Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Syllabus For CSIR Examination June 2013
Hochgeladen von
sndppm78780 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten3 Seitencsir
Originaltitel
Syllabus for CSIR Examination June 2013
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldencsir
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
12 Ansichten3 SeitenSyllabus For CSIR Examination June 2013
Hochgeladen von
sndppm7878csir
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Syllabus for CSIR Examination June 2013
Jan 2: Composition, structure and function of carbohydrates
3: metabolism of carbohydrates
4: composition, structure and function of proteins (Ramachandran plot ,sec structures,domains,motifs)
5: metabolism of amino acids
6: Nucleic acids
7: metabolism of nucleic acids
8: vitamins, enzymes, enzyme kinetics, mechanism of enzyme catalysis
9: stabilizing interactions (vanderwalls, electrostatic, hydrogen bonding , hydrophobic
interactions), glycolysis
10: TCA, Oxidative phosphorylation, Photophosphorylation, PPP(including inhibitors)
11: DNA replication
12: Chromosomes: deletion, insertion, transition, transversion, translocation( include types of
chromosomes )
13 :Mutagens (include disorders &ploidies)
14: DNA damage and repair mechanisms
15: Recombination (homologous, site specific recombination),transposons
16: Transcription(include difft RNA pol, types of RNA)
17& 18: capping, elongation, termination, RNA processing, RNA editing, Splicing,
polyadenylation, RNA transport
19: Translation(include aminoacyl tRNA synthetase)
20: genetic code
21:transcriptional and translational inhibitors
22:post translational modification of proteins
23 : regulation of prokaryotic gene expression(Operon)
24: Virus and phages including lytic and lysogeny)
25 &26: regulation of eukaryotic gene expression
27: gene silencing (nucleosomes,heterochromatin ,euchromatin)
28:structure of membrane(lipid bilayer),lipids(glycerophospholipids,spingolipids etc)
29 &30: membrane transport(diffusion,osmosis,ion channels,pumps,carriers,active & passive
transporters)
31: all organelles
Feb 1:Cytoskeleton
2: cellular communication: ECM, collagen, integrin, gap and tight junctions etc (including
disorders)
3: cell division and cell cycle
4 & 5: Cancer ( oncogenes.tumor suppressor genes, cancer and cell cycle, virus induced
cancer,apoptosis,therapeutic interventions of uncontrolled cell growth)
6: Innate & adaptive immunology,antigens,antibodies,Ag-Ab complex
7 &8: antibody diversity,monoclonal antibodies,antibody engineering
9 &10: MHC ,antigen processing and presentation,activation and differentiation of B & T cells,
BCR & TCR
11 & 12:Complement system,Toll like receptors,cytokines
13:Hypersensitivity,Autoimmune disorders,immune deficiencies
14: Photosynthesis ( C3,C4,CAM),ETC
15: Respiration and photorespiration ( include alternative oxidase,inhibitors of pathways)
16:Nitrogen metabolism, plant hormones
17 & 18: sensory photobiology: phytochromes,cytochromes,stomatal
movements,photoperiodism and biological clocks
19: solute transport( through xylem & phloem)
20:sec metabolites( biosynthesis of terpnes,phenols and other nitrogenous compounds MEP
pathway,mevalomic acid pathway,shikimic acid pathway)
21 & 22: Floral system(ABC model-genes involved etc-chapter 24 Taiz & Zieger)
23: Stress physiology
24: Mendelian principles,concept of gene( pseudoallele,complementation test)
25: codominance,incomplete dominance,gene interactions,pliotropy,genomic
imprinting,penetrance & expressivity,phenocopy
26: linkage & crossing over,sex linkage,sex limited & sex influenced characters
27: linkage maps,tetrad analysis,mapping with molecular markers
28: microbial genetics(transformation,transduction,sexduction
March 1: human genetics: pedigree analysis, genetic disorders, Quantitative genetics
( polygenic inheritance, heritability, QTL mapping)
2: Ecology: Environment, habitat, niche, resource partitioning, character displacement,
population growth curves, r &K selection, demes and dispersal
3: species interactions: competition, herbivory, carnivory, symbiosis, community ecology
4: ecological succession, energy flow(GNP,NNP)
5: Evolution: Oparin & Haldane concept, evolution of prok & euk, evolutionary time scale,
eras, periods & epoch, Neutral evolution
6:population genetics-Hardy Weinberg law, migration & random genetic drift,adaptive
radiation, allopatric & sympatric, convergent evolution, sexual selection, co-evolution,
Altruism, Kin selection, reciprocal altruism
7: Blood and circulation, Cardiovascular system(heart structure, ECG, Cardiac cycle)
8: Respiratory system, Digestive system
9: Nervous system
10: endocrinology (basic mechanisms of hormone action, hormones and diseases)
11: Bioremediation and phytoremediation, Biosensors
12: Vaccines, gene therapy
13: rDNA tech: analysis of RNA, DNA and proteins, gel electrophoresis, isoelectric
focusing gels
14: molecular cloning of RNA & DNA in bacterial & euk systems, DNA fragments in plasmid,
phage, cosmid, BAC,YAC vectors
15: protein sequencing, DNA sequencing, in vitro mutagenesis and deletion techniques,
detection of post translational modification of proteins
16: analysis of gene expression at RNA & protein level, microarray based tech, RFLP, RAPD&
AFLP tech
17: ELISA, RIA, Western blot, Fluocytometry, microscopy (from Prescott),FISH, GISH
18: Difft spectroscopy, Circular dichroism, NMR,ESR, mass speck, X 2 test
19: Taxonomy (+2 NCERT, Campbell biology)
20: biogeography
21-31: +2 NCERT, Campbell biology
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Tanker Voyage Charter Party - Preamble Vegoilvoy CPDokument6 SeitenTanker Voyage Charter Party - Preamble Vegoilvoy CPDiego Carballo100% (2)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
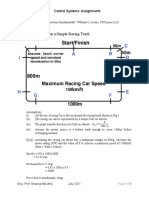
- Electric Car Driven On A Simple Racing Track: Kenyatta University Control Systems: AssignmentsDokument5 SeitenElectric Car Driven On A Simple Racing Track: Kenyatta University Control Systems: Assignmentsezekiel chege0% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Tanker Cargo Calculations Jan-2018 2019Dokument9 SeitenTanker Cargo Calculations Jan-2018 2019Gurjit Singh100% (4)
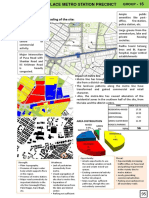
- UD Rajendra PlaceDokument4 SeitenUD Rajendra PlaceSaudamini ChattopadhyayNoch keine Bewertungen
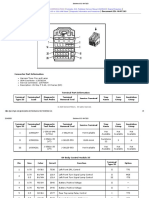
- Body Control Module X5Dokument3 SeitenBody Control Module X5Men PanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 06 Handling Hauling & Stringing of Line Pipes - REV BDokument6 Seiten06 Handling Hauling & Stringing of Line Pipes - REV Bmaneesh singh100% (1)
- Of Of: Coffee Ofcommerce BengaluruDokument3 SeitenOf Of: Coffee Ofcommerce Bengalurusndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- OM CyberSecurityDokument7 SeitenOM CyberSecuritysndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Effect of The Corporate Social ResponsibilityDokument16 SeitenThe Effect of The Corporate Social Responsibilitysndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- T #R+ Arqrrffi - L Cffia I T Rri: Rrs # 6ffi1Dokument7 SeitenT #R+ Arqrrffi - L Cffia I T Rri: Rrs # 6ffi1sndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Spray ReagentsDokument25 SeitenSpray Reagentssndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Manual Grinding MachineDokument34 SeitenInstruction Manual Grinding Machinesndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Complementary Therapies in Medicine: Journal of Animal and Veterinary AdvancesDokument1 SeiteComplementary Therapies in Medicine: Journal of Animal and Veterinary Advancessndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple Sequence AlignmentDokument24 SeitenMultiple Sequence Alignmentsndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wayanad List of Akshaya CentresDokument2 SeitenWayanad List of Akshaya Centressndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Gionee Mobile India - Store LocatorDokument9 SeitenGionee Mobile India - Store Locatorsndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacognostical and Preliminary Phytochemical Investigation of Embelia Ribes Burm FDokument4 SeitenPharmacognostical and Preliminary Phytochemical Investigation of Embelia Ribes Burm Fsndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ammonium Sulfate TableDokument2 SeitenAmmonium Sulfate Tablesndppm7878Noch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Standard: Safety Code For Scaffolds and LaddersDokument33 SeitenIndian Standard: Safety Code For Scaffolds and LaddersNizar MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- A320 Memory ItemsDokument8 SeitenA320 Memory ItemsIan Albert MaligaligNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valve TappetDokument3 SeitenValve TappetLokesh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
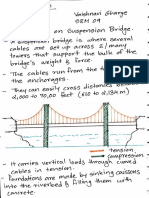
- TOS Suspension Bridge Sem 9Dokument3 SeitenTOS Suspension Bridge Sem 9VAISHNAVI GHARGENoch keine Bewertungen
- Genie S-100 - Genie S-105 - Genie S-120 Genie S-125 - Genie S-100HD - Genie S-120HDDokument1 SeiteGenie S-100 - Genie S-105 - Genie S-120 Genie S-125 - Genie S-100HD - Genie S-120HDCrisz Giovanny Toapanta MedinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- DecelostatDokument41 SeitenDecelostatManoj KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Report Sumul Dairy, Surat: Surat District Co-Operative Milk Producers' Union LTD.)Dokument40 SeitenA Report Sumul Dairy, Surat: Surat District Co-Operative Milk Producers' Union LTD.)Hiteshpatel1267% (3)
- BucharestDokument51 SeitenBucharestfyahyaieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Han MaekDokument50 SeitenHan MaekAnonymous B1AOOsmRMiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brennen 2005 - Fundamentals of Multiphase FlowsDokument90 SeitenBrennen 2005 - Fundamentals of Multiphase FlowsElias TorcaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Toyota Etios Liva 478Dokument3 SeitenToyota Etios Liva 478SouravSengupta0% (1)
- TATA Safari VTT Dicor Owners ManualDokument169 SeitenTATA Safari VTT Dicor Owners ManualRahulNoch keine Bewertungen
- CAT Product LineDokument16 SeitenCAT Product LineKas Kasanova100% (1)
- MBA - Contemporary Management (ESL72-FD) - Final Project Report (SWVL) - GroupDokument29 SeitenMBA - Contemporary Management (ESL72-FD) - Final Project Report (SWVL) - GrouphananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing Survey and Channel ProjectDokument69 SeitenMarketing Survey and Channel ProjectRoyal ProjectsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Machine Serial Number IdentificationDokument7 SeitenMachine Serial Number Identificationعقيد السبئيNoch keine Bewertungen
- CitiesSkylines UserManual enDokument36 SeitenCitiesSkylines UserManual enYulianto Adi NugrohoNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Response of A Turbulent Boundary Layer To A Step Change Surface Roughness Part 1. Smooth To RoughDokument41 SeitenThe Response of A Turbulent Boundary Layer To A Step Change Surface Roughness Part 1. Smooth To RoughFreddie RomeroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eis 1 25Dokument50 SeitenEis 1 25Subhabrata GhoraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hours of Work and Hours of RestDokument26 SeitenHours of Work and Hours of RestZin Maung TunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guide For Flashing EU FXX N53 DME and EGS Using ESYS.v.1.12Dokument7 SeitenGuide For Flashing EU FXX N53 DME and EGS Using ESYS.v.1.12asdfNoch keine Bewertungen
- Site Plan Name of Work:-Proposed Construction of 90Mtr. Span Steel Giirder Bridge On Tapovan-Karchho Motor Road at K.M. 02 Plan - A & BDokument1 SeiteSite Plan Name of Work:-Proposed Construction of 90Mtr. Span Steel Giirder Bridge On Tapovan-Karchho Motor Road at K.M. 02 Plan - A & Bakshay kothiyalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lowe's - Shopping Cart PDFDokument5 SeitenLowe's - Shopping Cart PDFJoshua MartinezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Skid ControlDokument16 SeitenSkid Controlsangeethsreeni100% (3)