Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
RQAns 4 Systems Comm
Hochgeladen von
Ronak ParmarOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
RQAns 4 Systems Comm
Hochgeladen von
Ronak ParmarCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Cambridge University Press 2011
4Systems and
communications
Answers to Revision questions: 4 Systems & communications 1 Cambridge IGCSE Computer Studies
Below each answer there is a page reference for the coursebook. Tis is there to help you focus
your revision. If you fnd that you get an answer wrong, you can use this guide to return to the
coursebook to revise the areas that need some extra attention. Please note these are example
answers only and do not represent the only possible answers.
1 An operating system is a set of programs and data fles that manages a computers hardware
and the other programs that run on the computer. It controls the peripheral devices, allocates
memory between application programs, performs housekeeping tasks on the backing storage,
shares the processor between application programs.
See Functions of an operating system on page 93.
2 a A command line interface requires the user to type commands at a keyboard. Te user
needs to remember the commands (although help is usually available) and the string
of options can be complex to get right. Only one command (program) at a time can
beexecuted.
b A graphical user interface enables the user to use a pointing device to select commands and
options from menus. Several programs can be open in various windows.
See User interface on page 98.
3 a A graphical user interface uses windows, icons, menus and a pointing device.
b In the future, user interfaces may use voice commands or gestures to control the computer.
See User interface on page 98.
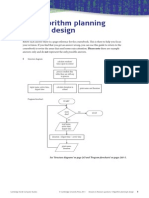
4
See File management on page 101.
Disk
C:\
Folders Files and sub-folders
Programs
My Documents
Letter 2011-Jan.doc
Photos
Homework
Recycle Bin
France 2010
John birthday
Hampton Court
timetable.doc
tudors.doc
ICT survey.xls
Cambridge University Press 2011 Answers to Revision questions: 4 Systems & communications 2 Cambridge IGCSE Computer Studies
5 A fle manager enables the user to print, copy, move and list fles.
See File management on page 101.
6 a A bufer is an area of memory that holds data temporarily ready to be sent to a program or
peripheral device.
b A peripheral device is a device that links to the processor, such as a printer, a monitor or
a webcam. (See page 93 and glossary.)
c An interrupt is a signal from a peripheral device or a program to the processor asking for
some service (e.g. a printer may send an interrupt to ask for more data).
d Polling is a process in which the processor asks each peripheral device in turn if it needs
a service.
e Handshaking is a process in which a peripheral device and the processor (or two computers
on a network) establish communication.
See Peripheral device control on page 102.
7 Te operating system handshakes with the peripheral device (e.g. a printer) to establish initial
communication. Te printer driver flls the print bufer and requests the host controller to send
the data to the printer. When the printer has dealt with the data, it tells the driver to fll the
bufer again. Tis means that data is not sent too quickly and does not get lost.
See Peripheral device control on page 104.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 1-3-6 Operating SystemsDokument5 Seiten1-3-6 Operating SystemsHamail MustafaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS-Controls Hardware & SoftwareDokument5 SeitenOS-Controls Hardware & SoftwareAthuai DoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Operating SystemDokument20 SeitenIntroduction To Operating SystemLaksana Dewa0% (1)
- Unit IDokument86 SeitenUnit Imvmohitkumar17Noch keine Bewertungen
- Processes and Memory Utilization in Windows 10Dokument3 SeitenProcesses and Memory Utilization in Windows 10Deprr 悪夢Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1431-2 (1) .PDF Version 1-1Dokument12 Seiten1431-2 (1) .PDF Version 1-1Muhammad KamranNoch keine Bewertungen
- CMSC 125 Operating Systems 1. Operating System Objectives and FunctionsDokument9 SeitenCMSC 125 Operating Systems 1. Operating System Objectives and Functionsadugnaw azanawNoch keine Bewertungen
- Softwareupdate - CopyDokument37 SeitenSoftwareupdate - Copyletangletty07Noch keine Bewertungen
- What Are The Three Main Purposes of An OperatingDokument6 SeitenWhat Are The Three Main Purposes of An OperatingAbhinish Swaroop75% (4)
- Chapter 1-Silberschatz OSDokument2 SeitenChapter 1-Silberschatz OSEnrique SchererNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Software Cost Increases As The Hardware Cost Decreases in Parallel To The Development of Technology. at The Beginning The Reverse Was TrueDokument6 SeitenThe Software Cost Increases As The Hardware Cost Decreases in Parallel To The Development of Technology. at The Beginning The Reverse Was TrueSibelŞentürkNoch keine Bewertungen
- 03 Activity 3 - ARGDokument4 Seiten03 Activity 3 - ARGstapaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems and MultimediaDokument58 SeitenOperating Systems and Multimediashivang.goyal02Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - 2 Operating SystemsDokument17 SeitenUnit - 2 Operating Systemsimran hameerNoch keine Bewertungen
- APPLICATIONSDokument11 SeitenAPPLICATIONSChristopher WalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 4 (Comp Science)Dokument27 SeitenUnit 4 (Comp Science)Alex ogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Rev MidtermDokument17 SeitenRev MidtermraqibappNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPPC 10 Lecture Notes 1 Overview of Operating Systems PDFDokument13 SeitenCPPC 10 Lecture Notes 1 Overview of Operating Systems PDFBlessious Joseph LandoyNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSINTRODokument25 SeitenOSINTROlovishsindhwaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Sklill PDFDokument6 SeitenComputer Sklill PDFKhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 Operating System: Structure Page NoDokument12 SeitenUnit 2 Operating System: Structure Page NoJignesh PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument61 SeitenOperating SystemPaul MuasyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer SoftwareDokument6 SeitenComputer Softwarejbmaina100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computing FundamentalDokument10 SeitenComputing Fundamentalmmm2025Noch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Science - CE - 2013 - Section ADokument48 SeitenComputer Science - CE - 2013 - Section ASayyed Salman Mehdi MosviNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS Functions Memory Management Processor Allocation File SharingDokument139 SeitenOS Functions Memory Management Processor Allocation File SharingAavyaan SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System NotesDokument118 SeitenOperating System Notesjitendrabudholiya620Noch keine Bewertungen
- CS405-Operating SystemsDokument15 SeitenCS405-Operating SystemsSHIVAM KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 3 - SoftwareDokument10 SeitenModule 3 - SoftwareRoden LacabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 2Dokument24 SeitenAssignment 2accord123Noch keine Bewertungen
- OSDokument26 SeitenOSYasir Ahmed KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bishwajit Mazumder Nursing Instructor Dhaka Nursing College, Dhaka Level:-Midwifery 1 YearDokument34 SeitenBishwajit Mazumder Nursing Instructor Dhaka Nursing College, Dhaka Level:-Midwifery 1 YearBishwajitMazumderNoch keine Bewertungen
- CHAPTER 2 Intro To Operating SystemDokument14 SeitenCHAPTER 2 Intro To Operating SystemalexNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 3 Computer Software: StructureDokument12 SeitenUnit 3 Computer Software: StructureCamilo AmarcyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems An Overview Author University of KashmirDokument125 SeitenOperating Systems An Overview Author University of KashmirvvasileNoch keine Bewertungen
- OS NotesDokument8 SeitenOS NotesPritam KiskuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer - Module 3Dokument72 SeitenComputer - Module 3ushalatasharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.5 System SoftwareDokument8 Seiten1.5 System SoftwareHammad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Intro To ItDokument3 SeitenAssignment Intro To ItNadita VaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Information Technology BasicsDokument32 SeitenInformation Technology BasicsM. O. Adan94% (18)
- Operating Systems NotesDokument17 SeitenOperating Systems NotesJobanie Diaz Fajutar PanganibanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Platform Technology (TP)Dokument5 SeitenPlatform Technology (TP)小松菜Noch keine Bewertungen
- R18 PPS Unit-IDokument50 SeitenR18 PPS Unit-Ishaikshadmaan2000Noch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Computers and Operating SystemsDokument14 SeitenIntroduction to Computers and Operating SystemsSaffa IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Operating System: Engr. Nuzhat MadinaDokument19 SeitenTypes of Operating System: Engr. Nuzhat Madinadua tanveerNoch keine Bewertungen
- AnswersDokument6 SeitenAnswersSourav DasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems NotesDokument61 SeitenOperating Systems NotesGumzz LeoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRB Study Materials Operating System: WWW - Governmentexams.co - in 1Dokument9 SeitenTRB Study Materials Operating System: WWW - Governmentexams.co - in 1Jeyaraman DhanarajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument48 SeitenOperating SystemSalie Dia CanamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osunit 1 Part 1Dokument22 SeitenOsunit 1 Part 1Lakshmi SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating SystemDokument7 SeitenOperating SystemL NNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System: Time: 3 HRS.) (Marks: 100Dokument17 SeitenOperating System: Time: 3 HRS.) (Marks: 100Aditya Darekar100% (1)
- Kesi Introduction To Computers and OsDokument31 SeitenKesi Introduction To Computers and OspussiahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os Notes (1) MergedDokument61 SeitenOs Notes (1) MergeddiplomadosthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Os NotesDokument49 SeitenOs NotesdiplomadosthaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 1: Computer Architecture and Operating System FundamentalsDokument6 SeitenTutorial 1: Computer Architecture and Operating System FundamentalsSLIM SHADYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDokument15 SeitenUnit 1 - Operating System - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inyashika sarodeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesVon EverandOperating Systems Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 8 Social EconomicDokument2 SeitenRQAns 8 Social EconomicRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 10 Prog AlgorithmsDokument2 SeitenRQAns 10 Prog AlgorithmsRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 11 Logic Gates CircDokument2 SeitenRQAns 11 Logic Gates CircRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ - 2 DataDokument2 SeitenRQ - 2 DataRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 1 Gen App SoftwareDokument2 SeitenRQ 1 Gen App SoftwareRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 5 Types Computer SysDokument2 SeitenRQAns 5 Types Computer SysRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 9 Algor Plan DesignDokument2 SeitenRQAns 9 Algor Plan DesignRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 2 DataDokument3 SeitenRQAns 2 DataRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic GatesDokument3 SeitenLogic GatesCostasNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 3 HardwareDokument3 SeitenRQAns 3 HardwareRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns - 6 The Sys - Life CycleDokument2 SeitenRQAns - 6 The Sys - Life CycleRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 9 Algor Plan DesignDokument3 SeitenRQ 9 Algor Plan DesignRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 10 Prog AlgorithmsDokument1 SeiteRQ 10 Prog AlgorithmsRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns - 7 Range - Scope of AppDokument2 SeitenRQAns - 7 Range - Scope of AppRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQAns 1 Gen App SoftwareDokument2 SeitenRQAns 1 Gen App SoftwareRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 8 Social EconomicDokument1 SeiteRQ 8 Social EconomicRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 4 Systems CommDokument1 SeiteRQ 4 Systems CommRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ - 7 Range - Scope of AppDokument2 SeitenRQ - 7 Range - Scope of AppRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 5 Types Computer SysDokument1 SeiteRQ 5 Types Computer SysRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ - 6 The Sys - Life CycleDokument1 SeiteRQ - 6 The Sys - Life CycleRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- RQ 3 HardwareDokument2 SeitenRQ 3 HardwareRonak ParmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course OutlineDokument2 SeitenCourse OutlineHassan HajirNoch keine Bewertungen
- OpenVPN Access Server v1 5 Sysadmin Guide Rev 1Dokument59 SeitenOpenVPN Access Server v1 5 Sysadmin Guide Rev 1Bakhtiyar UdinNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Write Test Cases - Sample Template With ExamplesDokument10 SeitenHow To Write Test Cases - Sample Template With ExamplestraoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAN StandardsDokument41 SeitenLAN StandardsNetwork BullNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSEC Physics Review - Introduction To Logic GatesDokument16 SeitenCSEC Physics Review - Introduction To Logic GatesKevin Small100% (3)
- MAC Layer Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks: S-MAC, T-MAC, B-MAC, P-MAC and Z-MACDokument29 SeitenMAC Layer Protocols for Wireless Sensor Networks: S-MAC, T-MAC, B-MAC, P-MAC and Z-MACSrinivas GopisettiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Activity File Class 12 - Saksham PDFDokument37 SeitenPhysics Activity File Class 12 - Saksham PDFAmutha GNoch keine Bewertungen
- Redacted Notes Made Ridiculously SimpleDokument11 SeitenRedacted Notes Made Ridiculously SimpleHuyIdolNoch keine Bewertungen
- ALSTOM SCADA ArchitechtureDokument20 SeitenALSTOM SCADA ArchitechtureSomnath Gupta100% (1)
- Boot and Diagnose PCs from USB with HDSDOSDokument2 SeitenBoot and Diagnose PCs from USB with HDSDOSrocco1100% (1)
- Product Profile - Kinetix® 6500 - 2094-pp005 - En-P PDFDokument4 SeitenProduct Profile - Kinetix® 6500 - 2094-pp005 - En-P PDFNicolás A. SelvaggioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stranchat: Department of Computer Science, Christ UniversityDokument54 SeitenStranchat: Department of Computer Science, Christ UniversityAryanKumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Writing Games with PygameDokument25 SeitenWriting Games with PygameAline OliveiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Student Information SystemDokument14 SeitenProject Student Information SystemAkshay Gonewar100% (2)
- 1.3.2 Computer Architecture and The Fetch Execute CycleDokument3 Seiten1.3.2 Computer Architecture and The Fetch Execute CycleDemet KansuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows Server 2019-MS Docs PDFDokument40 SeitenWindows Server 2019-MS Docs PDFAvez AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Azure Developer MCQ - Capture User, Session, EventsDokument7 SeitenAzure Developer MCQ - Capture User, Session, EventsAmit SharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Using ClamAV in The TerminalDokument3 SeitenUsing ClamAV in The TerminalsporanoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- PN6500 Series Spec SheetDokument2 SeitenPN6500 Series Spec SheetAdalberto Cavalo eucaliptoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 1-Lesson 2 - Understanding Basic Concepts in ICTDokument29 SeitenModule 1-Lesson 2 - Understanding Basic Concepts in ICTJohn Moises Libres50% (2)
- Introduction To SuperMap IserverDokument46 SeitenIntroduction To SuperMap IserverArif W. SunarsoNoch keine Bewertungen
- HDP Release NotesDokument39 SeitenHDP Release Notesabhimanyu thakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aquos Asia2007Dokument32 SeitenAquos Asia2007XiyizAibicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dbms & Prog LangDokument37 SeitenDbms & Prog LangTech_MXNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dzamindar MyFAX Brochure Pg5Dokument1 SeiteDzamindar MyFAX Brochure Pg5Johnson LukoseNoch keine Bewertungen
- Po SprinterDokument133 SeitenPo SprinterDavide DellacàNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cubot X9 CeDokument4 SeitenCubot X9 CeSaqib HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- CDM-570L IP v1 - Module 1.6.23 Release NotesDokument5 SeitenCDM-570L IP v1 - Module 1.6.23 Release NotesGUnndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- SettingsproviderDokument15 SeitenSettingsproviderJorge luisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Run Shell Scripts and Date Conversions in DatastageDokument10 SeitenRun Shell Scripts and Date Conversions in DatastageUlasa RaghavaNoch keine Bewertungen