Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Waves Damping
Hochgeladen von
jemwesleyOriginalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Waves Damping
Hochgeladen von
jemwesleyCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
6.
1
WAVES WAVES
DAMPING AND RESONANCE
IN AN OSCILLATING SYSTEMS
LEARNING OUTCOMES
By the end of this lesson, the student should
be able to:
Describe damping in an oscillating system
Describe resonance in a oscillating system Describe resonance in a oscillating system
What can you say about the amplitude of the
swing?
What can you do to maintain or increase the
amplitude?
At the start, the pendulum oscillates
with maximum amplitude.
The amplitude of the oscillation
decreases with time and finally stops.
What causes the pendulum to stop?
Air friction causes the amplitude of the
pendulum to decrease.
When the pendulum oscillates, it has energy.
This energy is used to overcome air friction.
As time passes, more energy of the pendulum As time passes, more energy of the pendulum
is being used to overcome air friction.
This causes the energy of the pendulum to
decreases.
As a result, the amplitude becomes smaller.
The pendulum is said to experience damping.
Damping
Damping is the decrease in the amplitude of
an oscillating system when its energy is lost
as heat energy.
The amplitude of an oscillating system will The amplitude of an oscillating system will
gradually decrease and become zero when
the oscillation stops.
Activity 2:
Damping effect in a
vibrating system
Set up the apparatus as
shown below.
Fix a saw blade
horizontally on the leg of
a laboratory bench using a laboratory bench using
a G-clamp.
At the other end of the
blade, fix a piece of
plasticine (50 g)
Move the plasticine to
the position X and
release it.
Observe the position Y
reached by the plasticine.
Observe subsequent Y
positions of the plasticine.
Observation:
What changes do you
observe in the position
Y over several
oscillations?
Conclusion:
Position Y decreases
Conclusion:
The position Y becomes _________ to the
equilibrium position each time the plasticine
oscillates.
closer
Why does the spring oscillate closer and closer to the
equilibrium position?
Its amplitude decreases.
What happens to the energy possessed by the
plasticine and the blade?
Energy possess decreases and lost to heat.
What happens to the oscillation of the blade after a What happens to the oscillation of the blade after a
long time?
It will stop.
What is the name given to this phenomenon?
Damping
How do you overcome the damping effect of the
oscillation
Give external force or push the plasticine ball.
A mother puts her
baby to sleep in a
sarong cradle. She
needs to
continuously move
the sarong cradle up
and down.
What happen to the sarong cradle
when the mother stops moving the
cradle up and down?
Amplitude decreases
Suggest a reason for the
movement of the sarong cradle
discussed in (a).
Damping, lost energy to heat Damping, lost energy to heat
What must you do if you want to
help the mother to maintain the
movement of the cradle?
Move the cradle up and down
/ give external force
Forced oscillation & Damping
The swing will stop
The boy is given a
The swing will stop
swinging due to
damping.
The boy is given a
periodic push at the
correct timing will
continue to swing
without stopping.
A system oscillates at
its natural frequency
when no external
force is applied to it.
When a periodic force
If a periodic force is
applied to the swing
at its natural
frequency, the
amplitude of the
Forced oscillation & Damping
When a periodic force
is applied to an
oscillating system, the
response depends on
the frequency of the
periodic force.
amplitude of the
swing increases as the
energy of the swing
increases.
The swing is said to
be in resonance and it
oscillates with a
maximum amplitude.
Resonance in an oscillating system
To enable an oscillating system to go on
continuously, an external force must be
applied to the system.
The external force supplies energy to the The external force supplies energy to the
system. Such a motion is called a forced
oscillation
Natural frequency is the frequency of a
system which oscillates freely without the
action of an external force.
Resonance in an oscillating system
Resonance occurs when a system is made to
oscillate at a frequency equivalent to its
natural frequency by an external force. natural frequency by an external force.
The resonating system oscillates at its
maximum amplitude.
Bartons pendulum
The frequency of a simple pendulum depends
on the length of the pendulum.
In Bartons pendulum experiment, there are
many pendulums tied to the rope. Two of
the pendulum are of the same length the pendulum are of the same length
When pendulum B oscillates, all the other
pendulums are forced to
oscillate.
Bartons pendulum
But pendulum D oscillates with the largest
amplitude, ie, pendulum D resonates
Pendulum B and pendulum D are of the same
length.
Frequency B equal Frequency D Frequency B equal Frequency D
Therefore, pendulum B causes pendulum D
to oscillate at its natural frequency.
Effects of resonance
Breaking glass
The frequency of the sound is equal to the
natural frequency of the glass. Resonance
occurs and the glass vibrates with largest
amplitude and it breaks. amplitude and it breaks.
Tacoma Bridge collapsed in 1940
The wind have the same frequency as the
natural frequency of the vibration of the
bridge. Resonance occurred and caused the
bridge to collapse.
Question 1
A system vibrates with a natural
frequency. If a forced vibration of the
same frequency is given to the system,
what will happen? what will happen?
A. Damping
B. Vibration
C. Resonance
When does an oscillating system
experiences damping?
A. When the amplitude of oscillation
decreases
Question 2
decreases
B when the period decreases
C when the frequency increases
D when the amplitude remains
constant
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Activity Properties of Alkanes N AlkeneDokument1 SeiteActivity Properties of Alkanes N AlkeneZaizahirawati MklNoch keine Bewertungen
- Classification Test For HydrocarbonsDokument6 SeitenClassification Test For HydrocarbonsHeather GutierrezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Genotype Phenotype WorksheetDokument3 SeitenGenotype Phenotype WorksheetJohn G Villar100% (1)
- CH 7 Ionic BondsDokument27 SeitenCH 7 Ionic Bondsapi-239855791Noch keine Bewertungen
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDokument57 SeitenPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationLeah Hope CedroNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAB 4 (Reaction of Halogens With Water and Sodium Hydroxide)Dokument8 SeitenLAB 4 (Reaction of Halogens With Water and Sodium Hydroxide)Marie ChapmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grade 10 - ch2, 100Dokument2 SeitenGrade 10 - ch2, 100NayLinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fluid Dynamics HydrodynamicsDokument21 SeitenFluid Dynamics HydrodynamicssaneleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hydrogenation of AlkenesDokument2 SeitenHydrogenation of AlkenesNur FarahinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Gas LawDokument52 SeitenChapter 1 - Gas LawLolindah ChinNoch keine Bewertungen
- New Physics f4 FormulaDokument15 SeitenNew Physics f4 FormulaFazli SarinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Accelerated Motion (Uam)Dokument33 SeitenUniform Accelerated Motion (Uam)Knightmare9871Noch keine Bewertungen
- Work - Energy - and PowerDokument14 SeitenWork - Energy - and Powerraj78678Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electron ConfigurationDokument62 SeitenElectron ConfigurationCarmi Mari MoratinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metallic Bonding: Chemical Bonding Is Different in Metals Than It Is in Ionic, Molecular and Covalent CompoundsDokument7 SeitenMetallic Bonding: Chemical Bonding Is Different in Metals Than It Is in Ionic, Molecular and Covalent CompoundsKenzy HamdyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamic NotesDokument51 SeitenThermodynamic NotesAnand MurugananthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum Mechanical ModelDokument24 SeitenQuantum Mechanical ModelStanly De LeonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Charge and CurrentDokument33 SeitenElectric Charge and CurrenthasminNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Particulate Nature of MatterDokument21 SeitenChemistry Particulate Nature of MatterFandyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7 - Conservation of Energy and MomentumDokument40 SeitenChapter 7 - Conservation of Energy and Momentumascd_msvuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inter Molecular Forces and Liquids and SolidsDokument53 SeitenInter Molecular Forces and Liquids and Solidsdevender singh100% (2)
- Modern PhysicsDokument74 SeitenModern PhysicsLàXsun ShrèsthàNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kinetic Mastering PhysicsDokument16 SeitenKinetic Mastering PhysicsKyle DonagheyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Melc 124 127 ThermochemistryDokument44 SeitenMelc 124 127 ThermochemistryFmae antoinette100% (1)
- Biomolecules (2022)Dokument51 SeitenBiomolecules (2022)Raymon Inolino IletoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 04 17 GC2 Properties of Liquids and The Effect of IntermolecularDokument31 Seiten12 04 17 GC2 Properties of Liquids and The Effect of IntermolecularMay Ann Sabangan0% (1)
- MCQ From Sound & WaveDokument3 SeitenMCQ From Sound & WaveRaktimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5.1 ElectronDokument53 Seiten5.1 ElectronFarish MikhaelNoch keine Bewertungen
- PE and KE Practice KEYDokument2 SeitenPE and KE Practice KEYRaymond ColladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Notes 2 - The Periodic TableDokument33 SeitenChemistry Notes 2 - The Periodic TableErin KabezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkanes and AlkenesDokument73 SeitenAlkanes and AlkenesRosemaryTanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lattice EnergyDokument30 SeitenLattice EnergyNitya DewiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quantum NumbersDokument12 SeitenQuantum NumbersSoub kuopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Entropy A Detailed ExplanationDokument20 SeitenEntropy A Detailed ExplanationgovindkaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesDokument35 SeitenChapter 11 F2 Stars and GalaxiesBernardNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pressure in LiquidsDokument18 SeitenPressure in LiquidsNatasha54321Noch keine Bewertungen
- 11.7 States of Matter Phet LabDokument3 Seiten11.7 States of Matter Phet Lababbymingus60% (1)
- Energi Kisi Dan Born HaberDokument31 SeitenEnergi Kisi Dan Born HaberNovi CherlyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 4 Density and Relative DensityDokument12 SeitenClass 4 Density and Relative DensityMollel TajiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Some Important Point: Modern PhysicsDokument5 SeitenSome Important Point: Modern PhysicsBhanuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Newton's 2nd Law of MotionDokument37 SeitenNewton's 2nd Law of MotionPrincess Shanne GalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pasay S9LT Q1 W3 4 04Dokument6 SeitenPasay S9LT Q1 W3 4 04Frederick EspejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PropertiesDokument41 SeitenPropertiesMarielle LabradoresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electronic Structure of AtomsDokument98 SeitenElectronic Structure of AtomsDexter EnthusiastsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 5 - Thermochemistry GC2Dokument44 SeitenChapter 5 - Thermochemistry GC2helalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 1Dokument24 SeitenMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 1ridwan71% (7)
- Definitions For Photosynthesis 1Dokument7 SeitenDefinitions For Photosynthesis 1api-242369572Noch keine Bewertungen
- Uniform Circular MotionDokument25 SeitenUniform Circular MotionGIDEON TEMIDAYO JUDENoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2Dokument8 SeitenModule 2Ashner NovillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Lab ReportDokument3 SeitenPhysics Lab ReportnouraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Atomic Structure Full Notes 50 PageDokument52 SeitenAtomic Structure Full Notes 50 PageSubhajit GoraiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Week 8 9 Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityDokument44 SeitenPhysics Week 8 9 Rotational Motion and The Law of GravityMark Lorens Staana100% (1)
- Chemistry Gas Laws ExercisesDokument6 SeitenChemistry Gas Laws Exercisesjag1231Noch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Properties of MatterDokument4 SeitenThermal Properties of MatterPeter KachouhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Force & Electric Field IDokument60 SeitenElectric Force & Electric Field IImran ParvezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Understanding Gas Pressure and Atmospheric PressureDokument30 SeitenUnderstanding Gas Pressure and Atmospheric Pressuretidanni100% (1)
- 0620 Properties of MetalsDokument10 Seiten0620 Properties of MetalsTadisa ChiwiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1020-Lewis and Shapes PDFDokument4 Seiten1020-Lewis and Shapes PDFJaya Chitra Degala RamaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationDokument15 SeitenThe Modern Periodic Table Chemistry PresentationShee YingNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Final NotesDokument15 SeitenPhysics Final NotesalzainaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NOTES Universal Gas Law F4Dokument1 SeiteNOTES Universal Gas Law F4jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- PT3 Kelantan Sains SkemaDokument17 SeitenPT3 Kelantan Sains Skema纪泽勇100% (1)
- Physics Perfect Score Module Form 5Dokument48 SeitenPhysics Perfect Score Module Form 5jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physics Perfect Score Module Form 4Dokument52 SeitenPhysics Perfect Score Module Form 4jemwesley100% (1)
- 6.2 Reflection of 6.2 Reflection of WavesDokument15 Seiten6.2 Reflection of 6.2 Reflection of WavesjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4.pecutan Momentum&gravity PDFDokument7 Seiten4.pecutan Momentum&gravity PDF'Izzat NordinNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 CroDokument7 Seiten7 CrojemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.linear Motion2Dokument10 Seiten3.linear Motion2jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thecharacteristic SoundDokument12 SeitenThecharacteristic SoundjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 0 ElectricityDokument26 Seiten2 0 ElectricityLojk LeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.1 Linear Motion 2012Dokument18 Seiten2.1 Linear Motion 2012cikgusuriyatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 5 Applications of SoundDokument9 Seiten2 5 Applications of SoundjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wave Motion How Do Waves Transfer Energy? Longitudinal & Transverse WavesDokument30 SeitenWave Motion How Do Waves Transfer Energy? Longitudinal & Transverse Wavessuemozac100% (3)
- Wave Motion How Do Waves Transfer Energy? Longitudinal & Transverse WavesDokument30 SeitenWave Motion How Do Waves Transfer Energy? Longitudinal & Transverse Wavessuemozac100% (3)
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Times SPM 2011 PhysicsDokument37 Seiten(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Times SPM 2011 PhysicsjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9.3 Transistor Notes: Saturday, April 3, 2010Dokument14 Seiten9.3 Transistor Notes: Saturday, April 3, 2010jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- MentoringDokument17 SeitenMentoringjemwesley100% (2)
- Skema Paper 3Dokument10 SeitenSkema Paper 3jesunathan44@yahoo.comNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Perfect Score SBP Fizik SPM 2012Dokument78 SeitenModul Perfect Score SBP Fizik SPM 2012Cikgu Faizal100% (5)
- 10 HeatDokument6 Seiten10 HeatjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2.0 ElectricityDokument26 Seiten2.0 ElectricityjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 TransisstorDokument11 Seiten2 TransisstorjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics 2003Dokument1 SeiteAnswer Chapter 1: Introduction To Physics 2003jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 0 ElectricityDokument26 Seiten2 0 ElectricityLojk LeongNoch keine Bewertungen
- WavespptDokument27 SeitenWavespptjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sains Form 1Dokument1 SeiteSains Form 1jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jeopardy Cell Division2Dokument142 SeitenJeopardy Cell Division2jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument15 SeitenChapter 3jemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fizik Kertas 1 Percubaan SPM 2012 P PinangDokument30 SeitenFizik Kertas 1 Percubaan SPM 2012 P PinangjemwesleyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mech ANM 2019R1 WS04D-Anisotropic HyperelasticityDokument14 SeitenMech ANM 2019R1 WS04D-Anisotropic HyperelasticityDong LINoch keine Bewertungen
- Fea 2 Marks and AnswersDokument20 SeitenFea 2 Marks and AnswerssnvijayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3TF8 Reversing Contactors - Motor Starters - SiemensDokument2 Seiten3TF8 Reversing Contactors - Motor Starters - SiemensAlberto Morillo ParelladaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Staad Input FileDokument18 SeitenStaad Input FileKP SahuNoch keine Bewertungen
- RigsPresentation PDFDokument16 SeitenRigsPresentation PDFAndrei ClaudYuNoch keine Bewertungen
- GPB 180Dokument1 SeiteGPB 180sungkarsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thw500 Tds (TT - 0416) EnglishDokument2 SeitenThw500 Tds (TT - 0416) EnglishMasood KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- sl2019 685Dokument3 Seitensl2019 685avm4343Noch keine Bewertungen
- Jig Boring, Jig Grinding and BroachingDokument14 SeitenJig Boring, Jig Grinding and Broachingjineesha p jNoch keine Bewertungen
- Howard B (1) - Petroleum Engineers Handbook, Part 4Dokument331 SeitenHoward B (1) - Petroleum Engineers Handbook, Part 4yayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wafflemat Design WhitepaperDokument13 SeitenWafflemat Design WhitepaperantiacidoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project Name: Xflow Local Protection Water Mist System Area Reference: Main EngineDokument5 SeitenProject Name: Xflow Local Protection Water Mist System Area Reference: Main EngineAlexDorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mfaf BK: ScopeDokument23 SeitenMfaf BK: ScopesbalajimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theoretical Model of Buoyancy-Induced Heat Transfer in Closed Compressor RotorsDokument7 SeitenTheoretical Model of Buoyancy-Induced Heat Transfer in Closed Compressor RotorsmhjianNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 5985707401435677780Dokument3 Seiten4 5985707401435677780Ibrahim AwadNoch keine Bewertungen
- JD - Field Service EngineerDokument2 SeitenJD - Field Service EngineerRajesh PotluriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles of Dynamics4Dokument524 SeitenPrinciples of Dynamics4Christien MarieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine Operation Procedrue (A)Dokument148 SeitenTurbine Operation Procedrue (A)ashishmathew100% (1)
- DI7140N - EN-Expansion JointDokument1 SeiteDI7140N - EN-Expansion JointHai PhanNoch keine Bewertungen
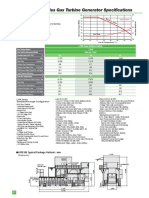
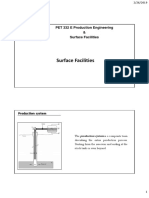
- PET 332 E Production Engineering & Surface FacilitiesDokument13 SeitenPET 332 E Production Engineering & Surface Facilities000Noch keine Bewertungen
- LEWA Ecoflow Variable Eccentric Pump Drive Type LDC: PerformanceDokument2 SeitenLEWA Ecoflow Variable Eccentric Pump Drive Type LDC: Performancenima azariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proforma Invoice: Bill ToDokument2 SeitenProforma Invoice: Bill ToExpert Trading & Ttechnical ServicesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Researchpaper Design Model of Built Up Stiffened Column Base Under Large Eccentric LoadDokument10 SeitenResearchpaper Design Model of Built Up Stiffened Column Base Under Large Eccentric LoadNishant GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of Excitation SystemDokument13 SeitenTypes of Excitation SystemRohit Akiwatkar33% (3)
- M 110yDokument2 SeitenM 110yjawadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15780Dokument16 Seiten15780uddinnadeemNoch keine Bewertungen
- 59 Why Nuts and Bolts Come Loose V1Dokument2 Seiten59 Why Nuts and Bolts Come Loose V1jillianixNoch keine Bewertungen
- Copper Tube DetailsDokument6 SeitenCopper Tube DetailsBhavin PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dept. Technical Reference Created by Approved byDokument1 SeiteDept. Technical Reference Created by Approved byakshatNoch keine Bewertungen