Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Bitszg553 Ec-3r Second Sem 2013-2014
Hochgeladen von
Shivam Shukla0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten1 SeiteBITS WILP
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenBITS WILP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
34 Ansichten1 SeiteBitszg553 Ec-3r Second Sem 2013-2014
Hochgeladen von
Shivam ShuklaBITS WILP
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 1
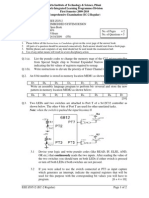
Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani
Work-Integrated Learning Programmes Division
Second Semester 2013-2014
Comprehensive Examination
(EC-3 Regular)
Course No. : BITS ZG553
Course Title : REAL TIME SYSTEMS
Nature of Exam : Open Book
Weightage : 50%
Duration : 3 Hours
Date of Exam : 06/04/2014 (AN)
Note:
1. Please follow all the Instructions to Candidates given on the cover page of the answer book.
2. All parts of a question should be answered consecutively. Each answer should start from a fresh page.
3. Assumptions made if any, should be stated clearly at the beginning of your answer.
Q.1. Answer following questions in short and to the point only.
(a) What are advantages of flash memory over EEPROM ? (Any two.)
(b) What are the advantages of microkernel approach in RTOS ?
(c) What is time and space exclusion policy in fault tolerant RTS ? What types
of redundancies are included in it?
(d) What are the faults that can occur while handling message queues which
may lead to timing anomaly?
(e) People say, there is nothing new in Real-Time Systems. All problems can
be solved in other branches of engineering. Do you agree after studying the
course? [5 X 2 = 10]
Q.2. A system of three tasks T
1
= (8,2), T
2
= (10,2), T
3
= (14,4,18) is scheduled with
executive cyclic clock driven scheduling algorithm.
A stream of sporadic jobs arrives as follows, S
i
= {(5, 2,15) ;(13,3,40); (14,2,35)}
Schedule these sporadic jobs applying acceptance test. [10]
Q.3. Now try to schedule these sporadic jobs (Q.2) using sporadic server and deadline
driven approach. T
2
now acts as sporadic server. [8]
Q.4. A set of hard real-time periodic tasks need to be scheduled using RMA. The
following information contains the details of these tasks and their use of shared
resources.
Can all the tasks meet their respective deadlines when priority ceiling protocol is
used for resource scheduling?
Tasks T
i
: T
1
(40,5,20); T
2
(30,5,25); T
3
(35,5,30);
T
4
(60,6,40); T
5
(55,5,50)
Resource Requirements : T
1
: [R
1
:3] ; T
2
: [R
2
:4] ;
T
3
: [R
2
:4 [R
1
:2]] ; T
4
: [R
1
:4 [R
2
:2]] ; T
5
: [R
2
:3]
[12]
Q.5. With the help of suitable Petri Net illustrations, show how Petri Nets can be
represented for
(i) Sequencing (ii) Branching (iii) Synchronization
(iv) Contention (v) Concurrency [10]
__________
No. of Pages = 1
No. of Questions = 5
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- 2019HT01605 - ES ZG553 - EC2MAssignmentDokument7 Seiten2019HT01605 - ES ZG553 - EC2MAssignmentvithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- BITS ZG553 Real Time Systems L-1 KGK 1564743779321 PDFDokument41 SeitenBITS ZG553 Real Time Systems L-1 KGK 1564743779321 PDFhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q.1. (2) Q.2. Q.3. (3) Q.4Dokument1 SeiteQ.1. (2) Q.2. Q.3. (3) Q.4vithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee Zg512 Ec-3r First Sem 2013-2014Dokument5 SeitenEee Zg512 Ec-3r First Sem 2013-2014Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTS Lecture 1 1642240037391Dokument24 SeitenRTS Lecture 1 1642240037391Gaurav BagdeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Course Handout AE ZG518 Electric & Hybrid VehiclesDokument5 SeitenCourse Handout AE ZG518 Electric & Hybrid VehiclesSindhuja ViswanathanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cs Zg524 Ec-3r First Sem 2020-2021Dokument2 SeitenCs Zg524 Ec-3r First Sem 2020-2021vithyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTS Assignment-2 Part AnsDokument11 SeitenRTS Assignment-2 Part AnsjitendraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bits Zg553 Rtos AllDokument797 SeitenBits Zg553 Rtos AllShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scheduling Algorithms in Real-Time Operating SystemsDokument41 SeitenScheduling Algorithms in Real-Time Operating SystemsVinadagu VishayaaluNoch keine Bewertungen
- Advance Digital Design Using VeilogDokument99 SeitenAdvance Digital Design Using Veilogpcjoshi02Noch keine Bewertungen
- EMBEDDED SYSTEMS (18CS2T40) - Mid Term Exam - 2021-2022Dokument1 SeiteEMBEDDED SYSTEMS (18CS2T40) - Mid Term Exam - 2021-2022MONTYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Overview of RTOSDokument22 SeitenOverview of RTOSveeramaniks408Noch keine Bewertungen
- Round Robin TechniqueDokument33 SeitenRound Robin TechniquevedaNoch keine Bewertungen
- QMZG528 Sep22 AnDokument4 SeitenQMZG528 Sep22 AnSooraj Dilip Kumar100% (1)
- Worklog 5761 SyncDokument14 SeitenWorklog 5761 Synctuanhai1989Noch keine Bewertungen
- Vlsi Model Question Paper 3 (June 2021)Dokument4 SeitenVlsi Model Question Paper 3 (June 2021)PushpalathaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Realtime Operating SystemsDokument1 SeiteRealtime Operating Systemssarala20021990100% (1)
- 5CS4-03 - Operating System - Kajal MathurDokument157 Seiten5CS4-03 - Operating System - Kajal MathurIshaan KhandelwalNoch keine Bewertungen
- DACDokument14 SeitenDACsharadaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit 2 - Week 1: Assignment 1Dokument294 SeitenUnit 2 - Week 1: Assignment 1shrimanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gaussian Random Number Generator Using Boxmuller MethodDokument27 SeitenGaussian Random Number Generator Using Boxmuller MethodAbhijeet Singh KatiyarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Task SchedulingDokument11 SeitenReal Time Task SchedulingPuspala Manojkumar100% (1)
- Unit 1 AssignmentDokument2 SeitenUnit 1 AssignmentYash PatilNoch keine Bewertungen
- GATE Questions - OS - CPU SchedulingDokument8 SeitenGATE Questions - OS - CPU SchedulingdsmariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Online End Semester Examinations (HCI)Dokument5 SeitenOnline End Semester Examinations (HCI)SyedHassanAhmedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real-Time System AssignmentDokument4 SeitenReal-Time System AssignmentTommy Kyen'de BilNoch keine Bewertungen
- BITS Pilani: Hardware Software Co-Design ES/SE/SS ZG626, MEL ZG651 Session 5Dokument28 SeitenBITS Pilani: Hardware Software Co-Design ES/SE/SS ZG626, MEL ZG651 Session 5vinay kumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Marking Scheme For Computer Networks ExamDokument18 SeitenMarking Scheme For Computer Networks Examtuyambaze jean claudeNoch keine Bewertungen
- CG Lab ManualDokument64 SeitenCG Lab ManualANUJ SINGHNoch keine Bewertungen
- RTS Ptu Sample Paper Lords MBDDokument48 SeitenRTS Ptu Sample Paper Lords MBDKaveesh NykNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lab RubricsDokument2 SeitenLab RubricsHasnain KhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 4 SchedulingDokument37 Seiten4 Schedulingreply2amit1986Noch keine Bewertungen
- Exploring Online Scheduling ApplicationsDokument28 SeitenExploring Online Scheduling ApplicationsNam C. TrầnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded System DesignDokument4 SeitenEmbedded System DesignMeenakshi SundaramNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5,6 Ldic New Course FileDokument49 Seiten5,6 Ldic New Course FileTarun PrasadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Real Time Systems 7th Sem ECE VTU Unit 1 Introduction To Real Time Systems RamisuniverseDokument10 SeitenReal Time Systems 7th Sem ECE VTU Unit 1 Introduction To Real Time Systems RamisuniverseMatthew BattleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pipes in RTOSDokument16 SeitenPipes in RTOSjayanthimurthyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Computer Graphics Practical FileDokument30 SeitenComputer Graphics Practical FileFotavo JugilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment Problems For OsDokument4 SeitenAssignment Problems For Osmanishbhavesh0% (1)
- 1 3Dokument59 Seiten1 3Anteneh AtumoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 08.705 RTOS Module 3 NotesDokument19 Seiten08.705 RTOS Module 3 NotesAssini HussainNoch keine Bewertungen
- 04 - 05-AI-Knowledge and ReasoningDokument61 Seiten04 - 05-AI-Knowledge and ReasoningderbewNoch keine Bewertungen
- ADPLL Design and Implementation On FPGADokument6 SeitenADPLL Design and Implementation On FPGANavathej BangariNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2 Module Exam SolutionDokument24 Seiten2 Module Exam SolutionPrateek SinghNoch keine Bewertungen
- Software Engineering - Functional Point (FP) Analysis - GeeksforGeeksDokument12 SeitenSoftware Engineering - Functional Point (FP) Analysis - GeeksforGeeksGanesh PanigrahiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Data Communication and Computer Networks DCCN - Eee314: Lab 2: IP Addressing Scheme and VLSMDokument5 SeitenData Communication and Computer Networks DCCN - Eee314: Lab 2: IP Addressing Scheme and VLSMUzzamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Task Scheduling IDokument21 SeitenTask Scheduling IbennettmatthewNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded Systems For Satellite Comm - Keynote SpeechDokument12 SeitenEmbedded Systems For Satellite Comm - Keynote SpeechMuhammad Faisal ArainNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture1 - Introduction To Embbeded System DesignDokument29 SeitenLecture1 - Introduction To Embbeded System DesignĐức Anh CNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Synchronization and Deadlocks 119961623287018 3Dokument29 SeitenProcess Synchronization and Deadlocks 119961623287018 3Dasaradh Dev100% (1)
- CJ MCQDokument98 SeitenCJ MCQMOHAMED SHAFEENoch keine Bewertungen
- NR-320502 Computer NetworksDokument6 SeitenNR-320502 Computer NetworksSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan-DspDokument6 SeitenDetailed Lesson Plan-DspemssietNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performance Measures and MetricsDokument21 SeitenPerformance Measures and MetricsVignesh Veera Prasad0% (1)
- 15A05606 Artifical Intelligence PDFDokument1 Seite15A05606 Artifical Intelligence PDFAnand Virat100% (1)
- Case Study: Library Book Circulation System: N. L. Sarda I.I.T. BombayDokument89 SeitenCase Study: Library Book Circulation System: N. L. Sarda I.I.T. BombayShraddha NaiduNoch keine Bewertungen
- Module 2 Cpu SchedulingDokument67 SeitenModule 2 Cpu SchedulingJoseph PrasanthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bitszg 553 Mid 2Dokument1 SeiteBitszg 553 Mid 2Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bits Zg553 Ec-3r First Sem 2013-2014Dokument1 SeiteBits Zg553 Ec-3r First Sem 2013-2014Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Goodreads - Books by B.v... of Notable Horoscopes)Dokument2 SeitenGoodreads - Books by B.v... of Notable Horoscopes)Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Homeopathy Beyond Flat Earth Medicine by Timothy RDokument119 SeitenHomeopathy Beyond Flat Earth Medicine by Timothy Rari_matrix100% (1)
- Handling TCM On ARMDokument3 SeitenHandling TCM On ARMShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vodafone Payment Receipt O809591667Dokument1 SeiteVodafone Payment Receipt O809591667titusbsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Akshay Net Fi April 2014Dokument1 SeiteAkshay Net Fi April 2014Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blaze 299Dokument1 SeiteBlaze 299Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Windows Update TroubleshootingDokument1 SeiteWindows Update TroubleshootingShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Study: Comparative Study of Arm Cores - Armv4 To Arm CortexDokument4 SeitenSelf Study: Comparative Study of Arm Cores - Armv4 To Arm CortexShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-System Programming Means That The Device Can Be Programmed in The Circuit by Using An Utility Such As The ULINK USB-JTAG AdapterDokument2 SeitenIn-System Programming Means That The Device Can Be Programmed in The Circuit by Using An Utility Such As The ULINK USB-JTAG AdapterShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The ID3 AlgorithmDokument7 SeitenThe ID3 AlgorithmShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Study: Atmel Atmega128 Architecture: Anupama KR & Meetha.V.Shenoy Embedded System Design 8051Dokument5 SeitenSelf Study: Atmel Atmega128 Architecture: Anupama KR & Meetha.V.Shenoy Embedded System Design 8051Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- User's Guide: TMS320C645x DSP Host Port Interface (HPI)Dokument44 SeitenUser's Guide: TMS320C645x DSP Host Port Interface (HPI)Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Objective: Classification Using ID3 and C4.5 Algorithms TasksDokument8 SeitenObjective: Classification Using ID3 and C4.5 Algorithms TasksShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Study 4Dokument4 SeitenSelf Study 4Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Self Study 1Dokument4 SeitenSelf Study 1Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction To Self StudyDokument3 SeitenIntroduction To Self StudyShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- In-Circuit and In-Application Programming of The 89C51Rx+/Rx2/66x MicrocontrollersDokument17 SeitenIn-Circuit and In-Application Programming of The 89C51Rx+/Rx2/66x Microcontrollersv1swaroopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Embedded SystemDokument3 SeitenEmbedded SystemShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Read MeDokument1 SeiteRead MeShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2009 OB OctDokument2 Seiten2009 OB OctShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee Zg512 Ec-3r Second Sem 2013-2014Dokument2 SeitenEee Zg512 Ec-3r Second Sem 2013-2014Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case StudyDokument6 SeitenCase StudyShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eee Zg512 Ec-3r Second Sem 2013-2014Dokument2 SeitenEee Zg512 Ec-3r Second Sem 2013-2014Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 8051 Learning BoardDokument6 Seiten8051 Learning BoardEmin KültürelNoch keine Bewertungen
- The 8051 Micro Controller and Embedded Systems CH4Dokument12 SeitenThe 8051 Micro Controller and Embedded Systems CH4Priyanka SadanandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assign I SolnDokument4 SeitenAssign I SolnShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2010 ObDokument3 Seiten2010 ObShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assign II SolnDokument4 SeitenAssign II SolnShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optional AssignmentDokument2 SeitenOptional AssignmentShivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Assignment 1Dokument2 SeitenAssignment 1Shivam ShuklaNoch keine Bewertungen
- North-South Railway Project - South LineDokument49 SeitenNorth-South Railway Project - South LinesuperNoch keine Bewertungen
- McMurdo FastFind 220 PLB DatasheetDokument4 SeitenMcMurdo FastFind 220 PLB DatasheetGiorgos PapadopoulosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Different Models of EIDokument13 SeitenDifferent Models of EIneena686236Noch keine Bewertungen
- Kumleben Commission ReportDokument232 SeitenKumleben Commission ReportJulian Rademeyer100% (2)
- Repeater Panel User GuideDokument24 SeitenRepeater Panel User Guideamartins1974Noch keine Bewertungen
- A320 Abnormal Notes: Last UpdatedDokument13 SeitenA320 Abnormal Notes: Last UpdatedDevdatt SondeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nail Malformation Grade 8Dokument30 SeitenNail Malformation Grade 8marbong coytopNoch keine Bewertungen
- Answer Set 5 - Fall 2009Dokument38 SeitenAnswer Set 5 - Fall 2009zachNoch keine Bewertungen
- 5 Waves AnswersDokument2 Seiten5 Waves AnswersNoor Ulain NabeelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Effect of Social Economic Factors On Profitability of Soya Bean in RwandaDokument7 SeitenEffect of Social Economic Factors On Profitability of Soya Bean in RwandaMarjery Fiona ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- 1.4 BG00381946 - ADokument1 Seite1.4 BG00381946 - AAnand KesarkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Negotiation SimulationDokument11 SeitenNegotiation SimulationJade Arbee BarbosaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sekonic L 758Dokument68 SeitenSekonic L 758mariosapereiraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Utah Vaccine AdministrationDokument1 SeiteUtah Vaccine AdministrationOffice of Utah Gov. Spencer J. CoxNoch keine Bewertungen
- IELTS Materials ReadingDokument9 SeitenIELTS Materials ReadingßläcklìsètèdTȜè0% (1)
- Kibera Mirror JULYDokument8 SeitenKibera Mirror JULYvincent achuka maisibaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Durham E-ThesesDokument203 SeitenDurham E-ThesesH Man SharifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Q4L6 Properties of KiteDokument8 SeitenQ4L6 Properties of KiteAltheus Miguel Dela CruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Frogs and ToadsDokument6 SeitenFrogs and ToadsFaris AlarshaniNoch keine Bewertungen
- Performace Task 2 Electric Field LinesDokument31 SeitenPerformace Task 2 Electric Field LinesStephanie Nichole Ian CasemNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Instructions: Installation Operation Maintenance NAF Duball DL Pocket ValveDokument12 SeitenUser Instructions: Installation Operation Maintenance NAF Duball DL Pocket ValveMauricio Contreras R.Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ringleman Chart FlareDokument12 SeitenRingleman Chart FlareguhadebasisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ga2 27:6:23Dokument1 SeiteGa2 27:6:23john HuntNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 7Dokument68 SeitenLecture 7Gay TonyNoch keine Bewertungen
- CongressWatch #197: RA 1337-Innovative Startup ActDokument1 SeiteCongressWatch #197: RA 1337-Innovative Startup ActMakati Business ClubNoch keine Bewertungen
- Model Questions and Answers Macro EconomicsDokument14 SeitenModel Questions and Answers Macro EconomicsVrkNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baptismal DelayDokument20 SeitenBaptismal DelayfiohdiohhodoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jahnteller Effect Unit 3 2017Dokument15 SeitenJahnteller Effect Unit 3 2017Jaleel BrownNoch keine Bewertungen
- User Manual For Scanbox Ergo & Banquet Line: Ambient (Neutral), Hot and Active Cooling. Scanbox Meal Delivery CartsDokument8 SeitenUser Manual For Scanbox Ergo & Banquet Line: Ambient (Neutral), Hot and Active Cooling. Scanbox Meal Delivery CartsManunoghiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shower Tapware: For More Information and Detailed Specifications Please Refer To Our Website: WWW - Plumbline.co - NZDokument11 SeitenShower Tapware: For More Information and Detailed Specifications Please Refer To Our Website: WWW - Plumbline.co - NZNoman KhanNoch keine Bewertungen