Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
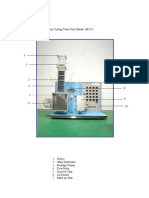
Volumetric Efficiency of Compressors
Hochgeladen von
fakedmppOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Volumetric Efficiency of Compressors
Hochgeladen von
fakedmppCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Discussion
Volumetric Efficiency of a compressor is the ratio of the actual delivered gas volume to the swept volume of
the cylinder.
In a compressor actual volume of air inside the cylinder for compression is less than the theoretical
calculated volume because of the clearance volume. When the air is compressed, and is delivered by
the discharge valve some volume of the air remains inside the clearance volume at high discharge
pressure. When the piston starts moving downwards, the suction valve does not opens immediately
because of this high pressure gas. When the piston moves downwards the pressure of the gas in the
clearance volume starts reducing due to expansion. Only when the pressure of this air reaches to
certain minimum level, the suction valve opens. Thus the portion of the suction stroke of the piston
goes unused and during this certain volume of the air is not sucked. This reduces the volume of the
air that can be sucked by the cylinder or the compressor.
Factors that affect volumetric efficiency
Delivery pressure.
How close to the isothermal process.
Compression ratio
Number of stages in the compressor.
Operating temperature.
Clearance volume of the pistons.
Valve operating speed.
Cooling.
How close to the isothermal process.
Speed of rotation of the engine.
Temperature and pressure variation along the line from the compressor outlet to orifice meter .
We can assume the tube is uniform and the frictional losses are negligible .
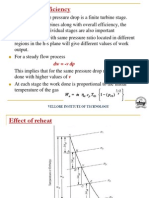
By using steady flow energy equation
q w = h + K.E + P.E
We can neglect the change of kinetic energy and potential energy .
Compressor
Orifice meter
W=0 ; K.E=0 ; P.E=0
q = h( enthalpy change)
but heat loses along the pipe. So the enthalpy decreases along the pipe . Temperature decreases .
Assuming ideal gas behavior
v= A.u A- cross section ; u velocity
P T
Variation of pressure and temperature
Pressure
Temperature
(length )
Note
There are some other ways that can affect the pressure and temperature
Temperature drop at the storing tank.
Pressurized air is kept in the tank for some time since the air is at high
temperature than atmosphere some amount of heat is rejected to atmosphere so there is a
temperature drop.
Pressure changes at the outlet pipe due to the valve action.
Because the air is delivered at a high pressure than the tank pressure there is
always a cyclic pressure variation.
Methods to measuring the pressure difference between the two ends of the orifice
Pressure sensors can be used
Gauge pressure sensors can be used to get the gauge pressure .Sensors can be directly used
to get the pressure more accurately .
Comparison between Graphs
Expected graph
Practical Graph
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0 20 40 60 80
Efficiency
Pressure
volumetric
efficiency
CALCULATIONS
Free air delivery =
At 10 lbs pressure
H=18mm Water
h= 24mm water
t1 =28C
t=32C
P1=760mmHg
M2=P1-
Volume swept by the piston per minute =*(
*Stroke* R.p.m
=0.736
By substituting values to above equation
= 0.274293
Pressure Efficiency
10 0.27429292
20 0.19074249
30 0.18523054
40 0.20457569
50 0.17117191
60 0.16365659
0
0.05
0.1
0.15
0.2
0.25
0.3
0 20 40 60 80
E
f
f
i
c
i
e
n
c
y
Pressure
Efficiency vs Pressure
Efficiency
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Modern Manufacturing Relies on Compressed AirDokument7 SeitenModern Manufacturing Relies on Compressed AirAjith NalakaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat and Mass TransferDokument28 SeitenHeat and Mass TransfersureshkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Window - Air - Conditioning - Test - Rig Lab ManualDokument6 SeitenWindow - Air - Conditioning - Test - Rig Lab ManualSandeep SainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- EXPERIMENT 1 ThrottlingDokument8 SeitenEXPERIMENT 1 ThrottlingJaphet MmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Con Refrig Lecture-SlideDokument27 SeitenAir Con Refrig Lecture-SlideboonwueNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorDokument6 SeitenPerformance Test On Two-Stage Reciprocating Air CompressorAji V s100% (2)
- Reciprocating Compressor GuideDokument15 SeitenReciprocating Compressor GuideShashank Muduli33% (3)
- Compressor & TheoryDokument41 SeitenCompressor & TheoryJaveed A. KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SOLTEQ Bench Cooling Tower TestDokument13 SeitenSOLTEQ Bench Cooling Tower TestAlohaaSwezzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch3 - CompressorsDokument49 SeitenCh3 - CompressorsShiau FenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Volumetric EfficiencyDokument7 SeitenVolumetric EfficiencyDumithJayathilaka100% (1)
- High Condensing TemperatureDokument3 SeitenHigh Condensing TemperatureluffydsiniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating Characteristics: Inlet Volumetric Rate of FlowDokument19 SeitenOperating Characteristics: Inlet Volumetric Rate of FlowSandi AslanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbines and CompressorsDokument70 SeitenTurbines and CompressorsAkshay Deshpande100% (1)
- Ramjet Engine Test RigDokument4 SeitenRamjet Engine Test RigRoy VaughnNoch keine Bewertungen
- TE-2 Unit - 4 &5 NotesDokument110 SeitenTE-2 Unit - 4 &5 NotesKrishna VamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mehran University of Engineering and Technology SZAB Campus Khairpur Mir'sDokument64 SeitenMehran University of Engineering and Technology SZAB Campus Khairpur Mir'sMarcusHuynh88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter Six Compressors: Air CompressorDokument8 SeitenChapter Six Compressors: Air CompressorMicky AlemuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Calculations and Performance of a Heat Pump SystemDokument8 SeitenCalculations and Performance of a Heat Pump SystemSaman KumaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nota PemampatDokument49 SeitenNota PemampatweafareezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shaft Power Cycle Presentation TraineeDokument44 SeitenShaft Power Cycle Presentation TraineeCharles EbukaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Capillary TubeDokument8 SeitenCapillary Tubeziko23100% (2)
- Thermodynamics Lab ReportDokument15 SeitenThermodynamics Lab ReportFahd Ghuman100% (2)
- Evaluate centrifugal compressor performanceDokument8 SeitenEvaluate centrifugal compressor performanceAnonymous yLPPdPwNoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbo-Machinery (Meng3201) : Chapter-3Dokument28 SeitenTurbo-Machinery (Meng3201) : Chapter-3Asnake Bahiru100% (1)
- Core Ag Engineering Principles - Session 1Dokument101 SeitenCore Ag Engineering Principles - Session 1peagricultureNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week - 09 - Pressure and Velocity MeasurementsDokument21 SeitenWeek - 09 - Pressure and Velocity MeasurementsMohammad MohiuddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- COMPRESSION RATIO GUIDEDokument14 SeitenCOMPRESSION RATIO GUIDEDirkMyburghNoch keine Bewertungen
- AIEEE Maths QuickReviewDokument19 SeitenAIEEE Maths QuickReviewSanthosh KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Nozzles and Turbines: Critical Pressure RatioDokument58 SeitenSteam Nozzles and Turbines: Critical Pressure RatioKrishna VamsiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Charles's Law ExperimentDokument7 SeitenCharles's Law ExperimentGil HernándezNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Performance of A Centrifugal FanDokument7 Seiten4 Performance of A Centrifugal Fanfinix33Noch keine Bewertungen
- Combined Convection and Radiation Lab ReportDokument8 SeitenCombined Convection and Radiation Lab ReportZAVEN TORTIANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heat Transfer Lab - 1Dokument31 SeitenHeat Transfer Lab - 1Nikhil JayanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Air Compressor Performance TestDokument7 SeitenAir Compressor Performance TestRajneeshKrNoch keine Bewertungen
- PressorsDokument8 SeitenPressorsManoj MisraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Id Abdisa Gemechu R/0017/08Dokument5 SeitenName: Id Abdisa Gemechu R/0017/08Abdisa GemechuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocating Air CompressorsDokument20 SeitenReciprocating Air CompressorsAshleen MarshallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 4Dokument41 SeitenChapter 4birhanubic23Noch keine Bewertungen
- ALUP Compressed Air Fundamentals-Part1 - GBDokument50 SeitenALUP Compressed Air Fundamentals-Part1 - GBmbrijbhushan75% (4)
- Learn Key Concepts of Air Compressors Including Types, Parts, and PV DiagramsDokument13 SeitenLearn Key Concepts of Air Compressors Including Types, Parts, and PV Diagramsjerick garlejoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaporator Vacuum System and Barometric CondenserDokument2 SeitenEvaporator Vacuum System and Barometric CondensersalcedopozasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 7Dokument5 SeitenChapter 7esraaoraby24Noch keine Bewertungen
- ReviewDokument31 SeitenReviewkarlobrondialNoch keine Bewertungen
- Feed Heaters PerformanceDokument57 SeitenFeed Heaters Performancemvpngp100% (1)
- Water Cooling TowerDokument8 SeitenWater Cooling TowerBalRam Dhiman100% (1)
- Learning Outcomes:: Some Other Ways of Classifying CompressorsDokument18 SeitenLearning Outcomes:: Some Other Ways of Classifying CompressorsRyan CalicaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermodynamics Lab Report H111J UnitDokument14 SeitenThermodynamics Lab Report H111J UnitKarim AbdallahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polytropic CompressionDokument22 SeitenPolytropic CompressionSonal Power Unlimitd50% (2)
- Actual Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemDokument10 SeitenActual Vapor Compression Refrigeration SystemJiggy Lawrence BathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Measure Pressure and Flow: Install The EMANT300 USB DAQ and Stepper Motor Training KitDokument13 SeitenMeasure Pressure and Flow: Install The EMANT300 USB DAQ and Stepper Motor Training KitakashawalkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reciprocating air compressor guideDokument25 SeitenReciprocating air compressor guideRichardt LootsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chem Lab Report 9-Gas LawDokument6 SeitenChem Lab Report 9-Gas LawNor Ashikin IsmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ratio of Specific Heats 2Dokument3 SeitenRatio of Specific Heats 2Anonymous CkDHEq7ENoch keine Bewertungen
- Turbine Heat Rate and EfficiecyDokument48 SeitenTurbine Heat Rate and EfficiecyPralay Raut100% (6)
- Volume Efficiency of A CompressorDokument13 SeitenVolume Efficiency of A CompressorKavindu UmayangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Axial Fan AssignmentDokument7 SeitenAxial Fan AssignmentMorgana RibeiroNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Von EverandSteam Engines Machinery's Reference Series, Number 70Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conductive Elastomer Mounting Flange EMI Gasket-SelectedDokument4 SeitenConductive Elastomer Mounting Flange EMI Gasket-SelectedfakedmppNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Lighting CatalogDokument32 Seiten2011 Lighting CatalogfakedmppNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmishieldingDokument225 SeitenEmishieldingBurak KarakaşNoch keine Bewertungen
- DimensionsDokument1 SeiteDimensionsfakedmppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Social ProjectDokument12 SeitenSocial ProjectfakedmppNoch keine Bewertungen
- 13 Multi-Evaporator and Cascade SystemsDokument25 Seiten13 Multi-Evaporator and Cascade SystemsPRASAD326100% (5)
- Tools and Work Piece MaterialsDokument9 SeitenTools and Work Piece MaterialsfakedmppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Types of CompressorsDokument3 SeitenTypes of Compressorsfakedmpp100% (1)
- Simple Planar LinkagesDokument18 SeitenSimple Planar LinkagesfakedmppNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Encyclopedia Chapter on Sizing Control ValvesDokument70 SeitenEngineering Encyclopedia Chapter on Sizing Control ValvesAriyandi Yuda PraharaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reticulate Ice Veins in Permafrost, Nort: DiscussionsDokument4 SeitenReticulate Ice Veins in Permafrost, Nort: DiscussionsFelipe PereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Access To ChemistryDokument422 SeitenAccess To Chemistrythphuongster100% (10)
- Experimental Techniques for Measuring Moisture ContentDokument20 SeitenExperimental Techniques for Measuring Moisture Contentdita megaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Temperature and Thermometers WorksheetDokument6 SeitenTemperature and Thermometers WorksheetDen AloyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS Physics Chapter - 1 Base & Derived Unit WSDokument2 SeitenAS Physics Chapter - 1 Base & Derived Unit WSMahbub KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CivilsyllDokument133 SeitenCivilsyllManoj ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- SAMSON Technical InformationDokument456 SeitenSAMSON Technical InformationSatit hunsaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neolt ShieldDokument2 SeitenNeolt Shieldluca danielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applied Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual 1565646222Dokument129 SeitenApplied Fluid Mechanics Lab Manual 1565646222Matamoros De La Cruz JorgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gr. 6 Science First Term Revision 2Dokument19 SeitenGr. 6 Science First Term Revision 2sultan alkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 2Dokument23 SeitenLecture 2علي سعيد سعودNoch keine Bewertungen
- Analysis of Water Hammering in Pipeline and Its CFD SimulationDokument6 SeitenAnalysis of Water Hammering in Pipeline and Its CFD SimulationDuzzysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Separating Liquids and Gases in Process EquipmentDokument22 SeitenSeparating Liquids and Gases in Process Equipmentعبد اللهNoch keine Bewertungen
- Liquefaction of Gases Lecture NotesDokument10 SeitenLiquefaction of Gases Lecture NotesmelvindavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- H2 Forces Lecture Notes PDFDokument20 SeitenH2 Forces Lecture Notes PDFJia Wei TanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pneumatics Midterm ExamsDokument19 SeitenPneumatics Midterm ExamsRedgeNoch keine Bewertungen
- II. Basic Thermodynamic Properties 1Dokument41 SeitenII. Basic Thermodynamic Properties 1Nard GuevarraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 700pax Series Absolute Pressure Modules: Instruction SheetDokument2 Seiten700pax Series Absolute Pressure Modules: Instruction SheetWuzekNoch keine Bewertungen
- Review On AMCA 203Dokument21 SeitenReview On AMCA 203saeed shoaeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- High-Rise Plumbing Design and Plumbing Codes: March 14, 2014Dokument5 SeitenHigh-Rise Plumbing Design and Plumbing Codes: March 14, 2014Nestor S. ReEyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inert - CEA4007Dokument83 SeitenInert - CEA4007DM2100% (1)
- WIND LOAD CALCULATIONSDokument3 SeitenWIND LOAD CALCULATIONSJovan BucolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fuel Injection Nozzle - Test: Testing and AdjustingDokument13 SeitenFuel Injection Nozzle - Test: Testing and AdjustingTri WahyuningsihNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full TextDokument66 SeitenFull Textיוליה רחמילובNoch keine Bewertungen
- General Principles of Bottom-Hole Pressure TestsDokument201 SeitenGeneral Principles of Bottom-Hole Pressure TestsTripoli ManoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Rubber HoseDokument24 SeitenTest Rubber HoseTakorn Weyhey100% (2)
- Engineeringexperv 00000 I 00146Dokument60 SeitenEngineeringexperv 00000 I 00146LALENoch keine Bewertungen
- Interfaces and Heat Transfer in Jet Impingement On A High Temperature SurfaceDokument131 SeitenInterfaces and Heat Transfer in Jet Impingement On A High Temperature SurfaceH. LEOCADIONoch keine Bewertungen
- HydrostaticsDokument7 SeitenHydrostaticsDeepak RamtekeNoch keine Bewertungen