Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Ccna
Hochgeladen von
Naeem Shahzad0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
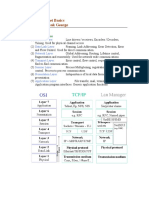
21 Ansichten3 SeitenData encapsulation is the process of adding headers and trailers to data at each layer of the networking model as it travels from its origin to its destination. Common Service Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is a network access method where nodes listen first to avoid collisions before transmitting data. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) provide broadcast control, security, and flexibility by logically grouping network ports on a switch.
Originalbeschreibung:
basic networking terms
Originaltitel
ccna
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
DOCX, PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenData encapsulation is the process of adding headers and trailers to data at each layer of the networking model as it travels from its origin to its destination. Common Service Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is a network access method where nodes listen first to avoid collisions before transmitting data. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) provide broadcast control, security, and flexibility by logically grouping network ports on a switch.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
21 Ansichten3 SeitenCcna
Hochgeladen von
Naeem ShahzadData encapsulation is the process of adding headers and trailers to data at each layer of the networking model as it travels from its origin to its destination. Common Service Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is a network access method where nodes listen first to avoid collisions before transmitting data. Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) provide broadcast control, security, and flexibility by logically grouping network ports on a switch.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als DOCX, PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 3
Corvit Systems
1: In networking terminology, what is data encapsulation?
Answer:
Data encapsulation is the process of putting headers and trailers around the data. Each layer
encapsulates the upper layers data into a new header and trailer. This process is repeated until
reaching layer 1 which is responsible for transmitting the data over the transmission medium.
2: What is CSMA/CD and how does it work?
Answer:
When the data i transmitted by two or three nodes on a network through the cable, there occurs
collision. So, CSMA/CA(Carrier Sense Multiple Access/ Collision Avoidance) is used,
Before transmitting the data on the cable, NIC(network Interface Card) checks the cable if any
transmission is going on. If no, sends the data or waits for the transmission to finish.
3: List the TCP/IP port for following:
a) FTP
b) TELNET
c) HTTP
d) SNMP
e) POP3
Answer:
FTP-21
TELNET-23
HTTP-80
SNMP-25
POP3-110
4: What are the advantages of UDP over TCP?
Answer:
a) Both are transport layer protocols.UDP is a connectionless protocol while TCP is a connection
oriented protocol
b) UDP provides low overhead data delivery than TCP
c) UDP find applications in the Domain Name System (DNS) , Video Streaming , Voice over IP
(VoIP) whereas TCP has applications in Web Browsers , E-mail , File Transfers
5: What is broadcast MAC address and what is its value?
Answer:
The broadcast MAC address is a type of layer 2 address that is used to deliver data to all devices
in the same broadcast domain of the sender. The source sends only one frame on the network and
the switch replicates it to all ports in the same broadcast domain of the source. The broadcast
MAC address has a value of FFFF.FFFF.FFFF.
6: What is a VLAN? And what does VLAN provide?
Answer:
VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network
It provides broadcast control; security and flexibility by logically grouping or segmenting a
network connected to administratively defined ports on a switch.
7: What is subnetting and why is it used?
Answer:
Subnetting is the breaking up of larger networks to become smaller, more easily managed
subnetworks. Subnetting is used to reduce network traffic and optimize network performance as
well as to simplify the management of the networks making it easier to identify issues with
networks.
8: Difference between ARP and RARP?
Answer:
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is used for mapping IP network address to the hardware
addresses that are working on the data link layer. Whereas, RARP (Reverse ARP) maps the IP
address from the ARP table that was requested by physical machine in a LAN.
9: Can you explain Protocol?
Answer:
Protocols is basically a set of rules that is required to be followed by a network for
communication. It provides the standards that a network should have to follow while
communicating to another network.
10: List out the 7 OSI layers?
Answer:
Seven OSI layers are:
Physical Layer
Data link Layer
Network Layer
Transport Layer
Session Layer
Presentation Layer
Application Layer
11: What is Routing?
Answer:
Routing is the process of finding a path on which data can pass from source to destination.
Routing is done by a device called routers, which are network layer devices.
12: What is a Frame Relay?
Answer:
Frame Relay is a WAN protocol that provides connection-oriented communication by creating
and maintaining virtual circuits. It has a high performance rating and operates at the Data Link
and Physical.
13: What are packets?
Answer:
Packets are the results of data encapsulation. These are data that has been wrapped under the
different protocols of the OSI layers. Packets are also referred to as datagrams.
14: What is MTU?
Answer:
MTU stands for Maximum Transmission Unit. It refers to the maximum packet size that can be
sent out onto the data line without the need to fragment it.
15: What is BootP?
Answer:
BootP is a protocol that is used to boot diskless workstations that are connected to the network. It
is short for Boot Program. Diskless workstations also use BootP in order to determine its own IP
address as well as the IP address of the server PC.
16: What is Route Poisoning?
Answer:
Route Poisoning is the process of inserting a table entry of 16 to a route, making it unreachable.
This technique is used in order to prevent problems caused by inconsistent updates on a route.
17: How does Hold-downs work?
Answer:
Hold-downs prevent regular update messages from reinstating a downed link by removing that
link from update messages. It uses triggered updates to reset the hold-down timer.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVon EverandCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyVon EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Steps To Clean A ComputerDokument9 SeitenSteps To Clean A Computerchawla_tarunNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find switch IP address and VLAN configuration stepsDokument9 SeitenFind switch IP address and VLAN configuration stepshatfied862Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Routing and SwitchingDokument26 SeitenCCNA Routing and SwitchingShaneVazNoch keine Bewertungen
- Login access methods and router configuration questionsDokument6 SeitenLogin access methods and router configuration questionschennai11Noch keine Bewertungen
- Short Notes-CS601 PDFDokument9 SeitenShort Notes-CS601 PDFHr QNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking QuestionsDokument9 SeitenNetworking QuestionsicysharmaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Networking Interview QuestionsDokument16 Seiten100 Networking Interview Questionsvijaysamuels1985Noch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedDokument20 SeitenCCNA Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedVibrant PublishersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Network Interview QuestionDokument23 SeitenComputer Network Interview QuestionHarpreet Singh BaggaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Link Layer Overview of TCP/IP ProtocolsDokument6 SeitenLink Layer Overview of TCP/IP Protocolsgani525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Interview Question: 1:: What Is Difference Between Switch & Hub?Dokument4 SeitenCcna Interview Question: 1:: What Is Difference Between Switch & Hub?Sayoni BasuNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA & Networking QADokument14 SeitenCCNA & Networking QAcovoltkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Osi and ProtocolsDokument7 SeitenOsi and ProtocolsGilgamesh berserkerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 50 CCNA Interview QuestionsDokument1 SeiteTop 50 CCNA Interview QuestionsmutyabaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Important Technical Questions 1Dokument16 SeitenImportant Technical Questions 1Navneet KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Questions and Answers:: 1:: What Is Difference Between Switch & Hub?Dokument6 SeitenCCNA Questions and Answers:: 1:: What Is Difference Between Switch & Hub?ccioanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking Basic & Ccna Interview Questions and Answers For FreshersDokument7 SeitenNetworking Basic & Ccna Interview Questions and Answers For FreshersSupriyo SahaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Guide to OSI Model Layers and Network ProtocolsDokument22 SeitenCCNA Guide to OSI Model Layers and Network ProtocolsshaikNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDokument5 SeitenDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NW Short Answers Unit III and IVDokument9 SeitenComputer NW Short Answers Unit III and IVgagan.kulal619Noch keine Bewertungen
- Cse ComputernetworkDokument22 SeitenCse ComputernetworkLakshmi BaskarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDokument4 SeitenDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Define Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationDokument4 SeitenDefine Communication, Write The Feature & Component of CommunicationAbu SayedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Imp QuestionsDokument10 SeitenImp QuestionsraveendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Line of Sight Is A) Straight Line B) Parabolic C) TX & RX Should Be Visible To Each Other D) None Ans: (C)Dokument4 SeitenLine of Sight Is A) Straight Line B) Parabolic C) TX & RX Should Be Visible To Each Other D) None Ans: (C)rssebagalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Interview QuestionDokument40 SeitenCCNP Interview QuestionanuvindkrNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ccna Interview Questions AnswersDokument30 SeitenCcna Interview Questions AnswersMistah RoflcopterNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top Networking Interview QuestionsDokument18 SeitenTop Networking Interview QuestionsMD SUMON HOSSAINNoch keine Bewertungen
- IT Notes Unit 5Dokument14 SeitenIT Notes Unit 5Deepankar Anil KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- OSI Reference Model and TCPDokument6 SeitenOSI Reference Model and TCPKommireddy Siva Kumar100% (1)
- Types of LAN Cables, DNS, OSI Model and Network Devices ExplainedDokument4 SeitenTypes of LAN Cables, DNS, OSI Model and Network Devices ExplainedArshad AliNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Networking Questions: Click Here For Part1Dokument6 Seiten100 Networking Questions: Click Here For Part1Jayendra N KadamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Networks 2 MarksDokument17 SeitenComputer Networks 2 MarksmohamedNoch keine Bewertungen
- LAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersDokument12 SeitenLAN and Ethernet Basics - Deepak George: OSI Network LayersUseful Videos DevotionalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer NetworksDokument36 SeitenComputer NetworksSameer NandanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Protocols Notes) Basic Networking Interview Questions & Answers 1. Define Network?Dokument99 SeitenProtocols Notes) Basic Networking Interview Questions & Answers 1. Define Network?Reyan RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNA Questions With Answers 1 - 15Dokument2 SeitenCCNA Questions With Answers 1 - 15siraj nooriNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP vs UDP: Advanced Networking Interview QuestionsDokument6 SeitenTCP vs UDP: Advanced Networking Interview QuestionsMohamed IbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Top 60 Networking QuestionsDokument30 SeitenTop 60 Networking QuestionsBESIGYE JONANNoch keine Bewertungen
- Networking & Mobile Comm IDokument16 SeitenNetworking & Mobile Comm Id4jkxzd5ybNoch keine Bewertungen
- DevNet Associate (Version 1.0) - Module 5 Exam Answers PDFDokument12 SeitenDevNet Associate (Version 1.0) - Module 5 Exam Answers PDFsamar zantourNoch keine Bewertungen
- CH 05Dokument10 SeitenCH 05Hari PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- 100 Networking Interview QuestionsDokument20 Seiten100 Networking Interview QuestionsJimmyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNANOTESDokument86 SeitenCCNANOTESSunkadahalli Govindaiah Bhanu PrakashNoch keine Bewertungen
- Network Engineer Interview QuestionsDokument34 SeitenNetwork Engineer Interview QuestionsMir Farhan Ali Abedi100% (5)
- Ccna Interview &answersDokument4 SeitenCcna Interview &answersHemanth968Noch keine Bewertungen
- 1.assignment On 15 Well-Known Protocols, Their Port Number and FunctionsDokument6 Seiten1.assignment On 15 Well-Known Protocols, Their Port Number and FunctionsLimitless StatusNoch keine Bewertungen
- CIS113 - FinalProject - Group 6Dokument3 SeitenCIS113 - FinalProject - Group 6Divin Alain IhorahoNoch keine Bewertungen
- TCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsVon EverandTCP/IP: Network+ Protocols And Campus LAN Switching FundamentalsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewVon EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (6)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Von EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Bewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (2)
- Software-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachVon EverandSoftware-Defined Networks: A Systems ApproachBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksVon EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNoch keine Bewertungen
- UnlDokument33 SeitenUnlNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Digital Literacy HandoutsDokument161 SeitenDigital Literacy HandoutsNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Primary Treatment Plan DiagramDokument1 SeitePrimary Treatment Plan DiagramNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture No. 3 Software Lifecycle Models: 1. Vision 2. Definition 3. Development 4. MaintenanceDokument13 SeitenLecture No. 3 Software Lifecycle Models: 1. Vision 2. Definition 3. Development 4. MaintenanceKhurram ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Breeder Management RevisedDokument28 SeitenBreeder Management RevisedNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 3 General KnowledgeDokument2 SeitenClass 3 General KnowledgeNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCNP Interview QuestionsDokument4 SeitenCCNP Interview QuestionsNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Treasury Sub Treasury Chalan FormDokument1 SeiteTreasury Sub Treasury Chalan FormNaeem ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Public Class Invoice Extends Javax - Swing.Jframe: Form:Invoice STR "Insert Into Invoice Values (" +Dokument5 SeitenPublic Class Invoice Extends Javax - Swing.Jframe: Form:Invoice STR "Insert Into Invoice Values (" +Smk TanvirNoch keine Bewertungen
- VC01-SD Video & Audio Encoder Technical SpecificationDokument7 SeitenVC01-SD Video & Audio Encoder Technical SpecificationLeopoldo Godinez HernandezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ofr02 166Dokument101 SeitenOfr02 166DCSAWNoch keine Bewertungen
- HashingDokument14 SeitenHashingm_sandhyarani1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Basic SQL QueriesDokument16 SeitenBasic SQL QueriesAshish ReddyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Administracion SAP HANA PDFDokument18 SeitenAdministracion SAP HANA PDFDiego Armando Achury IbañezNoch keine Bewertungen
- RH124Dokument2 SeitenRH124Mera KaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- GurmukhiDokument8 SeitenGurmukhijmaderaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Google Dorks For Credit Card DetailsDokument5 SeitenGoogle Dorks For Credit Card DetailsChanning Gonzales50% (2)
- TCL File I/O: Opening FilesDokument4 SeitenTCL File I/O: Opening FilesVeeranjaneyulu DhikondaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sap Business Object TRAININGDokument4 SeitenSap Business Object TRAININGSyedNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADBMS NotesDokument48 SeitenADBMS NotesŠhußhàm Rànjàn67% (3)
- CLL F189 TRM PTBDokument346 SeitenCLL F189 TRM PTBJean Carlos100% (6)
- All ExtensionlessDokument431 SeitenAll Extensionlesscyborg victimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Operating System Security StrategiesDokument39 SeitenOperating System Security StrategiesKimron EdwardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- IS303 Architectural Analysis: SMU SIS Personal NotesDokument86 SeitenIS303 Architectural Analysis: SMU SIS Personal NotesMelvrick GohNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Is A Bunch of KeysDokument5 SeitenThis Is A Bunch of KeysJeffrey BarnesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 101 Intro To The MP Post GuideDokument12 Seiten101 Intro To The MP Post Guiderpanther040% (1)
- Course: Web Programming Code: 15CS52T Study MaterialDokument5 SeitenCourse: Web Programming Code: 15CS52T Study MaterialKekw0% (1)
- Cheat Sheet: Symfony ConfigurationDokument2 SeitenCheat Sheet: Symfony ConfigurationKAMAL BOUBRIKNoch keine Bewertungen
- 20463C Curso SQL ServerDokument130 Seiten20463C Curso SQL ServerCarlos BenavidesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Post Office Management System A Java ProjectDokument41 SeitenPost Office Management System A Java Projectpankaj49sharma87% (15)
- AppSync 4.0 User and Administration GuideDokument342 SeitenAppSync 4.0 User and Administration GuidePavan NavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practicetorrent: Latest Study Torrent With Verified Answers Will Facilitate Your Actual TestDokument6 SeitenPracticetorrent: Latest Study Torrent With Verified Answers Will Facilitate Your Actual TestEDWARD KIWALABYENoch keine Bewertungen
- Python Course Content Core Concepts and Advanced FeaturesDokument10 SeitenPython Course Content Core Concepts and Advanced FeaturesNive SNoch keine Bewertungen
- Abbreviations List for IT and Computer ScienceDokument2 SeitenAbbreviations List for IT and Computer ScienceShakeelAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-5 Integration Server Administrators Guide PDFDokument1.198 Seiten10-5 Integration Server Administrators Guide PDFHarleen DhingraNoch keine Bewertungen
- EndnoteDokument4 SeitenEndnoteManisha SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Spring Ldap ReferenceDokument58 SeitenSpring Ldap Referenceskd_juNoch keine Bewertungen
- Addpac AP1005 DSDokument2 SeitenAddpac AP1005 DSEnrique RamosNoch keine Bewertungen