Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Hey Math Final
Hochgeladen von
Patrick YeboahOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Hey Math Final
Hochgeladen von
Patrick YeboahCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
5.
1 Quadratic Functions Standard Form- f(x)=ax^2 + bx + c
Ex: (2x+3) (x-4) f(x)= 3(x^2-2x) -3(x^2-2)
=2x^2-8x+3x-12 =3x^2-6x-3x^2+6
=2x^2-5x-12 =-6x+6
a^2-bx-c bx+c
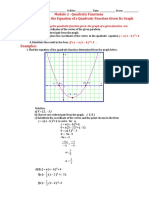
5.2 Graphing Parabolas
x= -b/2a and y= ax^2+bx+c (finding the vertex)
Draw a line across the vertex to find the axis of symmetry
Make a table with three points to draw a graph (the two y points have to be equal on either side of the y point for the vertex)
5.3 Graphing Parabolas in Vertex Form
If a>0, then upward facing parabola. If a<0, then downward facing parabola. [y=a(x-h)^2+k] (absolute value)
5.4 Factoring Quadratic Expressions
Guess and Check- (x+4) (x+1)= x^2+5x+4
a1- 3x^2+11x+6=(3x+2) (x+3). Why? (3x) (3)=9x and (2) (x)+2x. 2x+9x=11x
AC Method
Determine AC by multiplying the A term and C term. Find two numbers that add to the B term and multiply to AC. (Call the smaller number M and
the larger number N). Rewrite the original equation as Ax + Mx + Nx + C. Factor the new equation by grouping. Perform final factoring by applying
the distributive property.
5.6 Complex Numbers
i makes radicals negative
i=i i^2=-1 i^3=-i i^4=1 etc.
Completing the Square
Steps: Isolate the x terms and create a perfect square trinomial. Make sure to balance the equation. Factorwrite as a square of a binomial. Use the
square root method.
Ex. x^2+12x=-20
x^2+12x+36=16 (36 added to -20 to balance equation)
x+6= +/- 16
x=-6 +/- 4
x=-2 or x=-10
The Quadratic Formula
(If b^2-4ac>0 then 2 answers. If b^2-4ac=0 then 1 answer. If b^2-4ac<0 then no REAL answers.)
6.2 Zeroes of Polynomials
Zeroes are the opposites of x and y.
Ex. (x+1) (x-2)Zeroes are -1 and 2(2x-1) (2x-4)Zeroes are .5 and 2.
6.3 Dividing Polynomials- Is (x+4) a factor of: f(x)=x^3+3x^2-6x-8?
Direct Substitution: Plug in the zero for x- (-4^3-12^2+24-8)
Long Division: x+4/ x^3+3x^2-6x-8
Synthetic Division: -4
1 3 -6 -8
Factoring a Higher Degree Polynomial
Find a zero. Use bottom row> replace xs. Repeat until reduced to a quadratic. Factor the quadratic to get final two factors. (Use factoring methods)
Rational Roots Theorem
+/- Factors of the constant/ +/- Factors of the leading coefficient
Irrational Roots Theorem
If 3+2 is a zero, then 3-2 must be a zero.
6.8 Graphing Polynomial Equations
End Behavior: Pointing up to the right and down to the left is positive (vice versa is negative)
Odd Degrees: Point in opposite directions
Even Degrees: Point in the same direction
Opposite Directions: Odd
Same Direction: Even
(Remember degrees of polynomials and factors)
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Reviewing Key Concepts in Quadratic FunctionsDokument23 SeitenReviewing Key Concepts in Quadratic FunctionsLorica John LuisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter2 Quadraticequations PDFDokument18 SeitenChapter2 Quadraticequations PDFcm6699Noch keine Bewertungen
- Mathematics: Grade 9Dokument15 SeitenMathematics: Grade 9EDUARDO MALABAGNoch keine Bewertungen
- PolynomialsDokument42 SeitenPolynomialsapi-296824694Noch keine Bewertungen
- 2.2a Quadratic EquationsDokument45 Seiten2.2a Quadratic EquationsMario VNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find Zeros of Quadratic EquationsDokument9 SeitenFind Zeros of Quadratic EquationsShyam PatelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 1: QuadraticsDokument13 SeitenTopic 1: QuadraticsKaness Mathz100% (1)
- Add Maths Monthly Test March 2016Dokument10 SeitenAdd Maths Monthly Test March 2016Armadaramor ShiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Revision Summary of DSE Mathematics (Compulsory Part)Dokument27 SeitenRevision Summary of DSE Mathematics (Compulsory Part)Roy TsangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Revision DseDokument27 SeitenMath Revision Dseagentyikes100% (2)
- Solve Quadratic EquationsDokument29 SeitenSolve Quadratic EquationsElavarasi SubramaniamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture 4Dokument21 SeitenLecture 4Colin LongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic EquationsDokument18 SeitenQuadratic EquationsErwani KamaruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- C2 QuadraticDokument16 SeitenC2 Quadratickhai_83Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)Dokument47 SeitenSolving Quadratics by Factorising (1.02f)aaaaaaaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Equation That Become QuadraticDokument5 SeitenEquation That Become QuadraticJi YuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math-9 Q1 Sept.-6Dokument25 SeitenMath-9 Q1 Sept.-6James Kevin MarananNoch keine Bewertungen
- Math Primer ExcercisesDokument10 SeitenMath Primer Excercisessilly_rabbitzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 1 - PPT 1 - AMG 211 (Basic Algebraic Operations To Equations and Inequalities)Dokument36 SeitenWeek 1 - PPT 1 - AMG 211 (Basic Algebraic Operations To Equations and Inequalities)not funny didn't laughNoch keine Bewertungen
- Politecnico Di Torino: Bridging Course in Mathematics Sheet 1 PolynomialsDokument10 SeitenPolitecnico Di Torino: Bridging Course in Mathematics Sheet 1 PolynomialsJuan Luis GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Functions and InequalitiesRevisedDokument57 SeitenQuadratic Functions and InequalitiesRevisedShawnNoch keine Bewertungen
- Questions G9 10Dokument12 SeitenQuestions G9 10Roderick B. SumalloNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsDokument16 SeitenQuadratic Functions and Equations in One Variable: Form 4 MathsGGy Joe YeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- MSM 111 - Quadratic Functions - T3Dokument2 SeitenMSM 111 - Quadratic Functions - T3Chileshe SimonNoch keine Bewertungen
- MH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnDokument11 SeitenMH1811 Tutorial 1 - MC - 2020 - FN - Lmts - SolnYachen WuNoch keine Bewertungen
- QUADRATIC EQUATIONS SOLVEDDokument28 SeitenQUADRATIC EQUATIONS SOLVEDVinod Kr50% (6)
- Year I-Unit 2 Test: IB Mathematics HLDokument9 SeitenYear I-Unit 2 Test: IB Mathematics HLnadia sykesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic EquationsDokument28 SeitenQuadratic EquationsSri Devi NagarjunaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class 10 Revision Notes Quadratic EquationsDokument4 SeitenClass 10 Revision Notes Quadratic EquationsHanumantha Naik DNoch keine Bewertungen
- Find Equation from GraphDokument4 SeitenFind Equation from GraphMidoriya IzukuNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3.3 Linear FunctionsDokument28 Seiten3.3 Linear Functionsm_armoutiNoch keine Bewertungen
- AS Mathematics Revision Notes on Rotating Vectors, Quadratic Equations, Simultaneous Equations and MoreDokument12 SeitenAS Mathematics Revision Notes on Rotating Vectors, Quadratic Equations, Simultaneous Equations and MoreWillMeadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hand-Outs in MATH 9Dokument9 SeitenHand-Outs in MATH 9Lee EspeletaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2020 - 2021, Quadratic Function - 071819Dokument2 Seiten2020 - 2021, Quadratic Function - 071819Julius ChishikiNoch keine Bewertungen
- Add Math NotesDokument43 SeitenAdd Math NotesHalim OthmanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relations Between Roots and Coefficients:: B A C ADokument3 SeitenRelations Between Roots and Coefficients:: B A C Acici080525Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equations QuestionsDokument2 SeitenQuadratic Equations Questionsgiganigg100Noch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Quadratic Trinomial EquationsDokument13 SeitenSolving Quadratic Trinomial EquationsAmani Innerarity (Billy)Noch keine Bewertungen
- c1 RevisionDokument79 Seitenc1 Revisiontheone1998Noch keine Bewertungen
- Maths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Dokument34 SeitenMaths in Focus - Margaret Grove - ch9Sam Scheding0% (1)
- Background Exercises Answers/SolutionsDokument6 SeitenBackground Exercises Answers/SolutionsDung Hanh NguyenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equation: Identify Quadratic Equations With One UnknownDokument14 SeitenQuadratic Equation: Identify Quadratic Equations With One UnknownWan RafhanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Polynomial functions and factoring techniquesDokument43 SeitenPolynomial functions and factoring techniquesAnonymous na314kKjOANoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Add Maths NoteDokument9 SeitenForm 4 Add Maths NoteHayati Aini Ahmad100% (1)
- Math Reviewer Stem 2 2Dokument16 SeitenMath Reviewer Stem 2 2nejihyu21Noch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic Equations: Square Root MethodDokument8 SeitenQuadratic Equations: Square Root MethodMatthew TabucaoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving Quadratic Equations by Extracting Thesquare RootDokument9 SeitenSolving Quadratic Equations by Extracting Thesquare RootSour PlumNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsVon EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Cambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionVon EverandCambridge Mathematics AS and A Level Course: Second EditionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Von EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Noch keine Bewertungen
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsVon EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankVon EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankBewertung: 3 von 5 Sternen3/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageVon EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNoch keine Bewertungen
- Instructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYVon EverandInstructor's Manual to Accompany CALCULUS WITH ANALYTIC GEOMETRYNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesVon EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Boal ProposalDokument1 SeiteBoal ProposalPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmileDokument1 SeiteEmilePatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- EmileDokument1 SeiteEmilePatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dreamgirls (1981), Joseph and The Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat (1981), La Cage Aux FollesDokument2 SeitenDreamgirls (1981), Joseph and The Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat (1981), La Cage Aux FollesPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wte2 1.7Dokument4 SeitenWte2 1.7Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- GLBTDokument6 SeitenGLBTPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active RestDokument1 SeiteActive RestPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Question: How Does Annie Leibovitz Effectively Give Depth To The Superficial in Her Photography? Bio: WorksDokument1 SeiteQuestion: How Does Annie Leibovitz Effectively Give Depth To The Superficial in Her Photography? Bio: WorksPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deja VuDokument2 SeitenDeja VuPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Deja VuDokument2 SeitenDeja VuPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Active RestDokument1 SeiteActive RestPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cats History ResearchDokument7 SeitenCats History ResearchPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Precis 2Dokument2 SeitenPrecis 2Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTE Exercise 1Dokument1 SeiteWTE Exercise 1Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITS Primary SourcesDokument1 SeiteITS Primary SourcesPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 19 Hailing A CabDokument7 Seiten19 Hailing A CabPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTE Exercise 5Dokument2 SeitenWTE Exercise 5Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTE Draft 2.2Dokument6 SeitenWTE Draft 2.2Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Cats Defined the Mega-Musical Era of 1980s BroadwayDokument1 SeiteHow Cats Defined the Mega-Musical Era of 1980s BroadwayPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wte 3.2Dokument2 SeitenWte 3.2Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- P1 Draft 1Dokument3 SeitenP1 Draft 1Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- WTE Exercise 2Dokument2 SeitenWTE Exercise 2Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Cats Defined the Mega-Musical Era of 1980s BroadwayDokument1 SeiteHow Cats Defined the Mega-Musical Era of 1980s BroadwayPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Art Reveals Inner Values and Impacts RelationshipsDokument5 SeitenHow Art Reveals Inner Values and Impacts RelationshipsPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- NYU DormsDokument8 SeitenNYU DormsPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wte 2.5Dokument3 SeitenWte 2.5Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 2014 2015 Guest Blogger App2Dokument2 Seiten2014 2015 Guest Blogger App2Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plenary AssignmentDokument2 SeitenPlenary AssignmentPatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- ITS Reseach Paper Spring 2016Dokument1 SeiteITS Reseach Paper Spring 2016Patrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yebo Ah Patrick ResumeDokument2 SeitenYebo Ah Patrick ResumePatrick YeboahNoch keine Bewertungen
- 12 Calc 1 New AssignmentDokument7 Seiten12 Calc 1 New AssignmentTony WongNoch keine Bewertungen
- Week 06 - Cables and Suspension BridgesDokument40 SeitenWeek 06 - Cables and Suspension BridgesfefahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- School - Data - ADIS1 - Assignment - 20511 - Grade 10 Revision Worksheet 1 Term 1 - NewDokument4 SeitenSchool - Data - ADIS1 - Assignment - 20511 - Grade 10 Revision Worksheet 1 Term 1 - Newsharon VijuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Practice Exercises in ANALYTIC GEOMETRYDokument13 SeitenPractice Exercises in ANALYTIC GEOMETRYJan Leynard ParraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Test Bank For Intermediate Algebra Everyday Explorations 5Th Edition Kaseberg Cripe and Wildman 1111989338 9781111989330 Full Chapter PDFDokument23 SeitenTest Bank For Intermediate Algebra Everyday Explorations 5Th Edition Kaseberg Cripe and Wildman 1111989338 9781111989330 Full Chapter PDFryan.boyd506100% (14)
- Burton 1965Dokument16 SeitenBurton 1965Akash SoodNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quadratic TransformationsDokument7 SeitenQuadratic Transformationsapi-297405956Noch keine Bewertungen
- ECAT 7 Past Papers PakLearningSpotDokument10 SeitenECAT 7 Past Papers PakLearningSpotwww.mukkarram321Noch keine Bewertungen
- Families of Curves (Conic Section)Dokument1 SeiteFamilies of Curves (Conic Section)alainxanoricoNoch keine Bewertungen
- ch10 PDFDokument36 Seitench10 PDFcathyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Construction of Transmission Line Catenary From Survey DataDokument7 SeitenConstruction of Transmission Line Catenary From Survey DataAndrés MayorgaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Student Guide Precalculus Algebra MAC 1140 FALL 2009Dokument52 SeitenStudent Guide Precalculus Algebra MAC 1140 FALL 2009Jesse GoodrichNoch keine Bewertungen
- Conic Sections - Complete InfoDokument40 SeitenConic Sections - Complete InfoSesha Sai Kumar100% (1)
- Circles & Conic SectionDokument6 SeitenCircles & Conic SectionSonu KaleNoch keine Bewertungen
- Introduction to Conic SectionsDokument20 SeitenIntroduction to Conic Sectionsestherfe rafaelaNoch keine Bewertungen
- NC Math 2 Cumulative Review 2Dokument2 SeitenNC Math 2 Cumulative Review 2api-278028472Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Coffee Cup Caustic For Calculus StudentsDokument9 SeitenThe Coffee Cup Caustic For Calculus StudentsДимитрије НиколићNoch keine Bewertungen
- Exploration On The ParabolaDokument12 SeitenExploration On The ParabolaEllen Rodríguez pedersenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 15 - Graph of A Quadratic Function...Dokument10 SeitenLesson 15 - Graph of A Quadratic Function...jiemma parillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Section 2.5 PDFDokument11 SeitenSection 2.5 PDFEmcy Sicad AmbrocioNoch keine Bewertungen
- Problems On SFD BMDDokument41 SeitenProblems On SFD BMDatulkumargaur26100% (2)
- Questions With Answers PDFDokument5 SeitenQuestions With Answers PDFRyan Martinez100% (1)
- TSEAMCET-2022: Click Here To Download Other Syllabus PDFDokument11 SeitenTSEAMCET-2022: Click Here To Download Other Syllabus PDFsangu manikeshNoch keine Bewertungen
- Gdmphys 1Dokument8 SeitenGdmphys 1datarab284Noch keine Bewertungen
- Conic SectionsDokument21 SeitenConic SectionsFree lancerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solving and Graphing Quadratic Equations/TITLEDokument42 SeitenSolving and Graphing Quadratic Equations/TITLEtoinksNoch keine Bewertungen
- Quiz 2 Engineering DrawingDokument4 SeitenQuiz 2 Engineering DrawingVal Erick BambalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SMC 2017 Sol Extended PDFDokument24 SeitenSMC 2017 Sol Extended PDFTú MạcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Engineering Graphics (EG)Dokument8 SeitenEngineering Graphics (EG)Sudalai MadanNoch keine Bewertungen
- T2 Maths SP (11th)Dokument5 SeitenT2 Maths SP (11th)Vivek BNoch keine Bewertungen