Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
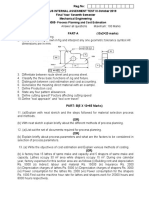
Quiz 2 Name: ID: Group: EMD5M11 / EDM5M5A Date
Hochgeladen von
Cayang_Bucuk0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
43 Ansichten8 SeitenThis document contains a quiz for a manufacturing processes course. It has two main sections on casting and joining processes. In the casting section, it asks 20 multi-part questions covering topics like casting defects, gating systems, risers, casting calculations, and different casting processes. The joining section asks 12 multi-part questions about welding processes like SMAW and TIG, brazing, adhesive joining, and factors in choosing a joining method. It also contains a section on machining with 10 multi-part questions about topics such as tool life calculation, CNC machines, grinding, cutting tools, and vibration issues in machining.
Originalbeschreibung:
anything
Originaltitel
9cafbafde53c0f1f72efd468b9976c1e(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOC, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenThis document contains a quiz for a manufacturing processes course. It has two main sections on casting and joining processes. In the casting section, it asks 20 multi-part questions covering topics like casting defects, gating systems, risers, casting calculations, and different casting processes. The joining section asks 12 multi-part questions about welding processes like SMAW and TIG, brazing, adhesive joining, and factors in choosing a joining method. It also contains a section on machining with 10 multi-part questions about topics such as tool life calculation, CNC machines, grinding, cutting tools, and vibration issues in machining.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
43 Ansichten8 SeitenQuiz 2 Name: ID: Group: EMD5M11 / EDM5M5A Date
Hochgeladen von
Cayang_BucukThis document contains a quiz for a manufacturing processes course. It has two main sections on casting and joining processes. In the casting section, it asks 20 multi-part questions covering topics like casting defects, gating systems, risers, casting calculations, and different casting processes. The joining section asks 12 multi-part questions about welding processes like SMAW and TIG, brazing, adhesive joining, and factors in choosing a joining method. It also contains a section on machining with 10 multi-part questions about topics such as tool life calculation, CNC machines, grinding, cutting tools, and vibration issues in machining.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOC, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 8
Faculty of Mechanical Engineering
Universiti Teknologi MARA
Shah Alam
Course Code : MEM5!
Course "ame : MA"UFACTUR#"$ %R&CESSES
Test ' Time : (ui) * ' +5 mins
,ou need to A"S-ER A.. /uestions0
Ans1ering 2onus /uestions 1ill 2e giving you e3tra marks 4if any50
A. Casting
60 Com7are and contrast the 2asic 7rocess 7rinci7les in sand casting, investment casting,
and pressure die casting. $ive sam7le * each0 8&ct9!+: 6! marks
*0 ;iscuss the 7ossi2ility and differences of 7roduct cost and /uality as7ects of sand
casting, investment casting, and pressure die casting0 8&ct9!+: 6! marks
<0 ;escri2e defects in sand casting due to im7ro7er selection and 7re7aration of moulding
materials0 -hat are the 7ossi2le remedies= 8&ct9!+: 6! marks
+0 ;escri2e the function of riser in casting0 Using Caine>s method? calculate the cylindrical
riser 4height and diameter e/ual5 necessary to feed a grey cast iron sla2 casting
!3!3<cm 1ith a side riser? casting 7oured hori)ontally into the mould0 8"ov 9!5:
@ Marks
Freezing Ration X of a mould is defined as a ratio of cooling characteristics of
casting to the riser.
A B SAcasting ' Ccasting
SAriser ' Criser
Caines empirical relationship for the freezing ratio:
A B a D c
,D2
Where ! riser volume"casting volume
a, # and c are constants $hose values for different materials are as follo$s%
a 2 c
Steel !06! !0!< 60!!
Aluminium !06! !0! 60!!
Cast iron? 2rass !0!+ !0!6@ 60!!
$rey cast iron !0<< !0!< 60!!
Aluminium 2ron)e !0*+ !0!6@ 60!!
Silicon 2ron)e !0*+ !0!6@ 60!!
50 #llustrate t1o of the $as ;efects in sand casting0 -hat are the causes for the defects and
ho1 can 1e rectify it= 8"ov 9!5: Marks
&uiz ' (ept )*''
(U#E *
"ame :
#; :
$rou7 : EM;5M66 ' E;M5M5A
;ate :
0 Select a 7roduct of your choice using sand casting 7rocess0 Friefly e37lain the 7rocedure
to 2e follo1ed for making a sand mould for this 7roduct0 8"ov 9!5: @ Marks
@0 ;etailed out maGor disadvantages of sand casting 7rocess and ho1 are they overcome=
8"ov 9!5: @ Marks
H0 Friefly discuss 1hy draft and shrinkage allo1ance is im7ortant for 7atterns= -hat is a
dou2le shrinkage allo1ance= 8"ov 9!5: Marks
I0 ;escri2e the follo1ing 7rocessesJ 8A7r 9!I: Marks
i5 %ressure die casting
ii5 .ost 1a3 casting
iii5 Continuous casting
iv5 #nvestment casting 8A7r 96!:
6!0 E37lain the follo1ingJ 8&ct 9!I: < Marks
i5 S7rue
ii5 Runner
iii5 %arting line
iv5 Core
v5 Riser
vi5 $ating system
660 E37lain < 7ossi2le casting defects due to im7ro7er gating system design in sand casting0
8&ct 9!I: < Marks
6*0 -hat are the general 7roduct ty7es 7roduced from the follo1ing casting 7rocesses are
used=
i5 %recision investment casting
ii5 Shell moulding
iii5 True centrifugal casting
iv5 %ressure die casting 8&ct 9!I: + Marks
6<0 $ive at least + im7ortant 7ro7erties re/uired for moulding materials in sand casting0
8A7r 96!: * Marks
6+0 -hat is $rain Fineness "um2er 4$F"5 and ho1 does it affect the 7ro7erties of the sand
mould= 8A7r 96!: * Marks
650 -hat are the advantages of die casting over sand casting in terms of its mechanical
7ro7erties or design ca7a2ilities= 8A7r 96!: < marks
60 ;iscuss at least < common defects generally encountered in casting 7rocesses0 8A7r 96!:
< Marks
6@0 .ist * casting 7rocesses that are em7loyed and e37lain 1hy these 7rocesses are suita2le
for that 7articular mould or die materialJ
i5 SandJ
ii5 Metal 8A7r 96!: < Marks
6H0 $ear 2eam can 2e made using shell moulding0 E37lain teh 7rocess se/uence and state
each * advantages and limitations of the 7rocess0 8A7r 96!: @ Marks
&uiz ' (ept )*''
6I0 State and e37lain * methods to reduce core shifting in sand casting0 8A7r 96!: < Marks
*!0 Ko1 1ould the end 7roducts of castings made 2y 7ermanent mould differ from sand
casting= 8A7r 96!: + Marks
*60 -hat sort of casting most suita2le forJ 8A7r 9!I: * Marks
i5 Steam tur2ine
ii5 Einc door handle
**0 -hat are the im7ortant considerations involved in choosing a casting method= 8A7r
9!I: * Marks
B. Joining
60 E37lain the 7ossi2le 1elding 7rocess suita2le for a 65mm thick 7late CS 4A#S# 6!555
Goined in flat 7osition0 ;etailed out the Goint and edge 7re7aration? 1elding method?
1elding consuma2les 4if any5 and 7recautions involved0 8&ct9!+: 6! marks
*0 E37lain and descri2e the differences 2et1een mechanical fastener'riveting? adhesive
Goining? soldering? 2ra)ing and 1elding0 8&ct>!+? "ov >!5? A7r >!I? &ct >!I L A7r
96!: <D + marks
<0 ;istinguish 1ith sketches the 1elding setDu7 2et1een M#$ 4$MA-5 and T#$
4$TA-5 1elding 7rocess0 E37lain the differences of 2oth 7rocesses0 8"ov >!5 L
A7r 96!: + Marks
&uiz ' (ept )*''
+0 Suggest suita2le 1elding 7rocess for making a stainless steel gasoline tanks and
e37lain the 1elding 7rocess used in detail0 8"ov 9!5: < Marks
50 -ith the hel7 of schematic sketches? com7are and contrast SMA- and $TA- in
terms of Source of Keat? Electrode and Shielding? Manual'Automatic o7eration?
Current'Keat in7ut and its a77lication0 8"ov 9!5: @ Marks
0 Metal Goining can 2e either 7ermanent or tem7orary Goints0 Com7are costs and the
relative advantages and disadvantages of those t1o methods0 $ive e3am7les to sho1
that factors affect the choice of the method for a 7articular Go20 8A7r 9!I: < Marks
@0 ;escri2e and e37lain the three 1elding classes of com7osition in the 1eld )one
4autogenous? homogeneous and heterogenous5 and name one 7rocess for each grou70
8A7r 9!I: + Marks
H0 9T1o 7lates 1ere 1elded together and then strength of the Goints 1as tested0 #t 1as
found that the 1eld 1as stronger than the 7lates>0 Comment on the statement 41ith
reasons etc50 8&ct 9!I: * Marks
I0 E37lain 2riefly the follo1ing t1o common ty7es of fusion 1eldingJ
i5 SMA-
ii5 SA-
6!0 E37lain the 7rinci7les underlying the resistance 1elding0 $ive * 7roducts that usesJ
i5 S7ot 1elding
ii5 Seam 1elding
C. TM
60 Car2ide tooling
The 2est and economical 7rocess in ma+ing car#ide tooling tools0 E37lain 1hy0
8&ct9!+: H marks
;escri2e the stages involved0 8&ct9!+: * marks
*0 ;efine? descri2e? e37lain the follo1ing terminologiesJ 8&ct>!+: + marks
i5 Slide1ay
ii5 Koning 7rocess
iii5 Ko2
iv5 Conventional machining
v5
Surface finish
Factors in selecting surface finish and surface cleaning. [Oct04] 4 marks
Describe the stages involved in Barrel Finishing and name !roducts suitable for the
!rocess. [Oct04] " marks
&uiz ' (ept )*''
<0 Machine tools M list four o7erations that can 2e 7erformed 2y a lathe machine0
8"ov9!5: * Marks
+0 ;escri2e the terminologies related to C"C metal cutting 7rocessJ
i5 A2solute 7ositioning
ii5 %oint to 7oint 4%T%5
iii5 Machining centre
iv5 Automatic tool changer
50 Continuous chi7 1ith FUE affects the dimensional accuracy? surface finish of the 1ork
7iece and the cutting tool life0 Ko1 can these 7ro2lems 2e im7roved= 8"ov 9!5: <
Marks
0 ;escri2e the e/uation introduced 2y F0- Taylor in metal cutting of tool life e,uation?
CT
n
B C0
i5 -hat are the t1o shortcomings of the e/uation=
ii5 A lathe machine using a medium car2on steel 1ork 7iece? cutting velocity of
+!m'min and a cement cutting tool insert 1as re7laced every hour0 Calculate the
tool life of the tool 1hen used under identical condition 2ut at s7eed of 5!m'min0
Assume the tool inde3 is B !0*H0 8"ov >!5 L &ct 9!I: 5 Marks
iii5 E37lain the meaning of the al7ha2ets in the e/uation C? T?
n
and C0 8&ct >!I L
A7r 96!:
iv5 $ive one im7roved e/uation for 7rediction the tool life0 8A7r 96!:
@0 Nigs and fi3turesJ 8"ov 9!5: + Marks
i5 Com7are and contrast 2et1een a Gig and a fi3ture0
ii5 E37lain the advantages of using Gigs and fi3tures0
H0 Suggest and e37lain a suita2le and economical 7rocess onJ 8"ov 9!5: Marks
i5 Coating Cutting Tools 1ith Titanium "itride 4Ti "5
ii5 Removing 2urr of small com7onents 1ith large /uantity like valve sto7 for
refrigerator com7ressor0
I0 ;escri2e the factors involved in selecting cutting tools0 8"ov 9!5: * Marks
6!0 -hy do some machining com7anies use cutting tools 1ith inserts0 8"ov 9!5: < Marks
660 -ork holding devices M list at least four and 2riefly descri2e them0 8"ov 9!5: <
Marks
6*0 ;efine machine tool0 ;escri2e the 7rocess that can 2e carried out using four identified
machine tools in your Machine Sho70 8&ct >! A7r 9!I: 5 marks
6<0 -hy grinding machine is made availa2le in almost all Machine Sho7= 8&ct>!: +
marks
6+0 A 7o7ular choice and higher utilisation than milling machine? give reasons 1hy grinding
machine is so0 8"ov 9!5: < Marks
650 FUE is common 7ro2lem in metal cutting as it affect dimensional accuracy and surface
finish of a 7roduct as 1ell as FUE reduces the life of a cutting tool0 ;iscuss some
solutions for this 7ro2lem0 8&ct>!: * marks
&uiz ' (ept )*''
60 ;iscuss three factors to consider in selecting a 7articular C"C machine to 2e used in
machining a 7articular 7art0 8&ct>!: < marks
6@0 ;escri2e the follo1ing terminologies involved in C"C machiningJ 8&ct>!: + marks
i5 #ncremental 7ositioning
ii5 %oint to 7oint 4%T%5
iii5 Machining centre
iv5 CAM
6H0 A factor in 7roduct reGection is due to vi2ration in C"C Machining 7rocess0 ;iscuss the
factors 4at least <5 to 2e considered in solving the 7ro2lem0 8&ct>!: < marks
6I0 Machine toolsJ 8A7r 9!I: + marks
i5 .ist < chi7s 7roducing machine tools that can 2e used for machining flat
surfaces0
ii5 .ist < chi7s 7roducing machine tools that can 2e used for machining
cylindrical round 7arts0
iii5 -hy grinding machine is one of the most im7ortant machine in any machine
sho70
*!0 Crater 1ear M e37lain crater 1ear and fundamental factors that influence its formation0
E37lain the ste7s to minimise it0 8A7r 9!I: + Marks
*60 "ame at least < holding devices used 1ith a lathe machine in machining various of
cylindrical 7arts and descri2e 2riefly one of them0 8&ct 9!I: * Marks
**0 ;iscuss at least + reasons 1hy in many metal cutting o7erations? machining using a
9thro1Da1ay inserts> is common0 8&ct 9!I: * Marks
*<0 ;escri2e 2rieflyJ 8A7r 96!: * Marks
i5 Rough machining
ii5 Steady rest
iii5 Magnetic chuck
iv5 Machining centre
*+0 .ist at least + o7erations that can 2e 7erformed on a lathe machine0 8A7r 96!: * Marks
*50 ;escri2e 1hy 7arts 7roduced on a lathe machine encounter many reGect due to 2ad
surface finish0 Friefly e37lain the reasons and action to minimise the 7ro2lem0
8A7r 96!: < Marks
*0 ;escri2e the function of cutting fluid0 8A7r 9!I: * Marks
*@0 ;efine MRR0 8A7r 9!I: < Marks
*H0 ;escri2e the criteria of selection of machine tool0 8A7r 9!I: * Marks
D. NTM
&uiz ' (ept )*''
60 USM M descri2e the 2asic 7rinci7les and give e3am7les of its use0 Use sketches to
su2stantiate your arguments0 8"ov 9!5: Marks
*0 ;iscuss maGor differences 2et1een TM and "TM0 $ive also their relative merits0
8&ct>! L A7r 96!: + marks
<0 Fased on the follo1ingJ 8&ct>! L A7r 96!: marks
i5 "ame the "TM
ii5 "ame the 7roducts that uses this 7rocess
iii5 ;escri2e the 7rocess
+0 ;escri2e the factors involved in the develo7ment of "TM0 8"ov 9!5: + Marks
50 ;iscuss + reasons for the 7urchase'use of "TM in 7reference to TM tools0
8A7r >!I L &ct 9!I: * Marks
0 ;escri2e the 2asic 7rinci7les of EFM and USM and give e3am7les of their use0 Sketches
may 2e used0 8A7r 9!I: H Marks
@0 Com7are and discuss < maGor differences of E;M? ECM and USM0 8&ct 9!I: Marks
H0 E37lain the follo1ingJ 8&ct 9!I: * Marks
i5 Slurry
ii5 ;ielectric
iii5 .aser
iv5 Electrode
I0 ;escri2e the follo1ing "TM0 8A7r 9!I: 5 marks
;escri2e the 7roducts made availa2le from the 7rocess0
&uiz ' (ept )*''
&uiz ' (ept )*''
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Manufacturing Process 1 Question BankDokument7 SeitenManufacturing Process 1 Question BankPranav Pandey67% (3)
- Report of Supply ChainDokument22 SeitenReport of Supply ChainkhanimmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parametric Bay Studies V4 - 0 (AISC)Dokument20 SeitenParametric Bay Studies V4 - 0 (AISC)v100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDokument3 SeitenGujarat Technological University: InstructionsDhruvin KagdiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shipbuilding Technology 4th Semester SyllabusDokument30 SeitenShipbuilding Technology 4th Semester SyllabusDiploma in Engineering Shipbuilding TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metal FormingDokument6 SeitenMetal FormingHarish Kumar SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDokument1 SeiteGujarat Technological UniversityBhagirath sinh ZalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part C: Production Techniques (ME C342) Open BookDokument2 SeitenPart C: Production Techniques (ME C342) Open BookpankazspamNoch keine Bewertungen
- SmartFrame Connection DetailsDokument29 SeitenSmartFrame Connection Detailsmeetvinayak2007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Aramco Specific Evaluations For WeldingDokument6 SeitenAramco Specific Evaluations For WeldingSiddiqui Abdul Khaliq89% (9)
- Interlocking Concrete Paver SpecsDokument6 SeitenInterlocking Concrete Paver Specscarolinetrippin100% (1)
- MP II - Nov 2011Dokument2 SeitenMP II - Nov 2011abhay_15865099Noch keine Bewertungen
- MT II Course Hand OutDokument3 SeitenMT II Course Hand OutvelavansuNoch keine Bewertungen
- May 2014Dokument3 SeitenMay 2014Arun Prakash NatesanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Au Qp-Adv in Casting and Welding-Dec2020Dokument3 SeitenAu Qp-Adv in Casting and Welding-Dec2020Ohmsakthi vel RNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bielas Caterpillar en General Reutilizacion 2010Dokument22 SeitenBielas Caterpillar en General Reutilizacion 2010ariel avalosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Me 2252Dokument3 SeitenMe 2252cbeprabhugmailNoch keine Bewertungen
- ASME B16.36-96 Bridas de OrificioDokument11 SeitenASME B16.36-96 Bridas de OrificioLuis MoralesNoch keine Bewertungen
- UG Syllabus 2010 11 NITtDokument33 SeitenUG Syllabus 2010 11 NITtNitin VarmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Design Guidelines for Surface Mount TechnologyVon EverandDesign Guidelines for Surface Mount TechnologyBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Production TechnologyDokument4 SeitenProduction TechnologysandchinniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manual For Fusion Welding of Rails by The Alumino-Thermic ProcessDokument49 SeitenManual For Fusion Welding of Rails by The Alumino-Thermic ProcesskrischaeverNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP IatDokument4 SeitenMP Iatazhagan.mecNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1617 Dec SKMM2713Dokument17 Seiten1617 Dec SKMM2713Shah MalikNoch keine Bewertungen
- MFET 3451 Experiment # 3 Metallography LaboratoryDokument5 SeitenMFET 3451 Experiment # 3 Metallography LaboratoryVicky NoomNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokument3 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)gowrisankarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPWI 3 of 4Dokument50 SeitenCPWI 3 of 4Jorge SobrevillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Faculty of Engineering and TechnologyDokument1 SeiteFaculty of Engineering and TechnologyaeropaschalNoch keine Bewertungen
- EP000122-001 - AN - Terminal Codes PDFDokument34 SeitenEP000122-001 - AN - Terminal Codes PDFfranciscopayanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial 2 BETP 1323 Sem 1 2014 2015Dokument2 SeitenTutorial 2 BETP 1323 Sem 1 2014 2015Tarmizi BahariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer ALL Questions Part-A 10x2 20: Department of Mechanical Engineering Internal Exam-IiiDokument1 SeiteAnswer ALL Questions Part-A 10x2 20: Department of Mechanical Engineering Internal Exam-IiitagoreboopathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study of The Chips Morphology in Turning by Stratified Sampling MethodDokument9 SeitenStudy of The Chips Morphology in Turning by Stratified Sampling MethodAbderrahim BelloufiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Time: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksDokument3 SeitenTime: 3 Hours Answer All Questions Maximum: 100 MarksAnonymous ZB6qyhD6Noch keine Bewertungen
- End Sem PyqDokument5 SeitenEnd Sem PyqJaspreet veeraNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2011 Nov Dec R2010Dokument2 Seiten2011 Nov Dec R2010anon_318963451Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bda 30502 Sem 2 1213Dokument5 SeitenBda 30502 Sem 2 1213Iskandar BellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ipc2004 000257Dokument9 SeitenIpc2004 000257Skazemi7Noch keine Bewertungen
- Test Project Sheet MetalDokument10 SeitenTest Project Sheet MetalSyed Idrus Syed OmarNoch keine Bewertungen
- 000 GPP GCX 00029 Welding and NDT MatrixDokument18 Seiten000 GPP GCX 00029 Welding and NDT MatrixGOPALAKRISHNAN SubramanianNoch keine Bewertungen
- QB Mem 103Dokument4 SeitenQB Mem 103Geetu KumariNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Performance of Pump As Turbine With Machined Impellers2018MATEC Web of ConferencesDokument6 SeitenThe Performance of Pump As Turbine With Machined Impellers2018MATEC Web of ConferencesDaniel Santacruz LNoch keine Bewertungen
- Webster Engine Works 4 Cycle Gas Engine: Displacement: .75 Ci Bore: .875" Stroke 1.25"Dokument21 SeitenWebster Engine Works 4 Cycle Gas Engine: Displacement: .75 Ci Bore: .875" Stroke 1.25"Julio Raizer100% (1)
- Project Report: On Analyze Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) With Respect To MIG Welding (GMAW)Dokument32 SeitenProject Report: On Analyze Submerged Arc Welding (SAW) With Respect To MIG Welding (GMAW)Rama Krishna Reddy DonthireddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Demo Weld Cost Calc XLDokument10 SeitenDemo Weld Cost Calc XLMarcelo Simão Do ValeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Code: R7210301 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R07) Supplementary Examinations, May 2013Dokument1 SeiteCode: R7210301 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R07) Supplementary Examinations, May 2013sivabharathamurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boring Bar ManualDokument41 SeitenBoring Bar ManualPranjal Chakraborty100% (1)
- ME 1203 Manufacturing TechnologyDokument5 SeitenME 1203 Manufacturing TechnologyajitsssNoch keine Bewertungen
- MP Previous Qp-Me3393Dokument21 SeitenMP Previous Qp-Me3393azhagan.mecNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shipbulding Technology 5th Semester SyllabusDokument33 SeitenShipbulding Technology 5th Semester SyllabusDiploma in Engineering Shipbuilding Technology100% (1)
- Design SummaryDokument20 SeitenDesign SummaryAgus HermantoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cat006 EngDokument2 SeitenCat006 EngSalsa AmorirNoch keine Bewertungen
- B-Tech. Mechanical UNIT-1: Bme 206 Manufacturing Technology - 1Dokument6 SeitenB-Tech. Mechanical UNIT-1: Bme 206 Manufacturing Technology - 1Michael ButlerNoch keine Bewertungen
- ME204Dokument2 SeitenME204raja93satNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokument2 SeitenQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)saranNoch keine Bewertungen
- 140k Motor Grader Jpa00001-Up (Machine) Powered by c7 Engine (Sebp5013 - 65) - Systems & ComponentsDokument16 Seiten140k Motor Grader Jpa00001-Up (Machine) Powered by c7 Engine (Sebp5013 - 65) - Systems & ComponentsJimmy Morales GonzalesNoch keine Bewertungen
- X60822 (Me2026 10122mee17 Me606 Ptme2026)Dokument2 SeitenX60822 (Me2026 10122mee17 Me606 Ptme2026)saranNoch keine Bewertungen
- Civil WorksDokument47 SeitenCivil WorksAbdulyekini AhmaduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Joining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsVon EverandJoining of Polymer-Metal Hybrid Structures: Principles and ApplicationsSergio T. Amancio FilhoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Friction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysVon EverandFriction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hines Roofing ChecklistDokument2 SeitenHines Roofing ChecklistCayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tutorial Chapter 4 - Heat ExchangerDokument3 SeitenTutorial Chapter 4 - Heat ExchangerCayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEC532 - Individual Activity Log Report Assessment FormDokument2 SeitenMEC532 - Individual Activity Log Report Assessment FormCayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ece590 April 2010Dokument13 SeitenEce590 April 2010Cayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.0 Objective:: TITLE: Flat Plate Boundary LayerDokument16 Seiten1.0 Objective:: TITLE: Flat Plate Boundary LayerCayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Update On Childhood Diabetes MellitusDokument51 SeitenUpdate On Childhood Diabetes MellitusJulie Carnetion DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab Report Format Structure of The ReportDokument4 SeitenLab Report Format Structure of The ReportCayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- SandcastingDokument7 SeitenSandcastingCayang_BucukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questionnaire On Foodpanda Vs ZomatoDokument4 SeitenQuestionnaire On Foodpanda Vs ZomatoPoddaturi Susheel74% (42)
- Project Report On Plastic Ban1Dokument15 SeitenProject Report On Plastic Ban1Silas Wilson67% (3)
- Amazon Company HRM PolicyDokument4 SeitenAmazon Company HRM Policyadeeba ghani100% (2)
- Stanley 25 Amp Automatic Battery Charger BC25BS ManualDokument12 SeitenStanley 25 Amp Automatic Battery Charger BC25BS ManualJoe ZhaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Distilled Spirit: Introduction (CAP 1)Dokument9 SeitenDistilled Spirit: Introduction (CAP 1)ned_nickNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 1 Customer ServiceDokument16 SeitenUnit 1 Customer ServiceGillian Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Staging Plan & MPC Report 180511 Compile PDFDokument19 SeitenDaily Staging Plan & MPC Report 180511 Compile PDFLutfii RisyandieNoch keine Bewertungen
- Masibus FIB MAS-AI-U-08-D - R0F - 0515 - Field Interface Board 8 CH Linearised RTD - TC InputDokument2 SeitenMasibus FIB MAS-AI-U-08-D - R0F - 0515 - Field Interface Board 8 CH Linearised RTD - TC InputKeval MistryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction Techniques in Hilly Area (Himachal Pradesh) : Adiba KhanDokument13 SeitenConstruction Techniques in Hilly Area (Himachal Pradesh) : Adiba Khanaayushi gadiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Legal Memorandum For ProsecutionDokument5 SeitenLegal Memorandum For ProsecutionAnge Buenaventura Salazar88% (8)
- Inventive IndianDokument168 SeitenInventive Indianvijay7775303Noch keine Bewertungen
- Bảng mã lỗi Wise15Dokument56 SeitenBảng mã lỗi Wise15Bach Nguyen XuanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Modul Lab AD I 2019 - 2020 - 1337415165 PDFDokument52 SeitenModul Lab AD I 2019 - 2020 - 1337415165 PDFClarissa Aurella ChecyalettaNoch keine Bewertungen
- AC Service Appointment and Maintenance FormDokument11 SeitenAC Service Appointment and Maintenance FormRiad RahmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Laparoscopic CatalogDokument44 SeitenLaparoscopic CatalogAhmad NuraliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bechtel International Inc. Case StudyDokument35 SeitenBechtel International Inc. Case Studytmd1977Noch keine Bewertungen
- Wake Up - ScreenplayDokument6 SeitenWake Up - ScreenplaySaravanakumar VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Santos Anesthesiology 2018Dokument15 SeitenSantos Anesthesiology 2018saeed namjooNoch keine Bewertungen
- ACA Massage Therapy Story: Analysis of Legal and Ethical Issues RaisedDokument3 SeitenACA Massage Therapy Story: Analysis of Legal and Ethical Issues Raisedglenn johnstonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Waukesha Mobileflex l5794 L7044gsi Epa Product Sheet PDFDokument4 SeitenWaukesha Mobileflex l5794 L7044gsi Epa Product Sheet PDFDODONoch keine Bewertungen
- GINA Severe Asthma Pocket Guide v2.0 Wms 1 PDFDokument22 SeitenGINA Severe Asthma Pocket Guide v2.0 Wms 1 PDFPhuong HuynhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bag Bath Return Demo For NursingDokument4 SeitenBag Bath Return Demo For Nursingjerica abesamisNoch keine Bewertungen
- B I F Mukhopadhyay2019Dokument84 SeitenB I F Mukhopadhyay2019deshmukhgeolNoch keine Bewertungen
- Andmeleht Alpha Continuity Plus 6kW 10kWDokument2 SeitenAndmeleht Alpha Continuity Plus 6kW 10kWAleksandar NikolicNoch keine Bewertungen
- TestDokument13 SeitenTestIan Cyrus RegodosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Flame RetardantsDokument4 SeitenFlame Retardants1985krNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 in Forensic BallisticsDokument9 SeitenModule 2 in Forensic Ballisticscriminologyalliance100% (2)
- AHA - Working On Slope RoofDokument2 SeitenAHA - Working On Slope RoofTopsun EnergyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Diffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Dokument41 SeitenDiffun Campus: "Molding Minds, Shaping Future"Mary Joy BernasolNoch keine Bewertungen
- 293005Dokument10 Seiten293005elsayedNoch keine Bewertungen