Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Under Ground Cable Maintenance
Hochgeladen von
Fawad AhmedCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Under Ground Cable Maintenance
Hochgeladen von
Fawad AhmedCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
UNDER GROUND CABLE MAINTENANCE
PROCEDURAL FLOWCHART:
CABLE FAULT LOCATION PROCEDURE:
Cable fault location as such has to be considered as a procedure covering the following
steps and not being only one single step.
Fault Indication
Disconnecting and Earthing
Fault Analyses and Insulation Test
Cable Fault Prelocation
Cable Route Tracing
Precise Cable Fault Location (Pinpointing)
Cable Identification
Fault marking and Repair
Cable Testing and Diagnosis
Switch on Power
INSTRUMENT USED FOR TESTING UGM:
There are many instruments used for testing and detecting underground cables but most
commonly used in KESC are following:
1. Surge Generators.
2. Seismic Phone
3. Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) or Impulse Reflect Generator (IRG)
4. Wheat Stone Bridge
Clearence to Operation Control (After Fault is Completely Removed From the Cable)
Jointing Department (For Jointing Faulty Portion Or Cable)
Testing Department (For Testing Cable Fault using Testing Instruments)
Operation Control (UGM)
Operation Centers (For Diagnosis Fault)
Operation Control
Complain Center
5. Cable Identifier Set
6. Route Checker.
SURGE GENERATOR:
The surge generator ignites an arc at the fault which creates a travelling wave
between the fault and the surge generator.
SEISMIC PHONE:
The Seismic phone is a directional acoustic listening device for the pinpointing of
flash-over faults on power cables. State-of-the-art technology and ease of handling
enables even users without training to locate accurately cable faults in conjunction
with a surge generator.
The Seismic phone measures the signals received by specially developed magnetic
and acoustic sensors, which are integrated in one housing.
The location of the buried cable can be determined by
the direction and intensity of the magnetic field,
produced by the impulse current of a surge generator.
With the bar graph-indicator of the Seismic phone,
the intensity of the strength of the magnetic
field can be measured. This has a maximum directly
above the cable.
A coincidence measurement is possible by receiving
and indicating the signals of both sensors simultaneously.
Seismic phone also allows measurement of the distance
between the sensor and the fault resulting from the difference in time taken by the
acoustic and magnetic signal.
TIME DOMAIN REFLECTOMETER:
The Teleflex TDR is a microprocessor controlled Reflectometer for cable fault pre-
location on electricity networks. Comfortable and easy operation is achieved by the
clear display structure and the automatic test sequence.
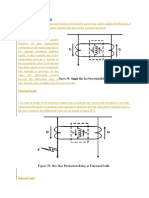
WHEAT STONE BRIDGE EQUIPMENT:
Bridge methods are basically used for prelocation of low resistive faults. By using a
high voltage source that is integrated in the latest generation of measuring bridge
instruments even high resistive faults can be prelocated.
The measuring bridge circuit according to Murray (Scientist) is applied on
arrangements, where beside the faulty core, one healthy core with same diameter and
conductor material is present.
In case of discontinuity of the cable diameter, the galvanometer will show the
average value of the total line resistance of the external loop. Therefore, as the result
is calculated via the galvanometer % indication, the indicated distance is incorrect, as
the line resistance section are in different relations to each other. For these
arrangements, the shirla (SHeath,Insulation test, fault Resistance and Location
Analyzer enables to define the different sections along the circuit and to be
considered by their individual material, cross section and length.
Basically the distance to the fault is calculated by
the following formula:
d=
JOINTING KIT PARTS DETAIL
1. STRESS CONTROL TUBING:
Provide effective stress control for termination kits and straight joints for XLPE
cable.
2. INSULATING TUBE:
Avoid short circuit fault caused by small animals such as mice, snakes and so on.
3. OUTER JACKET:
Use for covering and protecting cable.
4. SILICON GREASE:
It is used for lubricating and preserving rubber part of the cable.
5. SEALING MASTIC:
It can provide an effective moisture and environmental seal.
6. Al FERRULE:
Aluminum-copper cable ferrules are used for connection of aluminum and copper
conductor. The aluminum and copper connection is obtained using of friction method,
and it causes the elimination of disadvantageous effects on the aluminum with copper
contact.
7. COPPER MESH:
Flexible Copper Mesh Tape is normally used as an integral part of cable jointing kits
for power cables up to and including 36kv voltage rating.
8. ARMOUR CASE:
It is used protecting cable cores.
9. ABRASSIVE STRAP:
Used for cleansing copper things.
10. JUBILEE CLAMP:
It is designed to hold a soft, pliable hose onto a rigid circular pipe (or sometimes a
solid spigot) of smaller diameter.
TYPES OF CABLES:
(A) The cables for applications for low and medium voltage (upto and including
1.1KV) supply shall be one of the following: -
(i) PVC insulated and PVC sheathed
(ii) Cross linked polyethylene insulated, PVC sheathed (XLPE)
(B) The cables for applications for high voltage (above 1.1KV but upto and including
11KV supply) supply shall be one of the following: -
(i) PVC insulated and PVC sheathed
(ii) Paper insulated, lead sheathed (PILCA)
(iii) Cross linked polyethylene (XLPE) insulated, PVC sheathed
(C) The cables for applications above 11KV but upto and including 33KV supply
shall be one of the following: -
(i) Paper insulated lead sheathed (PILCA).
(ii) Cross linked, polyethylene insulated (XLPE)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- IRD Services2 - Vibration Measurement Tools Jan13Dokument2 SeitenIRD Services2 - Vibration Measurement Tools Jan13Avinash ThawaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Murphy Vibration SwitchesDokument20 SeitenMurphy Vibration SwitchessarkaftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Motor Management and Condition AssessmentDokument4 SeitenMotor Management and Condition AssessmentEngr Irfan AkhtarNoch keine Bewertungen
- TransformerDokument10 SeitenTransformerUjjawal ParasarNoch keine Bewertungen
- UNIT 11 Condition Monitoring On Hydro TurbineDokument4 SeitenUNIT 11 Condition Monitoring On Hydro Turbinemuaz_aminu1422100% (1)
- Maintenance and Replacement Policies For ProtectiveDokument14 SeitenMaintenance and Replacement Policies For ProtectiveZaHra TanhaNoch keine Bewertungen
- SLD Up3 CKR Mei 2020 PDFDokument116 SeitenSLD Up3 CKR Mei 2020 PDFDika Dewi PratiwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- TBEM CII Exim Bank Award ComparisonDokument38 SeitenTBEM CII Exim Bank Award ComparisonSamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Lockout Tagout Procedures Mining SafetyDokument3 SeitenElectrical Lockout Tagout Procedures Mining SafetyHakim MiswanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Main Tools and Techniques for Radio Network OptimizationDokument69 SeitenMain Tools and Techniques for Radio Network Optimizationreza56mNoch keine Bewertungen
- FLUKE - PDM OverviewDokument5 SeitenFLUKE - PDM OverviewofedulloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electrocution RefineryDokument3 SeitenElectrocution Refinerysonn the greatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ConfigurationDokument2 SeitenConfigurationDeepak GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance Management QA CHPDokument7 SeitenMaintenance Management QA CHPjasminezaidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Investigative Fault Analysis of 11KV Slip-Ring Induction MotorsDokument12 SeitenInvestigative Fault Analysis of 11KV Slip-Ring Induction MotorsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- An Overview of Cognitive Radio Architecture A Review: S.Venkateswari, R.MuthaiahDokument6 SeitenAn Overview of Cognitive Radio Architecture A Review: S.Venkateswari, R.MuthaiahAnonymous 1aqlkZNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read Acknowledgement Based Routing Misbehavior in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (RACK)Dokument7 SeitenRead Acknowledgement Based Routing Misbehavior in Mobile Ad-Hoc Networks (RACK)Aravinda GowdaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Two-Stage Failure Mode and Effect Analysis of Offshore Wind Turbines - 2020Dokument24 SeitenA Two-Stage Failure Mode and Effect Analysis of Offshore Wind Turbines - 2020johnNoch keine Bewertungen
- S - VII S. N - C S L T P C: Emester O ODE Ubject ReditsDokument27 SeitenS - VII S. N - C S L T P C: Emester O ODE Ubject Reditsanon_80026907Noch keine Bewertungen
- National Grid NSI 9 Testing High Voltage EquipmentDokument9 SeitenNational Grid NSI 9 Testing High Voltage Equipmentyagn_engineerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generic Terms of Reference For ESIADokument11 SeitenGeneric Terms of Reference For ESIADragoljub DjordjevicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aftac 2Dokument2 SeitenAftac 2Daniel GheorgheNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plant Condition Monitoring by Using Infrared ThermographyDokument17 SeitenPlant Condition Monitoring by Using Infrared ThermographyGoutham Reddy50% (2)
- Spare Parts ProcedureDokument3 SeitenSpare Parts Proceduresurya agung100% (1)
- Electrical Protection MaintenanceDokument12 SeitenElectrical Protection MaintenanceCyril DIPANDANoch keine Bewertungen
- Haer Hazardous Area Equipment RegisterDokument3 SeitenHaer Hazardous Area Equipment Registerselvan110663Noch keine Bewertungen
- Asset Tagging - SOP NIMSDokument6 SeitenAsset Tagging - SOP NIMSUmar TsaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- 043 Railway SILDokument16 Seiten043 Railway SILAgung WibowoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Meters - Newtek Electricals, Multifunction Energy Meters, VAF Meter, Smart MeterDokument18 SeitenDigital Meters - Newtek Electricals, Multifunction Energy Meters, VAF Meter, Smart MeterNewtek ElectricalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Design PPT LatestDokument18 SeitenCable Design PPT LatestjishnusajiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Specification, Boat Ambulance PDFDokument1 SeiteSpecification, Boat Ambulance PDFErick Galarza100% (1)
- Telecoms - Roll - Out - Plan - 2010-11 in The London Borough of MertonDokument6 SeitenTelecoms - Roll - Out - Plan - 2010-11 in The London Borough of MertonFuzzy_Wood_PersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dead Weight TestersDokument5 SeitenDead Weight TestersShrikant EkboteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Smart Grid Flexible PLC Solution Using C2000Dokument37 SeitenSmart Grid Flexible PLC Solution Using C2000abededeyem zelfaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electricity Distribution and SafetyDokument14 SeitenElectricity Distribution and SafetyMuhammadHafizBaharuddin0% (1)
- 2 - Generator MaintenanceDokument34 Seiten2 - Generator MaintenanceAmba James AsukNoch keine Bewertungen
- TOA Public Address System CatalogDokument16 SeitenTOA Public Address System CatalogHanif WiewekaNoch keine Bewertungen
- OTDR Application Trace Fiber Losses LengthDokument4 SeitenOTDR Application Trace Fiber Losses LengthHarrish GunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Product Reliability and MTBF2Dokument4 SeitenProduct Reliability and MTBF2sifuszNoch keine Bewertungen
- First Aid Training Report of Al Duqm Power StationDokument10 SeitenFirst Aid Training Report of Al Duqm Power StationMobin Thomas AbrahamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Planning and Scheduling Maintenance WorkDokument1 SeitePlanning and Scheduling Maintenance Worktco_99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Electrical Maintenance WorkshopDokument53 SeitenElectrical Maintenance WorkshopKANNA_2327Noch keine Bewertungen
- Marine Enviroment Exposure For Electrical DeviceDokument9 SeitenMarine Enviroment Exposure For Electrical DeviceThariq IndiartoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fire Safety Measures For Schools 2Dokument33 SeitenFire Safety Measures For Schools 2kavitaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Troubleshooting Induction MotorsDokument14 SeitenTroubleshooting Induction MotorsImelda LadrilloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Gland and Box Selection ChartDokument1 SeiteCable Gland and Box Selection ChartAdrianNoch keine Bewertungen
- TRANSFIX Users Guide MODBUS ProtocolDokument19 SeitenTRANSFIX Users Guide MODBUS ProtocolsantoshkumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Maintenance PlanDokument7 SeitenMaintenance PlanTafadzwa MurwiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Outlines 14-15 AllCoursesDokument35 SeitenCourse Outlines 14-15 AllCoursesarsathnmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Generator Electrical Test #3Dokument2 SeitenGenerator Electrical Test #3Santoshkumar GuptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dependability of Railway Control & Communications Systems v2Dokument28 SeitenDependability of Railway Control & Communications Systems v2Shashi Bhusan Singh100% (1)
- ElectromagneticCompatibilityMethodsAnalysisCircuitsandMeasurementThirdEdition 1 PDFDokument1.151 SeitenElectromagneticCompatibilityMethodsAnalysisCircuitsandMeasurementThirdEdition 1 PDFjotaruiz30Noch keine Bewertungen
- An Instrument For Detecting Corrosion in Anchorage Zones of Bridge Cables Using Guided WavesDokument6 SeitenAn Instrument For Detecting Corrosion in Anchorage Zones of Bridge Cables Using Guided WavesAnkush KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensor Design For Leakage Current Measurement On ADSS Fiber-Optic Cable PDFDokument6 SeitenSensor Design For Leakage Current Measurement On ADSS Fiber-Optic Cable PDFUdriste DanielNoch keine Bewertungen
- Project ReportDokument45 SeitenProject ReportRaj RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - 1: 1.1. Types of Faults in Cables 1.1.1. Open Circuit FaultDokument23 SeitenChapter - 1: 1.1. Types of Faults in Cables 1.1.1. Open Circuit Faultl.maheshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Fault Locators Surge Wave Generators An OverviewDokument4 SeitenCable Fault Locators Surge Wave Generators An OverviewSMART REFILLNoch keine Bewertungen
- Under Ground Cable Fault Detection and Location SystemDokument4 SeitenUnder Ground Cable Fault Detection and Location SystemBrightchip TechnologiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 Suparco ProjectsDokument3 Seiten4 Suparco ProjectsFawad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time DifferenceDokument4 SeitenTime DifferenceFawad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abdalli Ahmadi Ahmadi & Umm-AlhaimanDokument10 SeitenAbdalli Ahmadi Ahmadi & Umm-AlhaimanFawad AhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cable Laying SpecificationDokument16 SeitenCable Laying SpecificationdavidgarciavazquezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Logic Gates Programming in PLCDokument19 SeitenLogic Gates Programming in PLCRahul Sharma100% (6)
- Low-impedance busbar protection relayDokument32 SeitenLow-impedance busbar protection relayChristos ApostolopoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Reference DAPPERDokument124 SeitenReference DAPPERVictor Luiz MerlinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Bar Protection: External FaultsDokument4 SeitenBus Bar Protection: External FaultsChanderSinghWarkadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MDGF Protection Systems PresentationDokument77 SeitenMDGF Protection Systems Presentationjobpei2100% (1)
- Electrical Hazards and Protecting Persons: Power Guide 2009 / Book 06Dokument47 SeitenElectrical Hazards and Protecting Persons: Power Guide 2009 / Book 06hizbi7100% (1)
- Error Code MTU ADEC ECU 7Dokument24 SeitenError Code MTU ADEC ECU 7Sudiono Ajb92% (12)
- General Calculations Rev 4Dokument20 SeitenGeneral Calculations Rev 4KARTHIGEYAN.RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Megger FREJA 300Dokument10 SeitenMegger FREJA 300compu rentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Power Lines and Substations Short-Circuit ForcesDokument14 SeitenPower Lines and Substations Short-Circuit Forcesamit77999Noch keine Bewertungen
- EE2351 PSA 2marks 2013 - 2Dokument15 SeitenEE2351 PSA 2marks 2013 - 2Vijay RajuNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Simple Guide To Selection of Lightning and Surge ProtectionDokument5 SeitenA Simple Guide To Selection of Lightning and Surge Protectionyxp2237Noch keine Bewertungen
- Schneider Relay GuideDokument56 SeitenSchneider Relay GuideRajendra Prasath Thangamani100% (1)
- Symmetrical Fault AnalysisDokument39 SeitenSymmetrical Fault AnalysisViplav Chaitanya0% (1)
- Fluke 1653 Instruction ManualDokument80 SeitenFluke 1653 Instruction ManualSayed Ul Hassan0% (1)
- CCP enDokument94 SeitenCCP enBOUMELLISTE100% (1)
- ABB Transformers Protection CourseDokument56 SeitenABB Transformers Protection CourseWalid SonjiNoch keine Bewertungen
- At P DesignerDokument46 SeitenAt P DesignerdankorankoNoch keine Bewertungen
- PNC - P200 PDFDokument122 SeitenPNC - P200 PDFJohanes Nugroho Adhi Prakosa100% (3)
- Micom P127Dokument25 SeitenMicom P127Vijayaganthaan VisvanatthanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Documentation Guide: Optix Bws 1600G Backbone DWDM Optical Transmission System V100R007Dokument37 SeitenDocumentation Guide: Optix Bws 1600G Backbone DWDM Optical Transmission System V100R007Martin FonsecaNoch keine Bewertungen
- EDS309x D00012 M XXENDokument76 SeitenEDS309x D00012 M XXENOmnhickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transient Stability Analysis of 3-Machine 9-Bus Power System Using SimulinkDokument50 SeitenTransient Stability Analysis of 3-Machine 9-Bus Power System Using SimulinkIndri KndiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Siprotec4 7sa6 Catalog Sip E6Dokument42 SeitenSiprotec4 7sa6 Catalog Sip E6api-241473079Noch keine Bewertungen
- 220kv Sustation ChinhutDokument33 Seiten220kv Sustation ChinhutRaj VermaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bus Protection Seminar Jun2015Dokument134 SeitenBus Protection Seminar Jun2015sulemankhalid100% (1)
- 6 Vip300 CatalogueDokument24 Seiten6 Vip300 Catalogueanon_568723957Noch keine Bewertungen
- DC Short CKT CalculationDokument5 SeitenDC Short CKT CalculationRavishankar.AzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Be99 Brief 11-18-2013Dokument61 SeitenBe99 Brief 11-18-2013Malavika Menon100% (1)
- SIRIUS Safety Systems-Safety Integrated Position SwitchesDokument130 SeitenSIRIUS Safety Systems-Safety Integrated Position Switchesangeljavier9Noch keine Bewertungen
- VFDDokument16 SeitenVFDChristian RuedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (542)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemVon EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionVon EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Asset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresVon EverandAsset Integrity Management for Offshore and Onshore StructuresNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowVon EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Von EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Bewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsVon EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionVon Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (6)
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Third EditionVon EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Third EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionVon EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (331)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersVon Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionVon EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveVon EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (16)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsVon EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Von EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Industrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualVon EverandIndustrial Piping and Equipment Estimating ManualBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (7)
- Machinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideVon EverandMachinery Lubrication Technician (MLT) I and II Certification Exam GuideBewertung: 2 von 5 Sternen2/5 (1)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesVon EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Machine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesVon EverandMachine Learning and Data Science in the Oil and Gas Industry: Best Practices, Tools, and Case StudiesPatrick BangertBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (2)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationVon EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionVon EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (10)
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesVon EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (2)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataVon EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (22)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeVon EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (8)