Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Role of Sidbsyn I
Hochgeladen von
Jaspreet SinghOriginaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Role of Sidbsyn I
Hochgeladen von
Jaspreet SinghCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
ROLE OF SIDBI
Executive Summary
S ME s a r e ma j o r c o n t r i b u t o r s t o GDP , a n d a n e v e n l a r g e r c o n t r i b u t
o r t o e x p o r t s a n d employment. Given this background, banks will find SME
financing an attractive business oppor t uni t y r at her t han a compul s i on,
of l endi ng t o t he pr i or i t y s ect or . SI DBI and banks jointly have to play a pivotal
and proactive role in financing the SMEs.The present slow down in lending to the SME
sector is principally due to the risk aversion ar i s i ng out of a hi gh pr opor t i on of
t he l endi ng becomi ng non per f or mi ng. Thi s cal l s f or reassessment of the
strategy of lending to this sector and this reassessment has led us to t hr ee
pr i nci pl e el ement s of our s t r at egy. ( 1) One i s di r ect ed at t hos e uni t s
whi ch have linkages with large corporate undertakings as vendors or suppliers. To these units,
provision and flow of credit could be tied up with the large undertakings which would facilitate
recovery but more important than finance our proposal is that the linkage will have to be strong
enough to ensure a win win approach for both. This could be achieved by technology transfer
of the large undertakings to the small units accompanied by a greater oversight and
the quality of t he pr oduct s del i ver ed; ( 2) t he s ec ond l eg of our s t r at egy i s
ai med at devel opi ng a s et of standard products for units belonging to the same cluster of
industries; (3) the third leg of our strategy is to develop local financial intermediaries specifically
aimed at financing units in the tiny and small sectors and more particularly to the
former. These would be in the nature of the NBFCs but without any permission to accept
deposits from the public. They would draw their resources from the banking system, by
originating the loans and selling the same to the banks as a portfolio with appropriate
arrangements for risk sharing. Thi s r epor t , t her ef or e, emphas i z es t he need f or
new vehi cl es and i ns t r ument s vi z .
bankpr omot ed ( nondepos i t t aki ng) NBFCs , mi cr o cr edi t i nt er medi ar i es ded
i cat ed t o SMEfinancing, etc. Such micro credit intermediaries (funded by
individual or a group of banks)would be able to credit -rate and risk assess and serve
as instruments for extending quick credit to SME clusters, accredited to them. This report
will also reinforces the importance of SIDBIs.
The SIDBI banks being an important nerve of modern organized society can play
an important role in the SSIs transformation. They provide the infrastructure on
which agriculture; industries and trade of nation depend. They can allocate
available resources by mobilizing deposits and advancing credit into the best
possible uses according to national priorities. By opening branches in unbanked
and under-banked areas, the banks can spread magnetization, thereby
introducing a larger market economy in place of natural economy. By providing
loans to agriculture and small-scale sector they can solve the acute problems of
unemployment and under employment. Hence banks can rightly be called the
nations agents of economic development. But in developing countries like India
the role of SIDBI is not confined to accepting deposits and advancing loans.
They also accept, the accelerating flow of credit in accordance with the needs of
SSI development. They have shifted from restricted old conservative policies to
modern banking with lots of new techniques, which brings dynamism and
innovation in their functioning. The Government of India and the State
government have been pursuing a policy of protecting and promoting small-
scale industries for a long time. Small scale industries have been accorded pride
of place in the planned industrialisation process of the Indian economy, which
is characterized by among other factors low productivity in the SSIs abundant
labour and scarcity of capital. The Government of India felt that in spite of
various incentives provided for backward areas by both the central and state
governments industrial growth in backward areas has not been satisfactory
mainly because of inadequacy of infrastructure. It therefore felt the need to
have an institutional framework for expeditious improvement of existing
infrastructural facilities and creation of new infrastructural facilities where there
are not any.
OBJECTIVES
The major objective behind doing this project is to get a clear view about how SIDBI, an
apex institution in Small Industries Financing Programmes came into existence, is
organized and managed, its objectives, lending terms and conditions, lending purposes,
challenges faced and tackled.
SCOPE
The scope of this study is to get the knowledge about how credit granted by SIDBI helps
in Small Industrial development.
METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY
The data for this project is obtained in two ways- primary source and secondary source.
PRIMARY SOURCE DATA
The primary source data for this project has been collected by visiting the office of SIDBI
located at Bandra Kurla Complex, Mumbai.
SECONDARY SOURCE DATA
Secondary data for this project has been gathered through various books, newspapers and
internet.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryVon EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Von EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItVon EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaVon EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingVon EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceVon EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyVon EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyBewertung: 3.5 von 5 Sternen3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeVon EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnVon EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeVon EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerVon EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (271)
- PH Miracle Complete Whole Body Alkalizing Program-1201724Dokument20 SeitenPH Miracle Complete Whole Body Alkalizing Program-1201724joao carlos100% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreVon EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesVon EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersVon EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceVon EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (890)
- Book 7 More R-Controlled-VowelsDokument180 SeitenBook 7 More R-Controlled-VowelsPolly Mark100% (1)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureVon EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaVon EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Von EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Bewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealVon EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (73)
- O-L English - Model Paper - Colombo ZoneDokument6 SeitenO-L English - Model Paper - Colombo ZoneJAYANI JAYAWARDHANA100% (4)
- Full Final Absentism HyundaiDokument89 SeitenFull Final Absentism HyundaiJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- A. What Is Balanced/objective Review or Criticism?Dokument11 SeitenA. What Is Balanced/objective Review or Criticism?Risha Ann CortesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Buyers FancyFoodDokument6 SeitenBuyers FancyFoodvanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs On RH IncompatibilityDokument17 SeitenCs On RH IncompatibilityRupali Arora100% (2)
- 4th Summative Test Science 6Dokument5 Seiten4th Summative Test Science 6ANNALIZA FIECASNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Project Report ON "HR Policies and Its Implementation" AT "Deepak Nitrite Limited"Dokument72 SeitenA Project Report ON "HR Policies and Its Implementation" AT "Deepak Nitrite Limited"abhishek150286% (29)
- Mba Final Year Project On Customer SatisfactionDokument64 SeitenMba Final Year Project On Customer SatisfactionArun75% (20)
- Benefits of Studying Descriptive Case StudyDokument1 SeiteBenefits of Studying Descriptive Case StudyJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Witness 2Dokument1 SeiteWitness 2Jaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- ScribdDokument1 SeiteScribdJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syn HRM Coke PepsicoDokument11 SeitenSyn HRM Coke PepsicoJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Effectiveness of Grievance Handling MechanismDokument52 SeitenA Study On Effectiveness of Grievance Handling MechanismDivya VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Employee Engagement at NavionicsDokument13 SeitenSynopsis Employee Engagement at NavionicsJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- TQM in ToyotaDokument7 SeitenTQM in ToyotaJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- H.R Jaswinder SinghDokument2 SeitenH.R Jaswinder SinghJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Benefits of Studying Descriptive Case StudyDokument1 SeiteBenefits of Studying Descriptive Case StudyJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Greviance Handlind Iwp ReportDokument94 SeitenGreviance Handlind Iwp ReportJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full FileDokument75 SeitenFull FileJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full File EastmanDokument90 SeitenFull File EastmanJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality of Life at Ling TechnologiesDokument90 SeitenQuality of Life at Ling TechnologiesbhatiaharryjassiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Proejct Report 124Dokument92 SeitenProejct Report 124Nupur ChoubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Full File Quality of Life Central ExiceDokument93 SeitenFull File Quality of Life Central ExiceJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- A Study On Effectiveness of Grievance Handling MechanismDokument52 SeitenA Study On Effectiveness of Grievance Handling MechanismDivya VenugopalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis HR Policies Aachi MasalaDokument14 SeitenSynopsis HR Policies Aachi MasalaJaspreet Singh33% (3)
- Syn of Quality of Life at EastmanDokument16 SeitenSyn of Quality of Life at EastmanJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- REPORT On Trichy Customs and Central Excise DepartmentDokument79 SeitenREPORT On Trichy Customs and Central Excise DepartmentJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Absenteeism at HyundaiDokument58 SeitenAbsenteeism at HyundaiJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Absentesim at NiitDokument16 SeitenSynopsis Absentesim at NiitJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Absentesim at NiitDokument16 SeitenSynopsis Absentesim at NiitJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- "Analytical Study of Foreign Direct Investment in India": Project ReportDokument1 Seite"Analytical Study of Foreign Direct Investment in India": Project ReportJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- District Transport OfficeDokument1 SeiteDistrict Transport OfficeJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Synopsis Absentesim at NiitDokument16 SeitenSynopsis Absentesim at NiitJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Syn of Quality of Life at EastmanDokument16 SeitenSyn of Quality of Life at EastmanJaspreet SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quality of Life at Ling TechnologiesDokument90 SeitenQuality of Life at Ling TechnologiesbhatiaharryjassiNoch keine Bewertungen
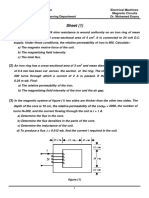
- Sheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMDokument2 SeitenSheet (1) : An Iron Ring Has A Cross-Sectional Area of 3 CMKhalifa MohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringDokument16 SeitenGujarat Technological University: Aeronautical EngineeringumodiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marketing of Agriculture InputsDokument18 SeitenMarketing of Agriculture InputsChanakyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- © 2020 Lippincott Advisor Nursing Care Plans For Medical Diagnoses - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19) PDFDokument7 Seiten© 2020 Lippincott Advisor Nursing Care Plans For Medical Diagnoses - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID 19) PDFVette Angelikka Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Roll Covering Letter LathiaDokument6 SeitenRoll Covering Letter LathiaPankaj PandeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Handbook MSC Marketing Sept2022Dokument58 SeitenCourse Handbook MSC Marketing Sept2022Tauseef JamalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Raptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12Dokument68 SeitenRaptor SQ2804 Users Manual English v2.12JaimeNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 20《经济学家》读译参考Dokument62 Seiten1 20《经济学家》读译参考xinying94Noch keine Bewertungen
- Optimum Work Methods in The Nursery Potting ProcessDokument107 SeitenOptimum Work Methods in The Nursery Potting ProcessFöldi Béla100% (1)
- An Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and Its ApplicatiDokument10 SeitenAn Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and Its ApplicatiI n T e R e Y eNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramDokument65 SeitenUnitary Small Air-Conditioners and Air-Source Heat Pumps (Includes Mixed-Match Coils) (RATED BELOW 65,000 BTU/H) Certification ProgramAmer GaladNoch keine Bewertungen
- Efficient Power Supply for Inductive LoadsDokument7 SeitenEfficient Power Supply for Inductive LoadsMary AndersonNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1 s2.0 S0959652619316804 MainDokument11 Seiten1 s2.0 S0959652619316804 MainEmma RouyreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Confined Space SafetyDokument33 SeitenConfined Space SafetyEneyo VictorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Heads of Departments - 13102021Dokument2 SeitenHeads of Departments - 13102021Indian LawyerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conservation of Kuttichira SettlementDokument145 SeitenConservation of Kuttichira SettlementSumayya Kareem100% (1)
- Mutaz Abdelrahim - Doa - MT-103Dokument17 SeitenMutaz Abdelrahim - Doa - MT-103Minh KentNoch keine Bewertungen
- COP2251 Syllabus - Ellis 0525Dokument9 SeitenCOP2251 Syllabus - Ellis 0525Satish PrajapatiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Study Quran Online - The Online Quran Teaching Academy UK - QutorDokument9 SeitenStudy Quran Online - The Online Quran Teaching Academy UK - QutorQutor co ukNoch keine Bewertungen
- Research of William Wells at HarvardDokument10 SeitenResearch of William Wells at HarvardARGHA MANNANoch keine Bewertungen
- Purp Com Lesson 1.2Dokument2 SeitenPurp Com Lesson 1.2bualjuldeeangelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speech TravellingDokument4 SeitenSpeech Travellingshafidah ZainiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Earth and Beyond PDFDokument5 SeitenEarth and Beyond PDFNithyananda Prabhu100% (1)