Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Micro Structure
Hochgeladen von
Suresh Senanayake0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten6 SeitenRoom Temperature Micro Structures
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenRoom Temperature Micro Structures
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
26 Ansichten6 SeitenMicro Structure
Hochgeladen von
Suresh SenanayakeRoom Temperature Micro Structures
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 6
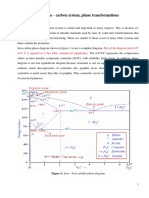
The Micro-structural nature of low carbon steel at Room Temperature
Objective is to illustrate the Room Temperature Micro-Structures of the following steels:
(a) Fe !"!!#$ %
(b) Fe !"!&$ %
(c) Fe !"'$ %
(() Fe !") $ %
(e) Fe *"! $ %
..
Three types of ferrous alloys:
+ ,ron : less than !"!!) wt $ % in -.ferrite at room Temperature
+ Steels: !"!!) - &"*' wt $ % --ferrite Fe
/
% at room Temperature
+ %ast iron : &"*' - 0"1 wt $
Fe + 0.005% an! Fe + 0.0"%
2ow carbon steel of both Fe !"!!#$ % an( Fe !"!&$ % can be categori3e( into wrought ,ron"
#rou$ht %ron : Fe + & ' 0.0( wt% ) + *la$ &%mpurities)
,n wrought ,ron4 Ferrite an( Slag (,mpurities) are soli(ifie( in to a past5 mass as illustrate(" The
structure is 6%% (- - ferrite)" 7rought ,ron is shape( b5 forging or rolling an( it is use( for chains4
anchors4 crane hoo8s4 etc"
The Micro-structure of those steels at room temperature will be as follows:
9age + of ,
Slag
Ferrite (-)
&a) Fe + 0.005%
The amount of phases present: 7eight Fraction at room temperature can be calculate( as follows:
2et ; < !"!!# (appro;imatel5) then 5 < 0"1 = !"!!# < 0"0>#
65 appl5ing 2ever Rule:
Ferrite (-)$ ; !"!!# < Slag $ ; 0"0>#---------------(*)
Ferrite (-)$ Slag$ < *!!-------------------------(&)
Ferrite (-)$: 0"0># < Slag$: !"!!# < *!!: 0"1
Then4
Ferrite (-)$ < *!! ; 0"0>#:0"1 < >>">$
Slag $ < *!! ; !"!!#: 0"1 < !"!1#$ (ie" !"*$)
&b) Fe + 0.0"%
The amount of phases present: 7eight Fraction at room temperature:
2et ; < !"!& (appro;imatel5) then 5 < 0"1 = !"!& < 0"0)
65 appl5ing 2ever Rule:
Ferrite (-)$ ; !"!& < Slag $ ; 0"0)---------------(*)
Ferrite (-)$ Slag$ < *!!-------------------------(&)
Ferrite (-)$: 0"0) < Slag$: !"!& < *!!: 0"1
Then4
Ferrite (-)$ < *!! ; 0"0):0"1 < >>"1$
Slag $ < *!! ; !"!&: 0"1 < !"&>>$ (ie" !"/$)
9age " of ,
-ow arbon *teel : Fe + & 0.0( . 0.( % )
The Structure contains - = Fe 9earlite (- Fe
/
% la5ers) as illustrate(" The strength of low carbon
steel is greater than wrought ,ron" 2ow carbon steels are use( for general constructional purposes such
as wire for nails4 rivets4 tubes4 etc"
Me!ium arbon *teel : Fe + & 0.( . 0./ % )
The Structure contains - = Fe 9earlite" The 9earlite content increases with the increase of %$" ?t
!")$ % the structure is completel5 9earlite (- Fe
/
% in la5ers) as illustrate(" These steel are use( for
machiner5 components such as @uts A 6olts4 Shafts an( Bears"
@ow:
( c) Fe + 0.0 %
This is a Me(ium %arbon Steel" The Micro-structure of this steel at room temperature will be as
follows:
The amount of phases present: 7eight Fraction at room temperature:
2et ; < !"' (appro;imatel5) then 5 < 0"1 = !"' < 0"/
65 appl5ing 2ever Rule:
Ferrite (-)$ ; !"' < 9earlite $ ; 0"/---------------(*)
Ferrite (-)$ 9earlite$ < *!!-------------------------(&)
Ferrite (-)$: 0"/ < 9earlite$: !"' < *!!: 0"1
9age ( of ,
- = Ferrite
9earlite (Car8)
Slag
- = Ferrite
9earlite (Car8)
Then4
Ferrite (-)$ < *!! ; 0"/:0"1 < >'"!$
9earlite $ < *!! ; !"': 0"1 < #">1$ (ie" 0"!$)
@ow4
( () Fe + 0./%
This is a eutectoi( steel containing of !")$ %" Dence no transformation ta8es place until the steel is
coole( to eutectoi( temperature (1&/
!
%)4 where though eutectoi( reaction austenite to pearlitic
transformation ta8es place" 1ence at room temperature we $et +00% 2earlite in the
microstructure"
EEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEEE
Remar8:
2earlite: ? mi;ture of alternate strips of ferrite an( cementite in a single grain" The (istance between the
plates an( their thic8ness is (epen(ant on the cooling rate of the materialF fast cooling creates thin plates that
are close together an( slow cooling creates a much coarser structure possessing less toughness" ? full5
pearlitic structure occurs at !")$ %arbon"
1i$h arbon *teel : Fe + & 0./ . +./ % )
The structure contains 9earlite an( %ementite (Fe
/
%) nee(les" Cue to high content of cementite the
strength is ver5 high" Therefore these steel are use( for Cies4 %utting tools4 etc"4 for which a ver5 high
9age 0 of ,
wear resistance is reGuire("
@ow4
( e) Fe + +.0%
This is a high carbon steel" The Micro-structure of this steel at room temperature will be as follows:
The amount of phases present: 7eight Fraction at room temperature:
2et ; < *"! (appro;imatel5) then 5 < 0"1 = *"! < #"1
65 appl5ing 2ever Rule:
9earlite$ ; *"! < %ementite $ ; #"1---------------(*)
9earlite$ %ementite$ < *!!-------------------------(&)
9earlite$: #"1 < %ementite$: *"! < *!!: 0"1
Then4
9earlite$ < *!! ; #"1:0"1 < )#"!1$
%ementite $ < *!! ; *"!: 0"1 < *'">/$
Following is the seGuences of change of phases of the three allo5s (Fe !"'$ %4 Fe !")$ % an(
Fe *"!$ %) cooling from the austenite region to room temperature"
9age 5 of ,
9earlite
%ementite (6lac8)
3lloy +: ,t is a D5po-eutectoi( steel containing !"'$ carbon"
3lloy ": ,t is a eutectoi( steel containing of !")$ %" Dence no transformation ta8es place until the
steel is coole( to eutectoi( temperature (1&/
!
%)4 where though eutectoi( reaction austenite to pearlitic
transformation ta8es place" Dence at room temperature we get *!!$ pearlite in the microstructure"
3lloy (: ,t is a h5per-eutectoi( steel containing *"!$ carbon" Curing cooling from the austenite range
this e;tra carbon shall be remove( from the austenite" The e;cess carbon is precipitate( out of soli(
solution but (uring the process it brings with it ferrite atoms an( the final precipitate is not pure carbon
but is cementite" ?s cooling an( cementite precipitation continue the remaining austenite becomes
gra(uall5 lower in carbon content" Then it changes to pearlite the reaction temperature being 1&/
!
%"
Finall5 we get a room-temperature microstructure of primar5 Fe
/
% plus 9earlite"
9age , of ,
Room
Temperature
1&/
!
%
Temperatur
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- রসায়নের পর্যায় সারণীDokument1 Seiteরসায়নের পর্যায় সারণীapi-33642484100% (1)
- Assessment of Welding ConsumablesDokument17 SeitenAssessment of Welding Consumablesmahmoud_allam3Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemical Process IndustriesDokument1.013 SeitenChemical Process IndustriesHameed Bin Ahmad100% (1)
- TTT Phase DiagramDokument9 SeitenTTT Phase Diagramhari krishnaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To NDTDokument50 SeitenIntroduction To NDTSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dac & DGSDokument14 SeitenDac & DGSAhmad Daniel100% (1)
- Improved Boiler Life and Efficiency with Inconel 622 Clad WeldsDokument7 SeitenImproved Boiler Life and Efficiency with Inconel 622 Clad Weldsc_e_z_a_rNoch keine Bewertungen
- Material Conversion TableDokument1 SeiteMaterial Conversion TableravikumarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lead-Tin Phase EquilibirumDokument19 SeitenLead-Tin Phase Equilibirummenonharsh91% (11)
- BS 970 En8dDokument1 SeiteBS 970 En8dsumeetsaini88Noch keine Bewertungen
- Condition MonitoringDokument22 SeitenCondition MonitoringSuresh Senanayake100% (1)
- Applitek - Detector in Vinyl Process PDFDokument24 SeitenApplitek - Detector in Vinyl Process PDFwiboonwiNoch keine Bewertungen
- P Block Elements MHT CET Synopsis PDFDokument15 SeitenP Block Elements MHT CET Synopsis PDFAbhishek Mandlik50% (2)
- Practical Metal Plate Work - With Numerous Engravings and DiagramsVon EverandPractical Metal Plate Work - With Numerous Engravings and DiagramsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Work, Energy and Power Cambridge OLDokument14 SeitenWork, Energy and Power Cambridge OLSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelVon EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNoch keine Bewertungen
- 9 Engineering AlloysDokument17 Seiten9 Engineering AlloysdavidtomyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blacksmithing on the Farm - With Information on the Materials, Tools and Methods of the BlacksmithVon EverandBlacksmithing on the Farm - With Information on the Materials, Tools and Methods of the BlacksmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sulfide OresDokument3 SeitenSulfide OresGustavo100% (1)
- Titration Guide MS - PG1682EN PDFDokument36 SeitenTitration Guide MS - PG1682EN PDFCJ PrettyNoch keine Bewertungen
- API 510 Data Sheet - AnswersDokument6 SeitenAPI 510 Data Sheet - Answersjithinjose86Noch keine Bewertungen
- O-Level Physics Assessment on PressureDokument5 SeitenO-Level Physics Assessment on PressureSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- O-Level Physics Assessment on PressureDokument5 SeitenO-Level Physics Assessment on PressureSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fe-Fe3c Diagram VerygoodDokument3 SeitenFe-Fe3c Diagram VerygoodRama Krishna Reddy DonthireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Materials Selection Assignment. LiveDokument10 SeitenMaterials Selection Assignment. Liverichward5Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iron-Carbon DiagramDokument3 SeitenIron-Carbon DiagramnaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SHEET STEEL SPECIFICATION FOR STAMPINGS AND COMMON STEELDokument5 SeitenSHEET STEEL SPECIFICATION FOR STAMPINGS AND COMMON STEELMike Fioren100% (1)
- Heat Treatment of SteelDokument26 SeitenHeat Treatment of SteelVishal KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3 EditedmmDokument25 SeitenChapter 3 EditedmmYasser RezkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metastable Iron-Carbon (Fe-C) Phase DiagramDokument3 SeitenMetastable Iron-Carbon (Fe-C) Phase DiagramupenderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anne A Ling and Normalizing of SteelDokument5 SeitenAnne A Ling and Normalizing of SteelTareef HashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Gray Cast Iron Brake Rotor MetallurgyDokument97 SeitenIntroduction to Gray Cast Iron Brake Rotor MetallurgyBhargav Suvagiya100% (1)
- Steels: Ii Beng (Hons) Mech Eng (Well Eng) Metallurgy & Manufacturing ScienceDokument39 SeitenSteels: Ii Beng (Hons) Mech Eng (Well Eng) Metallurgy & Manufacturing ScienceKareem YasserNoch keine Bewertungen
- Everything You Need to Know About Iron-Carbon Phase DiagramsDokument13 SeitenEverything You Need to Know About Iron-Carbon Phase DiagramsAbhishek SakatNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME IIA SA 47 Ferritic Malleable Iron CastingsDokument2 SeitenASME IIA SA 47 Ferritic Malleable Iron CastingsAmanda Ariesta ApriliaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 05 SteelsDokument4 Seiten05 SteelsRama Krishna Reddy DonthireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Publication 4 11889 199Dokument9 SeitenPublication 4 11889 199Mulia AridhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- A4-80 - A2-80 Material ClassDokument3 SeitenA4-80 - A2-80 Material Classcwfh779Noch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Carbon Diagram 6Dokument15 SeitenIron Carbon Diagram 6Harris DarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Carbon Phase DiagramDokument7 SeitenIron Carbon Phase Diagrampratap biswasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cast Steel: The Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram: AbstractDokument5 SeitenCast Steel: The Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram: Abstractchacha4500Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fe-Fe3C Phase Diagram ExplainedDokument6 SeitenFe-Fe3C Phase Diagram Explainedolid_zoneNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-27.5 Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramDokument52 SeitenCh-27.5 Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramManojNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Carbon Phase DiagramDokument4 SeitenIron Carbon Phase DiagramMizanur RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSE3094 HW#8 Solutions April 1, 2011 1) : A) The Data IsDokument5 SeitenMSE3094 HW#8 Solutions April 1, 2011 1) : A) The Data IsradarskiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron - Carbon SystemDokument21 SeitenIron - Carbon SystemYavana KeerthiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of Microstructure of Steels at Different Cooling Rates and Further Check Hardness of The SamplesDokument43 SeitenStudy of Microstructure of Steels at Different Cooling Rates and Further Check Hardness of The SamplesDeepu ChoudharyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding of Stainless SteelsDokument3 SeitenWelding of Stainless SteelsEswar Enterprises QcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weldability of Metals - NPTELDokument18 SeitenWeldability of Metals - NPTELKaushal Gandhi0% (1)
- Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramDokument11 SeitenIron Carbon Equilibrium Diagramganesh82Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Iron-Carbon Phase DiagramDokument16 SeitenThe Iron-Carbon Phase DiagramMeena SivasubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Master In Metallurgy And Materials Science TALLER N°2Dokument7 SeitenMaster In Metallurgy And Materials Science TALLER N°2ricardo alfonso paredes roaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ch-27.3 Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramDokument58 SeitenCh-27.3 Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramasjfgauojfgfNoch keine Bewertungen
- En 10025 S235JR SteelDokument2 SeitenEn 10025 S235JR SteelAgung Nak OtomotifNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram: AbstractDokument4 SeitenThe Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram: Abstractleodavid87Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Iron-Iron Carbide Equilibrium DiagramDokument15 SeitenThe Iron-Iron Carbide Equilibrium DiagramjhangeerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramDokument4 SeitenIron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramParameshwari PrabakarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sheet Pile Baja (JFESP)Dokument15 SeitenSheet Pile Baja (JFESP)berangketrNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8.heat TreatmentDokument7 Seiten8.heat Treatmentrohan_n_desai100% (2)
- E45 Laboratory4Dokument7 SeitenE45 Laboratory4nickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Lab 1Dokument6 SeitenThermal Lab 1Muhammad ZulhilmiNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITT CCTdiagrams (M)Dokument37 SeitenITT CCTdiagrams (M)Michael Vincent MirafuentesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Iron-Carbon Alloy SystemDokument36 Seiten2 Iron-Carbon Alloy SystemYour EntertainerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ffiffi: T (IlchDokument9 SeitenFfiffi: T (Ilchzuzu_boy6Noch keine Bewertungen
- Unit Cell Cubic StructuresDokument8 SeitenUnit Cell Cubic StructuresGuilherme Dos Santos MoreiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Metallurgy of Power BoilersDokument2 SeitenThe Metallurgy of Power Boilersdineshkbunker08Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry SPM NotesDokument12 SeitenChemistry SPM NotesArthas Rhee HermanNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram: AbstractDokument4 SeitenThe Iron-Carbon Equilibrium Diagram: AbstractRama Krishna Reddy DonthireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fe-Fe3C Phase Diagram and MicrostructuresDokument42 SeitenFe-Fe3C Phase Diagram and MicrostructuresTalaat Ahmed Mohamed El-Benawy100% (2)
- Metallury of SteelsDokument10 SeitenMetallury of SteelsDalitso MwanzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Iron Carbide Phase Diagram AnalysisDokument35 SeitenIron Carbide Phase Diagram AnalysisbotobotoakbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Metallurgy of Carbon SteelDokument5 SeitenThe Metallurgy of Carbon SteeltsoheilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bower Boiler SteelsDokument3 SeitenBower Boiler Steelsraut_1234100% (1)
- Metallabenzenes: An Expert ViewVon EverandMetallabenzenes: An Expert ViewL. James WrightNoch keine Bewertungen
- Intensity Level Vs FrequencyDokument1 SeiteIntensity Level Vs FrequencySuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pictures For BotanyDokument9 SeitenPictures For BotanySuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Physics: The Alpha Scattering ExperimentDokument3 SeitenNuclear Physics: The Alpha Scattering ExperimentSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radioactivity: Background RadiationDokument13 SeitenRadioactivity: Background RadiationSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- SpectrometerDokument12 SeitenSpectrometerSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- E AllDokument103 SeitenE AllOsman TolhildanNoch keine Bewertungen
- ElectricityDokument31 SeitenElectricitySuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument183 SeitenPDFSuresh Senanayake100% (1)
- Magnetic FieldDokument1 SeiteMagnetic FieldSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cambridge Kinematics EssayDokument12 SeitenCambridge Kinematics EssaySuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Welding Symbols 1Dokument8 SeitenWelding Symbols 1KrishnamoorthyGuruPrasathNoch keine Bewertungen
- Magnetic FieldsDokument1 SeiteMagnetic FieldsSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT EquipmentsDokument14 SeitenRT EquipmentsSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Simulating A 'Puzzle' Effect in Coreldraw® X6: Using A Regular ShapeDokument29 SeitenSimulating A 'Puzzle' Effect in Coreldraw® X6: Using A Regular ShapeSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Matter and Radiation NoteDokument19 SeitenMatter and Radiation NoteSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- V1 & V2 Cal Blocks For UTDokument1 SeiteV1 & V2 Cal Blocks For UTSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Semiconductor PhysicsDokument4 SeitenSemiconductor PhysicsSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bird MigrationDokument2 SeitenBird MigrationSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thermal Equilibrium and Zeroth LawDokument2 SeitenThermal Equilibrium and Zeroth LawSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Safety Q & ADokument1 SeiteRadiation Safety Q & ASuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ultrasonic Thickness Gauge, MiTech MT 160Dokument5 SeitenUltrasonic Thickness Gauge, MiTech MT 160Suresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- RT Safety Sample QuestionsDokument2 SeitenRT Safety Sample QuestionsSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiation Detection and Equipment Q & ADokument2 SeitenRadiation Detection and Equipment Q & ASuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Radiographic InterpretationDokument4 SeitenRadiographic InterpretationSuresh SenanayakeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aluminium Alloy en Ab-47100: Chemical Designation: en Ab-Alsi12Cu1 (Fe) Swedish Standard: Type - , (1)Dokument1 SeiteAluminium Alloy en Ab-47100: Chemical Designation: en Ab-Alsi12Cu1 (Fe) Swedish Standard: Type - , (1)Roberto Mendoza VillamilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appendices A 2020 PFAS RevDokument87 SeitenAppendices A 2020 PFAS RevOscar GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- International Exam - Volumetric AnalysisDokument5 SeitenInternational Exam - Volumetric Analysisalif satria100% (1)
- The Coordination Number and Oxidation State ofDokument24 SeitenThe Coordination Number and Oxidation State ofSubhasish SauNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ionic CrystalsDokument5 SeitenIonic CrystalsWayan TrimawiasaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spectroscopy Catalog 2018-19Dokument220 SeitenSpectroscopy Catalog 2018-19Juan alberto Ganoza GarciaNoch keine Bewertungen
- June 2021 (v1) MS - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry GCSEDokument10 SeitenJune 2021 (v1) MS - Paper 4 CIE Chemistry GCSEMAKNNIE KPOPNoch keine Bewertungen
- Aalco Metals LTD - Aluminium Alloy 5083 0 H111 Sheet and Plate - 149 PDFDokument2 SeitenAalco Metals LTD - Aluminium Alloy 5083 0 H111 Sheet and Plate - 149 PDFOvidiu ChertesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 14Dokument4 SeitenChapter 14Hania UmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mineral Comodity Summary - 2024Dokument216 SeitenMineral Comodity Summary - 2024ericallNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slater's rules determine shielding and ZeffDokument7 SeitenSlater's rules determine shielding and ZeffsadhuNoch keine Bewertungen
- LECTURE Naming CompoundsDokument63 SeitenLECTURE Naming CompoundsCheri BulahanNoch keine Bewertungen
- CSTPS ChemistryDokument146 SeitenCSTPS ChemistryRitesh MokhadeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chemistry Unit 2 Question PaperDokument16 SeitenChemistry Unit 2 Question PaperqeoobyogNoch keine Bewertungen
- Licorine LabDokument2 SeitenLicorine Labapi-254428474Noch keine Bewertungen
- Salicylic Acid InformationDokument3 SeitenSalicylic Acid Informationapi-343582965Noch keine Bewertungen
- Acid and BasesDokument4 SeitenAcid and BasesMika SaldañaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Three Plus TwoDokument7 SeitenThree Plus TwoRonak BhandariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Golongan I, Klorida Golongan Ii, Iii, Iv, VDokument5 SeitenGolongan I, Klorida Golongan Ii, Iii, Iv, VZigo KrenzNoch keine Bewertungen
- f1 c6 Periodic Table NotesDokument13 Seitenf1 c6 Periodic Table Notesjasonyeoh333Noch keine Bewertungen
- Sdfine ChemicalDokument262 SeitenSdfine Chemicalchvar80Noch keine Bewertungen