Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Transcription and Translation - Biotech
Hochgeladen von
Kriszha Anne MahinayCopyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Transcription and Translation - Biotech
Hochgeladen von
Kriszha Anne MahinayCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
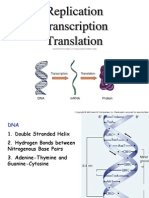
Protein Synthesis - Transcription and Translation
Review
Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
Protein synthesis requires two steps: transcription and translation.
DNA contains codes
Three bases in DNA code for one amino acid. The DNA code is copied to produce mRNA. The order
of amino acids in the polypeptide is determined by the sequence of 3-letter codes in mRNA.
DNA vs RNA
DNA RNA
Sugar: deoxyribose ribose
Bonds with Adenine: thymine uracil
# of Strands: two one
Kinds of RNA
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Messenger RNA contains genetic information. It is a copy of a portion of the DNA.
It carries genetic information from the gene (DNA) out of the nucleus, into the cytoplasm of the cell
where it is translated to produce protein.
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
This type of RNA is a structural component of the ribosomes. It does not contain a genetic message.
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Transfer RNA functions to transport amino acids to the ribosomes during protein synthesis.
Transcription
Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA from a DNA template.
It is like DNA replication in that a DNA strand is used to synthesize a strand of mRNA.
Only one strand of DNA is copied.
A single gene may be transcribed thousands of times.
After transcription, the DNA strands rejoin.
Steps involved in transcription
RNA polymeraserecognizes a specific base sequence in the DNA called a promoter and binds to it.
The promoter identifies the start of a gene, which strand is to be copied, and the direction that it is to
be copied.
RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA.
RNA polymerase assembles bases that are complimentary to the DNA strand being copied. RNA
contains uracil instead of thymine.
A termination codein the DNA indicates where transcription will stop.
The mRNA produced is called a mRNA transcript.
Processing the mRNA Transcript
In eucaryotic cells, the newly-formed mRNA transcript (also called heterogenous nuclear RNA or
hnRNA) must be further modified before it can be used.
A cap is added to the 5 end and a poly-A tail (150 to 200 Adenines) is added to the 3end of the
molecule.
The newly-formed mRNA has regions that do not contain a genetic message. These regions are
called introns and must be removed. Their function is unknown.
The remaining portions of mRNA are called exons. They are spliced together to form a mature
mRNA transcript.
The Nucleus
DNA is located in an organelle called the nucleus.
Transcription and mRNA processing occur in the nucleus.
The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane. After the mature mRNA transcript is produced, it
moves out of the nucleus and into the cytoplasmthrough pores in the nuclear membrane.
Translation
Translation is the process where
ribosomes synthesize proteins
using the mature mRNA
transcript produced
during transcription.
Overview
The diagram below shows a ribosome attach to mRNA, and then move along the mRNA adding
amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.
Translation - Details
A mature mRNA transcript, a ribosome, several tRNA molecules and amino acids are shown. There
is a specific tRNA for each of the 20 different amino acids.
Below: A ribosome attaches to the mRNA transcript.
A tRNA molecule transports an amino acid to the ribosome. Notice that the 3-letter anticodon on the
tRNA molecule matches the 3-letter code (called a codon) in the mRNA. The tRNA with the
anticodon "UAC" bonds with methionine. It always transports methionine. Transfer RNA molecules
with different anticodons transport other amino acids.
A second tRNA molecule bonds to the mRNA at the ribosome. Again, the codes must match.
A bond is formed between the two amino acids.
The tRNA bonded to methionine drops off and can be reused later.
The ribosome moves along the mRNA to expose another codon (GAU) for a tRNA molecule.
The only tRNA molecule that can bond to the GAU site is a molecule with a CUA anticodon.
Transfer RNA molecules with CUA anticodons are specific for asparagine.
Asparagine is now added to the growing amino acid chain.
Animation of Translation on the Internet
The link below will take you to an animation that summarizes transcription and translation.
http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=AP1302
Initiation and Termination Codes
An initiation codesignals the start of a genetic message. As the ribosome moves along a mRNA
transcript, it will not begin synthesizing protein until it reaches an initiation code.
Termination codes signal the end of the genetic message. Synthesis stops when the ribosome reaches
a terminator codon.
Genetic Code
The table below can be used to determine what amino acid corresponds to any 3-letter codon in the
mRNA.
First
Base
Second Base
Third
Base U C A G
U
UUU
phenylalanine
UCU
serine
UAU
tyrosine
UGU
cysteine
U
UUC
phenylalanine
UCC
serine
UAC
tyrosine
UGC
cysteine
C
UUA
leucine
UCA
serine
UAA
stop
UGA
stop
A
UUG
leucine
UCG
serine
UAG
stop
UGG
tryptophan
G
C
CUU
leucine
CCU
proline
CAU
histidine
CGU
arginine
U
CUC
leucine
CCC
proline
CAC
histidine
CGC
arginine
C
CUA
leucine
CCA
proline
CAA
glutamine
CGA
arginine
A
CUG
leucine
CCG
proline
CAG
glutamine
CGG
arginine
G
A
AUU
isoleucine
ACU
threonine
AAU
asparagine
AGU
serine
U
AUC
isoleucine
ACC
threonine
AAC
asparagine
AGC
serine
C
AUA
isoleucine
ACA
threonine
AAA
lysine
AGA
arginine
A
AUG (start)
methionine
ACG
threonine
AAG
lysine
AGG
arginine
G
G
GUU
valine
GCU
alanine
GAU
aspartate
GGU
glycine
U
GUC
valine
GCC
alanine
GAC
aspartate
GGC
glycine
C
GUA
valine
GCA
alanine
GAA
glutamate
GGA
glycine
A
GUG
valine
GCG
alanine
GAG
glutamate
GGG
glycine
G
Mutation
Mutations are changes in the DNA.
Frameshift
A frameshift mutation is usually severe, producing a completely nonfunctional protein.
The priniciple of a frameshift can be explained using the sentence below. If the letters are read three
at a time and one is deleted, the second sentence becomes meaningless.
Original DNA:
Frameshift mutation:
THE BIG RED ANT ATE ONE FAT BUG
THB IGR EDA NTA TEO NEF ATB UG?
Point Mutation
Point mutations involve a single nucleotide, thus a single amino acid.
In the sentence below, eliminating one letter does not change in the remaining three-letter words and
therefore may not cause a significant change in the meaning of the sentence.
Original DNA:
Frameshift mutation:
THE BIG RED ANT ATE ONE FAT BUG
THA BIG RED ANT ATE ONE FAT BUG
Silent, Missense, and Nonsense Mutations
Three kinds of point mutations can occur. A mutation that results in an amino acid substitution is
called a missense mutation.
A mutation that results in a stop codon so that incomplete proteins are produced, it is called a
nonsense mutation.
A mutation that produces a functioning protein is called a silent mutation.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Earphone Research Paper-JericDokument10 SeitenEarphone Research Paper-JericKriszha Anne Mahinay100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- Causal AnalysisDokument3 SeitenCausal AnalysisKriszha Anne MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Transcription and Translation - BiotechDokument10 SeitenTranscription and Translation - BiotechKriszha Anne MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- Project in APDokument9 SeitenProject in APKriszha Anne MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (895)
- SmartBro HotlineDokument1 SeiteSmartBro HotlineKriszha Anne MahinayNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Science10 Q3 Mod5 MutationDokument25 SeitenScience10 Q3 Mod5 Mutationjane mamon100% (1)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Virus Structure and ReplicationDokument64 SeitenVirus Structure and ReplicationLawrence RemuloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (588)
- Biology Revision Notes - Nervous Systems and HomeostasisDokument2 SeitenBiology Revision Notes - Nervous Systems and HomeostasisKenny Wong Siew FooNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- Protein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillDokument32 SeitenProtein Synthesis: It Is Expected That Students WillIMY PAMEROYANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (266)
- NullDokument561 SeitenNullizo_katenaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Central Dogma and Genetic MedicineDokument4 SeitenCentral Dogma and Genetic MedicineJuliana Rose de Leon100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- (Learning Materials in Biosciences) Melanie Kappelmann-Fenzl - Next Generation Sequencing and Data Analysis-Springer (2021)Dokument225 Seiten(Learning Materials in Biosciences) Melanie Kappelmann-Fenzl - Next Generation Sequencing and Data Analysis-Springer (2021)gndfbj100% (2)
- Microbiology: An Evolving ScienceDokument26 SeitenMicrobiology: An Evolving ScienceHong Quang Pham56% (9)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- Bio Tech Reviewer 1st QuarterDokument16 SeitenBio Tech Reviewer 1st QuarterNinong WallyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- CF+OYM (P1) 2024TE04A (06-09-2023) SolutionsDokument21 SeitenCF+OYM (P1) 2024TE04A (06-09-2023) SolutionsAbhimanyu BhasinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- 12 Review WSDokument11 Seiten12 Review WSJASON WILLSNoch keine Bewertungen
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2259)
- DLL Do SCI g10 Q3 Week6 22 23Dokument8 SeitenDLL Do SCI g10 Q3 Week6 22 23NURSHAHADAH ISMAELNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vincento Frazier - Gizmos Lab - Protein SynthesisDokument6 SeitenVincento Frazier - Gizmos Lab - Protein SynthesisToxic KikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Difference Between Missense and Nonsense MutationDokument5 SeitenDifference Between Missense and Nonsense MutationSol-Rod IsaacNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mader Chap012 10eTBDokument17 SeitenMader Chap012 10eTBDr. Michael DavidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleotides and Nucleic AcidsDokument65 SeitenNucleotides and Nucleic AcidsnutriNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- Post-Transcriptional ModificationDokument20 SeitenPost-Transcriptional ModificationZain YaqoobNoch keine Bewertungen
- Molecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsDokument7 SeitenMolecular Biology Previous Year QuestionsKrutika SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 2Dokument41 SeitenChapter 2Allyson OffreyNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- 2022 CytoskeletonDokument59 Seiten2022 CytoskeletonAwais RehmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyDokument9 SeitenDr. Harvey Laranang MicrobiologyPatricia L.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nucleic Acids and Overview of Central Dogma - SAC - Janine Teza S. VillenaDokument52 SeitenNucleic Acids and Overview of Central Dogma - SAC - Janine Teza S. VillenaNovie Carla GayosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Network Analysis of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Patents: ModernaDokument3 SeitenA Network Analysis of COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine Patents: ModernaMatthieu BecquartNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (120)
- Transfer of Genetic InformationDokument13 SeitenTransfer of Genetic InformationStevanus JonathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Protein Folding For Physicists: 1 Why Study Proteins?Dokument53 SeitenIntroduction To Protein Folding For Physicists: 1 Why Study Proteins?Alishba Faixan100% (1)
- SBI4U - Unit 3 AssignmentDokument16 SeitenSBI4U - Unit 3 AssignmentSageofsix980 Sageofsix980Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 Book RNASequenceStructureAndFunctioDokument533 Seiten2014 Book RNASequenceStructureAndFunctioOmar EladlNoch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Gene Expression Translation SDokument6 Seiten15 Gene Expression Translation SHelp Me Study TutoringNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dna Replication, Translation, and TranscriptionDokument43 SeitenDna Replication, Translation, and TranscriptionMaria VisitacionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Guide Unit 2.2 - Dna Replication & Protein SynthesisDokument35 SeitenStudy Guide Unit 2.2 - Dna Replication & Protein SynthesisGraceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)