Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
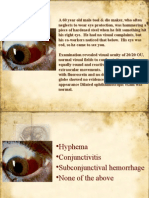
C Ophthal
Hochgeladen von
Vissalini JayabalanOriginalbeschreibung:
Originaltitel
Copyright
Verfügbare Formate
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
C Ophthal
Hochgeladen von
Vissalini JayabalanCopyright:
Verfügbare Formate
Guidelines and Criteria for Registration as a Specialist in Ophthalmology
Prepared by
Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology,
National Specialist Register
CONTENTS
Page
1.
Introduction
1
2.
Recognised specialist training
2
3.
List of recognised postgraduate qualifications
2
4.
Requirements for enrolment for specialist training
3
5.
Recognised specialist training programme
3
6.
Recognised specialist training centres
4
7.
Competence in core procedures required of a specialist on
completion of training in ophthalmology
4
8.
Certification of completion in specialist training in
ophthalmology
5
9.
List of Appendices
5
Appendix 1 : Postgraduate training programme structure
6
Appendix 2 : Criteria for recognition of specialist training
centres
23
Appendix 3 : Core procedures required for fulfillment of
training
32
10
11.
Ophthalmology Surgical And Procedural Skills (for fulfillment of
Specialist Registration)
Acknowledgements
39
43
1. Introduction
The National Specialist Register (NSR) has been established to assure quality
care to the public by determining the professional standards expected of
specialists in their respective fields. Specialists are credentialed on fulfilling the
training requirements and have the required competencies stipulated by the
relevant specialty sub-committees.
The Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology has defined the criteria
for credentialing as an ophthalmologist. To be registered with the NSR,
the candidate must have satisfactorily completed the training programme and
demonstrated clinical competence.
The following requirements need to be fulfilled:
i. Registration with the Malaysian Medical Council and possession of
a current Annual Practicing Certificate
ii. Possession of any postgraduate qualification in ophthalmology
registrable with the NSR
iii. Satisfactorily completed 6 years of recognised training in
ophthalmology of which at least 2 years is after obtaining the
postgraduate qualification
These guidelines deal with the training to be undertaken by trainees enrolled in
a recognised training programme. It is a review of the previous handbook and is
effective from 1
st
January, 2012.
1
2. RECOGNISED SPECIALIST TRAINING
The total duration of training shall be a minimum of 6 years. The trainee must
pursue 4 years of postgraduate training leading to the award of a recognised
qualification, followed by 2 years of supervised training.
3. LIST OF RECOGNISED POST-GRADUATE QUALIFICATIONS
(i) Sarjana Surgeri (Oftalmologi), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
(Master of Surgery (Ophthalmology), Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia)
(ii) Sarjana Oftalmologi, Universiti Malaya
(Master of Ophthalmology, University of Malaya)
(iii) Sarjana Perubatan (Oftalmologi), Universiti Sains Malaysia
(Master of Medicine (Ophthalmology), Universiti Sains Malaysia)
(iv) Any other equivalent qualification can be considered for recognition
by the Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology on a case-to-case
basis provided all training requirements and any other requirements as
determined by the specialty sub-committee have been fulfilled.
2
4. REQUIREMENTS FOR ENROLMENT FOR SPECIALIST TRAINING
A medical doctor who has:
i. at least 2 years of working experience after obtaining a basic medical
degree
AND
ii. full registration with Malaysian Medical Council
AND
iii. possession of a current Annual Practicing Certificate
5. RECOGNISED SPECIALIST TRAINING PROGRAMME
5.1 Postgraduate training leading to the Masters degree or
equivalent
The training shall be based on the Masters programme approved by the Malaysian
Universities Conjoint Committee of Ophthalmology (MUCCO) (Appendix 1).
5.2 Supervised training following postgraduate qualification
5.2.1 The aim of this 2 year period of training is to assist trainees to acquire
both knowledge and competence in the performance of procedures
to be credentialed as an ophthalmologist. It is an additional step
beyond post-graduate qualification where trainees will be assessed
for knowledge, skills and competence.
5.2.2 Supervised Postings
The trainee shall undergo supervised rotational postings of 3-6
months to fulfill their required core procedures and maintain the
logbook. A 6 monthly assessment of supervisors report must be
submitted. (Appendix 1)
3
6. RECOGNISED SPECIALIST TRAINING CENTRES
6.1 The Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology shall recognise individual
training centres based on specific criteria. (Appendix 2)
6.2 The list of current recognised training centres can be obtained from the
NSR secretariat upon request or its website: www.nsr.org.my. The list may
be updated from time to time.
7. COMPETENCE IN CORE PROCEDURES REQUIRED OF
A SPECIALIST ON COMPLETION OF TRAINING IN
OPHTHALMOLOGY
7.1. Trainees are required to be competent in the core procedures listed
(Appendix 3)
7.2 Trainees are recommended to use the Specialist Training in Ophthalmology
Personal Record and Surgical Logbook that can be obtained from the
Academy of Medicine of Malaysia. This logbook should continue to be used
after the trainee graduates. It is required for registration with the National
Specialist Register.
4
8. CERTIFICATION OF COMPLETION IN SPECIALIST TRAINING IN
OPHTHALMOLOGY
A certificate shall be awarded after the trainee has satisfactorily completed the
following:
a. Postgraduate training in Ophthalmology (Masters or equivalent)
AND
b. Two (2) years supervised postings following postgraduate training including
review of procedural log book and supervisor reports
AND
c. Successfully attended exit certification conducted by the Specialty Sub-
Committee of Ophthalmology, NSR
9. APPENDICES
Appendix 1: Postgraduate training programme structure
Appendix 2: Criteria for recognition of specialist training centres
Appendix 3: Core procedures required for fulfillment of training
5
APPENDIX 1
POSTGRADUATE TRAINING PROGRAMME STRUCTURE
(ADAPTED FROM THE MASTERS TRAINING PROGRAMME STRUCTURE
OF THE MALAYSIAN UNIVERSITIES CONJOINT COMMITTEE OF
OPHTHALMOLOGY (MUCCO))
OBJECTIVES
The postgraduate training programme in Ophthalmology aims to produce
graduates who:
1. are able to appropriately assess, diagnose and manage patients with ocular
and systemic related disorders
2. can assess and detect dysfunction of vision and the visual system, and
provide appropriate management for such conditions
3. are able to use current and appropriate technology in the diagnosis and
management of relevant ocular conditions
4. understand their role and are able to participate in the prevention of
blindness programme
5. understand their role as teachers and the importance of continuous
professional development in the advancement of Ophthalmology
6. are able to participate in eye research and development activities
7. can function effectively, ethically and professionally within the profession
LEARNING OUTCOMES
Phase I (Year 1)
At the completion of this phase, trainees possess:
1. good knowledge in basic medical and surgical sciences
2. good knowledge in ocular anatomy, physiology, pathology, basic optics and
ocular diseases
3. basic understanding on the optical principles of ophthalmic instruments and
their applications
4. skills in taking relevant history from patients and performing a complete
ophthalmic examination
5. skills in performing clinical refraction and interpret prescriptions
6. knowledge in basic ophthalmic microsurgery
7. skills in performing minor ophthalmic surgeries under supervision
8. good knowledge in basic research methodology
6
Phase II (Year 2 & 3)
At the completion of this phase, trainees possess:
1. in depth knowledge of ocular diseases and related systemic conditions
2. enhanced skills in eliciting history and performing a comprehensive
examination to arrive at appropriate differential diagnosis
3. the ability to decide on and interpret relevant investigations and manage
most cases with minimum supervision
4. the ability to perform common surgical procedures such as cataract surgery
with supervision
5. knowledge and skills in the assessment of low vision and its management
6. the ability to apply research methods in the conduct of their dissertation
project
Phase III (Year 4)
At the completion of this phase, trainees possess:
1. the ability to manage common and acute ophthalmic conditions
independently
2. the ability to perform common surgical procedures with minimal or no
supervision
3. an evidence-based approach to clinical decision-making and problem-
solving, through an ability to identify, critically analyze and interpret evidence
4. the ability to communicate effectively with patients, their relatives and
professional colleagues
5. knowledge on prevention of blindness programme planning and experience
on related activities
6. knowledge and skills to supervise junior trainees
7. the ability to conduct eye research and research in related sciences
8. good insight and the ability to recognize own limitations and seek appropriate
consultation
7
PROGRAMME STRUCTURE
Year
Phase
Curriculum
Assessment
1
1
Ophthalmology related to basic
medical sciences
Basic ocular sciences
Optics & refraction
Introduction to clinical ophthalmology
Part I
2
3
2
Clinical ophthalmology
Ophthalmology related to
general medicine & neurology
Part II
4
3
Advanced clinical ophthalmology
Part III
The course extends over a minimum period of 4 years and maximum period of
7 years.
8
SYLLABUS
PHASE I
BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES (in relation to Ophthalmology)
Anatomy
General nervous system
Central nervous system
Detailed anatomy of the eye, orbit and adnexae and the visual pathways
Head and neck anatomy
The respiratory system and cardiovascular systems
Histology
Embryology
Physiology
General physiology (in relation to Ophthalmology)
Cardiovascular system
Respiratory system
Haematological system
Nervous system
Endocrinology
Renal system
Homeostasis
Nutrition
Pathology
General principles of pathology including
Inflammation
Disturbance of growth
Healing and repair
Immunological mechanisms and hypersensitivity reactions
Vascular pathology
Degenerative disorders and aging
Shock & trauma
Neoplasia and the effects of treatment
Common tissue stains
9
Pharmacology
General pharmacological principles
Mode of action of drugs on receptors
Drug toxicity
Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of drugs
Molecular & cell biology
Cell structures and their biochemical functions
Normal cell functions and interactions
Connective tissue and extracellular matrix
Genetics
Principles of genetics
Modes of inheritance
Principle of gene therapy
Microbiology and immunology
Principles of microbial pathogenesis
Principles of sterilisation, disinfection and asepsis
Principles of antimicrobials
Principles of immunology
BASIC OCULAR SCIENCES Anatomy
of visual and ocular system Physiology
of visual and ocular system
Introduction to ocular pathology
Optics & refraction
Physical optics
Geometric optics
Clinical optics
Clinical refraction
Instruments
10
PHASE II SYLLABUS
Clinical history taking and examination
Ocular and systemic
Clinical ophthalmology
External eye diseases & orbit
Diseases of the uvea
Diseases of the lens
Diseases of the retina
Diseases of ocular motility
Glaucoma
Preventive ophthalmology
Investigations for ophthalmic diseases
Therapeutics
Paediatric ophthalmology
The diagnosis and management of common paediatric ophthalmic
conditions
Neuro-ophthalmology
Disorders of the visual pathways
Neuro-ophthalmic disorders of ocular motility
Ophthalmology in relation to medicine
Common neurological conditions affecting the eye
Endocrinology
Principles of resuscitation
Ophthalmic surgery
All surgery related to ophthalmology
11
SCHEDULES (TIMELINE)
PHASE I
Year 1
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Feb
Mac
Apr
May
Introduction
to eye
Basic
Science
Basic Sciences / Optics
Viva / Revision
Part I
exam
PHASE II
Year 2
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Feb
Mac
Apr
May
Presentations & Clinical session
1
st
Publication or
Case reports (1-3)
2
nd
Publication or
Case reports (4-7)
Present Research Proposal
Year 3
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Feb
Mac
Apr
May
Presentations & clinical session /
Medical & Neurology rotation (2 months)
Viva & clinical session
3
rd
Publication or
Case reports (8-10)
Pass up case
reports & log book
Part II
exam
PHASE III
Year 4
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Oct
Nov
Pass up 1
st
completed draft of
research report
Pass up corrected
copy of research
report
Research
report
presentation
Pass up final
copy of
research report
Dec
Jan
Feb
Mac
Apr
May
Pass up final copy
of publication or
case book
Pass up log book and obtain
supervisors approval to sit
for Part III exams
Part
III
exam
12
ASSESSMENTS
Assessments are carried out throughout the masters program from Year
1 to Year 4. Assessments serve as a guide to the trainee on what should be
achieved at different stages of the training. It also provides the trainee a means
to communicate any problems faced throughout different stages of the training
pertaining to the course.
These continuous assessments will be performed at specific intervals.
1. Supervisors report (at least twice a year)
2. End of rotation assessments (including medical and elective postings)
A log book is an official document which records information about all the
surgical and laser procedures that has been done by the trainee. The log book
should initially be submitted along with the case reports, one month before the
Part II examination and again before the Final Assessment. The initial submission
is for the supervisor to recognize any deficiency in the trainees surgical training
so that it will be rectified during the final year.
Trainees are recommended to use the Specialist Training in Ophthalmology
Personal Record and Surgical Logbook that can be obtained from the Academy
of Medicine of Malaysia. This is to ensure the continuity of the log book after
the trainee graduates and undergoes gazettement and may later undertake the
subspecialty training. It will also facilitate registration with the National Specialist
Registry. The logbook can be purchased from the academy.
13
SUPERVISORS REPORT
Master in Ophthalmology
Phase I Year 1
Name :
System : Open / Close
Hospital :
Supervisor :
Year of Entry :
Goals
Achievements
Comments
(student)
Comments
(supervisor)
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Assessment
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Assessment
Feb
Mac
Apr
May
Assessment
May
Part 1 Exam
14
Master in Ophthalmology
Phase II Year 1 (Starting after passing May Part I exams)
Name :
System : Open / Close
Hospital :
Supervisor :
Year of Entry :
Goals
Achievements
Comments
(student)
Comments
(supervisor)
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Assessment
1
st
Publication
or
Case reports
(1-3)
Research
proposal
presentation
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Assessment
Feb
Mac
Apr
May
Assessment
2
nd
Publication
or
Case reports
(4-7)
15
Master in Ophthalmology
Stage II Year 2 (Starting Year 2 in June after passing Part I Exams May)
Name :
System : Open / Close
Hospital :
Supervisor :
Year of Entry :
Goals
Achievements
Comments
(student)
Comments
(supervisor)
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Assessment
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Assessment
3
rd
Publication
or
Case reports
(8-10)
Feb
Mac
Apr
Assessment
Hand in
3 Publications
or
10 Case report
drafts to dept
by 1
st
February
May
Part II exam
16
Master in Ophthalmology
Phase III (Starting Year 4 in June after Passing Part II Exams in May)
Name :
System : Open / Close
Hospital :
Supervisor :
Year of Entry :
Goals
Achievements
Comments
(student)
Comments
(supervisor)
Jun
July
Aug
Sept
Assessment
Pass up
1
st
completed
copy of thesis
by 1
st
July
Pass up
corrected copy
of dissertation
by 1
st
August
Oct
Nov
Dec
Jan
Assessment
Pass up final
copy of
dissertation by
1
st
Nov
Pass up final
copy of case
book in
January
Feb
Mac
Apr
Assessment
Pass up
log book in
April
May
Final
assessment
17
CLINICAL POSTING ASSESSMENT FORM
Candidate : Supervisor(s) :
Posting/Rotation : Date :
No.
Competency
Level
(1-5)*
Comment by
supervisor
1
Inquiry skills (obtaining data information
from history, physical examination and
Investigations)
2 Problem solving and decision-making skills
3 Technical skills
4 Knowledge
5 Professional characteristics
6 Personal learning and assignments
7 Conduct and communication skills
8 Record keeping
9 Participation in teaching / learning activities
10 Leadership quality
Total for overall clinical competence**
* Level (1: Weak 2: Borderline 3: Satisfactory 4: Good 5: Excellent)
** Overall: Weak: < 15 Borderline: 15-19 Satisfactory: 20-29 Good: 30-39
Excellent: 40-50
*** For detail definition of each assessment, refer to individual university guidebook.
Overall comment / Recommendations by supervisor:
Supervisors signatures: Date:
Comment / Recommendations by Head of Department:
HOD signature: Date:
18
PROFESSIONAL EXAMINATION
PART I examination
Prerequisite
1. Successfully completed Phase I of the training program
2. Satisfactorily completed the log book
3. Obtained a satisfactory supervisor report
Component
A. Theory 50%
B. Clinical 30%
C. Optics and Refraction 20%
Section
Type
Number of Questions
Duration
%
marks
% to
total
marks
A
MCQ I
60 questions (Basic
Ocular Sciences, Optics
and refraction)
2 hrs
100
15
MCQ II
60 questions (Basic
Ocular Sciences, Optics
and refraction)
2 hrs
100
15
Essay
8 short notes questions
(Basic Ocular Sciences)
2 hrs 30 mins
100
20
Total for Theory 200 50
B
OSCE
10 stations
(Basic Ocular Sciences)
50 mins
100
15
Viva
1 session
(Basic Ocular Sciences)
30 min
100
15
Total for Clinical 200 30
C Clinical 1 case (Clinical refraction) 30 mins 100 10
OSCE
4 stations
(Optics & refraction)
20 mins
100
10
Total for Optics & Refraction 200 20
Grand Total 600 100
A candidate shall be deemed to pass the Part I examinations if he has obtained 50% or
more of the marks for each section of the examination and 45% or more of the marks for
each subsection of the examinations. A candidate is only allowed to obtain a borderline
mark (45.00 49.99%) in not more than one subsection under the same
section. A trainee who has failed the Part I examination may be permitted a second
attempt on
2 more occasions at 6 monthly intervals. The Part I examination must be passed not later
than twenty-four months from the date of initial registration as a candidate, failing which
the candidate shall be terminated forthwith from the course without notice.
19
PART II examination
Prerequisite
1. Successfully completed Phase II of the training program
2. Satisfactorily completed the log book
3. Satisfactory supervisor report and continuous assessments
4. Obtained ethical approval for research protocol at least 6 months before the
Part II examination
5. Submitted the first draft of 10 case reports or published/been accepted for
publication in journal according to merit points at least 3 months before the
Part II examination
Component
A. Theory 40%
B. Clinical 40%
C. Viva 20%
Section
Type
Number of Questions
Duration
%
marks
% to
total
marks
A MCQ I 60 questions 2 hrs 100 20
Essay
1 long essay &
4 short notes
1 hr 30 mins
100
10
Essay
1 long essay &
4 short notes
1 hr 30 mins
100
10
Total for Theory 200 40
B
Clinical
1 long case with refraction 1 hr 10 mins 100 15
6 short cases 30 mins 100 15
4 short cases
(Medicine in relation to OPH)
30 mins
100
10
Total for Clinical 300 40
C
Viva
Ophthalmology 30 mins 100 10
Medicine in relation to
Ophthalmology
30 mins
100
10
Total for Optics & Refraction 200 20
Grand Total 700 100
A candidate shall be deemed to pass the Part II examination if he has obtained 50% or
more of the marks for each section of the examination and 45% or more of the marks for
each subsection of the examinations. A candidate is only allowed to obtain a borderline
mark (45.00-49.99%) in not more than one subsection under the same section. A trainee
who failed the first attempt may be permitted a second attempt on 2 more occasions at 6
monthly intervals. A candidate who fails the examination on the third occasion shall not
be permitted to continue the course.
20
PART III examination
Prerequisite
1. At least one year after passing the Part II examination
2. Satisfactorily completed Phase III clinical training
3. Obtained a satisfactory supervisor report and continuous assessments
4. Submitted the research report not later than 6 months before the Final
Examination
5. Submitted case reports or publication (equivalent in merit points) not later
than 3 months before the Final Examination
6. Submitted the log book that has been certified 1 month before the Final
Examination
Assessment of dissertation
1. Research report will be evaluated by the internal, local and external examiners
appointed by the University.
2. Structure
a. Research Report
Oral presentation (20 min)
Viva (20 min)
b. Publication and Log Book (20 min)
3. Candidates should adhere to and make appropriate amendments and
corrections suggested by the examiners. A candidate is deemed to have
failed the examination if the amendments are not satisfactorily made within
the time given. Candidate may be permitted a second attempt on 2 more
occasions at 6 monthly intervals.
21
PUBLICATION AND PRESENTATION REQUIREMENTS
1. Publication
a. Case report / case series / letter to editor
Local journal 2 points
International journal 3 points
b. Original article
Local journal 3 points
International journal 4 points
c. Unpublished case report
1 case 1 point
*Minimum points for Publication is 10 points
2. Presentation
a. Oral presentation
Local 2 points
International 3 points
a. Poster presentation
Local 1 point
International 2 points
*Minimum points for Presentation is 5 points
22
APPENDIX 2
RECOGNISED CENTRES FOR TRAINING IN OPHTHALMOLOGY
SPECIALTY SUB-COMMITTEE OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
Application for departments to be recognised as centres for training in
Ophthalmology (w.e.f. 1
st
January, 2012)
Hospital / Institution:
Address:
Head of Department:
Date of Application:
A. GENERAL CRITERIA
THIS SECTION TO BE FILLED BY
APPLICANT
(FOR OFFICIAL USE)
THIS SECTION
TO BE FILLED BY
ASSESSOR
No.
Criteria
(Required criteria in brackets)
Data
on
Dept.
Meets
Minimum
Criteria
( / )
Notes
1. Total number of Ophthalmologists
registered in NSR
(A minimum of 2 is expected)
2. Total number of Medical Officer posts
filled
(A minimum of 4 including trainees)
3. Total number of beds for
ophthalmology including day care
(A minimum of 6)
23
4. Total number of Ophthalmology Clinic
sessions per week
(Minimum of 3)
5. Total number of operative sessions
per week
(Minimum of 2)
6. Total number of cataract surgeries
per month
(Minimum of 25)
7. Are microbiology services available?
(Yes) specify
8. Are biochemistry services available?
(Yes) specify
9. Are pathology services available?
(Yes) specify
10. Are diagnostic imaging services
available?
(Yes) specify
11. Is an anaesthetist available including
visiting?
(Yes) specify
12. Is there Intensive / Coronary Care
service available?
(Yes) specify
13. Is there a General Medical unit?
(Yes)
14. Is there a trauma / accident and
emergency unit?
(Yes)
24
B. SPECIFIC CRITERIA
No.
Names of Ophthalmologists in
Department
Postgraduate
Qualifications
and Year
Date
Registered
with National
Specialist
Register
1.
i.
ii.
iii.
iv.
v.
vi.
vii.
viii.
25
No.
Criteria
(Required criteria in brackets)
Data on
Dept
Meets
Minimum
Criteria ( / )
Notes
2. Annual workload of inpatients
(use previous year figures)
(should exceed 400)
3. Annual workload of new outpatient
cases (use previous year figures)
(should exceed 1500)
4. Annual workload of follow up cases
(use previous year figures)
(should exceed 6000)
5. Annual workload of major elective
operations done
(use previous year figures)
(should exceed 200)
6. Annual workload of minor operations
done (use previous year figures)
(should exceed 100)
7. Annual workload of emergency
operations done
(use previous year figures)
(should exceed 50)
8. Are surgical audits done in the
Department?
(minimum 3 per year )
9. Equipment
1. Total number of slit lamps
2. Total number of Binocular
Indirect Ophthalmoscope
3. Visual Field Analyser
26
4. A Scan
5. B Scan
6. Fundus Camera
7. Anterior segment camera
8. Other Imaging tools
(OCT/HRT/____________ )
9. Laser
(Type: Argon/YAG/_________ )
10. Indirect laser
11. Phacoemulsification
12. Operating Microscope
13. Vitrectomy machine
14. Others (specify)
10. Optometrist (minimum 1)
11. Technologist
12. Orthoptist
13. Number of Ophthalmology Textbooks
14. Number of Ophthalmic Journals
subscribed by Dept / Library
(state journals)
15. Internet facilities including access to
online journals (state journals)
16. Number of Ophthalmology CME
sessions per week
17. Will trainees be able to do hands on
surgical procedures on patients? (Yes)
18. Will there be an opportunity for
trainees to do a minimum of 20
cataract operations a year? (Yes)
19. Are there facilities for Wet Lab
Sessions? (Yes)
20. Will there be an opportunity for
trainees to participate in community
eye care projects
27
C. ADDITIONAL CRITERIA FOR CENTRES APPLYING FOR
OPHTHALMOLOGY SUBSPECIALTY TRAINING
Criteria Subspecialty
Department
Data
Remarks
1. Number of
practicing
subspecialty
trained
Ophthalmologist
with 2 years
experience
a. VR Surgery
b. Medical Retina
c. Glaucoma
d. Oculoplastics & Orbit
e. Cornea
f. Paediatric Ophthalmology
g. Neuro-Ophthalmology
h. Others (specify)
2. Number of
outpatient
subspecialty
visits per year
a. VR Surgery
b. Medical Retina
c. Glaucoma
d. Oculoplastics & Orbit
e. Cornea
f. Paediatric Ophthalmology
g. Neuro-Ophthalmology
h. Others (specify)
3. Number of
surgeries /
procedures
performed
per year
(for each
subspecialty)
a. VR Surgery
b. Medical Retina
c. Glaucoma
d. Oculoplastics & Orbit
e. Cornea
f. Paediatric Ophthalmology
g. Neuro-Ophthalmology
h. Others (specify)
28
4. Will there be
an opportunity
for candidates
to fulfill the
requirement
and gain
competency in
specified core
procedures?
Please state
YES/NO
a. VR Surgery
b. Medical Retina
c. Glaucoma
d. Oculoplastics & Orbit
e. Cornea
f. Paediatric Ophthalmology
g. Neuro-Ophthalmology
h. Others (specify)
Notes
1. Please enclose together with this application the following:
i. Previous 1 year census
ii. A list of key Ophthalmology textbooks and journals available in the
department/ Hospital
iii. A list of all teaching aids available in the Department (LCD projector, computers,
etc)
2. Period of Recognition
Recognition is given for a period of 3 years on condition that there are no
drastic changes in the minimum requirements during that period.
3. Recognition will be given as:
i. Suitable for General Ophthalmology training up to 6 months
ii. Suitable for General Ophthalmology training up to 6 years
iii. Suitable for Ophthalmology Subspecialty training
iv. Suitable for Specific Area of Training
4. Failure to gain recognition
If a department fails to get recognition, it will be informed in writing of the reasons.
The department may subsequently reapply when the requirements are met.
If criteria are lacking in any of the above, please state reasons why the department
should still be considered for recognition:
29
The Hospital/Institution agrees to pay expenses incurred should the Specialty
Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology decide to make a visit.
Hospital Ophthalmologist Date:
Official stamp:
Hospital Director Date:
Official stamp:
To be filled by representatives of the Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology:
Comments from visit (if visit is made):
30
RECOGNISED CENTRES FOR TRAINING IN OPHTHALMOLOGY
SPECIALTY SUB-COMMITTEE OF OPHTHALMOLOGY
Certification of the Department for Training in Ophthalmology
The Department of Ophthalmology of _____________________________
Hospital is granted / not granted recognition for training.
Recognition is granted as follows:
Suitable for General Ophthalmology training up to 6 months
Suitable for General Ophthalmology training up to 6 years
Suitable for Ophthalmology Subspecialty training
Suitable for Specific Area of Training in
from to
It is recommended that the total number of trainees in this department should not
exceed in number.
Reasons for not granting recognition:
Chairman, Date:
Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology
31
APPENDIX 3
CORE PROCEDURAL SKILLS
A. CLINICAL EXAMINATION SKILLS
No.
CORE PROCEDURES
Minimal Training necessary
for Competence
Observed Assisted Performed
1. Distant Vision including conversion 5
10
2. Near Vision 5
10
3. Visual assessment in children
Preferential looking
OKN
Matching
Objection to Occlusion
5
5
5
5
20
10
20
20
4. Colour - Vision Ishihara 2
Interpret
- 10
Perform
- 5
5. Colour - Vision D 15 2
Interpret
- 10
Perform
- 5
6. Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy including
contact and non contact lens
Optic disc and RNFL assessment
5
5
20
20
7. Intraocular Pressure measurement
and calibration of devices using:
- Applanation Tonometer
- Perkins Tonometer
- Tonopen
5
5
5
20
5
20
32
8. Pachymetry 2
10
9. Gonioscopy 3
30
10. Direct Ophthalmoscopy
20
11. Indirect Ophthalmoscopy with
indentation
5
20
12. Retinal Diagram 5
10
13. Extraocular Muscle Movements 5
20
14. Assessment of Nystagmus 5
5
15. Exophthalmometry 5
10
16. Visual Field Confrontation 5
20
17. Amsler Chart 5
20
18. Dry Eye Assessment 2
10
19. Placido Disc 2
10
20. Cover Test 5
20
21. Prism Cover Test 5
20
33
B. BASIC CLINICAL OPTOMETRY SKILLS
No.
CORE PROCEDURES
Minimal Training necessary for
Competence
Observed
Assisted
Performed
1. Refraction Retinoscopy
+ subjective refraction
Myopia (including high myopia)
Hyperopia
Myopia/Astig
Hyperopia/Astig
Astigmatism only
Pseudophakia
Aphakia
5
20
2. RAF Rule including Interpretation 5
10
3. Use of Focimeter 5
10
4. Use of Autorefractometer 2
10
5. Keratometry 5
30
6. Insertion and removal of Contact
Lenses
5
5
7. Contact lens fitting 5
10
8. Exposure to Low Vision Devices 5 5
34
C. OPHTHALMIC DIAGNOSTIC SKILLS
No.
CORE PROCEDURES
Minimal Training necessary for
Competence
Observed
Assisted
Performed
1. Bjerrum Perimetry 2
Interpret
- 10
Perform
- 5
2. Automated Perimetry 3
Interpret
- 30
Perform
- 5
3. Hess Chart 2
Interpret
- 10
Perform
- 5
4. A Scan and IOL Power Calculation 5
Interpret
- 30
Perform
- 30
5. Ocular Photography
- External
- Ant. Segment
- Optic disc
- Fundus
3 for each
5 for each
6. B Scan basic Interpretation 5
20
7. HRT 3
Interpret
- 20
8. OCT
- Macular
- Optic Disc
5
5
Interpret
- 20
- 20
9. Electrophysiology Tests 2
Interpret
- 5
10. Corneal topography 5
10
11. 100 Hue Colour Vision Test 2
Interpret
- 5
12. Fundus Fluorescein Angiography 5
Interpret
- 20
Perform
- 5
35
D. SURGICAL / PROCEDURAL SKILLS
No.
CORE / SPECIALISED
PROCEDURES
Minimal Training necessary
for Competence
Observed
Assisted
Performed
1. Eye Irrigation 3
10
2. Syringing and Probing
- Adults
- Paeds
5
3
20
3
3. I&C and I&D 3 7 10
3 in
Paeds
4. Lid T&S not involving lid margin 5 7 10
5. Entropion / Ectropion primary repair
2 2
6. STO Cornea / Lids 5
10
7. Tarsorraphy 5 5 5
8. DCR 2 3
9. Brow suspension
2
10. Excision of lid / eyebrow lesions 5 5 5
11. Lateral canthotomy 1
1
12. Removal of corneal / conjunctival
Foreign Body
3
10
13. Conjunctival Graft 3 5 10
14. Excision of pterygium / conjunctival
lesions
5 5 10
15. Harvesting buccal mucosa 3
16. Amniotic membrane transplant 3
17. Corneal Scraping 3
10
36
18. Glueing of corneal perforation 2 1 5
19. Corneal and Scleral T&S 3 5 10
20. Retrieval and processing of donor
eyes
1 1 1
21. Penetrating Keratoplasty 3
22. AC tap / Paracentesis /
Intracameral Injections
3
5
23. Laser Iridotomy 5
20
24. Laser Argon laser peripheral
iridoplasty
5
5
25. Cyclophotocoagulation 5
10
26. Laser suturelysis 3
27. YAG Laser Capsulotomy 5
10
28. Trabeculectomy / phaco
trabeculectomy +/- anti-metabolite
(primary, not repeat)
5 5
29. Glaucoma Drainage Device 3
30. Paediatric Glaucoma Surgeries
3
31. Paediatric Lens aspiration (limited
to children above 6 years of age)
3 3
32. ECCE (including converted phaco
cases)
5 5 20
33. Phacoemulsification 10 40 50
34. ROP Screening
10 50
35. EUA Paediatric
3 10
36. Retinoblastoma management / EUA 3
37. Pan Retinal Photocoagulation 3
50
37
38. Focal / Grid Laser 5
10
39. Laser to retinal breaks / lattice 3
10
40. Indirect Laser Photocoagulation
- Adults
- Premature infants
3
3
10
41. Cryopexy 3 3 3
42. Vitreous tap 3
5
43. RRD Surgery including sclera
buckling (Primary repair)
5
44. Vitreous Surgery 5
45. Insertion and removal of eye
prosthesis
3
5
46. Evisceration /
Enucleation without orbital implant
2
2
1
1
47. Evisceration /
Enucleation with implant
2
48. Exenteration 1
49. Squint surgery
- Adults
- Horizontal Squint in Paeds
patient
5
3
50. Subconjunctival Injection 5
10
51. Orbital Floor Injection 3
3
52. Intravitreal injection 3
5
53. Injection of anti-metabolite
(including preparation and disposal)
3
54. Injection of local anaesthesia
(peribulbar / retrobulbar / subtenon)
5
10
38
OPTHALMOLOGY SURGICAL AND PROCEDURAL SKILLS (for
fulfillment of Specialist Registration)
No CORE / SPECIALISED PROCEDURES
1. Eye Irrigation
2. Syringing and Probing
-Adult
-Paeds
3. I&C and I&D
4. Lid T&S not involving lid margin
5. Entropion / Ectropion primary repair
6. STO Cornea / Lids
7. Tarsorraphy
8. Excision of lid / eyebrow lesions
9. Lateral canthotomy
10.
Removal of corneal / conjunctival
foreign Body
39
11. Conjunctival Graft
12. Excision of pterygium / conjunctival lesions
13. Corneal Scraping
14. Glueing of corneal perforation
15. Corneal and Scleral T&S
16. Retrieval and processing of donor eyes
17. AC tap / Paracentesis / Intracameral Injections
18. Laser Iridotomy
19. Laser - Argon laser peripheral iridoplasty
20. Cyclophotocoagulation
21. Laser suturelysis
22. Laser Capsulotomy
23. Paediatric Lens aspiration (limited to children
above 6 years of age)
40
24. ECCE (including converted phaco cases)
25. Phacoemulsification
26. ROP Screening
27. EUA - Paediatric
28. Pan Retinal Photocoagulation
29. Focal / Grid Laser
30. Laser to retinal breaks / lattice
31. Indirect Laser Photocoagulation
-Adult
-Premature infants
32. Cryopexy
33. Vitreous tap
34. Insertion and removal of eye prosthesis
35. Evisceration /
Enucleation without orbital implant
41
36. Subconjunctival Injection
37. Orbital Floor Injection
38. Intravitreal injection
39. Injection of local anaesthesia
(peribulbar / retrobulbar / subtenon)
42
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
The Specialty Sub-Committee of Ophthalmology:
Dr. Pall Singh (Chairperson)
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wan Hazabbah Wan Hitam
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mimiwati Zahari
Dr. Bethel Indira Livingstone
Dr. Anusiah Selvathurai
Dr. Elias Hussein
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Andrew Tan Khian Khoon
Dato Dr. Y C Lee
The Specialty Training Committee:
Dr. Bethel Indira Livingstone (Chairperson)
Dr. Anusiah Selvathurai
Dr. Pall Singh
Dato Dr. Y C Lee
Dr. Mariam Ismail
Dr. Elias Hussein
Prof. Dr. Ropilah Abdul Rahman
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mohtar Ibrahim
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mimiwati Zahari
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Wan Hazabbah Wan Hitam
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mae-Lynn Catherine Bastion
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Andrew Tan Khian Khoon
Assoc. Prof. Dr. Choo May May
Prof. Dato Dr. Veera Ramani
Dr. Goh Pik Pin
Datin Dr. Rusnah Hussin
Dr. Thayanithi A/P K. Sandragasu
43
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- NATIONAL OPTOMETRY BOARDS (NOB) Part I BASIC SCIENCE: Passbooks Study GuideVon EverandNATIONAL OPTOMETRY BOARDS (NOB) Part I BASIC SCIENCE: Passbooks Study GuideNoch keine Bewertungen
- Regulations Relating To The Surgical Fellowship Examination in Ophthalmology Parts 1, 2 and 3Dokument13 SeitenRegulations Relating To The Surgical Fellowship Examination in Ophthalmology Parts 1, 2 and 3NoorNoch keine Bewertungen
- Scientific Foundations of OphthalmologyVon EverandScientific Foundations of OphthalmologyEdward S. PerkinsNoch keine Bewertungen
- Guia para Estudiar para IcoDokument16 SeitenGuia para Estudiar para IcoMaria Silvana Sequera LampeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Ophthalmology: Instructions For CandidatesDokument16 SeitenClinical Ophthalmology: Instructions For CandidatesdrlawrencekindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- 003 Part 1 FRCOphth Examination Application Pack 2012Dokument28 Seiten003 Part 1 FRCOphth Examination Application Pack 2012Farrukh Ali Khan100% (1)
- Dnb-Ophthalmology: Competency Based Training ProgrammeDokument33 SeitenDnb-Ophthalmology: Competency Based Training ProgrammeRakhiDcruzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Reviews in Ophthalmology Expert Consult - OnlDokument2 SeitenCase Reviews in Ophthalmology Expert Consult - Onldr. mostakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Based Ophthalmology GuideDokument12 SeitenCase Based Ophthalmology GuideGradestack100% (2)
- Ico Inst BK Visual SC 2018 Rev2Dokument20 SeitenIco Inst BK Visual SC 2018 Rev2drlawrencekindoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology CurriculumDokument71 SeitenOphthalmology CurriculumEdoga Chima EmmanuelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ophthalmology Revision LectureDokument80 SeitenOphthalmology Revision LectureCarla LaniganNoch keine Bewertungen
- 014 Duke Elder Examination Information For Candidates 2013Dokument9 Seiten014 Duke Elder Examination Information For Candidates 2013PartialChargeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric Ophthalmology Anatomy and ExaminationDokument21 SeitenPediatric Ophthalmology Anatomy and ExaminationGlydenne GayamNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pediatric OphthalmologyDokument12 SeitenPediatric Ophthalmologyapi-3743483Noch keine Bewertungen
- I Notes StrabismusDokument92 SeitenI Notes StrabismusPrincess EzzlynnNoch keine Bewertungen
- 432 OSCE Revision File PDFDokument20 Seiten432 OSCE Revision File PDFReza Affandi MohamadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Share Myopia Mcqs'sDokument4 SeitenShare Myopia Mcqs'sshumaila khan50% (2)
- Common Eye Problems and DiagnosisDokument84 SeitenCommon Eye Problems and Diagnosisvivekrajbhilai5850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Rana Al-Senawi - Arab Board 2014 Exam ExprinceDokument5 SeitenRana Al-Senawi - Arab Board 2014 Exam ExprinceMuhammed AbdulmajeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Case in Contact Lenses, 1e - 2001Dokument205 SeitenClinical Case in Contact Lenses, 1e - 2001Miguel PalaciosNoch keine Bewertungen
- Short Answer Questions For The MRCOphth Part 1Dokument159 SeitenShort Answer Questions For The MRCOphth Part 1Yaman Muhaisen100% (1)
- Viva and Osce Exams in Ophthalmology A Revision Study Guide 1st Ed 9783030430627 9783030430634 CompressDokument392 SeitenViva and Osce Exams in Ophthalmology A Revision Study Guide 1st Ed 9783030430627 9783030430634 CompressstingbeesparvNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lecture VI Binocular RefractionDokument17 SeitenLecture VI Binocular Refractionhenok biruk100% (1)
- Notes in Ophthalmology: MCQ, Osce, SlidDokument21 SeitenNotes in Ophthalmology: MCQ, Osce, SlidDrmhdh DrmhdhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Okap Samson Uveitis PDFDokument12 SeitenOkap Samson Uveitis PDFsharu4291Noch keine Bewertungen
- KERATOCONUSDokument22 SeitenKERATOCONUSAarush DeoraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Optics Made EasyDokument52 SeitenOptics Made EasyKwaku Afriyie KyeiNoch keine Bewertungen
- 16.retinal Detachment PDFDokument42 Seiten16.retinal Detachment PDFFrederica MutiaraNoch keine Bewertungen
- February April 2009 Part 2 FRCOphth Examination Final ReportDokument20 SeitenFebruary April 2009 Part 2 FRCOphth Examination Final Reportsafasayed0% (1)
- Bacterial and Viral ConjunctivitisDokument31 SeitenBacterial and Viral ConjunctivitisSiddhant GautamNoch keine Bewertungen
- I Notes RETINA PDFDokument251 SeitenI Notes RETINA PDFFelipe renquenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cycloplegic Refraction in Optometric Practice 1337594763401 2Dokument14 SeitenCycloplegic Refraction in Optometric Practice 1337594763401 2Strauss de LangeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part 1 FRCOphth Sample MCQs 20160818 PDFDokument15 SeitenPart 1 FRCOphth Sample MCQs 20160818 PDFAbdurrehman100% (1)
- 2020 Part 1 FRCOphth Information Pack PDFDokument29 Seiten2020 Part 1 FRCOphth Information Pack PDFABID ALINoch keine Bewertungen
- Esotropia PDFDokument41 SeitenEsotropia PDFputriNoch keine Bewertungen
- Speaking Topics From Past PapersDokument109 SeitenSpeaking Topics From Past PapersSukhdev Sunita Gautam100% (1)
- Case Studies PresbyopiaDokument33 SeitenCase Studies PresbyopiaMalaika ZubairNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eye Docs UveitisDokument90 SeitenEye Docs UveitisMuneeb ShahzadNoch keine Bewertungen
- or Read: Ophthalmology Mcqs With Answers PDF EbookDokument4 Seitenor Read: Ophthalmology Mcqs With Answers PDF Ebookarian tejaratNoch keine Bewertungen
- Direct OphthalmoscopeDokument16 SeitenDirect OphthalmoscopeMuhammed AbdulmajeedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Field InterpretationDokument52 SeitenVisual Field InterpretationUlquiorra Schiffer100% (1)
- Opinioes Exames Ebo e IcoDokument8 SeitenOpinioes Exames Ebo e Icoapi-3595301060% (1)
- Clinical OpticsDokument88 SeitenClinical OpticsKris ArchibaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Soft Toric LensesDokument5 SeitenSoft Toric Lensesdoni anandaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CPG 19Dokument78 SeitenCPG 19anon-24970100% (1)
- Pediatrics: The Eyes Have ItDokument14 SeitenPediatrics: The Eyes Have ItDrSyed Rahil IqbalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Glaucoma and LensDokument4 SeitenGlaucoma and Lenssarguss14Noch keine Bewertungen
- 15 Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy 2Dokument36 Seiten15 Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy 2Sri Rama Chandra ManchikantyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Step by Step Pediatric Cataract SurgeryDokument358 SeitenStep by Step Pediatric Cataract SurgeryAndrés QueupumilNoch keine Bewertungen
- Keratometer Easy To Understand PDFDokument2 SeitenKeratometer Easy To Understand PDFDanielle SangalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- Opthhalmology Examination ReviewDokument12 SeitenOpthhalmology Examination ReviewFaiq Syukri Bin SaparudinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Clinical Optometry Primary Eye CareDokument3 SeitenClinical Optometry Primary Eye CareDanielle SangalangNoch keine Bewertungen
- MCQ OphthalmologyDokument56 SeitenMCQ Ophthalmologypriya00991% (11)
- Fundamentals and Principles of Ophthalmology: Basic and Clinical Science CourseDokument4 SeitenFundamentals and Principles of Ophthalmology: Basic and Clinical Science Coursenuryusri99Noch keine Bewertungen
- Visual Field InterpretationsDokument35 SeitenVisual Field InterpretationsAhmadhassan RanaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anomalie VisionDokument13 SeitenAnomalie VisionblueiceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ocular Manifestations of Thyroid DiseaseDokument20 SeitenOcular Manifestations of Thyroid Diseasevivekrajbhilai5850Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nungki-Esodeviations & ExodeviationsDokument36 SeitenNungki-Esodeviations & ExodeviationsNia RoosdhantiaNoch keine Bewertungen
- ParagraphDokument12 SeitenParagraphVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Inggris - AdjectiveDokument7 SeitenInggris - AdjectiveUbaidillah HafidzNoch keine Bewertungen
- Pharmacology of Asthma Farmakologi Compatibility ModeDokument39 SeitenPharmacology of Asthma Farmakologi Compatibility ModeLuthfiy IrfanasruddinNoch keine Bewertungen
- K - 2 Chronic Respiratory DiseasesDokument21 SeitenK - 2 Chronic Respiratory DiseasesVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPP1M Terms ConditionsDokument1 SeiteSPP1M Terms ConditionsVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- BedahDokument57 SeitenBedahBella OktavianiNoch keine Bewertungen
- History TakingDokument26 SeitenHistory TakingVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome in A Premature BabyDokument29 SeitenRespiratory Distress Syndrome in A Premature BabyVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome in A Premature BabyDokument29 SeitenRespiratory Distress Syndrome in A Premature BabyVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 7 TrigeminalNeuralgiaDokument2 Seiten7 TrigeminalNeuralgiaVissalini JayabalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Dental MneumonicDokument30 SeitenDental Mneumonictmle44% (9)
- Comparison of Ftir Apodization Functions Using Modeled and Measured Spectral DataDokument4 SeitenComparison of Ftir Apodization Functions Using Modeled and Measured Spectral Dataገዛኽኝ ሱፋNoch keine Bewertungen
- Watchtower: What Say The Scriptures About Spiritualism - Proofs That Its Demonism - 1897Dokument126 SeitenWatchtower: What Say The Scriptures About Spiritualism - Proofs That Its Demonism - 1897sirjsslutNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Council of Nicaea and The History of The Invention of ChristianityDokument10 SeitenThe Council of Nicaea and The History of The Invention of Christianitybearhunter001Noch keine Bewertungen
- 4TH Semester B.A., LL.B B.A., LL.B (H)Dokument14 Seiten4TH Semester B.A., LL.B B.A., LL.B (H)BISTIRNA BARUANoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Regulating Activities by UnyteDokument14 SeitenNervous System Regulating Activities by UnytehellozenbokNoch keine Bewertungen
- John Zink - Flare - Upstream - ProductionDokument20 SeitenJohn Zink - Flare - Upstream - ProductionJose Bijoy100% (2)
- Katehi Grievance LetterDokument12 SeitenKatehi Grievance LetterSacramento BeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cold Calls Excerpt by Charles BenoitDokument25 SeitenCold Calls Excerpt by Charles BenoitHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Balance of Power in World Politics TDokument23 SeitenThe Balance of Power in World Politics TVali IgnatNoch keine Bewertungen
- DPP-Control and Coordination (Prashant Kirad)Dokument9 SeitenDPP-Control and Coordination (Prashant Kirad)ABHI TECH 983Noch keine Bewertungen
- Phed 239 Syllabus s14-1st Half-3Dokument7 SeitenPhed 239 Syllabus s14-1st Half-3api-249627241Noch keine Bewertungen
- Ucsp Module 6 W:B Answer SheetDokument5 SeitenUcsp Module 6 W:B Answer SheetAl Cheeno Anonuevo100% (1)
- English Grammar Book-Final - 2-5-21Dokument42 SeitenEnglish Grammar Book-Final - 2-5-21Manav GaurNoch keine Bewertungen
- FACIAL NERVE ParalysisDokument35 SeitenFACIAL NERVE ParalysisIgnasNoch keine Bewertungen
- Theri GathaDokument26 SeitenTheri GathaLalit MishraNoch keine Bewertungen
- GRADE 8 3rd Quarter ReviewerDokument9 SeitenGRADE 8 3rd Quarter ReviewerGracella BurladoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Appeal For Exclusion COA For An Act Committed in Good FaithDokument13 SeitenAppeal For Exclusion COA For An Act Committed in Good FaithPj Tigniman100% (6)
- Ieo Sample Paper Class-10Dokument2 SeitenIeo Sample Paper Class-10jairusr100% (1)
- National Social Protection Strategy GhanaDokument95 SeitenNational Social Protection Strategy GhanaSisiraPinnawalaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Principal Parts of Greek Verbs Appearing in James SwetnamDokument8 SeitenPrincipal Parts of Greek Verbs Appearing in James Swetnammausj100% (1)
- Table of Contents COPY 1 2Dokument15 SeitenTable of Contents COPY 1 2Keann Nicole SearesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Customer Communication.Dokument3 SeitenCustomer Communication.wilson wambuguNoch keine Bewertungen
- Jurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialDokument11 SeitenJurnal Teori Pertukaran SosialRhama PutraNoch keine Bewertungen
- Cisco SF300Dokument401 SeitenCisco SF300Rodney PolingNoch keine Bewertungen
- 11 Rabino v. Cruz 222 SCRA 493Dokument4 Seiten11 Rabino v. Cruz 222 SCRA 493Joshua Janine LugtuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Metabarons Univers GuideDokument155 SeitenMetabarons Univers Guidebilou hertNoch keine Bewertungen
- IEM Notes Unit-2Dokument2 SeitenIEM Notes Unit-2Ashish YadavNoch keine Bewertungen
- Examples in C++Dokument39 SeitenExamples in C++ZhvannNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brand Management Bacardi SamveditaDokument32 SeitenBrand Management Bacardi SamveditaSamvedita IndrajeetNoch keine Bewertungen