ball or if two
athletes collide heads during practice or
competition.
If the orbital floor of the eye socket is disrupted,
then the eye on the effected side may droop
down or have difficulty in moving due to the
inferior muscles being trapped in the fracture
site.
These fractures are commonly repaired by the
ENT Physician using an oral route and the
athletes may return to play in 4 to 6 weeks
with some protection for the next 3 to 4
months.
Orbital blowout fractures
There is often an implosion of
the orbital contents by the
trauma and the regions of least
structural integrity will give out
and that tends to be the orbital
floor and the medial orbital wall
as these soft tissues try to find a
place to go when the trauma is
impacted. This is the typical
appearance of a blowout fracture
into the maxillary sinus with a
trapdoor sort of appearance.
http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/IROCH/FacialTrauma/Captions/image15B.html
This 35 year old man was injured riding his motorcycle by a plumbing pipe sticking out from a truck
that backed out of a driveway in front of him. He was going about 35 mph and unable to stop. The
pipe struck him in the face, crushing the cheek and floor of the eye socket.
Dental Injuries
Lacerations in the mouth - clean
with a mixture of hydrogen peroxide
and water, suture if necessary.
Loose teeth
A tooth may become loose (partial displacement),
intruded, extruded, or avulsed.
This injury needs to be treated by a dentist so that
the tooth may be possibly saved.
Fractures of the tooth may extend into the enamel,
dentin, pulp, or root. Those that extend into the
enamel cause no symptoms and can be smoothed
by the DDS. Fractures involving the dentin cause
pain and increased sensitivity to hot and cold
items. Fractures exposing the pulp (nerve area)
lead to serve pain and sensitivity.
Dislocated tooth
Do not touch the root. It is very
sensitive. Rinse with normal, sterile
saline if dirty and attempt to replace the
tooth in the socket. If implantation by
the allied medical personnel is not
successful, then the tooth may be placed
either under the tongue or in a
commercially available "Save a Tooth
Kit".
What can you the ATC do for dental
pain or mouth injuries?
Dental kit - sponges, Cavit, temp bond.
DO NOT use super glue !!
Oil of Cloves
Viscous Xylocaine for pain.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Ch20 Test Bank 1 PDFDokument18 SeitenCh20 Test Bank 1 PDFMichaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exam V - BIOL 243Dokument12 SeitenPractice Exam V - BIOL 243Heather Dab isNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurologic ExamDokument1 SeiteNeurologic Examjiglly23100% (2)
- Neurological Status: Division For Foreign Students With Instruction Conducted in English Department of NeurologyDokument7 SeitenNeurological Status: Division For Foreign Students With Instruction Conducted in English Department of NeurologyHafizuddin YusofNoch keine Bewertungen
- 6.nerves of Head and NeckDokument36 Seiten6.nerves of Head and NeckDr P N N ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Managing Lockjaw Disorders in Dogs: TrismusDokument14 SeitenManaging Lockjaw Disorders in Dogs: TrismusmiloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fundamentals of Stroke and TIADokument12 SeitenFundamentals of Stroke and TIAMaria WibawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurologic Examination: Cranial NervesDokument68 SeitenNeurologic Examination: Cranial Nerves2013SecBNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Report - CC - Uraemic EncephalopathyDokument11 SeitenCase Report - CC - Uraemic EncephalopathyM CubedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brain Anatomy & PhysiologyDokument86 SeitenBrain Anatomy & PhysiologyMahmoud Abo El Magd100% (5)
- 12 Cranial Nerves MnemonicDokument7 Seiten12 Cranial Nerves Mnemonicmedicina151Noch keine Bewertungen
- Macroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Test BankDokument25 SeitenMacroeconomics 9th Edition Boyes Test BankMadisonKirbyeqko100% (54)
- AnatomyDokument91 SeitenAnatomysarahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Cranial NervesDokument13 Seiten12 Cranial Nervesapi-303065931Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pain Review PDFDokument770 SeitenPain Review PDFmoisescharajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dengue Breakbone Fever Case StudyDokument53 SeitenDengue Breakbone Fever Case StudyLeilani Rodriguez AmpoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDokument85 SeitenMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neurobiology of The Neuron and The NeurogliaDokument6 SeitenNeurobiology of The Neuron and The NeurogliaBarney CordovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3Dokument56 SeitenQuiz Anatomy Part 3 of 3Tuğcan YüksekNoch keine Bewertungen
- History and Physical Examination Checklist PDFDokument10 SeitenHistory and Physical Examination Checklist PDFgietsche_gelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cranial NervesDokument6 SeitenCranial Nervesvienny kayeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Clinical Neurology A Manual For Students in Patient-Doctor Ii Harvard Medical SchoolDokument29 SeitenIntroduction To Clinical Neurology A Manual For Students in Patient-Doctor Ii Harvard Medical SchoolKNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 - Dysphagia and StrokeDokument39 Seiten1 - Dysphagia and StrokeVeggy Septian Ellitha100% (1)
- Particulars (Bio Data) of Patient: Dept of P.G Studies in Roganidana, G.A.M.C Bangalore. ©private Circulation Only©Dokument28 SeitenParticulars (Bio Data) of Patient: Dept of P.G Studies in Roganidana, G.A.M.C Bangalore. ©private Circulation Only©kavalapparaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy - Head & Neck GangliaDokument3 SeitenAnatomy - Head & Neck GangliaArianna MohiuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Assessment: The Single Most Important AssessmentDokument10 SeitenNeuro Assessment: The Single Most Important AssessmentpapadaadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raeder Paratrigeminal SyndromeDokument4 SeitenRaeder Paratrigeminal SyndromeBhadresh MangukiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- cklst28 Health AssessmentDokument41 Seitencklst28 Health AssessmentJaden QuimsonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Anatomy - ForUploadDokument105 SeitenLecture 3 - Anatomy - ForUploadmeihoi HuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- DR Kakaza Lectures and Ward Round Notes - 0220Dokument61 SeitenDR Kakaza Lectures and Ward Round Notes - 0220sun108100% (1)