Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Introduction To Motorola 6800
Hochgeladen von
api-249964743Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Introduction To Motorola 6800
Hochgeladen von
api-249964743Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
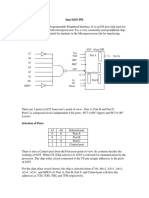
Rabel Talpur:12BME#025
40-pin chip
Developed by Motorola in 1975
16 address lines and 8 data lines
Used only +5V
Registers
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Control Unit
Program Counter
Stack Pointer
Status Flags
A
B
IX
PC
SP
CC
Accumulator A
Accumulator B
Index register X
Program counter
Stack pointer
Condition code register
The micro processor unit contains 2
accumulators designed ACCA and ACCB.
Each accumulators is 8 bits (one byte) long
and is used to hold operands and data from
the arithmetic logic unit
The index register (x) is a 16 bit (2 byte)
register which is primarily used to store a
memory address in the indexed mode of
memory addressing.
The index register may be decremented,
incremented and stored.
The condition code register is an 8 bit
register. each individual bit may get set or
cleared from of an instruction.
Each instruction effects the condition code
register differently.
The primary use of this register is execution
of the conditional branch instruction.
ALU is a digital circuit that performs integer
arithmetic and logical operations.
It is fundamental building block of central
processing unit.
It is a component of central processing unit
which direct the operation of processor.
It control communication and co-ordination
between i/o devices.
It reads interrupts instructions and
determine the sequence for processing the
data.
It performs the task of fetching, decoding,
managing, execution and finally storing
results.
Program counter contain the address of the
memory containing the next instruction to be
executed.
It is incremented automatically after each
instruction
In 6800, it is a 16 bits register
Used to point to the memory location where
all registers will be saved when an interrupt
occurs
It is a 16 bit register, contain an address of a
memory
16 address wires =it can address 2
16
memory
locations
It is an 8 bit microprocessor => 8 data bits
Speed up to 4 MHZ
Architecture
S.No 6800 8085
1 It has two
accumulators
Only one
accumulator is
present
2 Uses frequency 1 MHz uses frequency from
3 to 5 MHz
3 It has index register No index register is
present
4 Has 3 interrupts
(IRQ,NMI,SWI)
Has five interrupts
(Trap, RST 7.5,RST
6.5, RST 7.5, INTR)
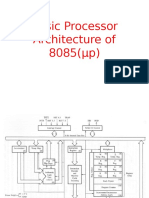
BLOCK DIAGRAM OF 6800
INTERRUPTS
IRO
mask able interrupt. When the interrupt
occurs the program counter, index register,
accumulators and condition code registers
are stored in the stack, the further interrupts
are disabled and the processor jumps to
memory location address of which is stored
in memory FFF8h - FFF9h. To return from the
interrupt the processing routine should use
RTI instruction. This interrupt can be
enabled/disabled using CLI/SEI instructions.
INTERRUPTS
IRQ
NMI
non-maskable interrupt. When the interrupt
occurs the program counter, index register,
accumulators and condition code registers are
stored in the stack, the further interrupts are
disabled and the processor jumps to memory
location address of which is stored in memory
FFFCh - FFFDh. To return from the interrupt the
processing routine should use RTI instruction.
This interrupt can not be disabled.
NMI
SWI
software interrupt. This interrupt can be only
invoked from the program. When the
interrupt occurs the processor stores the
program counter, index register,
accumulators and condition code registers in
the stack, disables the further interrupts and
jumps to memory location address of which
is stored in memory FFFAh - FFFBh. To return
from the interrupt the processing routine
should use RTI instruction. This interrupt can
not be disabled.
SWI
None.
Accumulator A (ACCA) is an 8-bit register
used for arithmetic and logic operations.
Accumulator B (ACCB) is an 8-bit register
used for arithmetic and logic operations.
I/O ports
REGISTERS
Index (IX) is a 16-bit register usually used for
temporary storage or as an index when
indexed addressing is used.
Program counter (PC) is a 16-bit register.
Stack pointer (SP) is a 16-bit register.
Condition code register contains the following
flags:
Half carry (H) - set if there was a carry from bit
3 to bit 4 of the result when the result was
calculated.
Interrupt mask (I) - set if the IRQ interrupt is
disabled.
Negative (N) - set if the most significant bit of
the result is set.
Zero (Z) - set if the result is zero.
Overflow (V) - set if there was an overflow
during last result calculation.
Carry (C) - set if there was a carry from the bit 7
during last result calculation.
Condition code register contains the following
flags:
Instruction Set
6800 instruction set consists of 72
instructions:
Data moving instructions.
Arithmetic - add, subtract, negate,
increment, decrement and compare.
Logic - AND, OR, exclusive OR, complement
and shift/rotate.
Control transfer - conditional, unconditional,
call subroutine and return from subroutine.
Other - clear/set condition flags, bit test,
stack operations, software interrupt, etc.
Addressing modes
Implied - the data value/data address is
implicitly associated with the instruction.
Accumulator - the instruction implies that
the data is one of the accumulator registers.
Immediate - 8-bit or 16-bit data is provided
in the instruction.
MEMORY
Program, size is 64 KB. data and stack
memories occupy the same memory space.
The total addressable memory .
DATA MEMORY
data can be anywhere in memory space.
MEMORY
DATA MEMORY
program can be located anywhere in
memory. Jump and subroutine call
instructions can be used to jump anywhere in
memory.
PROGRAM MEMORY
STACK MEMORY
stack can be placed anywhere in memory
space.
FFF8h - FFF9h: Pointer to IRQ interrupt-
processing routine.
FFFAh - FFFBh: Pointer to software interrupt-
processing routine.
STACK MEMORY
RESERVED MEMORY LOCATION
FFFCh - FFFDh: Pointer to NMI interrupt-
processing routine.
FFFEh - FFFFh: Pointer to RESET handling
code.
Some memory addresses may be reserved for
memory mapped I/O as the processor doesn't
have hardware I/O capability.
INSTRUCTION SET MOTOROLA 6800
PRESENTED
BY: MURK
SALEEM
12BME19
Group of instructions
executed by
microprocessor is
called as:
INSTRUCTION SET.
Motorola-6800 has 72
instructions.
1.ARITHMETIC
INSTRUCTIONS
OPERATION OPCODE/
MNEMONICS
ALL REGISTER
LABELS REFER
TO CONTENTS
1.Addition ADDA A+MA
ADDB B+MB
2.Add
Accumulators
ABA A+BA
3.Add With Carry ADCA A+M+C
4.Compliment
2`s (Negative)
NEG
00-MM
NEG A 00-AA
NEG B 00-BB
5.Subtract SUB A A-MA
SUB B B-MB
6.Subtract
Accumulators
SB A A-BA
Two`s
compliment
arithmetic is used
in MP6800
which allow us to
take the 2s
compliment of a
number.
The negative
instruction allows
us to operate on a
byte in memory
without first
fetching the
operand from
memory. In the
past, we have
loaded the
operand,
performed
operation and
then stored the
new operand
2. DATA HANDLING
INSTRUCTIONS:
OPERATION OPCODES/
NMEMONICS
ALL REGISTER
LABELS REFER
TO CONTENTS
1.Clear CLR 00M
CLR A 00A
CLR B 00B
2.Decrement DEC M-1M
DEC A A-1A
DEC B B-1B
3.Increment INC M+1M
INC A A+1A
INC B B+1B
4.Load
Accumulator
LDAA MA
LDAB MB
5.Rotate Left ROL M
ROL A A
ROL B B
CLEAR
instruction
allows us to
clear a memory
or either
accumulator. In
the past, we
have cleared
bytes of first
clearing the
accumulator
then storing the
result in the
proper memory
location.
However, the
CLR instruction
allows us to
clear a memory
location with a
single
instruction.
OPERATION OPCODES/
NMEMONICS
ALL REGISTER
LABELS REFER
TO CONTENTS
6.Rotate Right ROR M
ROR A A
ROR B B
7.Store
Accumulator
STA A AM
STA B BM
8. Transfer
Accumulator
TAB AB
TBA BA
TRANSFER
ACCUMULATOR copies
the contents of
accumulator A or B.
After this instruction is
executed, the number
originally present in
any accumulator(eg: A)
will be in both
accumulators.
3. LOGIC
INSTRUCTIONS:
OPERATION OPCODES/
NMEMONICS
ALL REGISTER LABELS
REFER TO CONTENTS
1. And AND A A.MA
AND B B.MB
2.Compliment,1`s COM
M M
COM A
A A
3.X-OR EOR A A (+) M
EOR B B (+) M
4.OR OR A A+MA
OR B B+MB
4. DATA TEST
INSTRUCTIONS:
OPERATION OPCODES/ NMEMONICS ALL REGISTER LABELS
REFER TO CONTENTS
1. Bit Test BIT A A.M
BIT B B.M
2.Compare CMP A AM
CMP B BM
3.Compare Accumulators CBA AB
BIT TEST this instruction is very similar to the AND instructions. In
both cases, the contents of the specified accumulator are ANDed with
the contents of the selected memory location. The difference is that
with the bit test instruction no logical product is produced. Neither the
contents of the accumulator nor memory are altered in any way.
However condition code are affected just as if the AND operation had
taken place. Consider BITA instruction, when executed, A is ANDed
with M. If result is 0000, the Z register is set. Otherwise, the Z register
is cleared.
5. INDEX
REGISTER AND
STACK POINTER
INSTRUCTIONS:
The index and stack pointer are 16-bit
registers. That allow us to control the
operation of these registers. Because of
the 16-bit format, the load, store, and
compare instructions are slightly
different.
OPERATION OPRANDS/
NMEMONICS
ALL REGISTER LABELS
REFER TO CONTENTS
1.Compare Index Reg. CPX (
)(M/M+1)
2.Decrement Index Register DEX X-1X
3.Decrement Stack Pointer DES SP-1SP
4. Increment Stack Pointer INS SP+1SP
5.Increment Index Register INX X+1X
The COMPARE REGISTER instruction allows us to compare the 16-bit
number in the index register with any two consecutive bytes in memory.
(as index register hold two bytes). The higher byte is defined as
while the lower byte is defined as
. When the CPX instruction is
executed,
is compared with 8-byte in the specified memory
location (M) and
is compared with byte immediately following the
specified memory location (M+1).
6.BRANCH INSTRUCTIONS:
Condition code register contains the following flags:
Half carry (H) - set if there was a carry from bit 3 to bit
4 of the result when the result was calculated.
Interrupt mask (I) - set if the IRQ interrupt is disabled.
Negative (N) - set if the most significant bit of the
result is set.
Zero (Z) - set if the result is zero.
Overflow (V) - set if there was an overflow during last
result calculation.
Carry (C) - set if there was a carry from the bit 7 during
last result calculation.
OPERATION OPCODE/
NMEMONICS
ALL REGISTER LABELS
REFER TO CONTENTS
1.Branch Always BRA NONE
2.Branch If Clear BCC C=0
3.Branch If Carry Set BCS C=1
4.Branch If Minus BMI N=1
5.Branch If Plus BPL N=0
6.Branch If Over-Flow Set BVS V=1
7.Branch If Over-Flow
Clear
BVC V=0
7. CONDITION CODE REGISTER:-
The 6800 uses these instructions in order to
direct access the condition codes.
OPERATION OPCODES/ NMEMONICS ALL REGISTER LABELS
REFER TO CONTENTS
1.Clear Carry CLC 0C
2.Clear Interrupt Mask CLI 0I
3.Clear Over-Flow CLV 0V
4.Set Carry SEC 1C
5.Set Interrupt Mask SEI 1I
6.Set Over-Flow SEV 1V
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Introduction to 6800/6802 Microprocessor Systems: Hardware, Software and ExperimentationVon EverandIntroduction to 6800/6802 Microprocessor Systems: Hardware, Software and ExperimentationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MicroprocessorsDokument4 SeitenIntroduction To MicroprocessorsNaga Chaitanya ChilukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Isa ArchitectureDokument108 SeitenIsa ArchitectureseyfiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EC6303 Signals and Systems PDFDokument82 SeitenEC6303 Signals and Systems PDFkiranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signal & Systems UNIT: 42 Author: Prof. S.C. Dutta RoyDokument1 SeiteSignal & Systems UNIT: 42 Author: Prof. S.C. Dutta RoySANJEEV KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Complex Instruction Set ComputerDokument17 SeitenComplex Instruction Set ComputerkangkanpaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT1402 Nov Dec+2009Dokument20 SeitenIT1402 Nov Dec+2009piccoloashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Signals and Systems PDFDokument4 SeitenSignals and Systems PDFkalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cadence TutorialDokument12 SeitenCadence TutorialAshraf HusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSE313 Course Syllabus 191 SAmdDokument3 SeitenCSE313 Course Syllabus 191 SAmdMasud SarkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Set 8085Dokument15 SeitenInstruction Set 8085MuhammadAli VellaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Set ArchitectureDokument8 SeitenInstruction Set ArchitecturekalpanasripathiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems Unit IVDokument11 SeitenEmbedded Systems Unit IVSreekanth PagadapalliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Set ArchitectureDokument92 SeitenInstruction Set ArchitectureAzka GilaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Book Computer ArchitectureDokument8 SeitenCourse Book Computer ArchitectureDr-Raghad Al-FahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To MTS 86C Microprocessor Training System PDFDokument30 SeitenIntroduction To MTS 86C Microprocessor Training System PDFassora100% (1)
- Reviewing The Basics of Microstrip LinesDokument6 SeitenReviewing The Basics of Microstrip LinesMateus LucasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Set 8085Dokument19 SeitenInstruction Set 8085internetwealthdonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Micro Program Control UnitDokument27 SeitenMicro Program Control UnitNaman GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- PTSP 2 Marks Questions Unit IDokument2 SeitenPTSP 2 Marks Questions Unit IramanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 0 000 0 0embedded System 8th Sem E&C (4 & Half Chapter) Notes Written by Arunkumar G, Lecturer, STJIT, RanebennurDokument198 Seiten0 000 0 0embedded System 8th Sem E&C (4 & Half Chapter) Notes Written by Arunkumar G, Lecturer, STJIT, RanebennurAnanth SettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Unified Algorithm For Elementary FunctionsDokument8 SeitenA Unified Algorithm For Elementary FunctionsCristo_Alanis_8381Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Instruction SetDokument27 Seiten8085 Instruction Setbostanci100% (1)
- Mirror AdderDokument51 SeitenMirror AdderjeevanprsdNoch keine Bewertungen
- Counters & Time DelaysDokument16 SeitenCounters & Time Delaysapi-3724082100% (16)
- Emtl CFDokument85 SeitenEmtl CFSivaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Instruction Addressing Modes ImppDokument87 Seiten8085 Instruction Addressing Modes ImppRohan VaidyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- MicrosequencerDokument38 SeitenMicrosequencerJonathan MejiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture2 ThirdmicroprocessorcDokument22 SeitenLecture2 Thirdmicroprocessorcxkurt358792100% (2)
- Ec1x11 Electron Devices and Circuits3 0 2 100Dokument2 SeitenEc1x11 Electron Devices and Circuits3 0 2 100Siva KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS1303 Theory of ComputationDokument26 SeitenCS1303 Theory of ComputationLavanya AshokNoch keine Bewertungen
- AZI - Computer Architecture - 672.7E Exams Questions List - 2018Dokument6 SeitenAZI - Computer Architecture - 672.7E Exams Questions List - 2018Murad QəhramanovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions 4 1Dokument95 SeitenQuestions 4 1Anik PaulNoch keine Bewertungen
- C5 - Intro To 8085 - Hardware PDFDokument39 SeitenC5 - Intro To 8085 - Hardware PDFsiti hajarNoch keine Bewertungen
- EI2353 DSDQbankDokument24 SeitenEI2353 DSDQbankRaja RockNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8 Microwave FiltersDokument53 SeitenChapter 8 Microwave FilterskhyatichavdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Verilog Hardware Description LanguageDokument61 SeitenVerilog Hardware Description LanguagesaravisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internal Architecture of 8051: Dinesh SharmaDokument45 SeitenInternal Architecture of 8051: Dinesh SharmaSushíl kanikeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assembler Language - 8051powerpoint PresentationDokument56 SeitenAssembler Language - 8051powerpoint PresentationtauseeeeeeeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 02 68k ArchitectureDokument41 Seiten02 68k ArchitectureMuad DawoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer OrganizationDokument396 SeitenComputer Organizationkanaka raghu sreeramaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robert BoylestadDokument1 SeiteRobert BoylestadMohit GaharanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 9 - The Registers and The Memory of The 68000 Intro To 68000 ProgramsDokument23 SeitenLecture 9 - The Registers and The Memory of The 68000 Intro To 68000 ProgramsdriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syllabus - Introduction To Telecommunication Networks CourseDokument2 SeitenSyllabus - Introduction To Telecommunication Networks CourseT FNoch keine Bewertungen
- Valliammai Engineering College: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringDokument9 SeitenValliammai Engineering College: Department of Electronics and Communication EngineeringCecilia ChinnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- COAL Lab 5 20032023 025520pmDokument9 SeitenCOAL Lab 5 20032023 025520pmmagnesium 123Noch keine Bewertungen
- RF Design ModelDokument10 SeitenRF Design Modelmathur_mayurNoch keine Bewertungen
- It1252 Digital Signal ProcessingDokument22 SeitenIt1252 Digital Signal ProcessingainugiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- MemristorDokument18 SeitenMemristorclionpoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAP (Simple-As-Possible) Computers: 10-1 ArchitectureDokument24 SeitenSAP (Simple-As-Possible) Computers: 10-1 ArchitectureAfrahly Afable100% (1)
- RF Active DevicesDokument13 SeitenRF Active DevicesRaj PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- HTSG Optimal Combining STBC and Spatial Multiplexing Mimo OfdmDokument14 SeitenHTSG Optimal Combining STBC and Spatial Multiplexing Mimo OfdmWahyu PerdanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8255 Ppi ExamplesDokument10 Seiten8255 Ppi Examplesvenky258100% (1)
- Architecture Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorDokument4 SeitenArchitecture Diagram of 8085 MicroprocessorbhatiaharryjassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8048 MCDokument4 Seiten8048 MCgouttNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee 309 M1Dokument7 SeitenEe 309 M1Basheer V.PNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mpi LabDokument21 SeitenMpi LabmajorjawarpartapNoch keine Bewertungen
- MICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualDokument53 SeitenMICROPORCESSOR 8085 Lab ManualAjay PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs2252 - MPMC 16 M With Answers Upto 2Dokument40 SeitenCs2252 - MPMC 16 M With Answers Upto 2archumeenabaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Microprocessor 8085 ArchitectureDokument19 SeitenMicroprocessor 8085 ArchitectureSindhujaSindhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Set of 8086Dokument47 SeitenInstruction Set of 8086api-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment 07 Logical OperationsDokument6 SeitenLab Experiment 07 Logical Operationsapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment 08 ComplementDokument4 SeitenLab Experiment 08 Complementapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment 06 Aritimetic OperationsDokument7 SeitenLab Experiment 06 Aritimetic Operationsapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Experiment 05 FamiliarizationsDokument6 SeitenLab Experiment 05 Familiarizationsapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zakir Mit Practical TtpdocxDokument1 SeiteZakir Mit Practical Ttpdocxapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Zakir Mit Theory TTPDokument1 SeiteZakir Mit Theory TTPapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mit Lab 3Dokument3 SeitenMit Lab 3api-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation FinalDokument1 SeitePresentation Finalapi-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mit Lab 4Dokument2 SeitenMit Lab 4api-249964743Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mpi Assignment Solution1Dokument15 SeitenMpi Assignment Solution1alkesh.eng0% (1)
- Verdeyen Laser Electronics SolutionsDokument27 SeitenVerdeyen Laser Electronics SolutionsKhalid TeslaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 EditDokument463 SeitenChapter 1 Edittthanhhoa17112003Noch keine Bewertungen
- Process Management 3.1 What Is A ProcessDokument11 SeitenProcess Management 3.1 What Is A ProcesspritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- A-Level Presentation - 01 Computer ArchitectureDokument40 SeitenA-Level Presentation - 01 Computer ArchitectureMugerwa CharlesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instruction Cycle 2009Dokument11 SeitenInstruction Cycle 2009Nor Syafiqah SuhaimiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Altair 8800 Operator's ManualDokument98 SeitenAltair 8800 Operator's ManualjavimmNoch keine Bewertungen
- BCS305: Computer Organisation: Mathatma Gandhi UniversityDokument11 SeitenBCS305: Computer Organisation: Mathatma Gandhi UniversityMrsRabail SaeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computing PrinciplesDokument160 SeitenComputing PrinciplesDeep PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpu Tutorial 2Dokument53 SeitenCpu Tutorial 2rktiwary256034Noch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 3 - Chapter 4 - REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONSDokument31 SeitenLecture 3 - Chapter 4 - REGISTER TRANSFER AND MICROOPERATIONSsaifsunnyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cpu Emulator PDFDokument37 SeitenCpu Emulator PDFAndrés Guarín CorreaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 - A Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDokument38 SeitenChapter 3 - A Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionKhang NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4 CPU ArchitectureDokument18 SeitenChapter 4 CPU ArchitectureSama A ShurrabNoch keine Bewertungen
- KCPSM6 User Guide 30sept14 PDFDokument124 SeitenKCPSM6 User Guide 30sept14 PDFGustavo GranadosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 PDFDokument127 SeitenChapter 1 PDFAhmed Al-MasoodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Microrprocessor Lecture NoteDokument119 Seiten8085 Microrprocessor Lecture NoteGoitom Haile100% (1)
- Inside The 8051Dokument123 SeitenInside The 8051mabat0Noch keine Bewertungen
- Calculus With Analytical Geometry B SC SM YousafDokument35 SeitenCalculus With Analytical Geometry B SC SM YousafFahad MemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- A/L ICT Competency 2.3Dokument4 SeitenA/L ICT Competency 2.3Mohamed Irfan100% (7)
- Reference: The 8051 Microcontroller: Architecture, Programming & Applications by Kenneth J. AyalaDokument27 SeitenReference: The 8051 Microcontroller: Architecture, Programming & Applications by Kenneth J. Ayalasachin rawatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ECE 445 - Fall 2020 - Lecture 4 - MIPS Machine Language and Program ExecutionDokument23 SeitenECE 445 - Fall 2020 - Lecture 4 - MIPS Machine Language and Program Execution陳柏鈞Noch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 InstructionsDokument24 Seiten8051 Instructionssasitharan33Noch keine Bewertungen
- SH-2 SH7047: Group Hardware ManualDokument764 SeitenSH-2 SH7047: Group Hardware ManualplamkaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design and Implementation of Simple As Possible Computer (SAP-1)Dokument51 SeitenDesign and Implementation of Simple As Possible Computer (SAP-1)Miguel San AntonioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionDokument62 SeitenTop Level View of Computer Function and InterconnectionAhsan JameelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ee6008 MBSD Eee Viist Au Unit IV PDFDokument10 SeitenEe6008 MBSD Eee Viist Au Unit IV PDFBala MuruganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stored Program Concept HOMEWORK FOR Y10-03-P13: Person DescriptionDokument3 SeitenStored Program Concept HOMEWORK FOR Y10-03-P13: Person DescriptionHasaan AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument16 SeitenPDFGaurav PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8085 Important Short Questions (Part-1)Dokument11 Seiten8085 Important Short Questions (Part-1)Ln Amitav BiswasNoch keine Bewertungen