Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
A Project Report On To Study On Business Excellence in HR, Bosch, Nashik"
Hochgeladen von
vinaykulagod100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
536 Ansichten81 SeitenMBA PROJECT REPORT
Originaltitel
Final Bosch
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenMBA PROJECT REPORT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
100%(1)100% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (1 Abstimmung)
536 Ansichten81 SeitenA Project Report On To Study On Business Excellence in HR, Bosch, Nashik"
Hochgeladen von
vinaykulagodMBA PROJECT REPORT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 81
A PROJECT REPORT ON
To study on Business Excellence in HR, Bosch,
Nashik
AT
BOSCH LIMITED
SUBMITED BY
DeepikaTipre
PROJECT GUIDE
Mrs.Sneha Oak.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to express our gratitude to the entire team of Bosch Ltd., Nasik.
Without their continuous support and guidance this project would not have
reached its final culmination.
To begin with, we would like to thank Mr. R.G.Mane (Deputy General
Manager)for providing us such a wonderful opportunity to do our summer
internship project at Bosch Ltd., Nasik. He gave us the opportunity to explore
many new aspects of the project and helped us in attaining knowledge regarding
various aspects which were totally unknown to us.
I would like to express our gratitude to Mr. B. G. Mujumdar (Deputy Manager)
and Mr.JatinSuley(Deputy Manager) for providing us all the information,
guidance, valuable suggestions & encouragement which helped us to complete
my project.
We express our sincere gratitude towards Mrs.Sneha Oak (Assistance
Manager) who helped and arranged all possible visits & training for us at
Bosch.
It was a pleasure to be associated with Bosch Ltd., Nasik. The experience that
we have gained has a profound impact on us. I carry high regards for the
complete team of Bosch Ltd, Nasik.
PREFACE
The summer training is an integral part of the MBA course. As a matter of fact
every management students, has to undergo practical training in an approved
business or organization, under the guidance of professional managers, as to
become aware of the real life, business situation and the environment. During
the course of training, the trainees are expected to use and apply their academic
knowledge and again valuable insight into corporate cultures with all its
environment operational complexity the said training offers, a valuable of the
trainings to meet their academic knowledge with the real world situation. I
undertook my training in BOSCH Ltd, Company. During the training period as
a project trainee, I visited various departments of the organization. In this report
I have put my best efforts to compile the data, to the highest level of accuracy.
Table of Contents:
Sr. no. Title Page no.
1 Introduction 4 to 17
2 Organization profile 18 to 36
3 Research Design and Methodology 37 to 39
4 Conceptual Background 40 to 56
5
Data Presentation, Analysis and
Interpretation.
57 to 73
6 Finding , Suggestion and Conclusion 74 to 81
Executive Summary
The aim of the study was to understand the Business Excellence and tool of the
Business Excellence called EFQM modeland check the Awareness among the
Associates. This programme is implemented by Bosch all over India. The
background study was done with understanding of the theory. The questionnaire
was then designed and made available to the HRL for its consent. The research
includes project objectives .To study on Business Excellence and
EFQMmodel in HR, Bosch, Nasik.. The organization profile and training
theory is discussed in brief. After finalizing the questionnaire, the M&SS were
informed through mails. The design and purpose of the study was explained to
them and the responses were taken on the questionnaire. The data were
collected and analyzed. The research includes primary data collection with
sample size of 73. Based on the analysis findings and recommendations were
given.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
1.1 Introduction:
INTRODUCTION OF BUSSINESS EXCELENCE:
Excellent Organizations achieve and sustain superior levels of
performance that meet or exceed the expectations of all their stakeholders.
BUSINESS EXCELLENCE The way to make product and services more
competitive.
Business excellence provides a proven framework for assessing the success and
sustainability of any organization. This proven framework considers all
processes such as supplier, internal and customer interfacing processes and
drivers of the organization including leadership, human resources, strategy,
information and knowledge management and provides insight into how these
processes and drivers link to overall results. The framework is applicable to all
types of organizations since the values of the organization, the business
environment it operates in, and the challenges it faces are considered.
The most commonly held belief is that business excellence is
associated with award programs. While the framework was originally developed
to support award programme by far the majority of organizations that use
business excellence today do so for self-assessment reasons. Self-assessments
enable you to identify the improvement opportunities that will drive future
organizational growth and success.
Many organizations do not conduct self-assessments because they
believe that it is too complex to perform often requiring specialist experts and
takes too long to complete.
Business excellence is the systematic use of quality management
principles and tools in business management, with the goal of improving
performance based on the principles of customer focus, stakeholder value, and
process management. Key practices in business excellence applied across
functional areas in an enterprise include continuous and breakthrough
improvement, preventative management and management by facts. Some of the
tools used are the balanced scorecard, Lean, the Six Sigma statistical tools,
process management, and project management.
In the 21st century, companies have to excel in their business
practices in order to compete in global markets. Business excellence is the
application of quality management strategies, techniques and tools to achieve
the world-class performance in managing business. The best performance in
business can be realized by identifying suitable performance measures and
metrics, systematically measuring the performance, comparing the performance
with the best-in-class performing companies and then eventually determining
the best practices and their effective implementation framework. Some of the
best practices should include continuous and breakthrough improvement,
proactive management, and management by objective and facts. There are
several successful tools that could be employed for business excellence and
some of them include balanced scorecard, six sigma, process reengineering,
supply chain management, and project management.
Business excellence refers to outstanding practices in managing the
organization and achieving results, based on a set of concepts such as results
orientation, customer focus, leadership and constancy of purpose, management
by processes and facts, people development and involvement, continuous
learning, innovation and improvement, partnership development, and public
responsibility (European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM)).
Business excellence involves self-assessment to identify improvement
opportunities, areas of strength, and to determine ideas for future organizational
development. The critical links between business excellence models, best
practice, and benchmarking are fundamental to the success of the models as
tools of continuous improvement.
The BEM is a widely used framework that helps companies to review
their performance and practices in a number of areas and identify targets and
actions for improvement. It is a benchmarking and audit framework originally
developed in the European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM) but
based on the philosophy of total quality management sees the need for holistic
development and growth of the organization.
Benefits of Business Excellence:
Research on the overall benefits of using BEMs indicates that organizations
with a BE approach obtain significant operational and financial benefits. Also,
research has shown that SMEs obtain benefits more quickly than large
organizations as they can move quickly to make changes to how their business
is run.
BEMs help managers and employees to understand their business better and so
support better decision making .BEMs help organizations to understand how
well all the different functions, units, processes, systems are working together to
produce the desired business results.
BEMs help managers and employees to have a common viewpoint on the health
of their organization and the key issues that are faced. This enables managers
and employees to unite together to tackle the issues and move the organization
forward.
Many SMEs cannot afford to have independent directors or consultants to
assess and appraise the management and health of their organization on a
regular basis. Regular BE self-assessments can go some way in fulfilling this
role and ensuring that due diligence is paid to the development of the business
and key risks are identified and addressed.
BE helps SMEs to implement a cohesive improvement strategy which
integrates a range of improvement initiatives, such as Improvement Teams,
Lean, Statistical Process Control (SPC), and Balanced Scorecard. BEMs can be
used as an overarching framework for managing and aligning various
organizational improvement initiatives.
BE helps organizations to address various business challenges. Strategic
Planning helps to address changes in the business environment such as the
financial crisis. 'Workforce focus' helps to address human resources, cultural
and social issues. 'Operations focus' helps to address multiple legal requirements
and international standards. 'Leadership' helps to address accountability,
corporate governance, environmental and societal issues.
BE assessments serve as an organizational health check.
External BE assessments provide an outsiders view on the health of the
organization and enable the organization to be considered for a quality / BE
award.
Achieving BE certification or winning a quality / BE award provides public
recognition.
BE assessments enable organizations to compare their performance against
others both domestically and globally.
BEMs provide a common framework for learning and sharing best practices
both within and between organizations.
BEMs help SMEs to develop a systematic and robust system that supports
rapid growth and expansion whilst ensuring alignment of strategy.
THE EFQM (EUROPEAN FOUNDATION FOR QUALITY
MANAGEMENT) EXCELLENCE MODEL:-
History:
In the 1950s Quality Assurance was gaining ground in Europe. It was a
well-developed discipline, practiced by many companies in a variety of formats.
However, it was believed that an actual European focus on Total Quality
Management (TQM), in which the best ideas from around the world could be
brought together, was missing. For that reason, 14 CEOs of prominent European
businesses created the European Foundation for Quality Management, later
referred to as EFQM. On October 19, 1989, the terms of reference of EFQM
were established. Mr. Cornelius van der Klugt, then CEO of Philips, was
confirmed as the first President of the EFQM
INTRODUCTION:
The EFQM Excellence Award is run annually by EFQM. It is designed
to recognize organizations that have achieved an outstanding level of
sustainable excellence, based on assessment against the EFQM Excellence
Model.
The EFQM Excellence Model, developed by EFQM and shown in the diagram
above, is a management framework used by over 30 000 organizations in
Europe and beyond. Often used as a diagnostic tool, the Model takes a holistic
view to enable organizations, regardless of size or sector to:
Assess where they are, helping them to understand their key strengths and
potential gaps in performance across the 9 criteria
Provide a common vocabulary and way of thinking about the
organization that facilitates the effective communication of ideas, both within
and outside the organization.
Integrate existing and planned initiatives, removing duplication and
identifying gaps.
The EFQM Excellence Model is used as a basis for self-assessment, an
exercise in which an organization grades itself against the 9 criteria. This
exercise helps organizations to identify current strengths and areas for
improvement against strategic goals. This gap analysis then facilitates definition
and prioritization of improvement plans to achieve sustainable growth and
enhanced performance. Find out more about self-assessment here.
1. Enablers - how we do things.
2. Results - outcomes which we target measure and achieve.
The need for a model
Regardless of sector, size, structure or maturity, organizations need to
establish an appropriate management system to be successful. The Excellence
Model is a practical tool to help organizations do this by measuring where they
are on the path to Excellence; helping them understand the gaps; and then
stimulating solutions. The British Quality Foundation (BQF), with the
European, is committed to researching and updating the Model with the inputs
of tested good practices from thousands of organizations both within and
outside of Europe. In this way they ensure the Model remains dynamic and in
line with current management thinking.
Business excellence refers to outstanding practices in managing the
organization and achieving results, based on a set of concepts such as results
orientation, customer focus, leadership and constancy of purpose, management
by processes and facts, people development and involvement, continuous
learning, innovation and improvement, partnership development, and public
responsibility (European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM)).
Business excellence involves self-assessment to identify improvement
opportunities, areas of strength, and to determine ideas for future organizational
development. The critical links between business excellence models, best
practice, and benchmarking are fundamental to the success of the models as
tools of continuous improvement.
CONCEPT:
In general, business excellence models have been developed by national
bodies as a basis for award programs. For most of these bodies, the awards
themselves are secondary in importance to the widespread adoption of the
concepts of business excellence, which ultimately leads to improved national
economic performance.
By far the majority of organizations that use these models do so for self-
assessment, through which they may identify improvement opportunities, areas
of strength, and ideas for future organizational development. Users of the
EFQM Excellence Model, for instance, do so for the following purposes: self-
assessment, strategy formulation, visioning, project management, supplier
management, and mergers.
When used as a basis for an organization's improvement culture, the
business excellence criteria within the models broadly channel and encourage
the use of best practices into areas where their effect will be most beneficial to
performance. When used simply for self-assessment, the criteria can clearly
identify strong and weak areas of management practice so that tools such as
benchmarking can be used to identify best-practice to enable the gaps to be
closed. These critical links between business excellence models, best practice,
and benchmarking are fundamental to the success of the models as tools of
continuous improvement.
Applicability
Self-assessment has wide applicability to organizations large and small, in the
public as well as the private sectors. Self-assessment using the EFQM
Excellence Model can give the management team a holistic overview of the
whole organization. Increasingly organizations are using outputs from self-
assessment as part of their business planning process and use the EFQM model
as a basis for operational and project review.
In its simplest form, the EFQM Excellence Model is a 9 box "Cause and Effect"
diagram. There are five 'enablers' and four 'results'. The 'enabler' criteria cover
what an organization does. The 'results' criteria cover what an organization
achieves. To improve the results it achieves, the organization must improve
what it does.
The 5 enablers are: Leadership; Strategy; People; Partnerships & Resources and
Processes, Products & Services. The 4 result areas are: Customer Results;
People Results; Society Results and Key Results.
The Model provides a non-prescriptive framework that helps to understand the
often complex cause and effect relationship within an organization
RADAR:
logic a dynamic assessment framework and powerful management tool
harnessing these has helped organizations of all sizes and from all sectors to
compare themselves with the attributes, qualities and achievements of
sustainable organizations. They can be used to develop a culture of excellence,
bring consistency to management style, access good practices, drive innovation
and improve results.
RADAR logic says that an organization needs to:
Determine the Results it is aiming for as part of its policy and strategy making
process. These results cover the financial and operational performance of the
organization together with perceptions of its stakeholders.
Plan and develop an integrated set of sound Approaches to deliver the required
results both now and in the future.
Deploy the approaches in a systematic way to ensure full implementation.
Assess & Review the approaches by monitoring and analyzing the results
achieved through ongoing learning activities.
The applications of RADAR logic helps organizations identify,
priorities, plan and implement improvements where needed:
RADAR LOGIC CYCLE:
The model can be used in four ways:
1. To help determine where an organization is on their journey towards
excellence.
2. To provide a common language to enable the exchange of ideas and
information, both within and outside the organization.
3. To integrate existing & planned activities, improving organizational
efficiency and effectiveness.
4. To provide a basic structure for the organization's management system.
EFQM Partners:
1.2 Statement of the Problem:
It was required to sharpen the distinctive competencies of the
organization by considering heavy competition in todays global world.
It was found that verification of all the standard practices in the
organization was difficult.
1.3 Objective of the study:
To understand the concept of EFQM model.
To set up Benchmark to attain overall Excellence for the organization.
To curve all the action plans, strategies, vision, goals & objective of the
organization under one roof.
To know the perception of the employees regarding Business Excellence
in Bosch.
1.4 Scope of the study:
This Research work will be useful for
Company 1. Communicates strategies to the organization
2 Translate Strategy into Meaningful Goals.
3. The study is conducted to know the level of
knowledge and skills given to the employees in the
organization
Researcher: 1 .Criteria 3 & 7.
2. Understand various concepts of Business Excellence &
EFQM model.
1.5 Limitation of the Project:
This project is only applicable in HR Department.
Company initiative and process are confidential
Geographically limited to Bosch, Nasik only.
1.6 Need of the Study:
To streamlinethe flow, linked & relationship between various department
of the organisation.
To focus on distinctive competencies of organisation.
To attain Excellence in quality for achieving high customer satisfaction,
value for stake holders, & also for employees working in organisation.
CHAPTER -II Organisarional Profile:
2.1 History and general information of Bosch
2.2 Organization
2.2.1 Vision and mission of Bosch
2.2.2 Values of Bosch
2.2.3 Awards for Bosch
2.2.4 Customers of Bosch
2.2.5 Competitors of Bosch
2.3 Products/Activities
2.3.1 Nashik plant product information
2.4 Corporate and functional practices
2.4.1 Organization chart of Nashik plant
2.4.2 HR organization chart
2.4.3 Corporate social responsibility
ORGANIZATION PROFILE
Name of the Organization: BOSCH (Motor Industries Co.Ltd.)
Year of Establishment: 1951 in India
Address: Post Box No.64
75/MIDC Estate, Satpur,
Trimbak Road, Nashik: 422007
Telephone No: (0253) 2350342-45
Fax No : (0253) 2294 999
Website: www.boschindia.com
Product of the Company: Manufacturing of Nozzles and Nozzle- Holders
At Nasik Plant
Areas of Marketing : Within India and Outside the India
Achievement : ISO certified, Best Innovation Award for
Safety, Health and Environment(SHE)
Initiative in 2006
Nasik/India
1.1 History and general information of Bosch Ltd.
Following economic liberalization in India in 1991, the Indian automotive
industry has demonstrated sustained growth as a result of increased
competitiveness and relaxed restrictions. Several Indian automobile manufacturers such as
Tata Motors, Maruti Suzuki and Mahindra and Mahindra, expanded their domestic and
international operations. India's robust economic growth led to the further expansion of its
domestic automobile market which attracted significant India-specific investment by
multinational automobile manufacturers. In February 2009, monthly sales of passenger cars
in India exceeded 100,000 units.
The first car ran on India's roads in 1897. Till the 1930s, cars were imported directly.
Embryonic automotive industry emerged in India in the 1940s. Following the independence,
in 1947, the Government of India and the private sector launched efforts to create an
automotive component manufacturing industry to supply to the automobile industry.
However, the growth was relatively slow in the 1950s and 1960s due to nationalization and
the license raj which hampered the Indian private sector. After 1970, the automotive industry
started to grow, but the growth was mainly driven by tractors, commercial vehicles and
scooters. Cars were still a major luxury. Japanese manufacturers entered the Indian market
ultimately leading to the establishment of MarutiUdyog. A number of foreign firms initiated
joint ventures with Indian companies.
In the 1980s, a number of Japanese manufacturers
launched joint-ventures for building motorcycles and light
commercial-vehicles. It was at this time that the Indian
government chose Suzuki for its joint-venture to manufacture
small cars. Following the economic liberalization in 1991 and
the gradual weakening of the license raj, a number of Indian
and multi-national car companies launched operations. Since
then, automotive component and automobile manufacturing growth has accelerated to meet
domestic and export demands.
In recent years, India has emerged as a leading center for the manufacture of small cars.
Hyundai, the biggest exporter from the country, now ships more than 250,000 cars annually
from India. Apart from shipments to its parent Suzuki, Maruti Suzuki also manufactures
smallcars for Nissan, which sells them in Europe. Nissan will also export small cars from its
new
Indian assembly line.
Tata Motors exports its passenger vehicles to Asian and
African markets, and is in preparation to launch electric vehicles
in Europe in 2010. The firm is also planning to launch an electric
version of its low-cost car Nano in Europe and the U.S. Mahindra & Mahindra is preparing to
introduce its pickup trucks and small SUV models in the U.S. market. Bajaj Auto is designing
a low-cost car for the Renault Nissan Automotive India, which will market the product
worldwide. Renault Nissan may also join domestic commercial vehicle manufacturer Ashok
Leyland in another small car project. While the possibilities are impressive, there are
challenges that could thwart future growth of the Indian automobile industry. Since the
demand for automobiles in recent years is directly linked to overall economic expansion and
rising personal incomes, industry growth will slow if the economy weakens.
3.2 Organization
In India, Bosch is a leading supplier of technology and services, and has a strong
presence in the country at numerous locations in diverse industry segments .Bosch set up its
manufacturing operations in 1953, and has grown over the years to 14 manufacturing sites
and 3 development centers. Bosch employs about 18,030 associates in India, and in business
year 2008 achieved total consolidated revenue of over Rs.6400 cores.
Bosch has been present in India for more than 80 years. First via representative office
in Calcutta(now known as Kolkata) and then from 1951 via its subsidiary Bosch Limited
(then Motor Industries Limited).
The company has developed excellent R&D and manufacturing facilities and a strong
customer base. Its market leadership is testimony to the high quality and technology of its
products. It has a strong presence in the Indian automotive services sector. Boschs service
network which spans across 1,000 towns and cities with over 4,000 authorized
representations to ensure widespread availability of both products and services.
RBIN(formerly BOSCH, Motor Industries Company Limited) is the largest subsidiary
of Bosch in India founded in 1951.It is the largest auto-component manufacturer in India
witha turnover of over Rs 4750 cores in 2009 with total employee strength of 10,000. Robert
Bosch GmbH holds around 70% stake in Bosch Limited. The company is headquartered in
Bangalore having its manufacturing facilities in Bangalore, Nashik, Naganathpura, Jaipur
and Goa. These plants are TS 16949 and ISO 14001 certified.
Plant locations in India
Bosch is also represented by five other group companies in India. Robert Bosch
Engineering and Business Solutions Ltd., a 100% subsidiary of Robert Bosch GmbH, which
is present in India since 1998, has emerged one of the largest Bosch development centers
outside Germany. It provides end to end engineering technology, consumer goods and
building technology solutions for all business sectors of automotive technology , industrial
technology, consumer goods and building technology.
Bosch Rexroth India Limited., established in 1974 in India, services customers in
Ahmadabad and Bangalore. Bosch Chassis Systems India Ltd. Established in 1982 as Kalyani
Breaks Limited in India is amongst the leading manufacturer of breaks in country. It currently
manufacturers a range of Hydraulic break systems meeting the stringent quality norms of
many leading Indian and International vehicle manufacturers. Bosch Automotive Electronics
India Private Ltd., is a 100% subsidiary of Bosch group. The company is based at
Naganathpura in Bangalore Bosch Electrical Drives India Private Ltd., is a joint venture
company. It is based near Chennai and manufactures and sells electrical drivers for various
automotive applications such as window lift drive, wiper system, engine cooling fans etc.
RBIN facilitates superior product availability and countrywide after sales services. It
manufactures and trades products as diverse as common rail injector and diesel and gasoline
fuel injection equipment. Industrial equipment, auto-electrical, gear pumps, power tools,
packaging machines, special purpose machines, security systems, Starter Generator
packaging machines, special purp Gasoline Systems(GS) and Automotive Aftermarket(AA).
3.2.1 Vision and Mission of Bosch Ltd:
Bangalore - 1953
Nashik - 1972
Nagnathpura 1989
Jaipur - 1999
3.2.2 Bosch Values
a. Future and result focus-
In order to ensure dynamic development of our company and to guarantee long-term
corporate success, we participate in shaping the changes in markets and technologies. By
doing so, we provide our customers with innovative solutions and our associates with
a. Future and result focus-
In order to ensure dynamic development of our company and to guarantee long-term
corporate success, we participate in shaping the changes in markets and technologies. By
doing so, we provide our customers with innovative solutions and our associates with
attractive jobs. We act result focused in order to secure growth and financial independence.
With the dividends generated, the Robert BOSCH foundation supports charitable activities.
b. Responsibility-
We accept that our actions must accord with the interests of society. Above all else,
we place our products and services in the interests of the safety of people, economic use of
recourses, and environmental sustainability.
c. Initiative and Determination-
We act on our own initiative, with an entrepreneurial but accountable spirit, and demonstrate
determination in pursuing our goals.
d. Openness and Trust-
We inform our associates, business partners, and investors in a timely and open
fashion of important developments within our company. This is the best for a trustful
relationship.
e. Reliability, Credibility and Legality-
We promise only what we can deliver, accept agreements as building, and respect and
observe the blow in all our business transactions.
f. Fairness-
We view mutual fairness as a condition of our corporate success when dealing with
each other and with our business partners.
g. Cultural Diversity-
We are aware of our companys regional and cultural origins and at the same time regard
diversity as an asset, as well as a precondition of our global success.
3.2.3 Awards and recognitions:
Jan. 07, 2010: NDTV Car & Bike Award - Automotive technology of the year
This accolade recognizes the contributions made by Bosch in India, for
localizing ABS (Antilock Braking System) production. Bosch is the only
automotive supplier to manufacture ABS in India for passenger cars and
light commercial vehicles. ABS is crucial to safety while driving, as it makes braking safer,
by preventing the wheels from locking.
April 15, 2009: DHL - CNBC TV18 International Trade Award
Bosch won this honor in the category of auto component industry, for doing
extremely well in exports through its low-cost solutions. The award
recognizes the companys commitment and innovations that address the needs
of the Indian market, and keep Brand India alive.
Feb. 20, 2009: NDTV Car & Bike Award Auto component
manufacturer
Bosch was chosen as the best in the auto component industry of India for the
year 2009. These awards are considered as benchmarks for auto excellence in
India and widely trusted by consumers, manufacturers and auto experts alike.
The award recognizes the best in the automobile industry of India.
Jan.7, 2009: UTVi Auto car Award
Bosch and Mahindra & Mahindra won the Best Innovation of the Year UTVi
Auto car Award. The award recognizes Bosch innovation start/stop system
which contributes to fuel efficiency at a very reasonable cost. The Mahindra
Bolero Micro Hybrid is the first vehicle in India to integrate this technology in
their new car.
June 21, 2008: Business Standard Award Star MNC of the year
Bosch was noted for its cutting edge technologies, especially for designing and
delivering low cost high quality fuel injection system and for pioneering the
common rail system in India.
Jan. 10, 2008: NDTV Car & Bike Award - 'Car Technology of
the year
Bosch not only setup the common rail injector and pump manufacturing projects in
record time, but also pioneered the new application of Common Rail in low cost car
segment. This is a revolutionary leap achieved by Bosch in India, which is the
pioneer of Common Rail technology in the rest of the world as well.
Jan, 12, 2007: NDTV Profit Car & Bike Award 2007
Automotive Technology of the year'
Audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers, these awards honored the best in the
Indian automotive industry for their handiwork in calendar year 2006.
Bosch was presented with the award for its application of ABS / ESP
technology.
Jan. 4, 2007: CNBC-TV18 Auto car Auto Award Auto component
manufacturer of the year
Bosch Limited was chosen for the mark that it has made both in the
domestic and international markets with its superior technology and
products. These awards seek to reward exemplary performance in the
industry in 2006 based on a comprehensive set of attributes including
design, technology, value, product experience and so on. The selection
processes truly reflects the choices and sentiments of all stakeholders
and justify their stature as benchmarks in auto excellence.
Aug. 17, 2006: Dun & Bradstreet American Express Corporate
Award - Top Indian company in the Auto Components sector
The award recognizes the twin virtues of size and growth in the
organizations of corporate India, from a derived list of top 500 companies
in the country. Bosch Limited was selected as the best amongst the top 10
auto component manufacturers in India.
Aug. 10, 2006: EEPC Award Star Performer for outstanding
export performance
The Engineering Export Promotion Council (EEPC) conferred the 'Star
Performer' for outstanding export performance in the large enterprises
category on Bosch Ltd, which garnered a total export figure of Rs. 423
crores in 2005, almost twice as high as Rs 193 crores in 2001.
Jan. 12, 2006: NDTV Profit Car India Award Safety & Technology
Award
Bosch was presented with this award for its pioneering work on the new
age direct injection diesel fuelling systems, with notable emphasis in the
range of common rail diesels. Also taken into account was the persistent
focus on unit injector systems which are entering the scene in the high
profile high aspiration D-segment cars. The jury considered not just the
technology but its bearing on safety, and the benefits it brought to automotive users
as well as the potential it has for India.
Jan. 8, 2005: OverdriveAuto Monitor Award Auto component
manufacturer of the year
Recognized for innovations in technology and the scale and size of manufacturing
capabilities, the award also commemorated the customer satisfaction earned by
Bosch over the years, performance, quality and diverse range of products. This
Annual Awards the Oscar for the automobile industry in India and recognizes
the best in the industry in association with reputed industry bodies like CII,
SIAM & ACMA.
3.2.4 Customers of Bosch:
BOSCH has a large customer base. The products of BOSCH are not only used in
India but also are exported and used by many world renowned automobile
manufacturing companies.
Customers outside India:
General Motors
Volkswagen
Peugeot
Nissan
Hatz
IVECO
FIAT
Mercedes Benz
Renault
BMW
Lombardi USA Inc.
Daimler Chrysler
Customers in India:
Ashok Leyland
Ford Tempo
BEML
Cummins India Ltd.
Swaraj Mazda
VST Tillers tractors Ltd.
Ford
KAMCO Diesel Engines
Simpsons Co. Ltd.
Kirloskar
L & T
John Deer
Ford Eicher
10
Internal | NaP/HRL3 | June 2011 | Bosch Limited 2011. All rights reserved, also regarding any disposal, exploitation, reproduction, editing,
distribution, as well as in the event of applications for industrial property rights.
No car without Bosch
17
Internal | NaP/HRL3 | June 2011 | Bosch Limited 2011. All rights reserved, also regarding any disposal, exploitation, reproduction, editing,
distribution, as well as in the event of applications for industrial property rights.
Customer Base
Automobiles
LCV / HCV / Locomotives PC / SUV
TATA Motors
Ashok Leyland
Mahindra & Mahindra
TCL
Maruti-Suzuki
Eicher Motors
GCL
Force Motors
Iveco
Ford
GM
Nissan
DC
Isuzu
Hyundai
CKEC
Indian Railways
Escorts Ltd.
3.2.5 List of competitors
Auto Line Industry Ltd.
Banco Products (India) Ltd.
Federal- Mogul Goetze (India) Ltd.
Ip Rings Ltd.
Kar Mobiles Ltd.
Menon Pistons Ltd
.
3.3 Products/Activities
At the Nashik plants Nozzles and nozzle holders are manufactured which are used in
the fuel injection system of diesel engines. The BOSCH Nashik is specialized in
manufacturing a variety of nozzles and nozzle holders and that at the cheapest possible
rate.
Types of Nozzles:-
DN nozzles: These are the pintle type nozzles. Pintle-type nozzles have a coaxial jet
and are used in pre-combustion chamber engines and turbulent chamber engines. The
nozzle opening pressures it between 115 and 400 bar
Orifice Nozzles: These Orifice nozzles or Pintaux nozzle have several Spray
orifices and are required for engines with direct injection. The nozzle opening
pressure is between 180 and 400 bar. For larger engines (more than 75 kW) also
cooled nozzles are used. These are termed as: DL, DLL, DSLA etc.
Orifice Nozzles DSLA, DL, DLL.
INJECTORS NOZZLES
Types of Nozzle Holders:-
Nozzle Holders are classified according to their shaft diameter.
1. P Type Nozzle Holder: its characteristic dia. Is 17mm.
2. Modular Type: Its characteristic dia. Is 21mm.
3. Forged Type: It is made out of forging.
Nozzle Body: -
Company is market leader in fuel injectors used in automobile industry. Fuel injector is
Heart of engine as it sprays the fuel into the combustion cylinder. It consists of
cylindrical and internally hollow body through which a needle is passed that is held by
means of spring against nozzle at bottom of the body. It has inlet bore for diesel at
inclination to the body of injector which enters the hollow section of the body.
The nozzle consists of stepped cylinder and needle pin .The stepped cylinder known as
nozzle body, is manufactured in soft and hard stages. The needle is manufactured in the
needle hard stage. The assembly stage combines both these parts into nozzle assembly.
Functional parameters of nozzle body are the inlet hole, spray holes and guide bore. Precision
requirements of these parameters are in microns.
Needle is fitted into the guide bore, where the step of the pin coincides with the pressure
chamber. The pin is held into the injector assembly by means of spring. At rest, the pin is
resting on the sack hole of the nozzle.
When the fuel enters the nozzle body through inlet hole, its pressure is high than the force at
which the pin is held by the spring in rest position. This difference in pressure causes the pin
to rise and the fuel gets sprayed through spray holes on the external periphery of the seat.
When the flow through the inlet stops, the impact of the pin causes to atomization of the fuel
through the spray holes. This flow of the fuel through spray holes is known as Hydraulic
through flow (HTF).
As a strategic measure, Common Rail Injector (CRI)products were introduced which can
meet emission norms up to BS4. The CRI component exports started in 2006. The CRI
production was started in 2007 and new product CRI contribution is planned to grow to 50%
of NaP turnover by 2010. The NaP contributed Rs.450 corers in the business of Bosch group
during last financial year.
3.3.1 Nashikplant(NaP )Product Introduction
(Source: www.bosch.com)
As a strategic measure, Common Rail Injector (CRI) products were introduced which can
meet emission norms up to BS4. The CRI component exports started in 2006. The CRI
production was started in 2007 and new product CRI contribution is planned to grow to 50%
of NaP turnover by 2010. The NaP contributed Rs.450 corers in the business of Bosch group
during last financial year.
SR.NO.
PRODUCT
Starting Year
Emission Norm
1. Nozzle Holder & Nozzles 1969
2. DLL Nozzle (DI) 1974
3. BS 2 Noz.Holder-P Type 2000 BS2
4. Chevy Injectors(Export) 2002 Euro 4
5. BX Injectors(Export) 2003
6. NBFE (Injectors) 2008 BS 2
7. CRI(Injectors) 2006
8. CRI(Injectors) 2008 BS 4
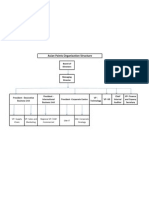
3.4. 1 Organization Chart of Bosch Ltd. Nashik :
DS/MG-IN, NaP/PT
NaP/PC
PT-N
MFC
QMM
HSE
OFE-PT
TEF
PT-PA
CLP
PUI
CFA
OFE-PC
HRL
PC-PA
PQ
ICO
Organization
Chart
MFH
MFN1
MFN
MHS
DBE
CIP-BPS
3.4.2 HR Organization Chart
HRL: Human Resource location
BVC: Bosch Vocational Center
PRS: Protection and Security
PA: Personal Assistant
MED: Medical
NaP HRL
HRL1
HRL2
HRL3
BVC
MED
PRS
HRL-PA
HRL31
HRL32
HRL33
CORPORATE SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
The Robert Bosch Foundation was set up in 1964 with the aim of translating the company
founders commitment to social and charitable causes into contemporary projects. Bosch has
undertaken numerous initiatives towards the betterment of the society across medical,
educational, social and vocational programs. Some of the key initiatives have been:
The donation of a distribution vehicle to the AkshayaPatra Foundation- a non-profit organization
that provides unlimited, wholesome and nutritious mid-day meals to students across India.
An active part in Nasik run initiative to work for the underprivileged in and around the city of
Nashik and at the same time to create awareness on the importance of health and fitness.
Relief work during Cargill war and Earthquake ravaged Gujarat.
Participation of every employee towards contribution of funds to aid the survivors of Tsunami of
2004.
Bosch has adopted two villages in Nashik (Dubewadi and Dahalewadi). Bosch provides help to
villagers in the form of basic education, clothing and health
Sales Office:
Ahmadabad.
Bangalore.
Chandigarh.
Chennai.
Guwahati.
Indore.
Jaipur.
Kochi.
Kolkata.
Lucknow.
Mumbai.
New Delhi.
Patna.
Raipur.
Ranchi.
Secunderabad.
Regional Offices:
Agra.
Chennai.
Jamshedpur.
New Delhi.
Pune.
Rajkot.
CHAPTER 3:
RESERCH DESIGN AND METHEDOLOGY:
3.1 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Research is an academic activity and as such as the term should be used in a
technical sense.
According to Clifford woody Research comprises defining and redefining
problems, formulating hypothesis or suggested solutions, collecting, organizing
& evaluating data Making deduction and reaching conclusion, and at last
carefully testing the conclusion to determine whether the fit the formulating
hypothesis. The purpose of research is to discover answer to question through
the application scientific procedure. The main aim of research is to find out the
truth which is hidden and which has not been discovering as yet.
Sources of Data Collection
1. Primary Data-
Primary data is that data which is collected for the first time. It also
happens to be of original character this type of data is collected through
survey with the help of questionnaire. This data is confidential and the
chances of error are minimized. Most of the people prefer primary data
collection because it is one on which all their further research depends.
Source of Primary Data
Observation
Interview Method
Collection of data through Questionnaires
In present the primary data was collected direct asking question
through Questionnaire & personal interview
2. Secondary Data-
Secondary data is one, which is already available and passed through the
statistical process.
Secondary data provides the starting point for research and offer
advantage of low cost and ready availability.
In this project the secondary data was used in the form of data
presentation of questionnaire.
Sources of Secondary Data :
The sources of the secondary data are company internal record,
magazines and through Internet search.
3. Sample Description:
3.1 Method of sampling selection:
Probabilities Sampling:
Simple random sampling: This type of sampling is also known as chance
sampling or probability sampling where each and every item in the population
has an equal chance of inclusion in the sample and each one of the possible
samples, in case of finite universe, has the same probability of being selected.
For example, if we have to select a sample of 300 items from a universe of
15,000 items, then we can put the names or numbers of all the 15,000 items on
slips of paper and conduct a lottery. Using the random number tables is another
method of random sampling. To select the sample, each item is assigned a
number from 1 to 15,000. Then, 300 five digits random numbers are selected
from the table. To do this we select some random starting point and then a
systematic pattern is used in proceeding through the table. We might start in the
4th row, second column and proceed down the column to the bottom of the
table and then move to the top of the next column to the right. When a number
exceeds the limit of the numbers in the frame, in our case over 15,000, it is
Simply passed over and the next number selected that does fall within the
relevant range. Since the numbers were placed in the table in a completely
random fashion, the resulting sample is random. This procedure gives each item
an equal probability of being selected. In case of infinite population, the
selection of each item in a random sample is controlled by the same probability
and that successive selections are independent of one another.
3.2 METHODOLOGY
The method adopted to collect data relevant to the research was extensive
direct interaction with various employee. The mode of interaction with the
employee
To take direct interview of the employee to find out their opinion about
Business Excellence and EFQM model.
To collect information through the questionnaire.
To take opinion of various Officers and Workers through the
questionnaire.
Processing and tabulation of data: - The data after being collected was
segregated and then final tabulation was done.
Analysis of data: - After the data is tabulated it needs to be inferred
otherwise data gathered in it is of little value or interest for analysis of data.
CHAPTER 4:
4.3 CONCEPTUAL DESCRIPTION OF THE TOPIC:
THE FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF EXCELLENCE:
Fig: THE FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS OF EXCELLENCE:
1.Achieving Balance Result:
Excellence organisation meet their Mission and progress towards their
Vision through planning and achieving a balanced set of result that meet both
the short term and long term need of their stakeholders and where relevant,
exceed them.
In practice, excellence organisation:-
a. Identify and understand the key result.
b. Gather stakeholders need and expectation for input to development, Review.
c. Use balance set of result to review their process, view for stakeholders long
Taking
Responsibility for
sustanabil future
Achieving Balanced
Result.
Adding Value for
customers.
Leading with Vision,
Inspiration and
Integrity.
Managing by
processes.
Succeeding through
People
Building Partnership
Nurturing Creativity
and Innovation.
and short priorities.
d. Define required outcomes and related performance indicators.
e. Deploy strategy and supporting policies in a systematic manner to achieve
the desired set of result.
f. Evaluate the set of results achieved to improve future performance.
g. Ensure transparency of reporting to key stakeholders.
h. Ensure that their leaders are provided with accurate and sufficient
information in timely decision making.
2. Adding with Vision, Inspiration and Integrity:
Excellence organizations know that customers are their primary
reason for being and strive to innovate and create value for them by
understanding and anticipating their needs and expectation.
In practice, Excellent organization:-
a. Identify customers group. Respond and anticipate their different need and
Expectation.
b. Build and maintain a dialogue with all their customers, based on Openness
and transparency.
c. Ensure their people have the necessary tools, Competencies, information and
empowerment.
d. Continually monitor and review the experience and perceptions of customers,
respond quickly.
e. Involve customers in development process, product, and services.
f. Compare their performance with relevant benchmark, understand strength.
3. Leading with Vision, inspiration and integrity:
Excellent organizations have leaders who shape the future and make it happen,
acting as a role model for its value and ethics.
In practices, excellent organizations have leaders who:-
a. Set and communicate clear direction and strategic focus.
b. Understand key business drivers.
c. Based on available information, experience makes sound, timely decision.
d. Leaders are flexible review, adapt and realign direction of organization.
e. Inspire people and create culture of Involvement, ownership. Improvement,
Accountability at all level.
f. Promote a culture which supports generation and development of new idea.
g. Leaders are role model, for integrity, social responsibility, and
ethicalbehavior.
4. Managing by Processes: -
Excellent organizations are managed through structured and strategically
aligned processes using fact-based decision making to create balanced and
sustained result.
In practice, excellent organization:-
a. Structured and aligned strategy in a way that adds real value for their
stakeholders, achieving the optimum balance of efficiency, Effectiveness.
b. Analyze, categories and priorities their processes and adopt appropriate
approaches to effectively managed.
c. Develop meaningful performance indicator, related outcomes.
d. Base decisions on reliable information, use all available knowledge to
interrupt current and predicted performance of relevant processes.
e. Use data on current performance and capabilities of processes to identify
opportunities for, and generate, innovation.
f. Involve their people continually reviewing, improving and optimising the
Effectiveness and Efficiency of their process.
g. Deliver high level of stakeholders confidence by ensuring risk identification
5. Succeeding through People:-
Excellent organisations value their people and create a culture of empowerment
for the balanced achievement of organisational and personal goal.
In practice, excellent organization:-
a. Understand the skill and competencies required achieving Mission, Vision.
b. Create culture of innovation, skill, creativity are develop and value.
c. Ensure that the people can contribute to their own and the organizations
on-going process, true partnership.
d. Align personal and team objectives with the organizations strategic goal.
e. Diversity of the people.
f. Foster organizational development through shared Values, accountability
ethics and a culture of trust and openness.
g. Clearly define the level of performance required to achieve goal.
6. Nurturing Creativity and Innovation:-
Excellent organizations generate increased value and level of performance
through continual and systematic innovation by harnessing the creativity of
their stakeholders.
In practice, excellent organization:-
a. Establish and manage network to identify opportunities for innovation.
b. Set clear goal and objectives or innovation and refine their strategy.
c. encourage to generate approaches for innovation.
d. Create a culture of entrepreneurship.
e. Use innovation to enhance organizations reputation, image and attract new
customers, partners, and talent.
7. Building Partnerships: -
Excellent organizations seek, develop and maintain trusting
relationship with various partners to ensure mutual success. This partnership
may be formed with amongst others, customers, society, key suppliers,
educational bodies or Non-government organization.
In practice, excellent organization:-
a. Seek partners to enhance their capabilities to generate stakeholder value.
b. Establish networks to enable to identify potential partnership opportunity.
c. Identify strategic and operational partnership based on organizational and
strategic needs, complementary strengths and capabilities.
d. Work together with partners to achieve mutual benefit, resources.
8. Taking Responsibility for a sustainable Future:-
Excellent organization embed within their culture an ethical mind-set, clear
values and highest standards for organizationalbehavior, all of which enable
them to strive for economic, social and ecological sustainability.
In practice, excellent organization:-
a. Secure future by defining and communicating a core purpose that provide
basis for their overall Vision, Values, ethics and corporate behaviour.
b. Consider economical, societal and ecological sustainability as a reference
when balancing the sometime conflicting imperatives they face.
c. Considered the impact of their operations, product life cycle on society.
d. Ensure safe and healthy working environment.
e. Ensure their people act with integrity and adopt the highest standard of ethical
behaviour.
f. Encourage people, stakeholders to participate in society benefit activity.
g. Allocate resources to provide for long term needs rather than just short term
gain and where relevant, becomes and remain competitive.
4.4 THEORETICAL BACKGROUND:
BOSCH PLAN:
Bosch strongly believes that our well trained and enthusiastic people add significant
contribution to our success. They are trained and empowered for taking appropriate decision
in their field area. All employees are encouraged to share their idea, thoughts and concern to
make NaP Bosch a better and more enjoyable place at work. We create a culture of equality.
Based on RB/HR mission Attractive Employer, INDS LT strategy Preferred Employer
and NaP vision mission we have formulated our people strategy SAM3 which states
Develop and maintain right competencies ; involve employees in improvement activities.
All our people related actions are based on above aspects.
Fig: RADAR format of 3a1: People plan support the organizational strategy.
3a1:People plan support the organizational
strategy.
Results:1. Align Peoples Plan with Strategy.
2. People Competencies, Employee Satisfaction.
Approach:1. Employee Involvement & Empowerment
2. Attract, Retain and Motivate Employees.
3. Salary Structure Review.
4. Personnel Marketing
Deployment:1. Communication Training
2. Structure meeting with BEU.
3. Open House Session for Associates.
4. Recruitment and Session planning.
5. Skill Matrix
6. Employee Motivation.
7. Employee Involvement-Suggestion Scheme, Best performing
team.
Assessment & Review: How can we measure our result?
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of 3a2: People Involve in Developing Strategy.
3a2: People I nvolve in Developing Strategy.
Results:People Involvement in Developing Strategy and Incising
Belongings.
Approach:1. HR, IR Conference.
2. Meeting with BEU.
3. Open House.
4. Welfare Committees.
5. Departmental meeting
6. Employee Satisfaction survey.
Deployment:1.Transfer Policy for Associates.
2. Flexible Timing for ladies.
3. Changes in Weekly off by involving Labour Union.
4. Wage Settlement, Incentive Schemes, Productivity
Improvement, Working Condition, New Promotional Policy.
All are decide involving Labour union.
Assessment & Review:Input for HR Strategy Development.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of 3a3: Manage recruitment, Career development, mobility and
Succession
3a3: Manage recruitment, Career
development, mobility and Succession
planning.
Results:3a3: Manage recruitment, Career development, mobility and
Succession planning.
Approach:1. Equal Opportunity.
2. Best Talent.
Deployment: 1. Institutional Campus.
2. Interview
3. Placement agencies.
4. Succession planning is identified with Bosch tools.
Management Potential Review
Assessment & Review: 1. Employee sourced from internal and external
factor.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format 3a4: Use all feedback to improve Strategy.
3a4: Use all feedback to improve
Strategy.
Results: Improve Strategy through feedback.
Approach:1. Leadership
2. Communication
3. Work Environment.
4. Rewards and recognition
5. Health and Safety
6. Community and Society
Deployment:1. Systematic approach on Communication deployed.
2. Training committee meeting.
3. Focus on Health and Safety awareness.
4. Internal customer satisfaction survey.
5. Create awareness about CSR activities.
Assessment & Review:Action plans are reviewed and monitored by
Departmental Head and Plant Head to ensure
timely implementation.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of 3b1. Understand the required skills and competency.
3b1. Understand the required skills and
competency.
Results:Right Competencies is formulated focusing on Training and
Developmentactivities.
Approach:Target Competencies Current Competencies
Compare competencies Competence Development
Evaluation Competency model.
Deployment:M&SS- 1. Competency management model.
2. PRED.
Skill Matrix:
Assessment & Review:
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of 3b2: Ensure training and development plans help people
match the skills andfuture capabilities
3b2: Ensure training and development plans help
people match the skills and future capabilities.
Results: match training and requirement of employee.
Approach:1. Training Committee.
2. Updated Training Evaluation Scheme
Deployment:1. Safety and Behavioral Training.
2. Induction program for new entrants.
3. Specific external training, job rotation, Transfers,
Internationalassignments.
Assessment & Review:1. Effectiveness of M&SS evaluated after 3
months by concerned department head using
Kirkpatrick model.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of 3b3: Align individual, Team Objectives with Organization
Strategy.
3b3: Align individual, Team Objectives with
Organization Strategy.
Results:1. Help people to improve performance to improve and
maintain their mobility and employability.
2. Ensure their people have necessary tools, competencies,
information, empowerment to be able to maximise their
contribution.
Approach:1.Top, Senior Manager finalised plant target are came to
Respective Process owners. Departmental target
Individual target. = Target setting.
2. 1. Training- Team Building
2.Employee Education
3. Membership of professional institute
4. Seminars, training, higher education, International assignments.
Deployment: 1. PRED Discussion of review of previous year is done
2. Target is decided by mutual understanding.
3. Achieve these targets.
4. Rewards and recognition.
5. Development plan for high performance
6. For low performance- Performance improvement
Assessment & Review: PRED Review is done every year.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
A mahiti
Fig: RADAR format of : Peopleare aligned, involvedandempowered.
3c: Peopleare aligned,
involvedandempowered.
Results: : Peopleare aligned, involvedandempowered.
Approach:1.Createaculturewherepeoplesdedication, skills, talents
& creativityare developed & valued.
2. Encouragetheirpeopletobethecreators&
Ambassadors totheOrganizationssuccess.
3. Ensure that the people have an open mind set&use
Creativity &innovationenabled throughthecultureof
Entrepreneurship
Deployment: 1. Suggestion schemes.
2. Mr Customer
3. Family Day.
4. Safety
5. In House Magazine
6.Bosch Sport Committee.
7. Project like Nasik Run.
Assessment & Review:Every year since 35 yrs.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of 3c: Peopleare aligned, involvedandempowered.
3c: Peopleare aligned,
involvedandempowered.
Results: Peopleare aligned, involvedandempowered.
Approach:1.Createaculturewherepeoplesdedication, skills, talents
& creativityare developed & valued.
2. Encouragetheirpeopletobethecreators&
ambassadors totheOrganizationssuccess.
3. Ensure that the people have an open mind set&use
Creativity &innovationenabled throughthecultureof
entrepreneurship
Deployment: 1. Suggestion schemes.
2. Mr Customer
3.Family Day.
4. Safety
5. In House Magazine
6.Bosch Sport Committee.
7. Project like Nasik Run.
Assessment & Review:Every year since 35 yrs.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
Fig: RADAR format of3d: People communicateeffectivelythroughout theorganization
3d: People
communicateeffectivelythroughout
theorganization
Results:.1. Understand communication needs of peopleanddevelop communication
Strategy& channels.
2. Communicate clear strategic focus, &ensure people understand &
contribute to organizationssuccess.
Approach: 1. importantvisitsof customers,
2. TopBoschExecutives.
3. Future business plans,
4. Boschaudits
Deployment:1.NaP leadership has communicatedtoallseniormanagers.
2. Employee Satisfaction Survey.
3.
Assessment & Review:.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
3e.
Results:.
Approach:
Deployment:
Assessment & Review:.
Customer:
Support:
:
Organization
CHAETOR 5
DATA PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS, AND INTERPRETATION:
Que. 1:What does EFQM stand for?
Observation: -
This chart shows how much associates know the meaning of EFQM model.
75.71% associates know the correct answer. And 24.29% associates dont know
the correct answer
Interpretation: -
From the above graph it is inferred that the maximum number of
Associates are able to answer the question. It is a positive or plus point to the
organization since it helps in implementing the additional knowledge acquired
in their work.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 75.71 24.29
75.71
24.29
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
What does EFQM stand for?
Que.2:What is Excellence?
Observation: -
This chart shows how much associates know the meaning of Excellence.72.86%
associates are pass with correct answer. And 27.14% associates are confused
with the correct meaning of Excellence.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the real meaning of Excellence is understood to the
Associates. Associates are showing positive attitude to the Business Excellence.
They know that the Business Excellence is not an extra work, not the temporary
Achievement. It is Sustained Success.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 72.86 27.14
72.86
27.14
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
What is Excellence?
Que3:Excellent organisations achieve expectation of
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 68.57% Associates are pass with the correct answer.
And 31.43% Associates are fail with Wrong answer. Some associates are
confused with the answer.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that Goal of the Business Excellence is understood to
associates in some amount. Some confusion should be removed. Business
Excellence is beneficial to all the level. It is not a single benefit. This should be
communicating to the Associates.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
% Pass % Fail
Employees 68.57 31.43
68.57
31.43
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
Excellent organisations achieve expectation of
Que4:How many criteria are there in EFQM model of Business Excellence?
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 72.86% associates know the correct answer of the
Question. And 27.14% Associates are not able to answer correctly.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are able to understand the EFQM
model and memorised the criteria in EFQM model. They become familiar with
this model and its criteria.
0
20
40
60
80
% Pass % Fail
Emplyees 72.86 27.14
72.86
27.14
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
How many criteria are there in EFQM model of
Business Excellence?
Que.5:Strategy means
Interpretation: -
This chart shows that the 70% associates are pass with the correct answer. And
30 % are not able to answer this question correctly.
Inference: -
It is observed that the associates know the theme behind the Strategy.
They are aware of the meaning of Strategy.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
% Pass % Fail
Emplyees 70 30
70
30
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
s
Strategy means
Que 6:Future & Result focus is a part of which of the following?
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 71.43% Associates are know the real meaning of
Bosch Guidelines. And 28.57% Associates are not able to answer this correctly.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the Bosch Vision, Mission is very well known by
the Associates. They are aware of their guidelines.
0
20
40
60
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 71.43 28.57
71.43
28.57
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
s
Future & Result focus is a part of which of the
following?
Que7:What is the Maximum possible score an organization can achieve during
an external DBE CII assessment?
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 68.57% Associates are pass with the correct answer.
And 31.42% Associates are fail with wrong answer.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are somehow confused with the
maximum score achievable. . Score breakdown is not completely understood to
the Associates.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
% Pass % Fail
Employees 68.57 31.42
68.57
31.42
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
s
What is the Maximum possible score an organisation can
achieve during an external DBE CII assessment?
Que 8: Which of the following is not a Result Criteria?
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 68.57% Associates are pass with the correct answer.
And 31.42% Associates are fail with wrong answer.
Interpretation: -
Most of the Associates are aware of the Criteria and their division.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 71.43 28.57
71.43
28.57
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
s
Which of the following is not a Result Criteria?
Que.9: Business Excellence is aligned with
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 68.57% Associates are pass with the correct answer.
And 31.42% Associates are fail with wrong answer.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are somehow knowing the bas for
Business Excellence.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
% Pass % Fail
Employees 68.57 31.43
68.57
31.43
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
s
Business Excellence is aligned with
Que.10:Shape the future together is a part of which of the following?
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 72.86% associates are pass with the correct answer.
27.14% Associates are not able to answer this correctly.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are able to recognize the Bosch
Vision, Mission very well.
0
20
40
60
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 72.86 27.14
72.86
27.14
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
s
Shape the future together is a part of which of the
following?
Que.11: EFQM model consists of
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 75.71% Associates are pass with the correct answer.
And 24.29% associates are not able to answer this correctly.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are able to recognize the criteria
very well.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 75.71 24.29
75.71
24.29
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
EFQM model consists of
Que.12:Excellence model is a
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 75.71% Associates are pass with the correct answer.
And 24.29% associates are not able to answer this correctly.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are able to understand the base of
Business Excellence.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
% Pass % Fail
Employees 75.71 24.29
75.71
24.29
P
a
r
t
i
c
u
l
a
r
Excellence model is a
Que.13: NaP Strategic theme is
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 91.43% Associates are pass with correct answer. And
8% are not able to answer this question correctly.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the associates are able to understand the Bosch
Vision and Mission, Bosch Leadership Godliness very well.
0
20
40
60
80
100
% Pass % Fail
Employees 91.43 8.57
91.43
8.57
P
e
r
c
e
n
t
a
g
e
NaP Strategic theme is
Observation: -
This chart shows result of survey. In the 1
st
question 75.7% Associates are pass
and 24.3% are fail. In 2
nd
72.9% are pass and 27.1% are fail. In 3
rd
68.6% are
pass and 31.4% are fail with wrong answer. In 4
th
72.9% are pass and 27.1 %
are fail. In 5
th
70% are pass and 30% are fail. In 6
th
71.4% are pass and 28.6%
are fail. In 7
th
68.6% are pass and 31.4% are fail. In 8
th
71.4% are pass and
28.6% are fail. In 9
th
68.6% are pass and 31.4 are fail in 10
th
72.9 are pass and
27.1% are fail. In 11
th
75.7 are pass and 24.3 are fail with wrong answer. In 12
th
75.7 % are pass and 24.3 % are fail. In 13
th
91.4% are pass and 8.57% are fail.
Interpretation: -
In above graph, averagely 65-70 % Associates are pass in each question. It
shows that the awareness among the associates is 65-70%. It shows the good
result of training program of Business Excellence. Impact of training program is
good on associates. They have good amount of knowledge about the Business
Excellence and EFQM model.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
% Pass 75.7 72.9 68.6 72.9 70 71.4 68.6 71.4 68.6 72.9 75.7 75.7 91.4
% Fail 24.3 27.1 31.4 27.1 30 28.6 31.4 28.6 31.4 27.1 24.3 24.3 8.57
A
x
i
s
T
i
t
l
e
Overall pass and fail percentage
Que.14:Your overall sustenance of knowledge gained in EFQM model after
training is
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 1% Associates obtained 1 mark, 19% Associates
obtained 2 marks. 44% Associates obtained 3 marks, 6 % Associates obtained 4
marks.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the most of the Associates are obtained 3 marks.
This shows the good result of Knowledge. It is positive sign for Company.
0
10
20
30
40
50
1 mark 2 marks 3 marks 4 marks
Marks 1 19 44 6
1
19
44
6
E
m
p
l
o
y
e
e
s
Your overall sustenance of knowledge gained in
EFQM model after training is
Que.15:How much do you apply your knowledge of EFQM model in your
workplace?
Observation: -
This chart shows that the 2% Associates obtained 1 mark, 26% Associates
obtained 2 marks. 39% Associates obtained 3 marks, 3 % Associates obtained 4
marks.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the most of the Associates are obtained 3 marks.
This shows the good result of Implementation of Knowledge. This shows that
Associates are happy with this theory. And it help them in their workplace.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
1 mark 2 marks 3 marks 4 marks
Marks 2 26 39 3
2
26
39
3
E
m
p
l
y
e
e
s
e
How much do you apply your knowledge of
EFQM model in your workplace?
Observation: -
This chart shows result of survey. In the 14
th
Question 69.64% Associates are
pass and 30.36% are fail. In 15
th
64.64% are pass and 35.36% are fail.
Interpretation: -
It is observed that the most of the Associates are good in Substance
of Knowledge as well as implementation of their knowledge. It shows good
result. This is a profit for organization.
CHAPTER VII FINDINGS
0
20
40
60
80
% Pass % Fail
Series1 69.64 30.36
Series2 64.64 35.36
69.64
30.36
64.64
35.36
A
x
i
s
T
i
t
l
e
Overall implementation Percentage
Findings:
A. Positive:
1. Awareness of Business Excellence among the Associates issatisfactory.
They have sufficient knowledge about Business Excellence.
2. Departments goals are clearly defined and achieved through Business
Excellence.
3. Knowledge gain in Training of Business Excellence is satisfactory.
4. All the associates are enthusiastic about Business Excellence. They play
their role in the systematic way.
Suggestions & Recommendations:
1. For creating more awareness among the Associates, Games, Quiz
competion should be implemented. So that they can easily understand the
concepts.
2. Suggestion Schemes for Business Excellence should be implemented. So
that they can suggest their thoughts.
3. Basic format of working is implemented. So that throughout year
Documents are updated accordingly. So the burden of documentation is
reduces. Working pattern of throughout year should be parallel to the
requirement of documentation of Business Excellence.
Conclusion:
By going through the task of undertaking and understanding the Business
Excellence carried in Bosch, Nasik plant, the researcher came to conclude that
Business Excellence is Beneficial for Bosch ,Nasik. It gives Profit to not only
Bosch but its all stakeholders.
Bosch Ltd, Nasik is very particular about their work in Business
Excellence. HR Bosch shows positive attitude for the Business Excellence.
From the research, Researcher concludes that the knowledge about
business Excellence in all the Associates aregood, and they are Happy with this
theory.
Abbreviations :
Ltd. Limited.
M & SS - Managers and Supervisors and Superintendents.
HRL Human Resource Location.
Nap Nashik Plant.
RBIN Robert Bosch India.
CFA- Accounts and Finance department.
HRL- Human Resource Location.
MFN1- Manufacturing of Nozzles.
MFC- Manufacturing of Common Rail Injectors.
3.Bibliography :
Websites:
www.google.com
www.managementparadise.com
www.bosch.com
Company magazines and newspapers:
Bosch Ltd. Profile.
Sa.Na.Vi.Vi.
Previous survey report.
Bosch Journal.
Business Excellence
Questionnaire
1. What does EFQM stand for?
a. European Foundation for Quality Management
b. European Federation for Quality & Method
c. European Foundation of Quality & Method
d. European Federation for Quality Management
2. What is Excellence?
a. Success
b. Sustained Success
c. Temporary Achievement
d. Initiative
3. Excellent organisations achieve expectation of
a. Stakeholders
b. Management
c. Community
d. All above
4. How many criteria are there in EFQM model of Business Excellence?
a. 5
b. 4
c. 8
d. 9
5. Strategy means
a. Deciding to Win
b. Designing to Win
c. Playing to Win
d. All of these
6. Future & Result focus is a part of which of the following?
a. NaP Vision.
b. NaP Mission.
c. Bosch Leadership Guidelines
d. Bosch Values
7. What is the Maximum possible score an organisation can achieve during an external
DBE CII assessment?
a. 900
b. 800
c. 700
d. 1000
8. Which of the following is not a Result Criteria?
a. People
b. Customer
c. Policy and Strategy
d. Society
9. Business Excellence is aligned with
a. Organisational Strategy
b. Departmental Strategy
c. Organisational system
d. Business Result
10. Shape the future together is a part of which of the following?
a. NaP Vision
b. NaP Mission
c. Bosch Leadership Guidelines
d. Bosch Values
11. EFQM model consists of
a. 5 Enablers, 4 Results
b. 4 Enablers, 5 Results
c. 4 Enablers, 4 Results
d. 5 Enablers, 5 Results
12. Excellence model is a
a. Tool
b. Solution
c. Extra Work
d. Software
13. NaP Strategic theme is
a. Leadership in Production.
b. Cost Effectiveness
c. Trust your Associates
d. Most preferred Partner
14. Your overall sustenance of knowledge gained in EFQM model after training is
a. Excellent
b. Very Good
c. Satisfactory
d. Poor
15. How much do you apply your knowledge of EFQM model in your workplace?
a. 1-25%
b. 25-50%
c. 50-75%
d. 75-100%
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- MR GMAT Combinatorics+Probability 6EDokument176 SeitenMR GMAT Combinatorics+Probability 6EKsifounon KsifounouNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appolo TyreDokument63 SeitenAppolo Tyresanthoshchandu.santhoshmohan100% (2)
- Project Report BoschDokument31 SeitenProject Report BoschRushikesh Gulve50% (6)
- BKT b2b Project ReportDokument17 SeitenBKT b2b Project ReportAshok Kumar0% (1)
- MCQ PharmacokineticsDokument10 SeitenMCQ PharmacokineticsHarshit Sharma100% (1)
- Ashok LeylandDokument78 SeitenAshok LeylandKajal Kaundal33% (3)
- Project Report On Commercial Vehicles IndustryDokument26 SeitenProject Report On Commercial Vehicles IndustryVivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- KTM - Group ADokument39 SeitenKTM - Group ASukrat Nath0% (1)
- Transformers Classics: UK Vol. 3 PreviewDokument10 SeitenTransformers Classics: UK Vol. 3 PreviewGraphic PolicyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Report On VolkswagenDokument70 SeitenFinal Report On Volkswagenvjbhardwaj80% (20)
- Business Excellence FrameworkDokument36 SeitenBusiness Excellence FrameworkCarlos Joaquín DuarteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashok Leyland Report 2011-2012Dokument76 SeitenAshok Leyland Report 2011-2012Mukesh Kumar Rajpurohit100% (1)
- Bosch Organization StudyDokument49 SeitenBosch Organization Studynandish73100% (1)
- 1888 Speth Ars Quatuor Coronatorum v1Dokument280 Seiten1888 Speth Ars Quatuor Coronatorum v1Paulo Sequeira Rebelo100% (2)
- VolvoDokument14 SeitenVolvoasishagarwal86Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch CoDokument26 SeitenBosch CoAnilKotthurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Strategy of BMW (Automobile Industry)Dokument74 SeitenMarketing Strategy of BMW (Automobile Industry)Vaibhav KalraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Employee SatisfactionDokument71 SeitenProject On Employee SatisfactionvinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asain PaintsDokument118 SeitenAsain PaintsMagesh GurunathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Project REPORTDokument17 SeitenSummer Project REPORTSudhir KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mercedes Benz Strategy PDFDokument8 SeitenMercedes Benz Strategy PDFHepitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Mercedes BenzDokument47 SeitenIntroduction To Mercedes BenzVeenal D'silva100% (4)
- Internship Robert BoschDokument109 SeitenInternship Robert Boschapi-194640150% (1)
- Ashok Leyland Competitors DataDokument3 SeitenAshok Leyland Competitors DataSanket PathakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Project On Bosch IndiaDokument21 SeitenStrategy Project On Bosch Indiarohitraj.iitm3326100% (6)
- Fernández Kelly - Death in Mexican Folk CultureDokument21 SeitenFernández Kelly - Death in Mexican Folk CultureantoniadelateNoch keine Bewertungen
- Importers in BOC List As of June 2, 2015Dokument254 SeitenImporters in BOC List As of June 2, 2015PortCalls88% (8)
- Bosch Case StudyDokument26 SeitenBosch Case StudyNeetesh Singh75% (4)
- RPT-Project Report FinalDokument29 SeitenRPT-Project Report Finalarvind3041990100% (3)
- Market Mapping of Eicher Trucks and BusesDokument72 SeitenMarket Mapping of Eicher Trucks and BusesSonam Bagha100% (1)
- Toyota HR ProjectsDokument90 SeitenToyota HR Projectsvinaykulagod50% (2)
- Robert Bosch Shashidhar 05116Dokument86 SeitenRobert Bosch Shashidhar 05116peter983693561950% (2)
- A Report of Industrial Training at BoschDokument48 SeitenA Report of Industrial Training at BoschLijo John86% (7)
- A Report On Organizational Study at BoschDokument42 SeitenA Report On Organizational Study at BoschVarun reddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- VW Achievements in MotorsportsDokument1 SeiteVW Achievements in MotorsportsStevue ChristieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brembo Profile PDFDokument25 SeitenBrembo Profile PDFNakanakanaknakNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Assignment On Organizational Structure of VOLTASDokument7 SeitenAn Assignment On Organizational Structure of VOLTASRaushan Kumar Naik100% (2)
- Asian Paints Org StructureDokument1 SeiteAsian Paints Org StructureupasanabsinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AL Company Profile & ProductsDokument40 SeitenAL Company Profile & ProductsGaurav ChaudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vehicle Segments On Ashok LeylandDokument61 SeitenVehicle Segments On Ashok LeylandStartechnico TechnocratsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Escorts LimitedDokument11 SeitenEscorts LimitedBhaskar RoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- BMW - Promotional & BrandingDokument65 SeitenBMW - Promotional & BrandingVikram MayuriNoch keine Bewertungen
- An Internship Report On Customer Satisfaction of Mercedes-BenzDokument80 SeitenAn Internship Report On Customer Satisfaction of Mercedes-Benznash_world7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Federal Mogul Organization StudyDokument14 SeitenFederal Mogul Organization Studychaitra r100% (1)
- DTDokument28 SeitenDTLovelypreet Mann100% (1)
- Presentation On Eicher Motors LTDDokument21 SeitenPresentation On Eicher Motors LTDSeerat Jangda50% (2)
- Hero Cycles Training ReportDokument19 SeitenHero Cycles Training Reportsharanjeet4u100% (3)
- B2b Sales of A CompanyDokument6 SeitenB2b Sales of A CompanyPRANAV GOYAL100% (1)
- Abhijeet Nigam Internship ReportDokument45 SeitenAbhijeet Nigam Internship ReportAbhijeet Nigam0% (1)
- Mercedes BrandingDokument14 SeitenMercedes BrandingAmit MalhotraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research Analysis: Prepared by Darshan PatiraDokument8 SeitenResearch Analysis: Prepared by Darshan Patiradarshan jainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bosch Jaipur Plant: Summer Training atDokument46 SeitenBosch Jaipur Plant: Summer Training atJohn DoeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asian Paints Expansion Strategy in Middle EastDokument8 SeitenAsian Paints Expansion Strategy in Middle EastKshitij JindalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Report of Mercedes Auto Saved)Dokument41 SeitenProject Report of Mercedes Auto Saved)jatin9621100% (4)
- HCCB S&M PDFDokument5 SeitenHCCB S&M PDFSamdeesh SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- SEM-4 GCSR Company ReportDokument30 SeitenSEM-4 GCSR Company ReportHNSMBA 2016Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Project Bharat BenzDokument24 SeitenMarketing Project Bharat BenzSoumya Siddharth Rout64% (11)
- History of ASHOK LEYLANDDokument12 SeitenHistory of ASHOK LEYLANDRajanikantJadhav100% (1)
- Internship Study at Bosch CompanyDokument19 SeitenInternship Study at Bosch CompanyDIPUBKGNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ashok LeylandDokument33 SeitenAshok Leylandpg1875% (4)
- ACCDokument23 SeitenACCyaduvansi,rajesh100% (2)
- Customer Satisfaction Study of Toyota Cars at Ravindu ToyotaDokument87 SeitenCustomer Satisfaction Study of Toyota Cars at Ravindu ToyotamuralimadhavaregurigupthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summer Training Report: Motherson Sumi System Limited (MSSL)Dokument47 SeitenSummer Training Report: Motherson Sumi System Limited (MSSL)Atul YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 5.1Dokument16 SeitenModule 5.1marlize viviersNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Business Excellence JourneyDokument32 SeitenThe Business Excellence JourneyPuguh HariantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Strategy Execution Exemplar Balanced Score CardDokument2 SeitenStrategy Execution Exemplar Balanced Score CardArun AroraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Amended MGT702 Major Project 2021Dokument23 SeitenAmended MGT702 Major Project 2021kajal prasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Continious Improvement 1Dokument3 SeitenContinious Improvement 1sakhar babuNoch keine Bewertungen
- JUBL ProjectDokument61 SeitenJUBL ProjectvinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rashmi SasnurDokument55 SeitenRashmi Sasnurvinaykulagod100% (1)
- ReportDokument68 SeitenReportvinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vidya Posh AkDokument50 SeitenVidya Posh AkvinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Project 1Dokument87 SeitenFinal Project 1vinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReportDokument77 SeitenProject ReportvinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project On Employee Satisfaction1Dokument48 SeitenProject On Employee Satisfaction1vinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality of Work Life StudyDokument64 SeitenQuality of Work Life StudyvinaykulagodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Value Creation-How-Can-The-Semiconductor-Industry-Keep-Outperforming-FinalDokument7 SeitenValue Creation-How-Can-The-Semiconductor-Industry-Keep-Outperforming-FinalJoão Vitor RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aerospace Propulsion Course Outcomes and Syllabus OverviewDokument48 SeitenAerospace Propulsion Course Outcomes and Syllabus OverviewRukmani Devi100% (2)
- TNT Construction PLC - Tender 3Dokument42 SeitenTNT Construction PLC - Tender 3berekajimma100% (1)
- Tahap Kesediaan Pensyarah Terhadap Penggunaan M-Pembelajaran Dalam Sistem Pendidikan Dan Latihan Teknik Dan Vokasional (TVET)Dokument17 SeitenTahap Kesediaan Pensyarah Terhadap Penggunaan M-Pembelajaran Dalam Sistem Pendidikan Dan Latihan Teknik Dan Vokasional (TVET)Khairul Yop AzreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alan Ross CV Expert Road Safety AdviserDokument4 SeitenAlan Ross CV Expert Road Safety AdviserAnna Sophia YorkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Artificial IntelligenceDokument1 SeiteArtificial IntelligenceTeresaNoch keine Bewertungen
- VB6 ControlDokument4 SeitenVB6 Controlahouba100% (1)
- 1603 Physics Paper With Ans Sol EveningDokument8 Seiten1603 Physics Paper With Ans Sol EveningRahul RaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- MS0800288 Angh enDokument5 SeitenMS0800288 Angh enSeason AkhirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovations in Teaching-Learning ProcessDokument21 SeitenInnovations in Teaching-Learning ProcessNova Rhea GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brother LS2300 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualDokument96 SeitenBrother LS2300 Sewing Machine Instruction ManualiliiexpugnansNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air India CpioDokument5 SeitenAir India CpioVicky GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- OPGWDokument18 SeitenOPGWGuilhermeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colorectal Disease - 2023 - Freund - Can Preoperative CT MR Enterography Preclude The Development of Crohn S Disease LikeDokument10 SeitenColorectal Disease - 2023 - Freund - Can Preoperative CT MR Enterography Preclude The Development of Crohn S Disease Likedavidmarkovic032Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Equivalent SDOF System Model For Estimating The Earthquake Response of R/C Buildings With Hysteretic DampersDokument8 SeitenAn Equivalent SDOF System Model For Estimating The Earthquake Response of R/C Buildings With Hysteretic DampersAlex MolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesDokument9 SeitenMICROHARDNESS TESTER HMV-2 - SeriesRicoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hotel Industry Report Provides Insights on Growth, Costs, and FinancialsDokument12 SeitenHotel Industry Report Provides Insights on Growth, Costs, and FinancialssparasavediNoch keine Bewertungen
- Art 1207-1257 CCDokument5 SeitenArt 1207-1257 CCRubz JeanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Registration Form: Advancement in I.C.Engine and Vehicle System"Dokument2 SeitenRegistration Form: Advancement in I.C.Engine and Vehicle System"Weld TechNoch keine Bewertungen
- Trends in Email Design and MarketingDokument18 SeitenTrends in Email Design and MarketingDaria KomarovaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Connotative and Denotative, Lexical and StylisticDokument3 SeitenConnotative and Denotative, Lexical and StylisticEman Jay FesalbonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Christian Ministry Books: 00-OrientationGuideDokument36 SeitenChristian Ministry Books: 00-OrientationGuideNessieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Commissioning Procedure for JTB-PEPCDokument17 SeitenCommissioning Procedure for JTB-PEPCelif maghfirohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gautam KDokument12 SeitenGautam Kgautam kayapakNoch keine Bewertungen