Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Effect On Tensile Strength After Washing
Hochgeladen von
Harmendar S KothariOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Effect On Tensile Strength After Washing
Hochgeladen von
Harmendar S KothariCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
EFFECT OF WASHING ON TENSILE STRENGTH
OF DENIM FABRIC
CHING MAN YI
BA (Hons) Scheme in Fashion and Textiles
(Fashion Technology Specialism)
INSTITUTE OF TEXTILES & CLOTHING
THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
2011
EFFECT OF WASHING ON TENSILE STRENGTH
OF DENIM FABRIC
A Thesis Submitted
in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirement
for the Degree of
Bachelor of Arts (Honours)
Scheme in
Fashion & Textiles
(Fashion Technology Specialism)
under the Supervision of
Dr. C. W. Kan
by
Ching Man Yi
Institute of Textiles & Clothing
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
April 2011
I
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my academic supervisor,
Dr. C. W. Kan, for his supervision and constant encouragement
during my study, I would like to thank him for his many days
patient tutoring, Thank you, Dr Kan.
It is my honor to study the topic of about the properties for
different washing condition for tensile strength because it is
much related to our daily life and it should be more interest.
I would like the thanks all my friends. Especially, I am deeply
thankful for my friend, Becky Chan, Eve Chan, Eric Chan, Paul
Wong and Steve Tse, who have shared my hard and good time.
Finally, I would like to thanks my family for a many years caring
support.
II
CERTIFICATE OF ORIGINALITY
I hereby declare that this thesis is my own work and that, to the best of my knowledge
and belief, it reproduces no material previously published or written, nor material that
has been accepted for the award of any other degree or diploma, except where due
acknowledgement had been made in the text.
_____________________________________________________________(Signed)
Ching Man Yi (Name of student)
III
IV
ABSTRACT
As denim is one of the tradition item and the denim washing have
very stable performance.
However, there are some of the comments that when the fabric has
longer washing time, use of the chemical on the washing procedure
will affect the physical performance such as the tensile strength
will decrease.
In order to achieve an optimum the effect of washing process on
the denim woven fabric in different washing time, Enzyme Wash,
Enzyme wash with bleach, Enzyme wash with stone and Enzyme wash
with stone and bleach were carried out for cotton and cotton -
spandex denim fabric. The effect of the washing parameters, such
as the temperature, time and pH on the result of the cotton and
cotton spandex denim after treatment were studied by assessment
of the tensile physical properties and elongation to break.
The study concluded that cellulase treated in cotton and cotton
denim got a larger various change than the original denim. The
cellulase treatment decreases the strength of the properties of
the tensile strength and elongation to break.
V
CONTENT
Page
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I
HONOURS DECLARATION II
TURNITIN DECLARATION III
ABSTRACT IV
CONTENTS V
LIST OF TABLES IX
LIST OF FIGURES X
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1
1.1 Background of Study
1.2 Objective
1.3 Scope of Study
1.4 Chapter Summary
1
2
3
4
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 5
2.1 Introduction 5
2.2 Denim 5
2.2.1 Material 5
2.2.2 Yarn of the Denim Fabric 11
2.2.3 Indigo Dye 12
2.3 Washing method on Denim Fabric 13
2.3.1 Background 13
VI
2.3.2 Desizing of cotton 15
2.3.3 Stone Washing 15
2.3.4 Cellulase Enzyme Wash 16
2.3.5 Definition of Cellulase Enzyme 17
2.3.6 Cellulase Types 18
2.3.7 Principle and Effect of Enzyme 20
2.3.8 Controlling Parameters 22
2.4 Tensile Strength 23
CHAPTER 3 RESEARCH MECHODOLOGY 27
3.1 Introduction of Experimental Details 27
3.2 Experimental Arrangement 27
3.3 Fabric Specification 36
3.4 Cellulase Wash on Denim Wash 38
3.4.1 Apparatus 38
3.4.2 Preparation of the Specimen 42
3.4.3 Chemicals 42
3.4.4 Experimental Procedures 42
3.5 Tensile Strength 45
CHAPTER 4 RESULT & DISCUSSIONS 50
4.1 Effect of washing on tensile
strength of cotton fabric in warp
direction
50
VII
4.2 Effect of washing on tensile
strength of cotton fabric in weft
direction
56
4.3 Effect of washing on tensile
strength of cotton spandex fabric
in warp direction
60
4.4 Effect of washing on tensile
strength of cotton spandex fabric
in weft direction
65
4.5 Effect of washing on tensile
strength of cotton fabric in warp and
weft direction
70
4.6 Effect of washing on tensile
strength of cotton - spandex fabric
in warp and weft direction
75
4.7 Effect of washing on elongation to
break of cotton fabric in warp
direction
79
4.8 Effect of washing on elongation to
break of cotton fabric in weft
direction
84
4.9 Effect of washing on elongation to
break of cotton - spandex fabric in
warp direction
88
VIII
4.10 Effect of washing on elongation to
break of cotton - spandex fabric in
weft direction
93
4.11 Effect of washing on elongation to
break of cotton fabric in warp and
weft direction
97
4.12 Effect of washing on elongation to
break of cotton - spandex fabric in
warp and weft direction
101
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION 106
5.1 Conclusion 106
5.2 Recommendation 108
REFERENCE 110
IX
LIST OF TABLE
Page
Table 3-1 Experimental Arrangement 28
Table 3-2 Enzyme Wash Washing Recipe 31
Table 3-3 Enzyme Wash with Bleach Washing Recipe 32
Table 3-4 Enzyme Wash with Stone Washing Recipe 33
Table 3-5 Enzyme wash with Stone and Bleach Washing
Recipe
34
Table 3-6 Specification for Cotton Denim 37
Table 3-7 Specification for Cotton Spandex Denim 37
X
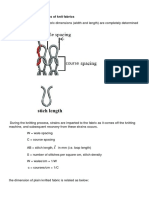
LIST OF FIGURE
Page
Figure 2-1 Longitudinal view for cotton fiber 500X 7
Figure 2-2 Cross-Sectional view for cotton fiber 500X 7
Figure 2-3 Constitution of Cellulose Polymer 8
Figure 2-4 Constitution of Spandex fiber 10
Figure 2-5 Cross-Sectional view for Spandex Filament 10
Figure 2-6 The influence of pH on the activity of
cellulase enzyme
19
Figure 2-7 The influence of temperature of the
activity of a cellulase enzyme
19
Figure 2-8 The actions of cellulase enzymes on a
cellulase molecule
21
Figure 3-1 Side Loading Washing Machine 38
Figure 3-2 Hydroextractor Machine 40
Figure 3-3 Tumble Drier Machine 41
Figure 3-4 Instron, 4411 Tensile Tester 46
Figure 3-5 Grab Breaking Strength Test Specimens 46
Figure 3-6 Load Extension Curves in KES tensile test 49
Figure 4-1 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of Cotton
Fabric (Tensile Strength)
51
Figure 4-2 Enzyme Wash with Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
52
Figure 4-3 Enzyme Wash with Stone In Warp Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
54
XI
Figure 4-4 Enzyme Wash with Stone and Bleach In Warp
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
55
Figure 4-5 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of Cotton
Fabric (Tensile Strength)
56
Figure 4-6 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
57
Figure 4-7 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
58
Figure 4-8 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
59
Figure 4-9 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of Cotton -
Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
60
Figure 4-10 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
62
Figure 4-11 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
63
Figure 4-12 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
64
Figure 4-13 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of Cotton -
Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
66
XII
Figure 4-14 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton Spandex Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
67
Figure 4-15 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
68
Figure 4-16 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
69
Figure 4-17 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
70
Figure 4-18 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
72
Figure 4-19 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
73
Figure 4-20 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
and Weft Direction of Cotton Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
74
Figure 4-21 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile
Strength)
75
XIII
Figure 4-22 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
76
Figure 4-23 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
77
Figure 4-24 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
and Weft Direction of Cotton - Spandex
Fabric (Tensile Strength)
78
Figure 4-25 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
80
Figure 4-26 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
81
Figure 4-27 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
82
Figure 4-28 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
83
Figure 4-29 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
84
Figure 4-30 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
85
Figure 4-31 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
86
XIV
Figure 4-32 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
88
Figure 4-33 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
89
Figure 4-34 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
90
Figure 4-35 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp Direction
of Cotton Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
91
Figure 4-36 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Elongation To Break)
92
Figure 4-37 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
93
Figure 4-38 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
94
Figure 4-39 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction
of Cotton Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
96
XV
Figure 4-40 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Elongation To Break)
97
Figure 4-41 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
98
Figure 4-42 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
99
Figure 4-43 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
100
Figure 4-44 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
and Weft Direction of Cotton Fabric
(Elongation To Break)
101
Figure 4-45 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To
Break)
102
Figure 4-46 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Elongation To Break)
103
Figure 4-47 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric
(Elongation To Break)
104
XVI
Figure 4-48 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp
and Weft Direction of Cotton - Spandex
Fabric (Elongation To Break)
105
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
I
Chapter 1 Introduction
1.1 Background of Study
Denim Fabric, appeared in America in the late of 18
th
century.
It is a cotton twill textile and the weft passes under two or
more warp fibers.
Denim was traditionally colored blue with the indigo dye. Indigo
dye is one of the dyestuffs with a distinctive blue color. For
the natural dye which come from some of the several species of
plant. But nowadays, the indigo procedure is synthetic and not
natural.
Denim is one of the most fashionable items in the fashion and
textile industry today. It can provide the durability and
different appearance effect for the garment when it is conduct
the different denim garment, and most people wearing the denim
garment.
Deterioration in the denim fabric of the textile product is often
important to the physical properties in deciding when the article
has reached the end of its using life [1].
Today, when the consumer buys the denim garment, they will
concern with the durability and physical use of the garment. They
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
2
have the concept that denim can provide the good function for
long time to use. However, after the different washing condition
on the denim fabric, the percentage of shrinkage or the strength
of the fabric will also change.
In this project, all of the denim woven came from the same raw
manufacturer. And the denim washing was carried out under
different combinations of washing parameter, such as Enzyme Wash,
Enzyme wash with bleach, Enzyme wash with stone and Enzyme wash
with stone and bleach. All of these include 10, 20, 30, 40, 50,
60, 70, 80 and 90 minutes washing duration.
The relationship between different washing conditions that is
relative to the tensile strength has not been studied before.
Hence, the project focuses on the comparison of the different
washing condition on denim woven to the tensile strength.
1.2 Objective
1. To assess the effect of denim washing parameter denim fabric
on tensile strength.
2. Using the tensile strength method to compare the tensile
properties on different types of the denim washed fabric.
3. Using the elongation to break method to compare the breaking
properties on different types of the denim washed fabric.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
3
1.3 Scope of Study
In the study, the denim fabric was treated with different set
of condition with different combination: Enzyme Wash, Enzyme
wash with bleach, Enzyme wash with stone and Enzyme wash with
stone and bleach in 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80 and 90 minutes
washing times. After the treatment, tensile strength test will
be conducted to compare the difference between different washing
condition and their properties.
The physical properties will be compared the tensile strength
result in different type of washing condition. Tensile test, is
available for most types of the fabric no matter it is light fabric
weight or heavy fabric weight. Also, it is one of the simple,
relatively inexpensive and also can provide the fully
standardized. Furthermore, the user can very quickly to evaluate
the result.
In order to have a deeper understanding about issue of the washing
characteristic of denim fabric, it will be essential to carry
out the laboratory testing.
By carrying out the above experiment and evaluation, the
objectives of this study can be achieved.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
4
1.4 Chapter Summary
The project comprises of five chapters.
Chapter 1 Introduces background, objectives, significant and
scope of the study are introduced.
Chapter 2 contains a brief introduction of literature review as
well as the knowledge of denim fabrics, washing condition and
the physical testing especially tensile strength.
Chapter 3 provides experimental details which includes
experimental arrangement and the specifications of the denims
fabric. Besides, experimental procedures for the denim fabric
wash and evaluations of various physical properties of the
treated denims fabric.
Chapter 4 elaborates the results and discussions of evaluations
on different types on denims fabric for the tensile strength.
Chapter 5 gives conclusion of overall study and recommendation
of future studies on the washing on denim.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
5
Chapter 2 Literature Review
2.1 Introduction
In order to carry the experiments of the denim washing, evaluated
of the different type of the denim fabric and analysis of the
data more effective, literature review was done. Fundamental
understanding the about the denim fabric include the material,
washing method, tensile strength properties and the enzyme
treatments also introduce.
2.2 Denim
2.2.1 Material
Denim is the heavy fabric with the wide fabric range there are
from 6 to 16 oz per sq. yard. Traditionally, it is usually weaving
from the 100% cotton, made from yarn dyed warp and undyed weft
yarn. The typical cotton construction is a warp - faced 3/1 right
hand side twill. As more dyed warp yarns are faced on one side
of the fabric, the face side of the denim is bluer. Meanwhile,
denim is a cotton twill fabric that dyed with the indigo. Indigo
is one of the natural dye come from the plant. As indigo only
can dye on the surface of the thread, when there have the stone
washes or the enzyme washes, the color will be faded. Hence the
irregular fading will appear on the fabric.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
6
The most commonly used material of the denim fabric is cotton
and spandex.
Cotton, which is a fiber that is unicellular, natural fibers
obtained from the boll from the cotton plant. The cotton fiber
is a single plant cell and the structure is complex.
Cotton fibers are staple length and the range is about 0.31 to
6.35 centimeters. And the length of the yarn is 2.22 to 3.18
centimeters long during manufacture.
The color of the cotton fiber varies from creamy white to dirty
grey, and never appear the true white.
Besides, it appears as a flat, twisted ribbon. Fiber tip, there
are less than one - quarter for the fiber length, tapers to a
cylindrical point. On the other, the end of seed is irregular,
having been torn from the epidermis for the cotton seed.
Moreover, it is the cellulose fiber there have the convolutions
along the and length and the kidney bean[2] cross-sectional
shape there are shown on the Figures 2-1 and 2-2
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
7
Figure 2-1 Longitudinal view for cotton fiber 500X [3]
Figure 2-2 Cross-Sectional view for cotton fiber 500X [3]
Cotton fiber comprise have 91% cellulose, and other component
is include the small amount of protoplasm, pectin, waxes, fatty
substance, salts, water and organic acid [4].
Cellulose is the structural component of primary cell wall for
the green plants. Cellulose is not having taste, it is odourless,
and it is insoluble in water or most organic solvent, but it can
be broken down into glucose when treating it with the
concentrated acid at the high temperature.
Cellulose is a straight change polymer which linked glucose units
of at least 1500 units length and forming a linear polymer of
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
8
-D-glucopyranose [5] and it is shown on the Figure 2 3.
The cellulose molecules group together to form microfibrils
which also like as the ribbon-like form, and a more or less
rectangular cross-section and in turn can form even larger
structural building blocks [6].
The hydroxyl group on the glucose for the chain from the hydrogen
bonds with oxygen molecules on the neighbor chain. Holding the
chains sideby-side and form the microfibrils and there have the
high tensile strength. This is very important in the cell wall
when the microfibrils meshed onto the carbohydrate matrix.
Figure 2-3 Constitution of Cellulose Polymer [5]
Cotton fiber is one of the fiber there are cheap, light weight,
soft and easy to find the material.
It is widely use on the textile industry because for their
structure. According to the longitudinal view shown on the Figure
2-1, the shape is like the flat twisted tube there have the lumen.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
9
This structure can provide the circulation of the air that can
less clingy even the fabric is very heavy.
Even thought the fine of cotton has 13-19 m, it also can provide
the stable in dimensional, good strength and the soft hand.
Cotton fiber is a hydrophilic fiber which has the high absorbency
of moisture, and the moisture content of cotton is about 8 9%,
Water can enter the inner space of the cotton. Cotton fiber can
absorbs the water from the water vapor emitted by the body, so
the skin does not become wet and let the people feel more
comfortable.
As cotton fiber is composed of cellulose, it can be attacked by
the mildew. Also, is also weakened by the resin chemical that
is used in finishing and the acid. But the more advantage is that
it cans highly resistance to alkalis.
Spandex fiber is the elastomeric fibers which can be stretched
repeatedly to at least twist their original length at the room
temperature.
Spandex manufactured which there are the fiber-forming substance
for the long chain synthetic polymer, and there at least 85% of
a segmented polyurethane [2], the generic group member shown as
Figure 2-4
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
10
Figure 2-4 Constitution of Spandex fiber [2]
Spandex as a filament in the variety of deniers, the range is
from 20 5400 deniers. Normally, 20 210 deniers are used for
lightweight stretchable fabric, 140 560 deniers mostly for
medium stretchable. And 70 2240 are support the more
stretchable material such as the swimwear or other functional
garment.
Under the microscope, the monofilament spandex fiber appears
either square or the round appearance in the cross section there
shown as Figure 2-5.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
11
Figure 2-5 Cross-Sectional view for Spandex Filament [2]
Spandex fiber is a soft, pliable and supple with a hand much like
of a rubber band. When the chemical property of spandex is taking
into consideration, it has resistance to most of the acid or the
dry cleaning solvents but will damage by the alkalies. However
spandex fiber can be degraded by the sodium hypochloride chlorine
bleach so that it is not allow using it.
Generally speaking, spandex is less susceptible to deterioration
by the light and the chemicals. It is easier to handle because
it can allow machine washable and dry cleanable.
2.2.2 Yarn of the Denim Fabric.
Denim is the durable heavy fabric. Normally, the yarn used in
the denim weaving have the consider yarn count, the range is from
6 to 10 Ne. Ne is the unit of the yarn in the direct system
of cotton. Ne is defined by the number that of the certain length
per the standard weight of the yarn. When there are the higher
count number, the thinner the yarn and vice. Normally, in denim
fabric, warp yarn are thicker that the weft because weaving
process, the warp yarn need held in a higher tension.
The yarn used in denim is a simple yarn, that is describes as
a spun yarn based for the fiber length. Spun yarn is composed
of staple fibers that are twisted together. Moreover, sinmoke
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
12
yarn can be described by the number of part it have. Based on
the description method, there have threes of yarn such as single
yarn, ply yarn and cord. And denim weaving is used for the single
yarn.
Single yarn, which is the product for the first twisting
operation, and is performed by the spinning machine which is
different to the ply yarn and cord yarn there have the second
and third twisting operation to combines two or more yarns
together. The strength of the yarn can be increase and so that
available for the denim fabric.
2.2.3 Indigo Dye
Indigo dye, which is the important of the natural dyes there have
been sustained to use. Indigo is a blue dye come from the certain,
such as from the Indigofera tinctoru in India. The group of
the colorants Indigo is one of the oldest known as the natural
dyes. The naturally is that occur material is indican, the
colorless glucoside of indoxyl[7]. When it is subjected to a
fermentation process, free indoxyl was generated by the enzyme
hydrolysis and the compound undergoes oxidation in air to indigo.
Due to indigo dye is not a soluble, so there is a challenging
dye. If it is necessary to dissolved, there should be undergo
the chemical change. Reduction transform the indigo into the
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
13
white indigo when the fabric removed from the dyebath, the
indigo will quickly mix the oxygen and join it to an insoluable,
intensely to colored indigo.
In fact, environment will affect the color of indigo, as in the
vapour phase, the situation is approaches a monomolecular state,
and the indigo it shown the red. When it is pronounced positive
solvatochromism, in non polar solvents it should be violet.
And if in the polar solvents, there should be blue. Also, when
applied the fabric in Vat dye, it should be blue.
Indigo dye is imparting in a blue color and has a good wet fastness
property. Indigo have the moderate lightfastness, and even there
have the fading of the color, there without change of the color.
As there are available for using in the jeans and the denim item.
2.3 Washing method on Denim Fabric.
2.3.1 Background
Originally, all of the indigo jeans were stiff and uncomfortable
when first purchased, due to the finishing system used for denim
fabric. Normally, the warp yarns are dyed either in rope form
or slash form. The difference is the type of investment involved
and the result of the warp dyeing. Usually, rope dyeing will gives
a more even result between side to centre due to the dividing
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
14
processes afterward. It is then followed by the sizing and
weaving.
Following weaving, the fabric is singed to burn off the surface
hair of the fabric, then padded through a finish bath containing
lubricants and the starch, and sent through a mechanical
shrinkage process.
After the desizing processing, the resulting of the fabric still
rigid. In previous time, the user would wear the jeans in normal
wearing or processed the jeans in a multiple home launderings
to improve the softness of jeans.
In order to exempt the extra processing by the customer, the denim
fabric manufacturers conduct the pre-washing jeans and abrade
the denim with stone or cellulose enzyme to achieve the softness
hand feel and the unique style.
Actually, if the manufacturers necessary to abrade the surface
of the denim fabric, they will select the stone washing or the
cellulose enzyme. For Stone washing, it is physically abrading
the fabric and cellulose enzyme is providing the chemical
abrasion.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
15
2.3.2 Desizing of cotton
Desizing is an important at the beginning stage in the processing
of cotton fabric. Waxes and synthetic water soluble sizes are
relatively simply removed from the fabric by scouring in the warm
water, and really would not respond to enzyme treatment alone.
Enzyme can remove the starch-based sizes, and the benefit is not
causing any physical chemical damage on the material. Even starch
and cellulose are both of long chains of glucose units linked
together, and they are different in the way that these units are
linked that amylases have no effect on cellulose and cellulases
have no result on the starch.
Starch is a combination of two similar carbohydrates of differing
molecular size and shape, amylopectin and amylase. Starch can
be mode to swell in water to form gel when it is meet the hot
water, thus there can remove starch successfully from the fabric.
As the progress of size removal can most conveniently be followed
by iodine coloration, the unhydrolysed starch can provide an
intense purple blue color, while glucose gives no color.
2.3.3 Stone Washing
Stone wash which the fabric washed along the pumice stones. The
denim fabric and the stone spinned together in the large
industrial washing machines. The degree of color fading is
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
16
depending on the time that denim fabric and stone spinned
together. The ratio and size of the stone, liquor ratio and the
time setting, is very important for the stone wash.
There have some limitations for stone wash which is the cause
of the tear for the fabric. The increase the pollution of the
environment also caused by the stone wash because there have high
amount of disposition for the stone. Moreover, due to it require
removing the stone from the pocket, the labor cost will increase.
It is necessary to completely get rid of the stone, several
machine laundering is require in the process.
Although there have limitation of stonewashing, some factories
continuous to use because it can provide the vintage and used
look on the garment, and these varying degree for the abrasion
will appear in pocket side, seam, waistband and the body.
2.3.4 Cellulase Enzyme Wash
To minimize the unfavorable of the stonewashing, cellulase
enzyme is recommended to use. Enzyme wash is more environmental
friendly than the stone wash as the enzyme is the biodegradable
when can minimize the risk of pollution. It can also eliminate
through competition use of the stone and result in improperly
the quality of wastewater. In additional, cellulase enzyme can
reduce the overall processing time and complexity, gives a wider
abrasion shades [8]. As because it can control the appearance
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
17
of the abrasion, it can prevent the wastage of the fabric and
increased up to 50% of the productivity [9].
On the other hand, cellulase enzyme washing provides more
softened the hand feel of the fabric and can remain the strength
of the fabric, when compared with the traditional stone wash.
In addition, cellulase enzyme washing can reduce abrasion
intensity on the fabric. Other benefit is that it can prevent
the formation of the fuzz and pills on the surface of the fabric,
increase the smoothness, luster, and uniformity of the color,
and improve the handle and durability.
2.3.5 Definition of Cellulase Enzyme
Enzyme is the protein structure comprising of polypeptide chains,
a varying complexity. Cellulase which is the class of hydrolytic
enzymes chiefly by Fungi. The major constituents of cellulase
are -1,4-gluconases and the chain is linked by peptide linkage.
There have some factory may distinguish from one enzyme to
another such as the odor what they linked, the presence or absence
from the metal and the particular amino acid present. Enzyme
is a water-soluble, enormously effective catalysts which permit
reaction and have low-energy path for the reaction to proceed.
In fact, enzymes are biological catalysts that can accelerate
the rate of simple chemical reaction without undergoing
permanent chemical change and thus can be re-used.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
18
Actually, cellulase is deactivated to stop the reaction when
after the enzyme treatment, and the enzyme only can acts on the
specific location of the specific substrate under specific
environment without having any effect on other components of the
system.
2.3.6 Cellulase Types
Cellulase Enzyme only has limited exhibit optimum performance
within the tight range for about temperature and pH. Thus,
enzymes involved in the enzymatic degradation of cellulase can
be classified by the optimum condition for their action,
such and temperature and pH. There are two types of cellulase,
that is neutral cellulase and acid cellulase, used for the
textile manufacturing. Neutral cellulase operates around pH
6.0 8.0 and Acid cellulase operates around pH 4.5 5.5. The
influence of pH on the activity of cellulase enzyme should on
Figure 2-6. Meantime, the neutral cellulase use 50 to 60 while
the acid cellulase only needs to use the lower temperature that
is about 45 to 55. The influence of temperature on the activity
of a cellulase enzyme shown on Figure 2-7.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
19
Figure 2-6 The influence of pH on the activity of
cellulase enzyme [6]
Figure 2-7 The influence of temperature of the activity of a
cellulase enzyme [6]
It is very important to control carefully the processes
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
20
parameters in enzymatic treatment for the denim fabric.
Actually, neutral enzymes require longer cycle times, less
aggressive but give no backstaining when it is achieve at the
same effect [6]. Acid enzymes have are faster reactions and more
aggressive when the result in more chemical abrasion and loss
for the strength.
On the other hand, neutral cellulase can provide the less extent
of back staining than the acid cellualse due to its lower
penetrating in the action. As acidic cellulase act in acidic
conditions, it favors re-deposition of removed indigo dye from
the warp yarn to the white yarn on denim fabric during the
enzymatic treatment. Because of this, there will occur the back
staining of the reverse side of the fabric. All of these side
effects lower the contrast of the unique of denim fabric.
2.3.7 Principle and Effect of Enzyme
The major constituent of cellulase are the -1,4-gluconases. It
actually consists of a complex mixture of acting enzymes. The
(1-4) linkages between adjacent repeat units in cellulase
polymer chain are the sites for catalytic hydrolysis by cellulase.
They catalyze the primary reaction of hydrolytically splitting
the -1,4-glycosidic linkages in cellulase chain molecule [10].
The main working principle of the acting enzymes is to cleave
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
21
the long cellulase chains randomly to produce shorter chains and
finally glucose molecules are left. The actions of cellulase
enzymes on a cellulase molecule are shown in Figure 2-8.
Figure 2 -8 The actions of cellulase enzymes on a cellulase
molecule [6]
There have two major effect of cellulase on denim finishing is
that, first, give indigo-dyed cotton fabric and aged appearance
which as biostoning [11] and second is giving cotton fabric a
revived appearance by color brightening and softening. These
effects are caused by the synergetic action of cellulase and
mechanical agitation. The indigo dye particles remove along with
the cotton fiber. And the surface fibers for the denim fabric
are hydrolyzed by cellulase and the weaken fibers were removed
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
22
during abrasion of the fabrics.
The stonewashing effects achieved by pumice stones can be
replaces by cellulase washing which chemically degrade cotton
in less abrasive way compare with the traditional stonewashing
to give out the washed - outlook.
2.3.8 Controlling Parameters
There have some major parameters for the cellulase washing of
the denim. They are temperature, pH, agitation, time, enzyme
dosage and liquor ratio. Other also includes the hardness of
water, properties of the buffer solution used and ionic
surfactants will also affect the enzymatic treatment. During
this study, pH, agitation, temperature and time are discuss in
the denim fabric [12].
pH
Different type of enzyme has its own pH tolerance. The
performance of its maximal activity depends on the range of pH
value used. Upon the optimum pH range, the internal structure
of enzyme will be changed permanently.
Agitation
Mechanical agitation creates more accessible sites for cellulase
attack either because of the increased diffusion into the fabric
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
23
or the increased surface area after defibrillation.
Temperature
Enzymatic reactions increase with temperature within the optimum
temperature range where enzyme is stable and retains full
activity. Enzyme activity will decrease when deviation from the
optimum range.
Time
It depends on the liquid ratio, type of machine being used, the
materials of fabric and the desired effect on fabrics [12].
Longer the cellulase washing time will prolong the enzymatic
degradation of cellulase and also the time for further abrasion.
2.4 Tensile Strength
Tensile strength, it is one of the important properties in
relation to the measure the strength, and the modified for about
the grab test can be used the tensile fabric. The demonstration
about the strength for the fiber or the fabric structures is
regarded as the measure for the quality. Strength is very
important for the textile industry and most of the product will
conduct this test to ensure the quality. During measure the
quality, it is also include the flexibility, dye affinity
resilience or other more. Beside, the product quality will
depend on much of the end use. Such as the acid will reduce the
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
24
cotton fiber strength.
The following will go to introduce the terminology and the
definition about tensile. [13]
Load
According to tensile, the application of a load is normally
expressed in grams weight or pounds weight, and the application
load to the specimen in an axial direction causes a tension was
developed in the specimen.
Breaking load
Breaking load means the load that the specimen breaks.
Stress
Stress is that when the qualities of fine and uncouth structure
have to be compared, suitable units must be chosen.
Mass Stress
The crosssection of many type of fibers and the structure are
unequal, it is very difficult to measure about it. It is because
to abridge matters a dimension related to cross-section is used,
the linear density about the specimen. The linear density may
be articulated in denier or tex count and mass stress then will
becomes the ration of the force applied to the linear density.
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
25
Specific Strength or Tenacity
Tenacity that of a material is the mass stress at fracture and
alternative term of tenacity is specific strength.
Breaking Length
Breaking length is the length of the specimen which will just
break under its own weight when hung vertically.
Strain
When the load is applied to a specimen a assured amount of
stretching take place. This amount will differ with the initial
length about the specimen. The strain is that a term for used
to relate the stretch or elongation with the initial length.
Extension
There is the expressing the strain as the percentage get the
extension and the extension also refer to as the stain
percent.
Breaking extension
It is the extension about the specimen at the breaking point.
The load elongation curve
There are the really important curve is produced during the load
for the specimen is platted against the elongation. The curve
describe the behavior of the specimen from zero load and
CHAPTER 2 LITERATURE REVIEW
26
elongation up to the breaking point.
The stress strain curve
Some of the aims are more suitable to change the load-elongation
curve to a stress-strain curve, thereby enable more direct
comparisons to be made between different types of materials and
structure.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
27
Chapter 3 Research Methodology
3.1 Introduction of Experimental Details
In this chapter, the fabric specification, experimental
arrangements are describe. In additional, experimental details
including chemicals, recipes, apparatus and specimens
preparation and experimental principle are described.
3.2 Experimental Arrangement
Cotton and cotton - spandex denim fabric were treated with
different washing method such as Enzyme Wash, Enzyme Wash with
Bleach, Enzyme Wash with Stone and Enzyme wash with Stone and
Bleach. All of these washing methods were used with fixed
concentration and liquor ratio and applied with to different
washing duration for cotton and cotton spandex denim. The
experimental arrangement was shown on Table 3-1. Beside, the
details recipe and procedures of different denim washing method
was shown on Table 3-2, 3-3, 3-4 and 3-5 for enzyme wash, enzyme
wash with bleach, enzyme wash with stone and enzyme wash with
stone and bleach respectively.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
28
Table 3-1 Experimental Arrangement
Process Enzyme Wash
Chemical Neutral Enzyme
Time Range (mins) 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90
pH Value 6.5
Liquor Ratio 50 : 1
Temperature () 50
Amount 1% (OMG)
Process Enzyme Wash with Bleach
Chemical Neutral Enzyme
Chlorine
Time Range (mins) 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90
pH Value 6.5
Liquor Ratio 50 : 1
Temperature () 50
Amount 1% (OMG)
10% (OMG)
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
29
Table 3-1 Experimental Arrangement (cont)
Process Enzyme Wash with Stone
Chemical Neutral Enzyme
Pumice Stone
Time Range (mins) 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90
pH Value 6.5
Liquor Ratio 50 : 1
Stone Ratio 10:1
Temperature () 50
Amount 1% (OMG)
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
30
Table 3-1 Experimental Arrangement (cont)
Process Enzyme Wash with Stone and Bleach
Chemical Neutral Enzyme
Chlorine
Pumice Stone
Time Range (mins) 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90
pH Value 6.5
Liquor Ratio 50 : 1
Stone Ratio 10:1
Temperature () 50
Amount 1% (OMG)
10% (OMG)
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
31
Table 3-2 Enzyme Wash Washing Recipe
Step Process Chemical Time
(Min.)
pH Liquor
Ratio
Temp.
(C)
Amount
(on weight
of garment)
1 Desizing Detergent 30 6.5 50:1 70C 1%
2 Rinse 5 Room
Temp.
3 Drain
4 Enzyme
Wash
Neutral
Enzyme
10 to
90
6.5 50:1 50C 1%
5 Rinse 5 Room
Temp.
6 Drain
7 Softening Cationic
Softener
15 6.5 50:1 40C 20%
8 Tumble
Drying
30 70C
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
32
Table 3-3 Enzyme Wash with Bleach Washing Recipe
Step Process Chemical Time
(Min.)
pH Liquor
Ratio
Temp.
(C)
Amount
(on weight
of garment)
1 Desizing Detergent 30 6.5 50:1 70C 1%
2 Rinse 5 Room
Temp.
3 Drain
4 Enzyme Wash Neutral
Enzyme
10 to 90 6.5 50:1 50C 1%
5 Rinse 5 Room
Temp.
6 Drain
7 Bleaching Sodium
Hypochlorite
5 6.5 50:1 70C 10%
8 Neutralize Sodium
Thiosulfate
10 6.5 50:1 Room
Temp
10%
9 Rinse 5 Room
Temp
10 Drain
11 Softening Cationic
Softener
15 5.5 50:1 40C 20%
12 Tumble
Drying
30 70C
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
33
Table 3-4 Enzyme Wash with Stone Washing Recipe
Step Process Chemical Time
(Min.)
pH Liquor
Ratio
Stone
Ratio
Temp.
(C)
Amount
(on weight
of garment)
1 Desizing Detergent 30 6.5 50:1 70C 1%
2 Rinse 5 Room
Temp.
3 Drain
4 Enzyme Wash
Pumice
Stone
Neutral
Enzyme
Indonesia
Pumice
Stone
(3- 5 cm)
30 6.5 50:1 10:1 50C 1%
5 Rinse 5 Room
Temp.
6 Drain
7 Softening Cationic
Softener
15 6.5 50:1 40C 20%
8 Tumble
Drying
30 70C
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
34
Table 3-5 Enzyme wash with Stone and Bleach Washing Recipe
Step Process Chemical Time
(Min.)
pH Liquor
Ratio
Stone
Ratio
Temp.
(C)
Amount
(on weight
of
garment)
1 Desizing Detergent 30 6.5 50:1 70C 1%
2 Rinse 5 Room
Temp
3 Drain
4 Enzyme
Wash
Pumice
Stone
Neutral
Enzyme
Indonesia
Pumice Stone
(3- 5 cm)
30 6.5 50:1 10:1 50C 1%
5 Rinse 5 Room
Temp
.
6 Drain
7 Bleachin
g
Sodium
Hypochlorite
5 6.5 50:1 30C 10%
8 Neutrali
ze
Sodium
Thiosulfate
10 6.5 50:1 Room
Temp
10%
9 Rinse 5 Room
Temp
10 Drain
11 Softenin
g
Cationic
Softener
15 5.5 50:1 40C 20%
12 Tumble
Drying
30 70C
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
35
The following is going to describe the each process.
Desizing
It is a procedure for removal the sized applied when denim fabric
making in weft yarn. The fabric is dipped into a bath with the
detergent solution, following pH 6.5, liquor 50:1 and treated
70C for 30 minutes.
Rinse
When completed each of the each of the washing processes, there
is still have liquid on the surface to be cleaned up, the rinse
procedure first requires a cleaning step.
Bleaching
For this process, it is not necessary add the pumice stone and
by using the oxidative bleaching agent such as the Sodium
hypochlorite. Sodium hypochlorite is a normally as it have the
convenient and quick. Some of other agent used is sodium
percarbonate and sodium perborate.
Neutralize
Suitable neutralizations for after bleaching process are very
important in order to get rid of fabric strength, bad smell, or
skin irritation and yellowing of the garment.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
36
Softening
Denim fabric is very critical for the softening. Subject to denim
is a heavy material in compare with other type of the fabric,
and so is necessary to softening. But it is to care the
discoloration of denim such the shade change of the color or loss
of whiteness.
Tumble drying
When completed all of the wet process, it is necessary to have
the tumble drying to ensure the garment is whole dry, the time
normally is about 45 minutes to 60 minutes.
3.3 Fabric Specification
Cotton and cotton spandex denim fabric were pre-conditioned in
standard environment according to ASTM d1776 before measuring
the fabric specification. Beside, the specifications were
collected by using the standard method.
The specification of cotton and cotton spandex denim fabric were
shown on Table 3-6 and Table 3-7
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
37
Table 3-6 Specification for Cotton Denim
Composition 100% Cotton
Fabric Construction 3/1 Right Hand Twill
Weight 10 oz/yd
2
Warp Weft
Fabric Density 66 ends/inch 51 ends/inch
Yarn Count 7.5s 10s
Table 3-7 Specification for Cotton Spandex Denim
Composition 99% Cotton 1% Spandex
Fabric Construction 3/1 Right Hand Twill
Weight 10 oz/yd
2
Warp Weft
Fabric Density 70 ends/inch 57 ends/inch
Yarn Count 7.5s 12s + 20D
According to the specification table, cotton and cotton spandex
denim fabric are very similar. The major different is the cotton
spandex denim fabric have 1% spandex twist in weft yarn and
according to this reason, there will affect the performance of
washing method and the tensile strength result.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
38
3.4 Cellulase Wash on Denim Wash
3.4.1 Apparatus
Side Loading Washing Machine
Cellulase wash by using the Side Loading Washing Machine as shown
in Figure 3-1
Figure 3-1 Side Loading Washing Machine
For all of the cellulase denim washing, this was carried out by
150 lb side washing machine. They were washed basically on
controlled parameters and conditioned environment.
The Side Loading Washing Machine which was used had horizontal
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
39
and drum-type structure and the inner drum made for about the
stainless, and so that it could easily to be operated with
selected, temperature and the rotation speed. Besides, there had
not the central agitator which uses gravity and the side mounted
paddles to stir up the cloth. When the door was closed, it would
remain lock mechanically until the washing cycles are finished.
For the industrial washing machine, there have the
semi-automatic machine, the worker can choose the manual method
or the automatic method for handle machine. The moving for the
machine roller has divided into two different directions. After
the machine is toward left to roll, they will stop a few minutes.
Afterward, it will change to opposite direction to move and also
stop a few minutes. These steps will continuous to conduct until
the washing cycle complete.
It is suitable for various washing, for example, stone wash,
enzyme wash, bleaching and dyeing.
Hydroextractor
Hydroextractor is a machine which mostly used in the textile
processing industry. It has a heavy basket spinning at great
speeded and it uses high speed spinning to squeeze water from
the laundry. The speed of the machine can attain over 1500 RPM.
Besides, if the heavy material such as the jeans, sweater or
jacket is place on the hydroextractor for squeezed before drying,
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
40
the time of drying can reduce by one-half, so that it can save
the drying time, energy and also can reduce the damage of the
material.
The working procedure is the wet material is located in the
extractor, which has a wall of perforated metal, normally
stainless steel. The internal drum rotates at the high speed thus
throwing out the water containing in it. The Hydroextractor
Machine is shown on Figure 3-2
Figure 3-2 Hydroextractor Machine
Tumble Drier
The tumble drier, with is used to remove moisture from a load
for the textile material, normally shortly after they are cleaned
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
41
in a washing machine.
It is a front loading open pocket with inner stainless steel
basket machine, the inner stainless steel basket is fitted with
stainless steel paddles to ensure the tumbling effect smooth.
For the tumble drier there have two types of drying method that
is steam and electricity, and both types are suitable for the
industrial use.
The Tumble drier also can control the rotation direction,
temperature and timing. The Tumble Drier machine shown on Figure
3-3
Figure 3-3 Tumble Drier Machine
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
42
3.4.2 Preparation of the specimen
As prevent the edge of the material slippage during washing
process, lock stitch in necessary before washing.
All of the specimens were conditioned under standard atmospheric
pressure at 65% 2% relative humidity and 21 1 for at least
24 hours prior to denim washing.
3.4.3 Chemicals
A neutral enzyme is a powder form was used in enzymatic treatment
on denims. Moreover, detergent, sodium hypochlorite, sodium
thiosulfate and cationic softener would add on the following
steps.
Beside, the entire chemical added was depends on the weight of
the garment.
3.4.4 Experimental Procedures
In denim, garment washing is done to produce effects such as the
color fading with or without patchiness, crinkles, depilling or
stabilizes dimension etc. Normally, the process of garment
washing involves stage like product evaluation and preparation
desizing, braiding, bleaching, anti-chloring / post scouring,
over dyeing (optional), softening, hydro-extracting and tumble
drying. Various process effects for the special products can be
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
43
obtained by using combination of these procedures. Different
processing parameters can be set for each stage to enhance and
improve the effects.
All of the specimens were weight and the value used to calculate
the required of the chemical amount on weight of goods and also
the required volume of water for the denim washing.
Desizing
Sizing is the need for the weaving but is an obstacle for the
dyeing. The first processes by which we remove sizes on the
garment wash as known as desizing. Desizing can removal of size
applied when the denim fabric making in weft yarn. For this
project, it is used the detergent solution. And some factory will
containing polyacrylic acid and is more effectively removed by
using soda ash. The principle steps in the desizing procedure
are firstly, wetting out with the suitable wetting agent, and
steeping for affecting the swelling and softening, and following
is rising thoroughly in overflowing water.
The method of desizing of starch-sized textiles is described.
In this relationship, the denim fabric is dipped into a bath
containing with the enzyme mixtures as well as the detergent
solution, having a pH about 6.5 and the liquor ratio is 50:1,
following then treated at 70C for 30 minutes.
The next processed would following when desizing completed.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
44
Rinse
And the coming step is rinse, which is removing the detergent
on the fabric. After, it Drain away the solution.
Enzyme Wash
Enzyme Wash, which is one of the important step of the garment
wash. It is a bio-catalytic method wherein an ultra-soft handle
effect can be produced on denim. This effect of enzyme causes
the loss of surface fibre, which improves surface smoothness and
softness of the fabric. The method of enzyme wash of textiles
is described. The denim fabric is dipped into a bath containing
with the with the mixtures as well as the neutral enzyme, having
a pH for 6.5, the liquor ration is 50, following then treated
at 70C and run for 10 minutes to 90 minutes.
During the enzymes process, the temperature and pH control is
very important. For temperature, if there are above the optimum
temperature, the coil structure of enzyme will destroy and the
activity will decrease. Moreover, the pH value is that the enzyme
with board pH range for better consistency of the result. This
is a time for add the pumice stone, and add in this time is that
can speed up the rate of the abrasion. For this project neutral
enzyme is used for. And anionic surfactant may be harmful to the
enzyme, non-ionic detergent should be used. The degree of
decrease in activities of the enzyme may vary from on to each
other.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
45
Bleach Washing
Sodium Hypochlorite is used in this project, because it is a
slightly yellowish solution and also a clear on the odor.
In this relationship, the denim fabric is dipped into a bath
containing with the Sodium Hypochlorite, having a pH about 6.5
and the liquor ratio is 50:1, following then treated at 70C for
5 minutes.
When completed the denim washing, such as Enzyme Wash, Enzyme
wash with bleach, Enzyme wash with stone and Enzyme wash with
stone and bleach, the tensile strength analysis will conduct.
3.5 Tensile Strength
Tensile properties of specimens were measured by INSTRON, 4411
TENSILE TESTER and shown in Figure 3-4. And the test was followed
the ASTM 5034 09, standard test method for breaking strength
and Elongation of Textile Fabric (Grab Test) for evaluation the
tensile strength properties of denim fabric.
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
46
Figure 3-4 Instron, 4411 Tensile Tester
Specimen was cut 4 x 6 inches, so that the direction of test is
in the longer direction, shown on Figure 3-5
Figure 3-5 Grab Breaking Strength Test Specimens
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
47
The Flat Kaw one inch on a side and three inch apart at the start
of the test are used to clamp the fabric. When the jaws were
separated, the through-going yarns clamped in both jaws were
subjected to tension. Moreover, because of the interaction of
warp and weft yarn with attendant frictional forces a fabric
assistance effect develops and yarns adjacent to those actually
clamped in the jaws will help to support the load. Then, the grab
strength test mostly produces higher strength values of the
fabric [14].
The procedure was that the upper jaw for about the tester was
attached to a steel bar of proper capacity and design, so at full
load its deflection is completely elastic, and negligible. When
the force was used, the result comparative voltage change
produced by the gage was amplified and recorded as a direct
measure of the specimen load. The upper jaw moves an almost
imperceptible amount even at maximum load, the pulling jaw
actually elongates the test specimen at a constant rate, and the
instruments, and it was constant rate of extension tester.
The Instron tester that was various capacity load recording
cell can be installed so the specimens with a wide range of
breaking strength.
The Rate of loading or extension can influence the ultimate
breaking strength, so ASTM specifies the rate, and more property,
the time to break. The Specified pulling jaw speed is 12 1/2
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
48
inches per minutes and the yarn breakage will break within 20
3 seconds from the start of test.
For about the servo-mechanism, the lower or pulling jaw can be
moved at rates ranging from 1.0 to 20 inches per minutes. Gear
backlash was reduced to a minimum so that repeated stress
diagrams can be obtained. The jaw was driven downwards until a
selected load or strain develops, and then the jaw travel
direction was automatically reversed so that the load was removed.
The strain gage force recording cell is completely free of
inertia, so the tensile forces which develop in the test specimen
were immediately recorded.
For about the tensile testing machines, the elongation axis
for the automatic load elongation recorder runs at a constant
speed, and so the direct measure of jaw separation results.
The recorded jaw separation of flat jaw can be taken as a direct
measure of the specimens elongation. Such in a tensile test,
the gauge length at the start of the test was three inches. At
the instant of rupture, if the jaw moved 0.6 inches, the breaking
percent elongation could be calculated as (0.6 3) x 100 = 20%.
There might be slight elongation of the ends of the specimen held
in each jaw, it was called the jaw penetration, which might make
the gage length slightly greater than three inches. And for the
true elongation correspondingly slightly less, but this error
was usually negligible and was ignored in the calculation [14].
CHAPTER 3 ___RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
49
The tensile properties was measured by plotting the force
extension curve between zero and a maximum force of 500gf/cm,
the recovery curve as the specimen was allowed to return to its
original length which is also plotted to give the pair of curves
shown in Figure 3-6.
Figure 3-6 Load Extension Curves in KES tensile test
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
50
Chapter 4 Results & Discussion
The result of denim fabric under different washing methods and
analyze the warp and waft yarn its strength and impacts after
washing will be discussed in details.
4.1 Effect of washing on tensile strength of cotton fabric in
warp direction
Effect of enzyme washing on the tensile strength of cotton fabric
in warp direction
The data of enzyme wash for warp cotton fabric is shown in Figure
4-1.
In terms of warp yarn strength after washing, its strength tends
to be weaker after washing compare with the original.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
51
Figure 4-1 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of Cotton Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
According to the Figure 4-1, the yarn strength tends to be weaker
after longer time of washing. However, the yarn strength becomes
stronger in the raising time in 50 minutes washing. The possible
explanation could be the yarn after washing become higher level
of shrinkage. Therefore the higher density between the yarns as
the results of yarns could share the loading and withstand
tensile force, as we can see that the washing time from 40 minutes
to 50 minutes could withstand tensile force from 767.87(N) to
841.78 (N) approximately increased 10% tensile force.
However, after longer time of rinsing time. The enzyme chemical
further to damage of the yarn. The yarn strength tends to be weaker
after 60 minutes of washing. When the washing time of 50 minutes
to 60 minutes significantly decrease the tensile strength from
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
52
841.78(N) to 780.75(N) and so it is decease about 7% of tensile
force.
Beside, the yarn strength tend to be stable from 60 minutes to
90 minutes, as the tensile strength in 60, 70, 80 and 90 minutes
washing is 780.75 (N), 779.50 (N), 785.5 (N)and 785.77
(N)respectively.
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing on the tensile strength of
cotton fabric in warp direction
Figure 4-2 shows the effect of the enzyme wash with bleach in
the warp direction cotton fabric.
.
Figure 4-2 Enzyme Wash with Bleach In Warp Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
Based on Figure 4-2, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
53
washing in 10 minutes have significantly change in terms of
tensile strength from 879.96(N) to 794.18 (N) approximately
change in 10% in tensile strength.
It is surprise to find that the tensile strength from to 10 to
90 minutes has an up and down tends. However, the tends is that
the tensile strength is become stronger after longer times of
washing.
The fabric before washing and the fabric after washing in 90
minutes the tensile strength decrease from 879.96(N) to 871.05
(N) approximately 1 percent. The possible explanation could be
the yarn after washing become higher level of shrinkage.
Therefore the higher density between the yarns as the results
of yarns could share the loading and withstand tensile force
Effect of enzyme with stone washing on the tensile strength of
cotton fabric in warp direction
The information about enzyme wash with stone in the warp
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-3.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
54
Figure 4-3 Enzyme Wash with Stone In Warp Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For Figure 4-3, it is surprise to find that the tensile strength
that before wash and the fabric after washing in 10 minutes from
879.96 (N) to 946.75 (N) approximately increase in 7.6%. This
result is abnormal, this is because in normal situation, the
fabric before wash should be stronger than that of fabric after
washing in term of tensile strength.
In addition, it was find that that the tensile strength from to
10 to 90 minutes has an up and down tends. However, the washing
time of 50 minutes to 60 minutes significantly decrease the
tensile strength from 928.68 (N)to 857.18(N)and so it is decease
about 7% of tensile force.
After 50 minutes of rinsing time. The enzyme chemical and stone
further to damage of the yarn. The yarn strength tends to be weaker
after 60 minutes of washing.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
55
From 60 minutes to 90 minutes, the yarn strength tend to be stable,
as the tensile strength in 60, 70, 80 and 90 minutes washing is
857.18 (N), 863.89 (N), 868.27(N)and 850.20 (N)respectively.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing on the tensile
strength of cotton fabric in warp direction
The data for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in the warp
direction of the cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-4.
Figure 4-4 Enzyme Wash with Stone and Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
According to above Figure 4-4, the fabric before wash and fabric
after 10 minutes wash is slightly change in terms of tensile
strength from 879.96(N) to 855.48 (N) approximately change in
about 2% in tensile strength.
In addition, the yarn strength after washing in longer time has
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
56
significant decrease in terms of tensile strength.
In additional, it was observe that that the tensile strength from
to 10 to 40 minutes has an up and down tends and from 40 to 90
minutes, it has major decline for tensile strength.
4.2 Effect of washing on tensile strength of cotton fabric in
weft direction
Effect of enzyme washing on the tensile strength of cotton fabric
in weft direction
For the information of effect of Enzyme Wash in the weft direction,
the results are shown in Figure 4-5.
Figure 4-5 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of Cotton Fabric
(Tensile Strength)
Based on Figure 4-5, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
57
washing in 10 minutes have significantly change in terms of
tensile strength from 442.73(N) to 371.09(N) approximately
change in 15% in tensile strength.
Fabric after enzyme wash in different washing time, tend to be
stable in terms of tensile strength. However, from 50 minutes
to 90 minutes, it was found that the tensile strength become
weaker.
Effect of enzyme with Bleach washing on the tensile strength of
cotton fabric in weft direction
The effect of enzyme wash with bleach in the weft direction of
cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-6.
Figure 4-6 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
From Figure 4-6, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
58
washing in 10 minutes have significantly change in terms of
tensile strength from 442.73(N) to 376.51(N) approximately
change in 15% in tensile strength.
Moreover, it was find that that the tensile strength from to 10
to 90 minutes has an up and down tends and from 70 to 80 minutes,
it has major decline for tensile strength. From 80 to 90 minutes,
it has slightly increased in terms of tensile strength.
Effect of enzyme with stone washing on the tensile strength of
cotton fabric in weft direction
Figure 4-7 shows the data about the effect of enzyme Wash with
stone in the tensile strength in the weft direction of cotton
fabric.
Figure 4-7 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
59
According to Figure 4-7, the fabric before wash and the fabric
after washing slightly change in tensile strength.
From 10 to 60 minutes have down tends. From 60 to 70 minutes,
tensile strength becomes stronger. But after 80 minutes, the
tensile strength becomes weaker than 70 minutes.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing on the tensile
strength of cotton fabric in weft direction
Effect of enzyme wash with stone and bleach in the weft direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-8.
Figure 4-8 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
From Figure 4-8, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
washing in 10 minutes have significantly change in terms of
tensile strength from 442.73(N) to 372.35(N) approximately
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
60
change in 15% in tensile strength.
From 10 to 70 minutes, tend to be stable in terms of tensile
strength. However, from 70 minutes to 80 minutes, it was found
that the tensile strength drop down suddenly.
4.3 Effect of washing on tensile strength of cotton spandex
fabric in warp direction
Effect of enzyme washing on the tensile strength of cotton -
spandex fabric in warp direction
Figure 4-9 shows the data about the effect of Enzyme Wash in warp
direction of cotton spandex fabric.
Figure 4-9 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of Cotton - Spandex
Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For the data in Figure 4-9, it shown the fabric before wash and
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
61
the fabric after washing in 10 minutes have significantly change
in terms of tensile strength from 837.18(N) to 784.16 (N)
approximately change in 6% in tensile strength.
Further to 10 minutes washing declining the tensile strength when
compared with the fabric before washing, In 20 minutes washing
time. It is further declining the tensile strength in compare
with 10 minutes of washing time. It also occurred an up and down
tends between 10 minutes to 90 minutes washing. In addition,
longer time of washing have more harmful impacts in terms of
tensile strength. People may judge that warp yarn without spandex
will not be affecting the tensile strength. However, as we all
know fabric is weaving together, while weft yarn weak will result
in interdependency issues which make warp yarn tends to be easy
to break.
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing on the tensile strength of
cotton - spandex fabric in warp direction
Enzyme wash with bleach in warp direction of cotton - spandex
is shown on Figure 4-10.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
62
Figure 4-10 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For Figure 4-10, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
washing in 10 minutes have slightly change in terms of tensile
strength from 837.18(N) to 811.89 (N) approximately change in
5% in tensile strength.
It was occurred an up and down tends between 10 minutes to 90
minutes washing. From 70 to 90 minutes, the tensile strength
becomes stable.
Sodium hypochloride chlorine bleach can damage the spandex fiber,
as known as the fabric is weaving together, when the weft yarn
weak will result in interdependency issues which allow the
strength of warp yarn weaker.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
63
Effect of enzyme with Stone washing on the tensile strength of
cotton spandex fabric in warp direction
Enzyme wash with stone in warp direction of cotton - spandex data
is shown on Figure 4-11.
Figure 4-11 Enzyme Wash with Stone In Warp Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
According to Figure 4-11, it was astonish to find that the tensile
strength that before wash and the fabric after washing in 10
minutes from 873.18 (N) to 870.42 (N) approximately increase in
4%. This outcome is irregular as because in neutral circumstances,
the fabric after washing should be weaker than the fabric before
wash in term of tensile strength.
Moreover, from 10 to 90 minutes, it was occurred the up and down
tends. However, we observe that the washing time of 40 to 50
minutes have significantly decrease the tensile strength from
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
64
820.49 (N) to 762.95 (N) and it is decrease about 7% of tensile
force. In additional, for 60 to 70 minutes, it also have
significantly decrease in strength from 838.38 (N) to 756.69 (N)
and it is decrease about 10% of tensile force.
Effect of enzyme With Stone and Bleach washing on the tensile
strength of cotton spandex fabric in warp direction
Enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp direction of cotton
- spandex data is shown in Figure 4-12.
Figure 4-12 Enzyme Wash with Stone and Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For the Figure 4-12, it was found out that the fabric before wash
and the fabric after washing in 10 minutes have slightly change
in terms of tensile strength from 837.18(N) to 793.82 (N)
approximately change in 5% in tensile strength.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
65
In 10 minutes washing declining the tensile strength when
compared with the fabric before washing, in 20 minutes washing
time. It is further declining the tensile strength in compare
with 10 minutes of washing time. For 10 minutes to 90 minutes,
it occurred as unstable trend. Moreover, for longer time washing
have more damage impacts in terms of tensile strength.
As known as the fabric is weaving together, the weft yarn weak
will result in interdependency issues which allow the strength
of warp yarn weaker, since of this when the sodium hypochloride
chlorine bleach damage the spandex fiber in weft yarn, it also
will affect the warp yarn
4.4 Effect of washing on tensile strength of cotton spandex
fabric in weft direction
Effect of enzyme washing on the tensile strength of cotton
spandex fabric in weft direction
Enzyme wash in weft direction of cotton - spandex is shown on
Figure 4-13.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
66
Figure 4-13 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
As shown in Figure 4-13, the fabric before wash and the fabric
after washing in 10 minutes have much change in terms of tensile
strength from 375.42 (N) to 320.84 (N) approximately change in
17% in tensile strength.
Fabric after enzyme wash in different types of washing time, tend
to be stable in terms of tensile strength. However, from 70
minutes to 90 minutes, it was found that the tensile strength
become weaker, there is about 263.53 (N) to 255.07 (N).
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing on the tensile strength of
cotton spandex fabric in weft direction
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
67
Figure 4-14 shows the effect of the enzyme Wash with Bleach for
weft direction of cotton - spandex Fabric.
Figure 4-14 Enzyme Wash with Bleach In Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For the Figure 4-14, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
washing in 10 minutes have much change in terms of tensile
strength from 375.42 (N) to 320.84 (N) approximately change in
15% in tensile strength.
From 10 to 90 minutes, it have slightly up and downs tends, but
the trend is stable and when there have longer time washing, there
have more damage impacts as the strength of the fabric become
weaker.
Moreover, weft yarn twisted with the spandex fiber, and spandex
could damage by the sodium hycoloride chlorine bleach, so that
the strength result would become weaker.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
68
Effect of enzyme with stone washing on the tensile strength of
cotton spandex fabric in weft direction
Enzyme wash with stone in weft direction of Cotton - Spandex
information is shown on Figure 4-15.
Figure 4-15 Enzyme Wash with Stone In Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
In accordance with Figure 4-15, it can observe that the fabric
before wash and the fabric after washing in 10 minutes have
slightly change in terms of tensile strength from 375.42 (N) to
345.81 (N) approximately change in 8% in tensile strength.
In terms of weft yarn strength after washing, its strength tends
to be weaker after washing in overall.
From 10 minutes to 80 minutes, there have a little up and downs
tend. When 80 minutes to 90 minutes, there have significant drop
down, it is 321.78 (N) to 279.79 (N) and approximately change
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
69
in 13% in tensile strength.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing with stone and
Bleach on the tensile strength of cotton spandex fabric in weft
direction
Enzyme wash with stone and bleach for weft of cotton spandex
Data is shown on Figure 4-16.
Figure 4-16 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For Figure 4-16, the fabric before wash and the fabric after
washing in 10 minutes have large change in terms of tensile
strength from 375.42(N) to 312.88 (N) approximately change in
17% in tensile strength.
From 10 to 20 minutes, it is 312.88 (N) and 312.43 (N),and very
stable. When it is 30 minutes, the tensile strength increase
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
70
slightly. From 30 to 90 minutes, the trends are to tend to become
weaker. It is because there for have a longer washing time and
so there have more damage impacts in terms of tensile strength.
Moreover, sodium hypochloride chlorine bleach damage the spandex
fiber is one factor carry out the weft yarn will became weaker
in tensile strength result.
4.5 Effect of washing on tensile strength of cotton fabric in
warp and weft direction
Effect of enzyme washing on the tensile strength in warp and weft
direction of cotton fabric
Enzyme wash in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric is shown
on Figure 4-17.
Figure 4-17 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
71
In relation to Figure 4-17 is used to unite warp direction and
weft direction for analysis, and it can allow to read the overall
of the fabric for tensile properties.
The warpwise tensile was greater that the weftwise strength. And
the washing sample is slightly weaker than the original.
For the Enzyme washed sample, all of the warpwise and weftwise
tesnile strength were smaller than those of the original sample,
and decrease gradually as the processing time from 10 minutes
to 90 minutes.
Moreover, all of the warpwise and weftwise tesnile strength have
slighly up and down trend, according this information, it can
see the alter of warpwise and weftwise is very similar.
Effect of with bleach enzyme washing on the tensile strength in
warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
Enzyme wash with bleach in warp and weft direction of cotton
fabric is shown on Figure 4-18.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
72
Figure 4-18 Enzyme Wash with Bleach In Warp and Weft direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
According to Figure 4-18, the warpwise tensile was larger that
the weftwise strength. and the after washing sample is a little
weaker that the orginal stage.
For the enzyme wash with bleach sample, all of the warpwise and
weftwise strength have the slightly up and down trend, and means
that the warpwise and weftwise is very consistance.
Effect of enzyme with stone washing on the tensile strength in
warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
Enzyme wash with stone in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
is shown on Figure 4-19.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
73
Figure 4-19 Enzyme Wash with Stone In Warp and Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
For about Figure 4-19, the warpwise tensile was stronger that
the weftwise strength and it is similar with the normal prototype.
However, there have significant different than normal pattern
in warpwise yarn, it is significant weaker than the 10 minutes
to 50 minutes washing. After 60 minutes to 90 minutes, the it
is decrease gradually.
Beside, weftwise tesnile strength were smaller than those of the
original sample, and decline slowly as the processing time from
10 minutes to 90 minutes.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing on the tensile
strength in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
Enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp and weft direction of
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
74
cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-20.
Figure 4-20 Enzyme Wash with Stone and Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Tensile Strength)
According to Figure 4-20, the warpwise tensile was better that
the weftwise strength. And the washing sample is slightly weaker
than original stage. When after 80 minutes to 90 minutes, there
have significant decrease in tensile strength compare with the
original stage.
For the after washing sample, both warpwise and weftwise tensile
strength were smaller than those of the original, and their
decrease trend is very similar, and the structure of the fabric
is quite consistance and have not the major different of warp
yarn and weft yarn.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
75
4.6 Effect of washing on tensile strength of cotton - spandex
fabric in warp and weft direction
Effect of enzyme washing on the tensile strength in warp and weft
direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Enzyme wash in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric is mention
on Figure 4-21.
Figure 4-21 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction for
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
Based on Figure 4-21, the warpwise yarn strength have significant
stronger than the weftwise yarn. For about the washed sample,
both warpwise and weftwise tensile were smaller than those of
the original sample.
Warpwise have the slightly up and down trend and the weftwise
have decrease gradually as the processing time increase from 10
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
76
to 90 minutes. As it can see that the warp yarn and weft yarn
have slightly various.
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing on the tensile strength in
warp and weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Enzyme wash with bleach in warp and weft direction of cotton
fabric is mention on Figure 4-22.
Figure 4-22 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp and Weft of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
Based on Figure 4-22, the warpwise yarn strength have major
stronger than the weftwise yarn. For after enzyme washing with
bleach, both warpwise and weftwise was smaller than both of the
original stages.
As seen that in the warpwise direction, there have an up and down
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
77
trend but weftwise have not. It can observe that the enzyme
washing with bleach have more effect to the warp yarn. Even the
enzyme washing with bleach will effect the weft yarn after 10
minutes, afterward, the strength is become stable and it is
decrease a little gradually.
Effect of enzyme with stone washing on the tensile strength in
warp and weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Enzyme wash with stone in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
is shown on Figure 4-23.
Figure 4-23 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp and Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
According to Figure 4-23, the weftwise yarn is significant weaker
that the warpwise yarn. On the other hand, the have major
different than normal situation is that the original warpwise
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
78
yarn it is slightly weaker than the after 10 minutes, but compare
with 20 minutes to 90 minutes, the original warpwise is stronger
that the after washing once. Beside , it also observe that the
warp yarn have the up and down trend between 20 to 90 minutes.
Actually, the weftwise is more traditional because the after wash
is weaker that the original, and the strength of the weftwise
is decrease slowly but surely.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing on the tensile
strength in warp and weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp and weft direction of
cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-24.
Figure 4-24 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direcction of Cotton Spandex Fabric (Tensile Strength)
Based on Figure 4-24, both warpwise yarn have the significant
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
79
stronger that the weftwise yarn. After the enzyme wash with stone
and bleach, the warpwise yarn and weftwise yarn are smaller then
those of the original sample.
Actually, the trend of the warpwise have slightly up and down,
however, the weftwise yarn is decrease step by step, as the
weftwise is more traditional.
For the following paragraph, it is going to discuss the result
elongation to break for each washing method fabric.
4.7 Effect of washing on elongation to break of cotton fabric
in warp direction
Effect of enzyme washing for the elongation to break in warp
direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash in warp direction of cotton
fabric is shown on Figure 4-25.
In terms of elongation to break for warp yarn after washing, the
percentage of elongation to break tends to be higher after
washing compare with the original.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
80
Figure 4-25 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
In relation to Figure 4-25, the percentage for elongation to
break at original states is significantly lower that after 10
minutes wash. It is from 27.13% to 39.22% approximately increased
12% of the elongation to break.
Beside, from 30 minutes to 70 minutes, it found out that have
a slightly up and down tends. Actually, the change of the
percentage for elongation to break is very stable.
The elongation to break of the washed sample was the greatest
because it was fully relaxed and processed more yarn crimp
percentage. And the processing time of the washing had no
apparent effect on the elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing for the elongation to break
in warp direction of cotton fabric
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
81
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in warp direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-26.
Figure 4-26 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp Direction of Cotton
Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-26, the percentage of the elongation to
break is to major increase from the original to after 10 minutes
wash. It is from 27.13% to 38.34% and increase about 11%.
Moreover, from 10 minutes to 50 minutes, there have slightly up
and down tends. From 50 minutes to 90 minutes, the percentages
have to incline to increase.
The elongation to break of the washed sample was the highest
because it was processed more yarn crimp percentage and fully
relaxed. The dispensation time of the washing had no noticeable
effect on the elongation to break.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
82
Effect of enzyme with Stone washing for the elongation to break
in warp direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone in warp direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-27.
Figure 4-27 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp Direction of Cotton
Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to the Figure 4-27, the percentage of elongation to
break is main increase from original to 10 minutes wash, it is
27.13% to 38.34%, and have 11% increase.
From 10 minutes to 90 minutes, the percentages only have slightly
changed and about 5%.
It has higher elongation to break of the washed sample because
it was fully relaxed and processed more yarn crimp percentage.
The processing time of the washing had no visible effect on the
elongation to break.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
83
Effect of enzyme with Stone and Bleach washing for the elongation
to break in warp direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp
direction of cotton fabric is mention on Figure 4-28.
Figure 4-28 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-28, the fabric before wash and the fabric
after washing in 10 minutes have much change in terms of the
elongation to break from 27.13% to 40.55%, approximately change
in 13% in elongation to break.
Fabric after wash in different types of washing time, tend to
be stable in terms of the percentage of elongation to break, it
was found that the percentage decrease.
The elongation to break of the washed sample was the highest
because it was processed extra yarn crimp and fully relaxed. The
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
84
processing time of the washing had no evident effect on the
elongation to break.
4.8 Effect of washing on elongation to break of cotton fabric
in weft direction
Effect of enzyme washing for the elongation to break in weft
direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in weft
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-29.
Figure 4-29 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of Cotton Fabric
(Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-29, there have a faintly change in terms
of the elongation to break for the fabric before wash and fabric
after washing in 10 minutes. The percentage is that 21.15% to
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
85
23.00%, approximately change in 2% in elongation to break.
Fabric after the washing in different types of washing time, tend
for the adjust for the percentage to be stable in decrease.
The processing time of the washing had no evident effect on the
elongation to break. And the elongation to break of the washed
sample was the highest because it was processed extra yarn crimp
and fully relaxed.
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing for the elongation to break
in weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in weft direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-30.
Figure 4-30 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
86
For the data about Figure 4-30, the fabric before wash and the
fabric after washing in 10 minutes have little change in term
of percentage of elongation to break from 21.15% to 23.24%
approximately change in 2%.
It occurred a small up and down tends between 10 minutes to 90
minutes washing.
The elongation to break of the washed sample was the slightly
highest because it was processed extra yarn crimp and completely
relaxed and the washing time had no evident effect on the
elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with stone washing for the elongation to break
in weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone in weft direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-31
Figure 4-31 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
87
For the information about Figure 4-31, as see that the fabric
before washing and the fabric after washing in after washing in
10 minues have slightly change in terms of the elongation to break
from 21.15% to 22.3% approximately change in 1%.
Further to 10 minutes to 90 minutes, it is further declining the
elongation to break. It also occurred slightly up and down tends
between 10 minutes to 90 minutes washing.
The elongation to break of the washed sample was the greatest
because it was processed extra yarn crimp and fully relaxed.
Beside, the washing processing time had no evident effect on the
elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing for the elongation
to break in weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in weft
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-32
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
88
Figure 4-32 Enzyme Wash With Stone And Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-32, it found out that the fabric at original
stage and after washing in 10 minutes have little change in terms
of the elongation to break from 21.15% to 24.11% approximately
change in 3%. Beside, it was occurred an up and down tends from
10 minutes to 90 minutes.
Furthermore, the elongation to break of the sample was the
highest due to it was processed extra yarn crimp and fully relaxed
and the washing time have no affect on the elongation to break.
4.9 Effect of washing on elongation to break of cotton - spandex
fabric in warp direction
Effect of enzyme washing for the elongation to break in warp
direction of cotton - spandex fabric
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
89
Elongation to break for enzyme wash in warp direction of cotton
- spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-33.
Figure 4-33 Enzyme Wash In Warp Direction of Cotton - Spandex
Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-33, the percentage for elongation to break
at before wash is considerably lower that after 10 minutes wash.
It is from 27.45% to 36.09%, it was increased 9% of the elongation
to break.
From 10 minutes to 90 minutes, it occurred the little up and down
tends but the percentage is very stable.
The elongation to break of the washed sample was the greatest
because it was completely relaxed and processed more yarn
crimp.Beside, the washing time of had noeffect on the elongation
to break.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
90
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing for the elongation to break
in warp direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in warp direction
of cotton - spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-34
Figure 4-34 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp Direction of Cotton
- Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
From Figure 4-34, the percentage for elongation to break at
before wash is meaningfully lower than after 10 minutes wash.
It is from 27.45% to 37.22% and increased 10% of the elongation
to break.
From 10 minutes to 90 minutes, there have slightly up and down
tends. The vary of the percentage of the elongation to break is
very little.
Moreover, the elongation to break of the washed sample was
greatest as it was fully relaxed and provessed more yarn crimp
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
91
perventage. Moreover, the washing time havent affect the effect
on the elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with stone washing for the elongation to break
in warp direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone in warp direction
of cotton - spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-35.
Figure 4-35 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
Based on Figure 4-35, there have significantly lower percentage
for elongation to break at original states compare with after
wash. It is from 27.45% to 35.45% approximately increased 8% of
the elongation to break.
Moreover, the modify in the percentage of the elongation to break
is very slightly.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
92
Because it was fully relaxed and processed more yarn crimp
percentage, the elongation to break of the washed smple was
greatest, and the processing time of the washing had not apparent
effect on the elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing for the elongation
to break in warp direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp
direction of cotton - spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-36.
Figure 4-36 Enzyme Wash With Stone And Bleach In Warp Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
From the Figure 4-36, the percentage of elongation to break at
before wash is lower than after 10 minutes wash. It is from 27.45%
to 36.98% approximately increased 10% for the elongation to
break.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
93
Moreover, from 10 minutes to 90 minutes, the amend of the
percentage for the elongation to break is very little.
Due to it was fully relaxed and processed more yarn crimp
percentage, the elongation to break of the washed smple was the
greatest. Beside, the washing time had no effect on the
elongation to break.
4.10 Effect of washing on elongation to break of cotton - spandex
fabric in weft direction
Effect of enzyme washing for the elongation to break in weft
direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash in weft direction of cotton
- spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-37.
Figure 4-37 Enzyme Wash In Weft Direction of Cotton - Spandex
Fabric (Elongation To Break)
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
94
According to Figure 4-37, the percentage for the elongation to
break at original stages is lower than after 10 minutes. It is
from 28.81% to 34.07% approximatelly increased 5% of the
elongation to break.
From 10 minutes to 20 minutes, it is slightly increased. From
30 minutes to 90 minutes, there havent major change.
Due to it was fully relaxed and processed more yarn crimp
percentage, the elongation to break for the washed sample was
the greatest than origial. The processing time of the washing
havnet effect on the elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing for the elongation to break
in weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in weft direction
of cotton - spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-38.
Figure 4-38 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Weft Direction of
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
95
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-38, the percentage of the elongation to
break at original states is lowe than after 10 minutes wash. It
is from 28.81% to 34.75% approximately increased 6% of the
elongation to break.
If also found out that from 10 minutes to 90 minutes, the
percentage of the elongation to break is continuous increase but
slightly.
The elongation to breaked for the washed sample was the greatest
due to it was fully relaxed and processed more yarn crimp
percentage. Moreover, the processing time havent effect the
elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with stone washing for the elongation to break
in weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone in weft direction
of cotton - spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-39.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
96
Figure 4-39 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
In relation to Figure 4-39, the percnetage for elongation to
break at original states is lower than after 10 minutes wash.
It is from 28.81% to 33.18% approximately increased 6% of the
elongation to break.
From 10 minutes to 90 minutes, it found out there have slightly
up and down tends. And the percentage of the elongation to break
is continuous increased.
The washed sample was greatest of the elongation to break because
when after processed there occur more yarn crimp, also the yarn
is fully relaxed, the processing time of the washing had not
effect on the elongation to break.
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing for the elongation
to break in weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
97
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in weft
direction of cotton - spandex fabric is shown on Figure 4-40
Figure 4-40 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
In relation to the Figure 4-40, the percentage of elongation to
break at original states is lower that after 10 minutes wash.
It is from 28.81% to 35.46% approximately increased 7% of the
elongation to break.
Moreover, from 10 minutes to 90 minutes wash, there have
significant up and tends.
It is true that the elongation to break of the washed sample was
greatest percentage, the processing time of the washing havent
apparent effect on the elongation to break.
4.11 Effect of washing on elongation to break of cotton fabric
in warp and weft direction
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
98
Effect of enzyme washing for the elongation to break in warp and
weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash in warp and weft direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-41.
Figure 4-41 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-41 is used to unite warp direction and weft
direction for analysis, and it can allow to read the overall of
the fabric for the elongation to break.
The warpwise elongaton to break is greater than the weftwise.
However the warpwise and weftwise elongation to break of the
washed sample was the greater than original.
Meantime,both warpwise and weftwise have the slgihtly up and down
tends, according to this information, it can see the alter of
warpwise and weftwise is very similar.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
99
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing for the elongation to break
in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in warp and weft
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-42.
Figure 4-42 Enzyme Wash With Bleach In Warp and Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
Beased on Figure 4-42, the warpwise yarn elongation to break have
significant greatest than the weftwise yarn. For about the washed
sample, both warpwise and weftwise elongation to break of washed
sample was larger than the original sample.
Moreover, both of the warpwise and weftwise have the little up
and down tends. Based on these information, it can see the alter
of warpwise and weftwise is very similar.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
100
Effect of enzyme with stone washing for the elongation to break
in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in warp and weft
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-43
Figure 4-43 Enzyme Wash With Stone In Warp and Weft Direction
of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-43, the warpwise elongaton to break is
greater than the weftwise. However the warpwise and weftwise
elongation to break of the washed sample was greater than
original.
Beside, both of the warpwise and weftwise have slightly up and
down tends, according to these data, is can seen that the change
of warpwise and weftwise is very similar.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
101
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing for the elongation
to break in warp and weft direction of cotton fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp
and weft direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-44
Figure 4-44 Enzyme Wash With Stone and Bleach In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-44, the warpwise elongation to bre is
better than the weftwise. However, the warpwise and weftwise
elongation to break of the washed sample was the greatest.
At the same time, both of the warpwise and weftwise have similar
tends for the elongation to break. As because of this, the change
of warpwise and weftwise is very similar.
4.12 Effect of washing on elongation to break of cotton - spandex
fabric in warp and weft direction
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
102
Effect of enzyme washing for the elongation to break in warp and
weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash in warp and weft direction
of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-45
Figure 4-45 Enzyme Wash In Warp and Weft Direction of
Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-45, both of the warpwise and weftwise
elongation to break of washed sample is greatest than the
original sample.
Beside, for 10 minutes, 30 minutes to 90 minutes wash, all of
the warpwise elongation to break is higher than the weftwise,
but for the original sample and 20 minutes, the weftwise is
slightly higher than the warpwise. And both of the warpwise and
weftwise have similar tends for the elongation to break.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
103
Effect of enzyme with bleach washing for the elongation to break
in warp and weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with bleach in warp and weft
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-46
Figure 4-46 Enzyme Wash with Bleach In Warp and Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
Based on Figure 4-46, the warpwise elongation to bre is better
than the weftwise. On the other, the warpwise and weftwise
elongation to break of the washed sample was the greatest.
Beside, the warpwise of elongation to break for 10 minutes and
20 minutes is higher than weftwise. Original , 30 minutes to 90
minutes, all of these is weftwise is higher than the warpwise.
Both of the warpwise and weftwise have similar tends for the
elongation to break.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
104
Effect of enzyme with stone washing for the elongation to break
in warp and weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone in warp and weft
direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-47
Figure 4-47 Enzyme Wash with Stone In Warp and Weft Direction
of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
In relation to Figure 4-47, the percentage for elongation to
break in warpwise and weftwise at original states is lower than
after wash, the warpwise elongation to bre is better than the
weftwise for 10 minutes to 60 minutes and 80 minutes to 90 minutes.
Beside. At original states and 70 minutes, the weftwise
elongation is slighlty higher than warpwise. It can see that the
alter of warpwise and weftwise is very similar, they have the
slightly up and down tends for after wash sample.
CHAPTER 4 ______ RESULTS & DISCUSSION
105
Effect of enzyme with stone and bleach washing for the elongation
to break in warp and weft direction of cotton - spandex fabric
Elongation to break for enzyme wash with stone and bleach in warp
and weft direction of cotton fabric is shown on Figure 4-48
Figure 4-48 Enzyme Wash with Stone and Blech In Warp and Weft
Direction of Cotton - Spandex Fabric (Elongation To Break)
According to Figure 4-48, the warpwise elongation to bre is
better than the weftwise, the warpwise elongation is higer than
the weftwise for 10, 20, 30, 50, 70, 80 and 90 minutes wash,
original states, 40 and 60 minutes is weftwise elongation is
higher than the warpwise.
Both of the warpwise and weftwise have slightly up and down tends,
according to these information, it can see the alter of warpwise
and weftwise is very similar.
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION
106
Chapter 5 Conclusion & Recommendation
5.1 Conclusion
After the evaluation for the different times of the washing
condition of the cotton fabric and cotton spandex fabric, the
result obtain can be concluded.
During the washing, the starch surface fibres and some of the
dyestuff were removed by the abrading stone or hot water. The
tensile strength of these samples became weaker in both fabric
directions. The loss in the durability depended on the processing
time, as the longer of the processing time, the lower the
durability.
According to the analysis data, it could see the strength of the
enzyme wash with stone and bleach was the weaker. This was due
to the chemical degradation of cotton and cotton spandex fiber
by the oxidizing agent, sodium hypochlorite and the abrasion
action of the pumice stone. The processing time was critical as
prolonged bleaching would permanently and severely damage.
Compare with four of the washing types, enzyme wash with stone
were less damage for the tensile strength.
Beside, based on the measurement, enzyme wash, enzyme wash with
bleach and enzyme wash with stone and bleach wash, as see that
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION
107
as the washing time as longer and become weaker. However, for
the results that were between original after washing time, they
were not consistence, as because normally practice, when the
washing time was longer, the fabric would become weaker. For the
analysis, some of the fabric is suddenly become strength and some
are decreases.
This result was due to the process of desizing because it was
desized only with e detergent solution for 30 minutes.
Actually, for desizing process, it should be used for Amylase
chemical and process time was about 45 minutes. Because of this,
some of the starch remain on the surface of the fabric, and so
affect the tensile strength become irregular.
In fact, Enzyme wash with stone wash have the biopolishing effect
as find out that the original fabric was weaker than the after
wash fabric. It was because the cellulase can increase the
biopolishing of the cotton fabric to enhance the handle value.
Although the effects of the cellulase hydrolysis can stay as the
surface phenomena, much of the physical aspects of the fabric
like the tensile strength take place during the processing.
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION
108
5.2 Recommendation
The objectives of the study were achieved. Nevertheless, the
different time of the washing condition effect on cotton denim
and cotton denim fabric can be investigate in a broader and deeper
dimension in both experiments and evaluation.
According to the investigation, if the stone wash and bleaching
process are properly controlled, the durability will be retained
at an acceptable level,
In the study, four of the cellulase washing condition with on
enzyme concentration was selected for analysis. The effect of
the different levels of the factors such as the different
temperatures, pH condition, enzyme concentration, liquor ratios,
treatment times and magnitudes of mechanical agitation can be
used for the further study.
Moreover, only have two types of denim fabric were studied. When
there have difference fabric types like difference in
construction, warp and weft direction, yarn count weaving and
dyeing method, it is more available for the investigation.
In the evaluation aspect, the dimensional stability and the
fabric weight test was not investigated. As when the fabric there
has the high shrinkage for the washing, it will directly affect
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION & RECOMMENDATION
109
the tensile properties. Because, the fabric has the high
shrinkage after wash, warp and weft yarn will close together and
become higher density, and the fabric will become thicker,
tensile strength will become strength.
Another measurement that can be assessed is the tear strength
and resistance to flex abrasion because there should be fully
observation of the fabric properties. It is because tensile
strength cant reflect all the properties of the denim fabric.
110
REFERENCE
1. J. Webster, R.M. Laing, 1998, Fibres to Finished Fabric
proceedings, 173 174.
2. Kathryn L. Hatch, 1993, Textile Science, West Publishing
Company, 164 167, 245 251.
3. American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists,
AATCC Test Method 20-2007, Fiber Analysis : Qualitative,
AATCC Technical Manual 2008, 44
4. The Hong Kong Cotton Spinners Association in collaboration
with Hong Kong Productivity Council, Textile Handbook: 2007,
Hong Kong Cotton Spinners Association, 1-3.
5. M. Lewin, 2006, Handbook of Fiber Chemistry (3
rd
Edition),
Taylor & Francis, 546.
6. C.M. Carr, 1995, Chemistry of the Textiles Industry, Blackie
Academic & Professional, 6-7, 260-265.
7. R.M.CHRISTIE, 2001, Color Chemistry, Heriot Watt
University Scottish Borders Campus Galashiels UK,74 76
8. M. Sariisik, 2004, Use of Cellulase and Their Effects on Denim
Fabric Properties, AATCC Review, 4(1), 23-29.
9. A. Cavaco-Paulo, G.M. Gbitz, 2003, Textile processing with
enzymes, The Textile Institute, Woodhead Publishing Limited,
Cambridge England, 110-129.
10. H.A. Krssig, 1993, Cellulose : structure, accessibility and
reactivity, Amsterdam : Gordon and Breach Science, 200-205.
11. A. Cavaco-Paulo, G.M. Gbitz, 2003, Textile processing with
enzymes, The Textile Institute, Woodhead Publishing Limited,
111
Cambridge England, 111-128.
12. A. Cavaco-Paulo, G.M. Gbitz, 2003, Textile processing with
enzymes, The Textile Institute, Woodhead Publishing Limited,
Cambridge England, 111-128.
13. J.E. Booth, 1968, Principle of Textile Testing(3
rd
Edition),
Heywoon, 353 382
14. E.R. Kaswell, 1963, Wellington Sears handbook of industrial
textiles, New York, Wellington Sears, 468 - 471 , 554 - 559
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Spirality of Single Jersey Knitted FabricDokument13 SeitenSpirality of Single Jersey Knitted FabricKazi Saiful IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Indian Journal Examines Spirality in Weft-Knitted FabricsDokument5 SeitenIndian Journal Examines Spirality in Weft-Knitted FabricsObak Prithibi100% (1)
- Carr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureVon EverandCarr and Latham's Technology of Clothing ManufactureDavid J. TylerBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (1)
- Study of Loop Formation Process On 1x1 V-Bed Rib Knitting MachineDokument12 SeitenStudy of Loop Formation Process On 1x1 V-Bed Rib Knitting MachineIAEME PublicationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Evaluation of yarn diameter and its effect on fabric qualityDokument8 SeitenEvaluation of yarn diameter and its effect on fabric qualitySabeeh Ul HassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solved QP of Knit Tech April 2023Dokument4 SeitenSolved QP of Knit Tech April 2023RajendrakumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yarn Technology and Qu AlityDokument653 SeitenYarn Technology and Qu AlityYashi ShekharNoch keine Bewertungen
- Yarn Defect-Final - ReadyDokument47 SeitenYarn Defect-Final - Readyparash rajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Selection of YarnsDokument9 SeitenSelection of YarnsAkhilendra SonkarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mechanical Properties of Weft Knitted FabricsDokument6 SeitenMechanical Properties of Weft Knitted FabricsAhmad SamerNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cotton, Polyester & Cotton Polyester BlendDokument4 SeitenCotton, Polyester & Cotton Polyester BlendTanaji Santra100% (1)
- Woven Fabric Quality Parameters: Dimensions, Weight, Strength & MoreDokument2 SeitenWoven Fabric Quality Parameters: Dimensions, Weight, Strength & MoreObak Prithibi100% (3)
- Patterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafDokument33 SeitenPatterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafHifza khalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Prevention of BarreDokument5 SeitenPrevention of BarreKavi DhingraNoch keine Bewertungen
- BASE Textiles LimitedDokument76 SeitenBASE Textiles LimitedPushpa BaruaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textile Design & Fabric Manufacturing Short CourseDokument98 SeitenTextile Design & Fabric Manufacturing Short CourseMuhammad IlyasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tubetex and Lafer DifferenceDokument4 SeitenTubetex and Lafer Differencerakibul islam100% (1)
- Analysis of Weft Knitted Jersey FabricDokument6 SeitenAnalysis of Weft Knitted Jersey FabricNaimul HasanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ecoverde BrochureDokument12 SeitenEcoverde BrochureRicardina Rosibel Rodriguez MendozaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Relation between yarn count GSM and cost of accessoriesDokument31 SeitenRelation between yarn count GSM and cost of accessoriesMohammed Atiqul Hoque ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- Plasma Treatment For TextilesDokument30 SeitenPlasma Treatment For TextilesTuan Nguyen Minh100% (2)
- Knitting 3Dokument6 SeitenKnitting 3Sanaullah MuradNoch keine Bewertungen
- Determination of Loop Length, Tightness Factor and Porosity of Single Jersey Knitted FabricDokument6 SeitenDetermination of Loop Length, Tightness Factor and Porosity of Single Jersey Knitted FabrictanveerhusseinNoch keine Bewertungen
- International British Garments Skill Matrix Analysis: Operation Process Rating % Result Remarks Target AchievedDokument8 SeitenInternational British Garments Skill Matrix Analysis: Operation Process Rating % Result Remarks Target AchieveddpnairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Defects and Quality Optimisation of Core-Spun Yarn Containing SpandexDokument9 SeitenDefects and Quality Optimisation of Core-Spun Yarn Containing SpandexMohammed Atiqul Hoque Chowdhury100% (1)
- TQE Assgn 3-Problems SolvedDokument6 SeitenTQE Assgn 3-Problems SolvedSENTHIL KUMARNoch keine Bewertungen
- Controlled Compressive Shrinkage ProcessDokument4 SeitenControlled Compressive Shrinkage ProcessSaidur Rahman SajibNoch keine Bewertungen
- Airjet PracDokument12 SeitenAirjet PracJunaid SuhailNoch keine Bewertungen
- Color Reduction and CleaningDokument170 SeitenColor Reduction and CleaningDora BANoch keine Bewertungen
- Dyeing - Finishing Price - DadDokument1 SeiteDyeing - Finishing Price - Dadasrknit1Noch keine Bewertungen
- Determining Fabric Quality: Prepared By: Riza Leigh I. FiguesDokument55 SeitenDetermining Fabric Quality: Prepared By: Riza Leigh I. FiguesRizaLeighFiguesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter - Three: Yarn Count, Yarn Twist and Tensile TestingDokument57 SeitenChapter - Three: Yarn Count, Yarn Twist and Tensile TestingGadisa AbrahimNoch keine Bewertungen
- Factors Affecting Yarn StrengthDokument11 SeitenFactors Affecting Yarn StrengthAbhishek ThakurNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter-7 - Knitting DerivativesDokument39 SeitenChapter-7 - Knitting DerivativesMD Shakil Khan0% (1)
- Knitting Science Loop Length MeasurementDokument3 SeitenKnitting Science Loop Length MeasurementNiaz IslamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Unit - IiDokument27 SeitenUnit - IiJoseph KuruvilaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Finish Fabrics: ShirtingDokument3 SeitenFinish Fabrics: ShirtingKasra GolbanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Minimization of Defects in Knitted Fabric 02Dokument7 SeitenMinimization of Defects in Knitted Fabric 02Sarah SebâaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textile Industry Guide - Fibers, Yarns, Count and Garment ProductionDokument15 SeitenTextile Industry Guide - Fibers, Yarns, Count and Garment ProductionyuvaramrajNoch keine Bewertungen
- Title of The Project ThesisDokument87 SeitenTitle of The Project ThesisIrfan IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textiles - DiplomaDokument9 SeitenTextiles - DiplomamansiagrawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Innovation in YarnDokument6 SeitenInnovation in YarnDevendra VashisthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Slasher Sizing Machine - Main Parts of Slasher Sizing Machine - Textile LearnerDokument3 SeitenSlasher Sizing Machine - Main Parts of Slasher Sizing Machine - Textile LearnerTholkappiyan Ganesan100% (1)
- Fabric Spec KnittedDokument2 SeitenFabric Spec KnittedakshatgargmoderniteNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fibers Properties Textile MaterialsDokument19 SeitenFibers Properties Textile MaterialsGarmentLearner100% (1)
- Backed FabricsDokument5 SeitenBacked FabricsRashadul Islam WalidNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textile Dyeing and Printing: AssignmentDokument8 SeitenTextile Dyeing and Printing: AssignmentshailajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Manufacturing StepsDokument15 SeitenFabric Manufacturing StepsFazlul AzimNoch keine Bewertungen
- 3D FabricDokument17 Seiten3D FabricFaizan ShaikhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stone WashDokument3 SeitenStone WashMuhammad MustahsinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Structure and Design Final QuestionDokument1 SeiteFabric Structure and Design Final QuestionMs. Naznin Akter100% (1)
- Modern Developments in WeavingDokument13 SeitenModern Developments in WeavingRakeahkumarDabkeyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lec 9Dokument23 SeitenLec 9abhinavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Terry Towel Weaving MachineDokument29 SeitenTerry Towel Weaving Machinehamza hanif100% (2)
- Toyota's Global Service Network Supports Customers WorldwideDokument6 SeitenToyota's Global Service Network Supports Customers WorldwideHardik VavdiyaNoch keine Bewertungen
- India's Toy Market Has Potential To Double To $2 BN by 2025 - ReportDokument5 SeitenIndia's Toy Market Has Potential To Double To $2 BN by 2025 - ReportHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Find Business InformationDokument218 SeitenHow To Find Business Informationbibicul1958100% (1)
- RTP RT292 BITechGuide Feb 2021 FinalDokument10 SeitenRTP RT292 BITechGuide Feb 2021 FinalHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Shop Puppy Golden Retriever: Casetify Casetify CasetifyDokument1 SeiteShop Puppy Golden Retriever: Casetify Casetify CasetifyHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- How To Find Business InformationDokument218 SeitenHow To Find Business Informationbibicul1958100% (1)
- Essential Fabric Quality Reports For Bulk Cutting Approval of FabricsDokument7 SeitenEssential Fabric Quality Reports For Bulk Cutting Approval of FabricsHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fabric Troubleshooting GuideDokument38 SeitenFabric Troubleshooting GuideHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Damco Shipper - Training For VendorsDokument62 SeitenDamco Shipper - Training For VendorsHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Weaving CostDokument36 SeitenWeaving CostHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Thread GuideDokument36 SeitenThread GuideHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- McBride - Key Steps in Implementing A Kaizen EventDokument33 SeitenMcBride - Key Steps in Implementing A Kaizen EventHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ie DepartmentDokument15 SeitenIe DepartmentHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- World Denim Market Denim Market in India SWOT Analysis of Denim Industry (Either India or Orissa) Fill Below Table For Khorda, BhubnashewarDokument1 SeiteWorld Denim Market Denim Market in India SWOT Analysis of Denim Industry (Either India or Orissa) Fill Below Table For Khorda, BhubnashewarHarmendar S KothariNoch keine Bewertungen
- Manufacture Terry Towels PakistanDokument10 SeitenManufacture Terry Towels PakistanAli HaiderNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neps and Trash IndicatorDokument8 SeitenNeps and Trash IndicatorShoaib ArifNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ijftr 15 (1) 1-5Dokument5 SeitenIjftr 15 (1) 1-5amar9247Noch keine Bewertungen
- A Fascinating Colour Journey Through The Exciting World of Natural Dyes and TextilesDokument3 SeitenA Fascinating Colour Journey Through The Exciting World of Natural Dyes and TextilesMudassar Ali100% (1)
- Sunhat Pattern Full LBDDokument7 SeitenSunhat Pattern Full LBDJudy Zedalis100% (1)
- Textile Testing MethodsDokument42 SeitenTextile Testing MethodsNenadCirkovicNoch keine Bewertungen
- Baby BootiesDokument4 SeitenBaby BootiesBrids100% (2)
- Shibori Techniques Lesson 1Dokument8 SeitenShibori Techniques Lesson 1Beriadhwen100% (2)
- Time Flies Quilt in Eclectic Elements by Tim HoltzDokument23 SeitenTime Flies Quilt in Eclectic Elements by Tim HoltzRizia SouzaNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Industrial Revolution 1Dokument6 SeitenThe Industrial Revolution 1api-249544695Noch keine Bewertungen
- TH 9868Dokument121 SeitenTH 9868Keerthanasudarshan100% (1)
- Manta para NiñoDokument2 SeitenManta para NiñoEstela Del Barco de CefaliNoch keine Bewertungen
- Knitting NptelDokument6 SeitenKnitting NptelvivekNoch keine Bewertungen
- 954 in EnglishDokument3 Seiten954 in EnglishLarisa PanaitNoch keine Bewertungen
- Textile Industry - 01 LectureDokument40 SeitenTextile Industry - 01 Lectureisabelism100% (1)
- Operation Management ReportDokument14 SeitenOperation Management ReportClaudia SmithNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sock TutorialDokument20 SeitenSock Tutorialanuruddhaindatissa100% (1)
- Final Textile PresentationDokument20 SeitenFinal Textile PresentationGurpreet NarangNoch keine Bewertungen
- H&M MarketingDokument22 SeitenH&M MarketingNikhil Anand50% (2)
- Article 1 - Fast FashionDokument7 SeitenArticle 1 - Fast FashionDesh MondillaNoch keine Bewertungen
- 21 Sourcing Report 20Dokument100 Seiten21 Sourcing Report 20CalyveNoch keine Bewertungen
- Binder #84 With Foot #94: BerninaDokument3 SeitenBinder #84 With Foot #94: BerninaykuijpersNoch keine Bewertungen
- How to Crochet an Amigurumi RobotDokument2 SeitenHow to Crochet an Amigurumi RobotbizarreworldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Wet Processing I IntroductionDokument8 SeitenWet Processing I IntroductionTanmay JagetiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Applicability of Flax & HempDokument6 SeitenApplicability of Flax & HempMitu ChowdhuryNoch keine Bewertungen
- IK S12 BLAD WebDokument8 SeitenIK S12 BLAD WebInterweave50% (2)
- Thermal Conductivity of Needle Punched PreformsDokument10 SeitenThermal Conductivity of Needle Punched PreformsFashionnift NiftNoch keine Bewertungen
- Viyellatex Group Internship ReportDokument184 SeitenViyellatex Group Internship ReportAlauddin Ahmed Jahan95% (20)
- Maxshine Products Catalouge -2016 YearDokument35 SeitenMaxshine Products Catalouge -2016 YearGonzalo GonzalezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Book ListDokument10 SeitenBook ListtojinboNoch keine Bewertungen
- Functional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsVon EverandFunctional Safety from Scratch: A Practical Guide to Process Industry ApplicationsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentVon EverandProcess Engineering for a Small Planet: How to Reuse, Re-Purpose, and Retrofit Existing Process EquipmentNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyVon EverandGuidelines for the Management of Change for Process SafetyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines for Enabling Conditions and Conditional Modifiers in Layer of Protection AnalysisVon EverandGuidelines for Enabling Conditions and Conditional Modifiers in Layer of Protection AnalysisNoch keine Bewertungen
- Produced Water Treatment Field ManualVon EverandProduced Water Treatment Field ManualBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (5)
- Piping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationVon EverandPiping and Pipeline Calculations Manual: Construction, Design Fabrication and ExaminationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (18)
- Trevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationVon EverandTrevor Kletz Compendium: His Process Safety Wisdom Updated for a New GenerationNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressVon EverandNuclear Energy in the 21st Century: World Nuclear University PressBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (3)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksVon EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Chemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesVon EverandChemical Process Safety: Learning from Case HistoriesBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaVon EverandGuidelines for Developing Quantitative Safety Risk CriteriaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guidelines for Siting and Layout of FacilitiesVon EverandGuidelines for Siting and Layout of FacilitiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perfume Engineering: Design, Performance and ClassificationVon EverandPerfume Engineering: Design, Performance and ClassificationBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (5)
- Guidelines for Vapor Cloud Explosion, Pressure Vessel Burst, BLEVE, and Flash Fire HazardsVon EverandGuidelines for Vapor Cloud Explosion, Pressure Vessel Burst, BLEVE, and Flash Fire HazardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Bow Ties in Risk Management: A Concept Book for Process SafetyVon EverandBow Ties in Risk Management: A Concept Book for Process SafetyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsVon EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsBewertung: 4 von 5 Sternen4/5 (10)
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersVon EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNoch keine Bewertungen
- Robotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryVon EverandRobotics: Designing the Mechanisms for Automated MachineryBewertung: 4.5 von 5 Sternen4.5/5 (8)
- The HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesVon EverandThe HAZOP Leader's Handbook: How to Plan and Conduct Successful HAZOP StudiesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Recognizing and Responding to Normalization of DevianceVon EverandRecognizing and Responding to Normalization of DevianceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityVon EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityBewertung: 5 von 5 Sternen5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyVon EverandGuidelines for Engineering Design for Process SafetyNoch keine Bewertungen