Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Chapter 1-2
Hochgeladen von
Susin LimCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Chapter 1-2
Hochgeladen von
Susin LimCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
CHAPTER 1: Mole
Balances
Lecture 2
Failure is a step forward to success
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Topics
Lecture
1:
Chemical Identity
Reaction Rate
Lecture
2:
General Mole Balance Equation
Mole Balance for Different Reactor
Types
Lecture
3:
Mole Balance for Different Reactor
Types
Examples
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Types of Reactor:
1. Batch reactor
2. Continuous-Stirred Tank Reactor
(CSTR)
3. Plug Flow Reactor (PFR) or
Turbular Reactor
4. Packed Bed Reactor (PBR)
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Industrial reactors
Types of reaction
Liquid phase reaction Gas phase reaction
Semi batch reactor,
CSTR
Tubular reactor
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Different types of reactor:
1) Batch reactor
Physical shape: Tank
Used for:
small scale operation
process that is not suitable for continuous operation.
Advantage:
High conversion longer residence time
Disadvantage
High cost
Product variability
Not for large-scale operation
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Different types of reactor:
2) Continuous-Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
Physical shape: Tank
Continuous Flow, Steady state, Perfectly mixed
Used for:
Liquid phase reaction
process that is suitable for continuous operation.
Advantage:
Continuous operation
Disadvantage
Not for non-ideal mixing
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Different types of reactor:
3) Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)
Physical shape: Cylindrical pipe
Continuous Flow, Steady state, Perfectly mixed
Used for:
Gas phase reaction
Reaction rate varies axially NOT radially.
Reactant
Product
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Different types of reactor:
4) Packed Bed Reactor (PBR)
Physical shape: Cylindrical
Continuous Flow, Steady state, Perfectly
mixed
Used for:
Fluid-solid heterogeneous reaction (catalyst)
Reactant
Product
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Photos of real reactor systems
Batch reactor
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
CSTR
Photos of real reactor systems
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Photos of real reactor systems
PFR
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
General Mole Balance Equation
IN OUT + GENERATION = ACCUMULATION
For species A:
Any REACTOR with volume V
UNIT: moles/time
F
AO
F
A
G
A
dN
A
/dt
Number of moles of species
A in a system
Rate of generation of species
A in a system
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
IN OUT + GENERATION = ACCUMULATION
F
AO
F
A
G
A
dN
A
/dt
General Mole Balance Equation
dt
dN
dV r F F
dt
dN
G F F
A
V
A A A
A
A A A
0
0
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Mole Balance For Different
Reactor Type
Batch reactor
dt
dN
V r
A
A
dt
dN
dV r F F
A
V
A A A
0
dt
dN
V r
A
A
.
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Mole Balance For Different
Reactor Type
dt
dN
dV r F F
A
V
A A A
0
Continuous stirred
tank reactor (CSTR)
A
A A
r
F F
V
0
0
0
A A A
Vr F F
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Mole Balance For Different
Reactor Type
Plug Flow Reactor
(PFR)
dt
dN
dV r F F
A
V
A A A
0
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
Mole Balance For Different
Reactor Type
Packed Bed Reactor
(PBR)
-r
A
= mol A reacted
time. mass of catalyst
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
SUMMARY
Reactor Mole Balance Remarks
Batch Well mix, no
spatial
variation,
unsteady state
CSTR Well mix, no
spatial
variation,
steady state
PFR Steady state
PBR Steady state
dt
dN
V r
A
A
CCB 3043 Kinetics and Reactor Design
ANY QUESTION ???
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- United States Environmental Protection Agency: Region Viii 999 18th STREET - SUITE 300 Denver, Colorado 80202-2466Dokument10 SeitenUnited States Environmental Protection Agency: Region Viii 999 18th STREET - SUITE 300 Denver, Colorado 80202-2466Susin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Murchison - DPDokument70 SeitenMurchison - DPSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Peterhead CCS Project: Doc Title: Abandonment Concept For Injection WellsDokument43 SeitenPeterhead CCS Project: Doc Title: Abandonment Concept For Injection WellsSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- P&A of Valhall DP Wells PDFDokument115 SeitenP&A of Valhall DP Wells PDFSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tenarishydril 3Sb™ Connection: ScopeDokument10 SeitenTenarishydril 3Sb™ Connection: ScopeSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slickline Electronic Perforating Tool: AdvantagesDokument1 SeiteSlickline Electronic Perforating Tool: AdvantagesSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Owen Oil Tools: Through Tubing Perforating Charge Performance SummaryDokument1 SeiteOwen Oil Tools: Through Tubing Perforating Charge Performance SummarySusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quo Vadis, Extreme Overbalance?Dokument16 SeitenQuo Vadis, Extreme Overbalance?Susin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- JRC Charge Performance Data PDFDokument4 SeitenJRC Charge Performance Data PDFSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16 MENAPS 11 14 Gun Shock Prediction Andy MartinDokument24 Seiten16 MENAPS 11 14 Gun Shock Prediction Andy MartinSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roper 212r5625 Er220 Motor ChartDokument1 SeiteRoper 212r5625 Er220 Motor ChartSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- GEODynamics CONNEX Brochure 2008.10 - Rev2 Final PDFDokument12 SeitenGEODynamics CONNEX Brochure 2008.10 - Rev2 Final PDFSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dedication - 2019 - Hydraulic Rig Technology and Operations PDFDokument1 SeiteDedication - 2019 - Hydraulic Rig Technology and Operations PDFSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- North Side Spectral Noise LoggingDokument7 SeitenNorth Side Spectral Noise LoggingSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Rig Technology and OperationsDokument3 SeitenHydraulic Rig Technology and OperationsSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
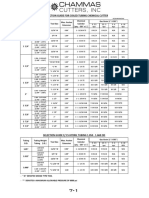
- Selection Guide For Coiled Tubing Chemical CutterDokument5 SeitenSelection Guide For Coiled Tubing Chemical CutterSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slickline Trigger OverviewDokument1 SeiteSlickline Trigger OverviewSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactive Marker Sub PDFDokument1 SeiteRadioactive Marker Sub PDFSusin LimNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- Check Valve, Hydraulically Operated, Type Z2SRK 10Dokument4 SeitenCheck Valve, Hydraulically Operated, Type Z2SRK 10Ahmed Abd ElhakeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exterran Drain: P&id No. P & Id TitleDokument15 SeitenExterran Drain: P&id No. P & Id Titledilip matalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Propeller Turbine Vs Kaplan TurbineDokument26 SeitenPropeller Turbine Vs Kaplan TurbineUmarKhan0% (1)
- Symbol Plant-3d-Isometrics PDFDokument9 SeitenSymbol Plant-3d-Isometrics PDFEvaldo BritoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bellows Sealed DN20Dokument3 SeitenBellows Sealed DN20Turbo Snail RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kpa Pump & MotorDokument2 SeitenKpa Pump & Motoredwin edarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure Test CertificateDokument10 SeitenPressure Test CertificateDav LalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 13 - Drilling HydraulicsDokument65 SeitenLecture 13 - Drilling HydraulicsMaria Luisa CepedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19-0165P-DR-GA-200 Reva - Container #2-3Dokument1 Seite19-0165P-DR-GA-200 Reva - Container #2-3Jaime Arturo Trujillo RemolinaNoch keine Bewertungen
- V Imp ExampleDokument24 SeitenV Imp ExamplealiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure RatingDokument1 SeitePressure RatingprakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pump Selection Condensate Pump: Deaerator Pressure With 10% Allowance Assuming Piping Pressure DropDokument3 SeitenPump Selection Condensate Pump: Deaerator Pressure With 10% Allowance Assuming Piping Pressure DropJom BonhayagNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ansul Line ProportionersDokument4 SeitenAnsul Line ProportionerskambiadoNoch keine Bewertungen
- System Curves - Goulds Pump.Dokument3 SeitenSystem Curves - Goulds Pump.sgrsthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aspen Flare System Analyzer V10 - AspenoneDokument38 SeitenAspen Flare System Analyzer V10 - AspenoneMiftah MasrurNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 - Hole Cleaning BMS 2013Dokument21 Seiten21 - Hole Cleaning BMS 2013Slim.B100% (1)
- Restriction Orifice CPPDokument9 SeitenRestriction Orifice CPPparykoochakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 Heat PDFDokument39 SeitenChapter 5 Heat PDFPankaj KanatheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydraulic Calculations Fire ProtectionDokument16 SeitenHydraulic Calculations Fire ProtectionGabriel LopezNoch keine Bewertungen
- List Shell Dep & Mesc SpeDokument9 SeitenList Shell Dep & Mesc Spewawan80% (5)
- 0331-CAL-ING-014-010-0001 - R0 - HVAC System - Hydraulic - Calculation - Report PDFDokument302 Seiten0331-CAL-ING-014-010-0001 - R0 - HVAC System - Hydraulic - Calculation - Report PDFOleg ShkolnikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wet Riser NewDokument19 SeitenWet Riser NewFaiz SalimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Check ValveDokument99 SeitenCheck ValvepganoelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 145 Bronze Y Strainer - Spec Sheet: Features & BenefitsDokument2 Seiten145 Bronze Y Strainer - Spec Sheet: Features & BenefitsHamza ChenakerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Rev 2 Air SystemDokument12 SeitenChapter 8 Rev 2 Air SystemAnonymous 340A7vnwV1Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9.5-Turbulent Boundary LayerDokument15 Seiten9.5-Turbulent Boundary LayershutdoNoch keine Bewertungen
- What Is Lamont Boiler?Dokument3 SeitenWhat Is Lamont Boiler?Muhammad Fahmi HidayatullohNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatic System ComponentDokument29 SeitenPneumatic System Componentbhadresh100% (1)
- Continuity EquationDokument15 SeitenContinuity Equationykhamidi3889Noch keine Bewertungen