Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Matriculation Chemistry Carbonyl Compound
Hochgeladen von
iki292Originalbeschreibung:
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Matriculation Chemistry Carbonyl Compound
Hochgeladen von
iki292Copyright:
Verfügbare Formate
1
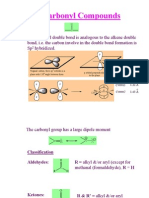
CARBONYL
COMPOUNDS
2
Objective
Describe aldehydes and ketones.
Draw the structure and name the
compound according to IUPAC
nomenclature and common names.
3
I!"ODUC!IO
#unctional group$ carbonyl% C&O
'eneral (ormula$ C
n
)
*n
O
Aldehyde + ,etone are isomeric
Carbonyl compounds are polar
In general% an aldehyde - reactive than ketone
towards nucleophilic addition reaction
4
I!"ODUC!IO
A.D/)0D/
" & alkyl% aryl 1 )
,/!O/
" + "2 & alkyl% aryl
C
O
R H
C
O
R R
34
35
34
35
5
aming o( Aldehyde
Aldehyde is named by substituting the letter 6e o(
the corresponding alkane with 6al
7asic name depends on the longest chain with
6C)O group
!he chain must be numbered by starting with
6C)O group as C58
6
aming o( Aldehyde
9tructure IUPAC name 'eneral name
)5C5)
methanal (ormaldehyde
C)
:
5C5)
ethanal acetyldehyde
C)
:
C)
*
5C5)
propanal propionaldehyde
O
O
O
7
aming o( Aldehyde
9tructure IUPAC name 'eneral name
C)
:
C)
*
C)
*
5C5)
butanal n5butyraldehyde
C)
:
;C)
*
<
:
5C5)
pentanal n5valeraldehyde
Ph5C5)
ben=aldehyde
;phenylmethanal<
ben=enecarbaldehyde
O
O
O
8
aming o( Aldehyde
O
C)
*
C5)
Phenylethanal
(phenylacetyldehyde)
CH
2
=CHCH
2
C-H
O
3-butenal
CH
3
CHCHC-H
O
OH
H
3
C-H
2
C
2-ethyl-3-hydroxybutanal
4 3 2 1
4 3 2 1
2 1
9
aming o( ,etone
,etone is named by substituting the letter 6e o(
corresponding alkane with 6one
!he longest chain with carbonyl group is
numbered so that C in carbonyl group gets the
smallest number
10
aming o( ,etone
9tructure IUPAC name 'eneral name
C)
:
CC)
:
propanone acetone
;dimethyl ketone<
C)
:
CC)
*
C)
:
7utanone methyl ethyl ketone
C)
:
CC)
*
C)
*
C)
:
*5pentanone
methyl propyl ketone
O
O
O
11
aming o( ,etone
9tructure IUPAC name 'eneral am
Ph5C5C)
:
phenylethanone
acetophenone
;phenyl methyl ketone<
Ph5C5Ph
diphenylmethanone
ben=ophenone
;diphenyl ketone<
C)
:
C)
*
CC)
*
C)
:
:5pentanone
diethyl ketone
O
O
O
12
O
C)
*
C5C)
:
phenylpropanone
CH
2
=CHCH
2
CCH
3
O
4-penten-2-one
CH
3
CCH
2
CH
2
CCH
3
O
2,5-hexanadone
O
O
OH
CH
2
CH
3
2-ethyl-2-hydroxycyclopentanone
5C)
*
C5C)
*
5
O
!,3-dphenylpropanone
5 4 3 2 1
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3
13
a.
c.
b.
d.
EXCERCISE
8. >rite the names o( the (ollowing compounds according to
IUPAC nomenclature
C)
:
O
CH
3
CHCH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CHCH
O
C)
*
C)
:
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
C
O
C)C)
:
C)
:
CH
3
CH
2
C
C)
*
C)
*
C)
*
C)
:
O
14
*. >rite down all structural (ormulae o( compound
with molecular (ormula C
?
)
8@
O and name them
according to IUPAC nomenclature.
15
Objective
/Aplain the preparation o( carbonyl compounds
through these reactions$
a<OAidation o( alcohols
b<O=onolysis o( alkenes
c< #riedel6Cra(ts acylation to produce aromatic
ketones
16
Preparation o( Carbonyl
8. OAidation o( Alcohols
BOC o( 8
o
"5O) to (orm aldehyde
BOC o( *
o
"5O) to (orm ketone
CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
-OH " PCC CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH=O
CH
2
Cl
2
!-butanol butanal
-OH =O
KMnO
4
H
+
cyclopentanol cyclopentanone
17
*. O=onolysis o( alkene
() H
3
CC=CHCH
3
H
3
CC=O " O=CCH
3
CH
3
CH
3
H
() O
3
() #n$H
2
O
() O=CH(CH
2
)
4
CH=O
() O
3
() #n$H
2
O
Preparation o( Carbonyl
18
D. #riedel5Cra(ts Acylation
5a good method (or preparing o( aromatic ketones
" R-C-Cl " %lCl
3
-C-R
O
O
" R-C-O-C-R " %lCl
3
-C-R
O O O
Preparation o( Carbonyl
19
Practice Questions
(a) CH
3
CH(&r)CH(CH
3
)OH " '
2
Cr
2
O
(
$H
2
)O
4
(b) CH
3
CH=CCH(CH
3
)
2
CH
3
() O
3
()H
2
O$#n
(c) " -C=O
%lCl
3
Cl
20
8. OAidation
*. "eduction
:. ucleophilic addition reaction
D. Condensation
?. )alo(orm reaction
C)/EICA. P"OP/"!I/9
21
!o eAplain the chemical properties with
re(erence to these reactions $
a< oAidation with ,EnO
D
% ,
*
Cr
*
O
F
%!ollens% #ehling%
7enedict and 9chi(( reagents to di((erentiate
between aldehydes and ketones.
b< reduction to alcohol using .iAl)
D
%a7)
D
and
catalytic hydrogenation.
Objective
22
8.@ OAidation
Aldehydes are easily oAidised to carboAylic acid by
strong oAidising reagents e.g. ,EnO
D
G)
4
% ,
*
Cr
*
O
F
G)
4
Eild oAidising agents such as !ollens2% 9chi((% #ehlings2
+ 7enedicts2 solutions can also oAidise aldehydes.
,etones are resistant towards oAidation because they do
not have hydrogen attached to the carbonyl carbon
atom.
KMnO
4
H
+
H
+
KMnO
4
RCHO
RCR
O
*o reacton
RCOOH
23
8.8 !O../92 !/9!
#or identi(ying aldehydes and ke!nes"
It is a miAture o( aHueous silver nitrate and
ammonia.
It contains Ag;)
:
<
*
4
In this reaction aldehyde #s !$#d#sed !
%a&'!$ylae #!n and a&(en)* is deposited on
the wall o( the the test tube as s#l+e& *#&&!&"
24
CH
Contoh
2[Ag(NH
3
)
2
]
+
+ OH
-
+
RCOO
-
+ NH
3
+
Ag 2 2
+
NH
4
+
2
cermin perak
CH
3
CH
2
CHO + OH
-
[Ag(NH
3
)
2
]
+
2
+
RCH
O
O
+
2[Ag(NH
3
)
2
]
+
OH
-
+
cermin perak
NH
4
+
2
+
2 2Ag
+ NH
3
+ CH
3
CH
2
COO
-
cermin perak
NH
4
+
2
+
2 2Ag
+ NH
3
+
O
C O
-
s#l+e& *#&&!&
s#l+e& *#&&!&
s#l+e& *#&&!&
E$a*,le-
25
8.* #/).I' and 7//DIC! !/9!;Cu
*4
tartarate compleA<
#ehling reagent will oAidise aldehydes but not
ketones
Used to identi(y aldehydes
"eaction with aldehydes will produce
%a&'!$ylae #!n and %!,,e&.I/ !$#de which is
red in colour.
In this reaction copper;II< is reduced to
copper;I<
26
/HuationI
B&#%k &ed
B&#%k &ed
'l)e
'l)e
RCHO
C 4
2+
OH
-
! + +
RCOO
-
C
2
O 2
+
+ H
2
O 3
CH
3
CH
O
3H
2
O +
+ 2C
2
O
+ + OH
-
! C 4
2+
CH
3
CO
-
O
exa+ple
27
8.: 9chi((2s reagent
Aldehyde reacts with 9chi((2s reagent to
give a pink colouration
,etone give negative result
28
"eduction
Aldehydes are reduced to 8
o
"5O) + ketones to *
o
"5
O)
"eagents ;a< .iAl)
D
1 a7)
D
in ether 4 )
4
;b< Jn% )
4
% heat
;c< )
*
;g<% i 1 Pt% heat
*.@ "eduction
29
CH
3
CH
2
CH CH
3
CH
2
CH
O
OH
H
,%lH
4
H
"
-C-CH
3
-CH-CH
3
O
OH
H
2
, *
-xa+ple.
30
!o eAplain the chemical properties
with re(erence to these reactions $
a< nucleophilic addition with )C%
'rignard reagent% alcohol% sodium
bisulphite and water.
Objective
31
In C&O% the e5 density is drawn more towards
the O atom making the C atom de(icient in e.
!hus% the C atom becomes the site (or u
5
attack.
>hen carbonyl C is attacked by u
5
% breaking
the carbonyl bond + tetrahedral intermediate
is (ormed
)ybridisation o( sp
*
C atom changes to sp
:
:.@ ucleophilic addition
32
!he )C is prepared Kin situ2 by the &ea%#!n !0 a
*#$)&e !0 1CN !& NaCN 2#h 3
2
SO
4
"eagents $ aC 1 ,C ;aH< (ollowed by dilute )
*
9O
D
-C=O
H
*aC*
H
2
)O
4
-C-OH
H
C*
CH
3
CHCCH
3
CH
3
O
'C*
H
2
)O
4
CH
3
-CH-C-CH
3
CH
3
OH
C*
:.8 Addition o( )C
33
yields gem5diols
H
H
C=O " H
2
O
H
"
C
H
H
OH
OH
H
3
CH
2
C
H
3
C
C=O " H
2
O
H
"
C
OH
OH
H
3
CH
2
C
H
3
C
:.* Addition o( >ater
34
Aldehyde yields hemiacetal + ketone yields hemiketal
R
H
C=O " ROH
H
"
C
R
H
OH
OR
he+acetal
R
R
C=O " ROH
H
"
C
R
R
OH
OR
he+/etal
:.: Addition o( alcohol
35
)emiacetal + hemiketal in acidic solution react
(urther to (orm acetal + ketal
H
"
C
R
H
OR
OR
acetal
H
"
C
R
R
OR
OR
/etal
C " ROH
R
H
OH
OR
C " ROH
R
R
OH
OR
36
/Aamples$5
H
C=O " CH
3
OH
H
"
C
H
OH
OCH
3
CH
3
C=O " CH
3
OH
H
"
C
OH
OCH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
37
HCHO
()R012
()H
3
O
"
RCH
2
OH
!
o
%lcohol
RCHO
()R012
()H
3
O
"
R-CH-R
2
o
%lcohol
OH
RCR
()R012
()H
3
O
"
R-C-R
3
o
%lcohol
OH
O
R
-xa+ple.
38
3
*aH)O
3
react 4th aldehyde 5 /etone to 6or+
carbonyl b7ulphte 4hch 7 7oluble n 4ater
38h7 reacton 7 u7ed 6or pur6caton o6 aldehyde
9 /etone 6ro+ other non-7oluble or1anc
co+pound7
3Pure carbonyl co+pound 7 obtaned 4hen
treated 4th a:ueou7 ba7e
:.? Addition o( sodium bisulphite
39
*aH)O
3
" -C-CH
3
-C-CH
3
O
OH
O)O
2
-
*a
"
&7ulphte
7alt
)odu+
b7ulphte
40
!o eAplain the chemical properties with
re(erence to these reactions $
a< condensation with )
:
and ammonia
derivatives eg hydra=ine%
phenylhydra=ine% hydroAylamine and *%D 6
dinitrophenylhydra=ine as identi(ication
test (or carbonyl compounds.
b< iodo(orm test to identi(y compounds
with these structures
Objective
41
3
*H
3
5 t7 der;at;e7 react a7 nucleophle and
react 4th carbonyl co+pound7
3<n;ol;ed addton reacton 6ollo4ed by
dehydraton (el+naton o6 H
2
O +olecule to 6or+
C=*)
R
C=O " *H
3
D.@ Condensation
R
C
O-H
*-H
Carbnola+ne
=>n7table nter+edate
R
R
R
C=*H
R
H
" H
2
O
addton el+naton
42
R
C=O **H- -*O
2
R
H
H
*O
2
R
C=**H- -*O
2
" H
2
O
R
*O
2
2,4-dntrophenylhydra?ne
&rady7
rea1ent
yello4 9
oran1e
precptate
character7tc
reacton o6
carbonyl
co+pound7
-xa+ple.
43
)
:
derivatives ame Product ame
"5)
*
1
Ar5)
*
primary amine
C&5" 1
C&5Ar
imine
)
*
)
*
hydra=ine
C&)
*
)ydra=one
)
*
5O) hydroAyl amine
C&5O)
oAime
44
)
:
derivatives ame Product ame
)
*
)C
L
)
?
phenyl
hydra=ine
C&)C
L
)
?
phenyl
hydra=one
)
*
)C)
*
semi
carba=ide
C&)C)
*
semi
carba=one
O
O
3Carbonyl react 4th hydra?ne 9 phenylhydra?ne al7o 1;e
yello4 precptate
45
"eagent $ I
*
in aO);aH<% heat (orms aIO;9odium
iodate ;i<<
#ormation o( yellow precipitate% C)I
:
% indicate that
organic compound consist o( methyl carbonyl or
methyl alcohol$5
-C-CH
3
9 -C-CH
3
O
OH
H
?. Iodo(orm reaction
46
@-*-R%, R-%C8<O*.-
RCCH
3
RCC<
3
RCO
-
" CH<
3
O
O O
<
2
OH
-
OH
-
RCHCH
3
RCCH
3
RCC<
3
RCO
-
" CH<
3
OH
O
<
2
OH
-
OH
-
O
OH
-
O
<
2
47
-2%0P,-.-
CH
3
CH
2
CCH
3
CH
3
CH
2
C-O
-
" CH<
3
O
O
*a<O
-C-CH
3
-C-O
-
" CH<
3
O
O
<
2
$ *aOH
48
-2%0P,-.-
H-CCH
3
H-C-O
-
" CH<
3
O
O
<
2
$*aOH
-C-CH
3
-C-O
-
" CH<
3
OH
O
<
2
$ *aOH
H
49
Practice Questions
(a) CH
3
CCH
2
CH
3
" H
2
**H *O
2
*O
2
H
"
O
(b) CH
3
CCH
2
CH
3
" H
2
*OH
O
H
"
(c) CH
3
CCH
2
CH
3
" <
2
$ *aOH
O
(d) CH
3
C-CH
2
-Ph " ,%lH
4
O
50
Practice Questions
8he +olecular 6or+ula o6 an un/no4n co+pound % 7
C
(
H
!4
A O?onoly77 o6 % 1a;e t4o product7 & and C,
4hereby both & and C reacted 4th 2,4-
dntrophenylhydra?ne to 1;e 7old der;at;e7A &
1a;e po7t;e re7ult7 to 8ollen7 and <odo6or+ te7t7,
4hle C 1a;e ne1at;e re7ult to both o6 the te7t7A
)u11e7t the 7tructural 6or+ula o6 %, & and CA -xplan
your an74erA
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 15 - Aldehyde and KetonesDokument66 Seiten15 - Aldehyde and KetonesIrfan Raza100% (1)
- 1e Aldehyde & KetoneDokument48 Seiten1e Aldehyde & KetoneJonathan Wyatt100% (1)
- CH 16Dokument102 SeitenCH 16Amer KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehid Keton 08Dokument49 SeitenAldehid Keton 08Mochamad Herdi NurzamanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec - EnolDokument46 SeitenLec - EnolZamzam Siti MultazamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids: R-COH Aldehyde R-CO-R Ketone R-CoohDokument17 SeitenAldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids: R-COH Aldehyde R-CO-R Ketone R-CoohMoshe Cohen'sNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehid Keton 08Dokument48 SeitenAldehid Keton 08Priagung SetyawanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aldehyde and KetoneDokument39 SeitenAldehyde and KetoneCitra Siti PurnamaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matriculation Chemistry (Carbonyl Compound)Dokument50 SeitenMatriculation Chemistry (Carbonyl Compound)ridwanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Epoxidation & Opening PDFDokument84 SeitenEpoxidation & Opening PDFRajkumar ChinnuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohol, Phenol & Ether: A O CH C HDokument6 SeitenAlcohol, Phenol & Ether: A O CH C HJitendra KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl CompoundsDokument50 SeitenCarbonyl CompoundsFariz SharudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds 230Dokument60 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds 230mohtasim hasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPDokument18 SeitenChapter 17: Alcohols and Phenols: Phenol (Aromatic Alcohol) Alcohol SPKriti Tyagi100% (2)
- SCHEME TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Dokument11 SeitenSCHEME TRIAL CHEMISTRY SEM 3-Stpm 2013Zuraini Arshad100% (1)
- EstersDokument22 SeitenEstersSania KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument30 SeitenChapter 7c4.arsyadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summary of Important Organic ReactionsDokument41 SeitenSummary of Important Organic ReactionsKathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- DerivativesDokument58 SeitenDerivativesravi_balaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alkylation of Enolate IonsDokument13 SeitenAlkylation of Enolate IonsGabriel PekárekNoch keine Bewertungen
- C) Trigonal Planar: E-Pent-2-ene Z-Pent-2-ene Z-3-Methylpent-2-ene Z-2-Methylpent-2-eneDokument9 SeitenC) Trigonal Planar: E-Pent-2-ene Z-Pent-2-ene Z-3-Methylpent-2-ene Z-2-Methylpent-2-eneJessicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matriculation Chemistry Hydroxy Compound PDFDokument71 SeitenMatriculation Chemistry Hydroxy Compound PDFiki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- 3D Chemistry Concepts & Questions 2023-24 2.0Dokument63 Seiten3D Chemistry Concepts & Questions 2023-24 2.0Anushka ChauhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- C10K Carbonyl Chemistry EmailDokument37 SeitenC10K Carbonyl Chemistry EmailMatthew яeject'z BennettNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organometallic TurotialDokument2 SeitenOrganometallic TurotialkhemrajmahadewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solomon Organic Chemistry Chapter 19 SlidesDokument35 SeitenSolomon Organic Chemistry Chapter 19 Slidesdanrcg100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsDokument9 SeitenOrganic Chemistry I - Practice Exercise: Alkene Reactions and MechanismsElliot JamesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ald&KetoneDokument41 SeitenAld&KetoneFeng SpencerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ald&Ketone IDokument41 SeitenAld&Ketone IAbhay NarvekarNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch10 Reactions Worksheet and Key 05 7 09Dokument13 Seitench10 Reactions Worksheet and Key 05 7 09api-304182646Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1 AldehitketonDokument103 Seiten1 AldehitketonLuthfiani Widyawati Dwi AntariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 16Dokument87 SeitenChapter 16Hafizszul FeyzulNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Ex 3Dokument10 SeitenPractice Ex 3Irene WNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nomenclature Esters: AlkylDokument35 SeitenNomenclature Esters: AlkylAstri MaulidaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CC One ShotDokument29 SeitenCC One Shotbobbytext8904Noch keine Bewertungen
- Carbonyl Compounds Xi Xii Study MaterialsDokument171 SeitenCarbonyl Compounds Xi Xii Study MaterialsCristiano Hamdiansyah SempadianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Alcohols, Organic ChemistryDokument32 SeitenAlcohols, Organic Chemistryclassy43390% (1)
- Ald&ketone IDokument41 SeitenAld&ketone Iasney2512Noch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Key Assignment No. 5 Aldehydes and KetonesDokument5 SeitenAnswer Key Assignment No. 5 Aldehydes and KetonesREGINE CUEVASNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acids and Acid Derivatives Carbonyl PDFDokument124 SeitenCarboxylic Acids and Acid Derivatives Carbonyl PDFrvignesh2809Noch keine Bewertungen
- UNG - Carbox 3Dokument35 SeitenUNG - Carbox 3ShofiakhoerunnisaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH22Dokument23 SeitenCH22David LiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones: RCH Oh R C H O PCC Primary Alcohol O PCC Oh or (Cro /H)Dokument5 SeitenSynthesis of Aldehydes and Ketones: RCH Oh R C H O PCC Primary Alcohol O PCC Oh or (Cro /H)jlventiganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bi FunctionalDokument36 SeitenBi FunctionalchidambaramrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Organic Mind MapDokument37 SeitenOrganic Mind Mapkamalia8980% (5)
- 4.5 NotesDokument30 Seiten4.5 NotesMaria OnisorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument30 SeitenChapter 7Apichat Junsod100% (4)
- Acetoacetic Ester: C C C OCH CH H H O O H CDokument46 SeitenAcetoacetic Ester: C C C OCH CH H H O O H Calief ramdhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Factsheet 17Dokument3 SeitenChem Factsheet 17drdre12100% (1)
- Aldehydes and Ketones For IitjeeDokument65 SeitenAldehydes and Ketones For Iitjeevarundhall1994Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry - Classification and NomenclatureDokument20 SeitenChemistry - Classification and NomenclatureDevesh AgrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Handbook of Coordination Catalysis in Organic ChemistryVon EverandHandbook of Coordination Catalysis in Organic ChemistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and SaltsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionVon EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2)
- Physical Organic Chemistry—Ii: Specially Invited Lectures Presented at the Second IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry Held at Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 29 April–2 May 1974Von EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry—Ii: Specially Invited Lectures Presented at the Second IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry Held at Noordwijkerhout, Netherlands, 29 April–2 May 1974Th. J. De BoerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Metallabenzenes: An Expert ViewVon EverandMetallabenzenes: An Expert ViewL. James WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersVon EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Acids, Bases, and Salts with AnswersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976Von EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976A. FruchierNoch keine Bewertungen
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsVon EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Designing A Mobile Game Application ForDokument5 SeitenDesigning A Mobile Game Application Foriki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Actio Research DR SatirahDokument73 SeitenActio Research DR Satirahiki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- E Proceedings Ice2016Dokument801 SeitenE Proceedings Ice2016iki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Action ResearchDokument16 SeitenAction Researchiki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Infused, Ted - Google Classroom - A 2020 - 2021 Comprehensive and Simple User Guide To Online Teaching and Learning With Step by Step Instructions, Tips and Tricks For Teachers (2020)Dokument121 SeitenInfused, Ted - Google Classroom - A 2020 - 2021 Comprehensive and Simple User Guide To Online Teaching and Learning With Step by Step Instructions, Tips and Tricks For Teachers (2020)iki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- 9780299304300Dokument255 Seiten9780299304300iki292100% (1)
- 9781473615441 (1)Dokument449 Seiten9781473615441 (1)iki29280% (5)
- Java 2 - The Complete ReferenceDokument208 SeitenJava 2 - The Complete Referenceiki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1634858239Dokument360 Seiten1634858239iki292100% (1)
- PDFDokument360 SeitenPDFiki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cuking Book For StudentsDokument1.299 SeitenCuking Book For StudentsSladjan Stojkovic94% (18)
- Understanding Baking PDFDokument289 SeitenUnderstanding Baking PDFAlexandra Soares100% (2)
- 191 Secret Italian Family Recipes - Jack LiguoriDokument150 Seiten191 Secret Italian Family Recipes - Jack Liguoriiki292100% (1)
- 9783319395913Dokument214 Seiten9783319395913iki292100% (1)
- Database in JavaDokument779 SeitenDatabase in JavaKrishna SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- CS301 Handouts 1 45Dokument136 SeitenCS301 Handouts 1 45iki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cmu Itc 103Dokument505 SeitenCmu Itc 103iki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Database in JavaDokument779 SeitenDatabase in JavaKrishna SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Database PDFDokument106 SeitenDatabase PDFiki292Noch keine Bewertungen
- Database in JavaDokument779 SeitenDatabase in JavaKrishna SaiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem12 Oxidation/Reduction: Test - 80Dokument5 SeitenChem12 Oxidation/Reduction: Test - 80Ali EslamiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Internship Report (Prakriti and Riya)Dokument39 SeitenInternship Report (Prakriti and Riya)PrakritiNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Chemistry of Organic MoleculesDokument7 SeitenThe Chemistry of Organic MoleculesPangkat DalawaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pysical Organic Chapter OneDokument34 SeitenPysical Organic Chapter OneTeferaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Properties 1819 Alkanes Alkyl HalideDokument44 SeitenChemical Properties 1819 Alkanes Alkyl HalideAimee MangubatNoch keine Bewertungen
- US9005884Dokument10 SeitenUS9005884Thanh Hậu TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 45 PDFDokument7 Seiten45 PDFintan kusumaningtyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gama de Solventes Alifaticos en ChileDokument9 SeitenGama de Solventes Alifaticos en ChileFelipe OtarolaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Rekayasa Proses: Aplikasi Mordan Tanin Pada Pewarnaan Kain Batik Katun Menggunakan Warna Alam TingiDokument9 SeitenJurnal Rekayasa Proses: Aplikasi Mordan Tanin Pada Pewarnaan Kain Batik Katun Menggunakan Warna Alam TingiHanif Ni'matus ShalihahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Worksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3Dokument4 SeitenWorksheet Elements Compounds Mixtures ks3eric sivanesh0% (1)
- Zwitterion On Mishaps and Tragedies in Making MDMADokument2 SeitenZwitterion On Mishaps and Tragedies in Making MDMAinvitacionsNoch keine Bewertungen
- AminesDokument39 SeitenAminesStudent 365Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/41Dokument20 SeitenCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/41derekloh999Noch keine Bewertungen
- 16 Introduction To Organic ChemistryDokument9 Seiten16 Introduction To Organic Chemistryizabel0% (1)
- Activity 02 Finding The Percentage of Water of Crystallisation in Hydrated Iron II SulfateDokument1 SeiteActivity 02 Finding The Percentage of Water of Crystallisation in Hydrated Iron II SulfateA09387465992739270% (1)
- Unit - 5 Chapter: - 13 Hydrocarbons: Let's RecallDokument39 SeitenUnit - 5 Chapter: - 13 Hydrocarbons: Let's RecallHitz D.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cabling Products and Solutions: CATALOGUE 2010/2011Dokument196 SeitenCabling Products and Solutions: CATALOGUE 2010/2011Georgi PanayotovNoch keine Bewertungen
- Astm-D 1394Dokument7 SeitenAstm-D 1394moktar albhlolyNoch keine Bewertungen
- AISI 321 SpecificationsDokument1 SeiteAISI 321 SpecificationsMatija BušićNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principles and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryDokument56 SeitenPrinciples and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological ChemistryappleNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACJC H2 CHEM P1 (Worked Solution)Dokument26 SeitenACJC H2 CHEM P1 (Worked Solution)Zach EganNoch keine Bewertungen
- Extraction of Lithium From Lepidolite by Sulfation Roasting and Water LeachingDokument5 SeitenExtraction of Lithium From Lepidolite by Sulfation Roasting and Water LeachingMaria José FuturoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chloride Removal From Recycled Cooling Water Using UHLADokument8 SeitenChloride Removal From Recycled Cooling Water Using UHLAHamed TorabyNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9701 s06 QP 2Dokument12 Seiten9701 s06 QP 2Hubbak KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Oct 2022 Unit 6 MSDokument26 SeitenOct 2022 Unit 6 MSFarayan IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Carboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeDokument52 SeitenCarboxylic Acid and Its DerivativeThe RockNoch keine Bewertungen
- PblockDokument13 SeitenPblockmandalyuvraj1582Noch keine Bewertungen
- Pfe FST ... &Dokument87 SeitenPfe FST ... &Lahcen BOULBAZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrochemical Series of MetalsDokument2 SeitenElectrochemical Series of MetalsSohaib BashirNoch keine Bewertungen
- U.S. National Fire Protection Association: Hazards of Materials For Emergency Response" Is ADokument5 SeitenU.S. National Fire Protection Association: Hazards of Materials For Emergency Response" Is AProduction AdvisorNoch keine Bewertungen