Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
The Simplex Method1
Hochgeladen von
shahidsarkCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Simplex Method1
Hochgeladen von
shahidsarkCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
The Simplex Method
Can be used to solve LP models when there are any number of variables.
It begins with a feasible point and then tests if the value of the objective function
is optimal. If not, it moves to a better solution.
The generation of a solution requires solving a system of linear equations. The
search continues until no improvement in the solution is possible i.e when we
have reached the optimal solution.
REQUIREMENTS OF THE SIMPLEX METHOD
All constraints must be stated as equations
The right hand side of a constraint cannot be negative.
All variables are restiricted to nonnegative values.
For add a slack variable on the left hand side to convert it to an
equation.
We have more variables than equations.
A Basic Solution is one in which we assign the value zero to some variables and
then solve for the remaining variables.
Nonbasic variables are the ones which have been assigned the value zero.
Basic variables are the ones computed by solving the system of equations.
A basic feasible solution is one which satisfies the nonnegativity constraint also.
By the corner point method we get ,
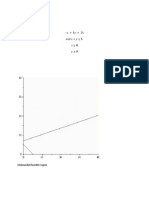
The plot below shows the feasible region in yellow
>
Restating the problem in terms of equations;
Optimal value occurs at a corner point. At these points, at least two of the four
variables are zero.
Also, if any two of the four variables are zero, we get a corner point. The simplex
method starts with the corner point (0,0) and moves to another corner point
which gives a better solution.
Check: At every corner point any two of the four variables are zero.
Corner Point Solution
A(0,0)
B(4,0)
C(3,2)
D(0,4)
Initial Simplex Table
[(
)]
Select the varaiable with the most negative coefficient in the objective function
row as the entering variable. This will add the greatest possible per unit profit.
Find the ratios by dividing entries of R by the corresponding entries of the pivot
column.
Leaving variabl e is the one with the smallest ratio. (Else one of the constraints
will be violated).
So
Convert the pivot element to 1 by using EROs and all other entries in the pivot
column ore zero. Read off the new solution.
Converting all other entries in column 1 to zero by using
[(
)]
The iterative process continues till all indicators in the last row are nonnegative.
It is not possible for us to improve upon the BFS. No negative indicators means we
have an optimal solution,. The optimal solution is
Max value of z = 12
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Pepsi ChangDokument2 SeitenPepsi ChangshahidsarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- B. If The Objective Is To Maximize The Discount Show That The LP Model IsDokument5 SeitenB. If The Objective Is To Maximize The Discount Show That The LP Model IsshahidsarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Graphical Solutions of Linear InequalitiesDokument6 SeitenGraphical Solutions of Linear InequalitiesshahidsarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Empty Feasible Region Maximize Z 8x-3y SubjectDokument4 SeitenEmpty Feasible Region Maximize Z 8x-3y SubjectshahidsarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Banco RealDokument17 SeitenBanco Realshahidsark100% (1)
- Economic Problems of Pakistan: UnemploymentDokument7 SeitenEconomic Problems of Pakistan: UnemploymentshahidsarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- GroupsDokument1 SeiteGroupsshahidsarkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Service Sector of PakistanDokument2 SeitenService Sector of Pakistanshahidsark100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- A Beginner's Guide To Fragility, Vulnerability, and RiskDokument104 SeitenA Beginner's Guide To Fragility, Vulnerability, and RiskSaharAkthamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Variables and Quantifiers PDFDokument12 SeitenVariables and Quantifiers PDFSebastián SilvaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vdoc - Pub The Maple Handbook Maple V Release 3Dokument522 SeitenVdoc - Pub The Maple Handbook Maple V Release 3marceloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gulis Laboratory 6 PDFDokument17 SeitenGulis Laboratory 6 PDFAlie DysNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME - 424 Introduction To Finite Element AnalysisDokument18 SeitenME - 424 Introduction To Finite Element AnalysisWaleed TayyabNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab 06Dokument4 SeitenLab 06Artfull Shin ChanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Multiple IntegralsDokument31 SeitenMultiple IntegralsKotoriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method For Calculation Allowable Creep StressDokument13 SeitenMethod For Calculation Allowable Creep StressLeandro Augusto SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1Dokument17 SeitenLesson 1PIALOGO RONA GIANoch keine Bewertungen
- Stochastic ProgrammingDokument15 SeitenStochastic Programminganon_876010557Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 1 - Modelling, Computers and Error AnalysisDokument25 SeitenChapter 1 - Modelling, Computers and Error AnalysisJanagaraj SukumaranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math FW Mathematics 1 JLDokument37 SeitenMath FW Mathematics 1 JLManishNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pengaruh Metode Periodic Order Quantity (POQ) Terhadap Tingkat Efisiensi Pengadaan Material Proyek Di PT. Antero MakmurDokument7 SeitenPengaruh Metode Periodic Order Quantity (POQ) Terhadap Tingkat Efisiensi Pengadaan Material Proyek Di PT. Antero MakmurMiftahul Wijayanti DindaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aat Solutions - Ch03Dokument78 SeitenAat Solutions - Ch03Theodoros MaragakisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Foundations of MechanicsDokument21 SeitenFoundations of MechanicsUriel MorenoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cost Accounting Ch03Dokument86 SeitenCost Accounting Ch03michaelwainsteinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2 Introduction To Taguchi Method 2.1 BackgroundDokument4 SeitenChapter 2 Introduction To Taguchi Method 2.1 BackgroundanilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Study Skills For Adult StudentsDokument2 SeitenMath Study Skills For Adult StudentsAnthea ClarkeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be The Actual Value Which The: May EventDokument25 SeitenBe The Actual Value Which The: May EventBhavuk BansalNoch keine Bewertungen
- 01 Bcon141 Mod3 Lesson6 LinearProgrammingDokument86 Seiten01 Bcon141 Mod3 Lesson6 LinearProgrammingSheenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Premier University: Dept. of CSE Lab ReportDokument49 SeitenPremier University: Dept. of CSE Lab Report1685Md.Shahiduzzaman BhuiyanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Statistics and Probability - Midterm Examination (TOS)Dokument2 SeitenStatistics and Probability - Midterm Examination (TOS)Magz Magan93% (15)
- Gen Math First Quarter ExaminationDokument2 SeitenGen Math First Quarter ExaminationJoylass Pasac100% (1)
- Project Paper Proposal DONE!!!!Dokument24 SeitenProject Paper Proposal DONE!!!!Azri AlimorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math 9 Q1 M15Dokument13 SeitenMath 9 Q1 M15Ainee Grace DolleteNoch keine Bewertungen
- (International Series On Actuarial Science) David C. M. Dickson - Insurance Risk and Ruin-Cambridge University Press (2016)Dokument306 Seiten(International Series On Actuarial Science) David C. M. Dickson - Insurance Risk and Ruin-Cambridge University Press (2016)Parakh AhoojaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Curve FittingDokument32 SeitenCurve FittingHemanth JNoch keine Bewertungen
- Algebra I Teks SnapshotDokument2 SeitenAlgebra I Teks Snapshotapi-316941176Noch keine Bewertungen
- ENGR 3341 Probability Theory and Statistics: Professor's Contact InformationDokument5 SeitenENGR 3341 Probability Theory and Statistics: Professor's Contact InformationJenesicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dll-8-2-Multiplication and Division of Rational Algebraic ExpressionDokument9 SeitenDll-8-2-Multiplication and Division of Rational Algebraic ExpressionHero MirasolNoch keine Bewertungen