Beruflich Dokumente
Kultur Dokumente
Reflexes - What? How?: Biology
Hochgeladen von
samsunglover0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten9 Seitenschool books
Originaltitel
cha_02
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
PDF, TXT oder online auf Scribd lesen
Dieses Dokument teilen
Dokument teilen oder einbetten
Stufen Sie dieses Dokument als nützlich ein?
Sind diese Inhalte unangemessen?
Dieses Dokument meldenschool books
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
0 Bewertungen0% fanden dieses Dokument nützlich (0 Abstimmungen)
17 Ansichten9 SeitenReflexes - What? How?: Biology
Hochgeladen von
samsungloverschool books
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Verfügbare Formate
Als PDF, TXT herunterladen oder online auf Scribd lesen
Sie sind auf Seite 1von 9
24
BIOLOGY
Why did the driver apply brakes when
he saw just a wild cat?, responded a
student while reading the news.
Don't you too make sudden responses to
unexpected situations? Enlist such
situations.
The sudden withdrawal of legs while
stepping on fire accidentally.
You have already learnt about conscious
responses to the changes in the
surroundings. But responses need not
always be conscious. Analyse the science
article given below and list out, in order,
the activities that take place in the body
when sudden responses are made.
Arrange the enlisted data as a flow chart
in your Science diary.
Reflexes - What? How?
Reflex actions are sudden, involuntary reactions of the body in response to stimuli. They
occur without the involvement of the conscious areas of the brain. Therefore, all reflex
actions are unconscious actions. Reflex actions occur both from the brain and spinal
cord which are the parts of the central nervous system.
BIG TRAGEDY AVERTED
July15. The Neelimala road, an accident-prone area, with hair
pin curves and steep slopes, is again in the news. This time the
accident occurred when a wild cat jumped in front of a bus full
of passengers. Seeing the cat unexpectedly before him, the
driver applied the brake suddenly. The bus ran out of control
and was about to fall into a precipice when it hit against a mud-
wall. A great disaster was thus averted.
Fig - 2.1. Spinal cord
central canal
white matter dorsal root
ventral root grey matter
25
BIOLOGY
However, these actions are mainly formed from the spinal cord. The vertebral column
protects the spinal cord just as the skull protects the brain. Like the brain, the spinal cord
too has a covering of meninges. The central canal and the space between the layers of
meninges are filled with the cerebrospinal fluid. When sudden responses are required,
instructions are given by the spinal cord itself. Impulses reach the brain only after that.
Subsequently conscious responses are made. Reflex arc is the path of impulses in the
reflex action.
Reflexes formed from the brain are called cerebral reflexes. Blinking of the eye is a
cerebral reflex.
Reflexes may also be developed through constant practice and experience. The
application of sudden brakes by the driver and salivation at the thought of tasty food are
examples. Such responses are called conditioned reflexes.
Fig. 2.2. Reflec arc
The hand is
withdrawn by the
action of the muscle
The fingertip
unknowingly
touches a thorn.
The receptors
there become
excited.
Sensory neuron
carries impulses to
the spinal cord.
Motor neuron
carries the messages
from the spinal cord to
the effector muscles.
Inter neuron
connects the sensory
neuron and the motor
neuron.
26
BIOLOGY
List the changes in the physiological
activities of the boy running away from
the dog.
Rate of heart beat increases
Breathing rate increases
What might be the changes in the body
after he finds relief?
.....................................................................
Do you know why such changes take place
in the body?
In critical situations, reflex actions serve as a defence mechanism also. In such situations,
the nervous system as a whole becomes more alert. As a result physiological activities
may also change.
Look at the following cartoon
The Mastermind of Unconscious Activities
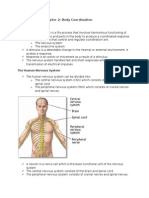
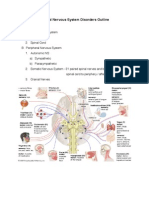
Our nervous system can be divided into two. The Central Nervous System (CNS) and
the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS). CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
Conscious decisions required for physiological activities are mainly formed in the brain.
However, in emergency situations immediate decisions are taken by the spinal cord.
Nerves connecting the central nervous system to the organs of the body constitute the
peripheral nervous system.
There are many activities which occur beyond our conscious area. Such activities are
controlled by the Autonomous Nervous System (ANS) which is a part of the peripheral
nervous system. The autonomous nervous system is composed of the Sympathetic
System and the Parasympathetic System. The sympathetic and parasympathetic
systems supply nerve fibres to most of the internal organs.
Observe the Figure, compare the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic
systems and prepare notes. Complete Table.2.1.
Vow....!
Alas!
27
BIOLOGY
Haven't you understood that the sympathetic system equips the body to face critical
situations? After overcoming the crisis, the parasympathetic system brings
physiological activities back to normal state.
We have learnt the role of the nervous system and the functions of its different parts in
sensing the changes taking place in the surroundings and responding to them
accordingly. But changes take place every moment not only in the external environment
but in the internal environment too. All these are internal stimuli. Some of them are
given below.
Actions of the sympathetic system Actions of the parasympathetic
when the boy runs away from the dog system when the boy finds relief.
Table-2.1
Secretion of saliva
decreases
Trachea
dilates
Functions of the
Stomach slow
down
Hormone secretion
increases
Peristalsis slows
down
Urinary bladder
regains the original
relaxed state
Rate of heart beat
decreases
Parasympathetic system Sympathetic system
Fig. - 2.3 Autonomous nervous system-Actions
Pupil dilates
Pupil constricts
Secretion of saliva
increases
Rate of heart
beat increases
Trachea constricts
Functions of the
stomach is stimulated
Hormone secretion
decreases
Peristalsis is enhanced
Urinary bladder
contracts
spinal cord
Sympathetic ganglia
Glycogen is converted
into glucose
Glucose is converted
into glycogen; secretion
of bile is enhanced
28
BIOLOGY
Variation in blood pressure
Change in water content
Change in CO
2
level
Receptors capable of perceiving such
stimuli are present in the internal organs
and muscles. For example, chemoreceptors
and baroreceptors. Excitation of these
receptors leads to the generation of
impulses which in turn will cause the
corresponding organs to act accordingly.
So far we have learned about the role of
the nervous system in perceiving stimuli
from the surroundings and from within
the body, and making responses. How do
the different parts of the nervous system
act in a co-ordinated manner? Analyze the
following illustration based on the
indicators, and complete the flow chart
given below.
Indicators
What are the parts of the central nervous system?
What are the parts included in the peripheral nervous system?
How does the brain communicate with organs?
How does the spinal cord communicate with organs?
Illustration-2.1
Brain
Organs
Cranial nerves (12 pairs)
Spinal nerves (31pairs)
Spinal cord
C
e
n
t
r
a
l
N
e
r
v
o
u
s
S
y
s
t
e
m
P
e
r
i
p
h
e
r
a
l
N
e
r
v
o
u
s
S
y
s
t
e
m
Nervous system
Peripheral
nervous system
29
BIOLOGY
The health of the nervous system is
essential for mental and physical well-
being. The health of the nervous system
may get disrupted due to several reasons.
You know about diseases like stroke and
paralysis. But there are many other
conditions that also adversely affect the
nervous system.
Alzheimer disease
This disease is caused by a continuous
degeneration of neurons in the brain. It
happens due to the accumulation of an
insoluble protein in the form of plaque in
nervous tissues. The chief symptom of the
disease is the complete loss of memory.
Even the memory regarding the day, date
and details about oneself like where one
is, who one's family members are, etc. are
lost. As a result, the working of the mind
topples. The patient becomes unaware of
his action or his behaviour towards others.
Gradually this leads to death. Even though
this disease is more common among aged
people, it may also affect people below
60. In this condition the patient needs the
presence and attention of others. Let's
hope that medical science will soon be
able to conquer this disease which is a
threat to individual health and
community health as a whole.
Parkinson disease
This disease is caused by the
degeneration of specific ganglions in the
brain. It results from the deficiency of a
neurotransmitter called dopamine. The
symptoms of this disease include tremor
due to the irregular movement of
involuntary muscles, uncontrolled flow of
saliva and the loss of balance of the body
due to the defective co-ordination of
muscular activities. Patients develop an
aversion to life and also depression.
Though treatment using dopamine is
possible a complete cure can not be
expected.
Epilepsy
The disease is caused by the irregularity
in the electric impulse in the brain. Fits due
to frequent and uncontrolled muscular
contractions and unconsciousness are the
symptoms. During the fits that may last for
seconds or minutes, clenching of the teeth,
biting of the tongue and frothy discharge
from the mouth are common. Today,
epilepsy is treated effectively with
medicines. However, medicines are to be
taken regularly.
A complete cure through treatment is not
possible for several diseases affecting the
nervous system. Those who nurse such
patients are to be extremely careful and
considerate. They must develop an
attitude of mind that will enable them to
look after the patients patiently, taking
into account their helpless and pathetic
condition. Only then we can attain
humaneness, the noble quality that a
higher state of brain entitles.
Discuss how we should behave with
people who suffer the pangs of various
diseases. Prepare a note and record it in
the Science diary.
The mechanisms to act according to the
changes that take place every moment in
the surroundings and within the body are
seen in other animals too. Analyse the
given descriptions and form inferences
about them.
30
BIOLOGY
In Unicellular Organisms
In unicellular organisms, plasma membrane and cytoplasm
play a major role in perceiving stimuli and emiting
responses. Chlamydomonas and euglena have specific
parts known as eyespot to detect the presence of light.
Seeing through sound too
Bats are not blind. They move during night not by seeing but
sensing the obstacles in their way. They produce sound
waves of high frequency. Since these sound waves cannot
be heard by us they are called ultrasonic sound. These waves
strike the objects ahead and bounce back. Analysing this
echo, the bat can interpret the exact position, distance, nature
etc. of the object.
Eyes - how many?
The eye of insects is made up of thousands of minute eyes
cal l ed ommati di a. On the outer surface of each
ommatidium, there is a lens with six sides. Behind it is
found a transparent conical structure below which
photosensitive (light sensitive) cells are seen. The image
formed in the eyes of insects is erect. Impulses from each
ommatidium reach the brain. The brain integrates thousands
of images and makes vision possible.
Eye Spot
Fig - 2.4
Fig - 2.5
Fig - 2.6
Fig - 2.7
Nervenet
Hydra is a multicellular organism having a simple structure. In
hydra nerve cells are extended all over the body like a net. It
is through this nervenet that communication between the body
and the external environment and elicitation of responses take
place.
31
BIOLOGY
Why hear?
Snakes do not have the power to hear. When the snake-
charmer plays the blow pipe (makudi) they dance not
because they hear the music, but to the movements of the
pipe. Snakes can sense the vibrations on the ground. They
frequently extend the tongue to sense the smell. Olfactory
particles that stick on to the tongue are received by the
receptors in a special organ called Jacobsons organ
situated in the roof of the mouth and the smell is detected.
The highly sensitive thermoreceptors in viper, python etc.,
help them to detect the presence of other animals at night.
The living world is full of many such wonders. Collect information about them and
prepare a magazine on the communication systems in animals. Whatever the diversities
be, responding to changes is the chief attribute of life. This attribute is common to all
organisms. This is one of the similarities that binds organisms with one another.
Fig.2.8.
Can't see, but ...
Even though plants cannot see things, they are able to sense
the presence of light and respond to it. In plants the green
pigment chlorophyll is synthesized in the presence of light.
This phenomenon is called photomorphogenesis. You have
learnt about the tip of the stem growing towards light. Light
influences flowering and in some plants seed germination
also. Plants are equipped for such responses by the protein
pigment called phytochrome.
Fig.2.9.
32
BIOLOGY
Follow up Activities
1) Analyse the following situations and answer the following questions.
Unknowingly touched fire
Experienced pain
Withdrew the hand
Applied antiseptic on burnt part
(a) Enlist the stimuli and responses
(b) Which is the conscious response?
(c) Is it after experiencing pain that the hand is withdrawn? Justify your opinion.
(d)List sequentially the parts through which impulses pass while experiencing
pain.
(e) Illustrate reflex arc.
2) "The sympathetic system and the parasympathetic system act like the accelerator
and brake of a vehicle". Evaluate whether this statement is completely true and
note down your opinion.
3) Analyse the following statements.
a) Other organisms do not have the ability to receive stimuli as man.
b) Even though nerves are absent, unicellular organisms can respond to stimuli.
Das könnte Ihnen auch gefallen
- Brain Facts Book PDFDokument96 SeitenBrain Facts Book PDFjlangseth100% (1)
- Lesson 6 - Musculoskeletal and Nervous SystemsDokument20 SeitenLesson 6 - Musculoskeletal and Nervous Systemsapi-307592530Noch keine Bewertungen
- Tract Continues Down Spinal Cord: Input Location Notes Lesion MedullaDokument10 SeitenTract Continues Down Spinal Cord: Input Location Notes Lesion MedullaherethemindNoch keine Bewertungen
- Histology of The TongueDokument13 SeitenHistology of The Tonguehendri100% (2)
- Brain CellsDokument4 SeitenBrain CellsJulius RicardeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement For Installation of Electrical DBDokument6 SeitenMethod Statement For Installation of Electrical DBsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Vagus Nerve Exercises To Rewire Your Brain: Stimulate Your Vagus Nerve With Natural Self-Healing Daily Exercises For Anxiety, Depression, Trauma & OverthinkingVon EverandVagus Nerve Exercises To Rewire Your Brain: Stimulate Your Vagus Nerve With Natural Self-Healing Daily Exercises For Anxiety, Depression, Trauma & OverthinkingNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Human BrainDokument27 SeitenThe Human BrainManuel Colindres 2.0Noch keine Bewertungen
- General Principles of GIT PhysiologyDokument22 SeitenGeneral Principles of GIT PhysiologyUsman Ali AkbarNoch keine Bewertungen
- This Paper Elaborates On The Various Methods of Cable Laying and The Advantages and Disadvantages of The SameDokument15 SeitenThis Paper Elaborates On The Various Methods of Cable Laying and The Advantages and Disadvantages of The SamesamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement For The Installation of Power and Lighting System WiringDokument4 SeitenMethod Statement For The Installation of Power and Lighting System Wiringsamsunglover0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BrainDokument22 SeitenAnatomy and Physiology of The BrainJonathan Delos ReyesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Just Breathe:: Breathing For HealthDokument14 SeitenJust Breathe:: Breathing For HealthmailbabuNoch keine Bewertungen
- Daily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreVon EverandDaily Vagus Nerve Exercises For Self-Healing (2 in 1): Natural Techniques & Habits To Help With Anxiety, Overthinking, Depression, Stress-Relief, Brain Fog, Inflammation & MoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument45 SeitenNervous SystemKemoy FrancisNoch keine Bewertungen
- E-Portfolio Psychology EssayDokument2 SeitenE-Portfolio Psychology Essayapi-253674771Noch keine Bewertungen
- Feedback Mechanisms To Maintain Homeostasis.: 1. SensorsDokument5 SeitenFeedback Mechanisms To Maintain Homeostasis.: 1. SensorsYaRNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Method Statement For 132kV Cable PullingDokument1 SeiteWork Method Statement For 132kV Cable PullingsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Method Statement For Cable Excavation TrenchesDokument5 SeitenWork Method Statement For Cable Excavation TrenchessamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- The Brain-Body Connection: Understanding the Impact of Physical Health on Mental HealthVon EverandThe Brain-Body Connection: Understanding the Impact of Physical Health on Mental HealthNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous Control: Reflex Action: Activity 18 Bs Biology 1-2Dokument4 SeitenNervous Control: Reflex Action: Activity 18 Bs Biology 1-2John Rudolf CatalanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Biology 12 Section Assignment 4.1 Part A: Reflex Ares Laboratory Lab Report Willis Lee HypothesisDokument5 SeitenBiology 12 Section Assignment 4.1 Part A: Reflex Ares Laboratory Lab Report Willis Lee HypothesisJames JungNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System ReviewDokument18 SeitenNervous System Reviewtherenam825Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 3Dokument109 SeitenChapter 3amala raviNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument3 SeitenNervous SystemshhhNoch keine Bewertungen
- Form 4 Science Chapter 2Dokument13 SeitenForm 4 Science Chapter 2Cheah Foo Kit50% (2)
- Control and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?Dokument22 SeitenControl and Coordination Do You Know Which Organs Make Up The Nervous System?So TemptedNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMDokument6 SeitenLesson 1-THE NERVOUS SYSTEMNatoya RichardsNoch keine Bewertungen
- The-Nervous-System-Written ReportDokument5 SeitenThe-Nervous-System-Written ReportHeileen S. San GabrielNoch keine Bewertungen
- I. Objectives A. General ObjectivesDokument32 SeitenI. Objectives A. General ObjectivesLeana Ella Rivera YemaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Function: Voluntary and Involuntary Responses - AvivaDokument6 SeitenFunction: Voluntary and Involuntary Responses - AvivaBrendaJooYeeNoch keine Bewertungen
- Disease and Disorder of Nervous SystemDokument11 SeitenDisease and Disorder of Nervous SystemHannah ۦۦNoch keine Bewertungen
- In Text Questions: NCERT Solutions For Class 10th: CH 7 Control and Coordination ScienceDokument8 SeitenIn Text Questions: NCERT Solutions For Class 10th: CH 7 Control and Coordination ScienceJignesh KiriNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS Path Pharm KelnerDokument9 SeitenCNS Path Pharm Kelnerjazzdoc007Noch keine Bewertungen
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Dokument4 SeitenFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408115Misbah NoreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Lesson 06 Nervous & Endocrine Systems PDFDokument6 SeitenLesson 06 Nervous & Endocrine Systems PDFZeus Tuñón BellónNoch keine Bewertungen
- Kepy 01 09 37 EtextDokument9 SeitenKepy 01 09 37 Etextmradul guptaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Influence of Nervous System On BehaviorDokument2 SeitenInfluence of Nervous System On BehaviorcynthiasenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Topic 3 Nervous System Part 2Dokument25 SeitenTopic 3 Nervous System Part 2fauzi ariffinNoch keine Bewertungen
- Health PresentationDokument20 SeitenHealth Presentationapi-214728543Noch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous SystemDokument9 SeitenNervous Systemfaresalesa2005Noch keine Bewertungen
- The Patient With Altered ConsciousnessDokument59 SeitenThe Patient With Altered Consciousnesssunilk09Noch keine Bewertungen
- Final Effects of Neurological Diseases in Our Nervous SystemDokument20 SeitenFinal Effects of Neurological Diseases in Our Nervous SystemAfesoj BelirNoch keine Bewertungen
- Control and Coordination - Class XDokument5 SeitenControl and Coordination - Class XMonika Mehan89% (19)
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190407991Dokument2 SeitenFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190407991Misbah NoreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Parts of The Nervous SystemDokument2 SeitenParts of The Nervous SystemRonel AsuncionNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert - Soln - Control and CoordinationDokument8 SeitenNcert - Soln - Control and CoordinationRagini BaghelNoch keine Bewertungen
- Neuro Assignment Himanshi Sumrani 1073 Maclp 3bDokument22 SeitenNeuro Assignment Himanshi Sumrani 1073 Maclp 3bhimsumraniNoch keine Bewertungen
- SnaDokument11 SeitenSnaFisiologiaUFCGNoch keine Bewertungen
- How Do Nervous System and Endocrine System WorkDokument21 SeitenHow Do Nervous System and Endocrine System WorkBryan BriesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Tulip Series English GuideDokument11 SeitenTulip Series English GuideUrwah hassanNoch keine Bewertungen
- B10 - The Human Nervous SystemDokument7 SeitenB10 - The Human Nervous SystemSahasra BhongirwarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Name: Cauilan, Darwin C. Score: Year and Section: Bs Pharma 1-A Set A DateDokument4 SeitenName: Cauilan, Darwin C. Score: Year and Section: Bs Pharma 1-A Set A DateDarwin CauilanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Perez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Dokument6 SeitenPerez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Jayzyl PerezNoch keine Bewertungen
- Summative PracticeDokument42 SeitenSummative PracticeDewi SallehNoch keine Bewertungen
- SPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationDokument12 SeitenSPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationSPM98% (50)
- Stress: Part I The Physiology of StressDokument7 SeitenStress: Part I The Physiology of Stressvijayalakshmi100% (1)
- Koteskey Chapter TwoDokument8 SeitenKoteskey Chapter TwoDoug YostNoch keine Bewertungen
- Solution 1:: Intext Exercise 1Dokument11 SeitenSolution 1:: Intext Exercise 1graceNoch keine Bewertungen
- Brainthe ControllerDokument4 SeitenBrainthe ControllerJacklynlim LkcNoch keine Bewertungen
- Fall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408121Dokument3 SeitenFall 2022 - ZOO403 - 1 - BC190408121Misbah NoreenNoch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 12 Coordination and ControlDokument22 SeitenChapter 12 Coordination and ControlXaundrae McDonaldNoch keine Bewertungen
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Dokument21 SeitenScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Nervous System)Denver TamayoNoch keine Bewertungen
- Stress and Physiological ResponseDokument11 SeitenStress and Physiological ResponseCampbell BellNoch keine Bewertungen
- Physiology Muhammad Ismail 12314Dokument12 SeitenPhysiology Muhammad Ismail 12314Asad SafdarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ncert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 7Dokument11 SeitenNcert Solution Cbse Class 10 Sci Chap 7Sneegdha DubeyNoch keine Bewertungen
- Psychology Week 3 NotesDokument9 SeitenPsychology Week 3 Notes01234Noch keine Bewertungen
- Key Brain TermsDokument52 SeitenKey Brain Termsroberto gomesNoch keine Bewertungen
- Which of The Following Is A Plant Hormone? (A) Insulin (B) Thyroxin (C) Oestrogen (D) CytokininDokument14 SeitenWhich of The Following Is A Plant Hormone? (A) Insulin (B) Thyroxin (C) Oestrogen (D) CytokininAnkur NayakNoch keine Bewertungen
- Anatomy Nervous SystemDokument13 SeitenAnatomy Nervous SystemDewa NurjaNoch keine Bewertungen
- CNS Path Pharm KelnerDokument9 SeitenCNS Path Pharm Kelnerjazzdoc007Noch keine Bewertungen
- IrritabilityDokument30 SeitenIrritabilityAnnesley RobanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18th ED Main Changes BSI Comm 1 March 2018Dokument4 Seiten18th ED Main Changes BSI Comm 1 March 2018Sean AkirangaNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - X - 1-20Dokument73 SeitenClass - X - 1-20samsunglover100% (1)
- The Indian Community School, Kuwait Divided SyllabusDokument2 SeitenThe Indian Community School, Kuwait Divided SyllabussamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Colossians Intro-SDokument3 SeitenColossians Intro-SsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 18th ED Main Changes BSI Comm 1 March 2018Dokument5 Seiten18th ED Main Changes BSI Comm 1 March 2018samsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Class - X - 1-20Dokument52 SeitenClass - X - 1-20samsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- PDFDokument256 SeitenPDFDuraipandi RajaNoch keine Bewertungen
- B1 109 2011Dokument8 SeitenB1 109 2011samsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Part Iv-History of The Church Lesson 21 The Early Christian ChurchDokument11 SeitenPart Iv-History of The Church Lesson 21 The Early Christian ChurchsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Presentation Gis Cam August 2016Dokument121 SeitenPresentation Gis Cam August 2016samsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- MEGHALAYADokument15 SeitenMEGHALAYAHiteshRawalNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Class IVDokument51 SeitenEng Class IVsamsunglover0% (1)
- Case Study Odisha Works Department Manoranjan MishraDokument20 SeitenCase Study Odisha Works Department Manoranjan MishraMuhammad AhmadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Eng Class IIIDokument26 SeitenEng Class IIIsamsunglover100% (1)
- Method Statement For Installation of Electric PVC Conduits and AccessoriesDokument6 SeitenMethod Statement For Installation of Electric PVC Conduits and AccessoriessamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Hvac Chiller Basics: Working Principle of Vapor Compression ChillerDokument2 SeitenHvac Chiller Basics: Working Principle of Vapor Compression ChillersamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Basic Principles of A HVAC SystemDokument2 SeitenBasic Principles of A HVAC SystemsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Method Statement For Installation of Electric PVC Conduits and AccessoriesDokument6 SeitenMethod Statement For Installation of Electric PVC Conduits and AccessoriessamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- CCTV Student HandbookDokument57 SeitenCCTV Student HandbookcrissdemonNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mail. 3. Show Profiles 4. Add. 5. OK. 6. Add Accounts 7. Prompt For A Profile To Be UsedDokument1 SeiteMail. 3. Show Profiles 4. Add. 5. OK. 6. Add Accounts 7. Prompt For A Profile To Be UsedsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 14 Days South Korea ItineraryDokument34 Seiten14 Days South Korea ItinerarysamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Work Method Statement For Cable TrayDokument4 SeitenWork Method Statement For Cable TraysamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Page 040Dokument1 SeitePage 040samsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Electric Quarter Turn Actuator Model HQ006 ManualDokument20 SeitenElectric Quarter Turn Actuator Model HQ006 ManualsamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10 Critical Tests For New Power Circuit BreakersDokument6 Seiten10 Critical Tests For New Power Circuit BreakerssamsungloverNoch keine Bewertungen
- Sensory Re-Education - EngDokument12 SeitenSensory Re-Education - EngFlorinCristianNoch keine Bewertungen
- Blue Brain Seminar ReportDokument34 SeitenBlue Brain Seminar ReportsajjadNoch keine Bewertungen
- Ward 2011 The Thalamic Dynamic Core Theory of Conscious ExperienceDokument23 SeitenWard 2011 The Thalamic Dynamic Core Theory of Conscious ExperienceAndrew-Robert GallimoreNoch keine Bewertungen
- Final Exam Review SheetDokument2 SeitenFinal Exam Review Sheetapi-264668182Noch keine Bewertungen
- ASSIGNMENT On Action PotentialDokument8 SeitenASSIGNMENT On Action PotentialRinta Moon100% (1)
- Atlas Human CnsDokument16 SeitenAtlas Human CnsAnonymous HQuX2LUsDNoch keine Bewertungen
- EEG1Dokument13 SeitenEEG1idno1008Noch keine Bewertungen
- Form 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseDokument16 SeitenForm 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseAcapSuiNoch keine Bewertungen
- BSDokument6 SeitenBSBeda MalecdanNoch keine Bewertungen
- Case Study On DrugsDokument2 SeitenCase Study On Drugsapi-329889139Noch keine Bewertungen
- ANAT 242 Course Outline PingliuDokument67 SeitenANAT 242 Course Outline PingliuAnonymous 9oTm71Noch keine Bewertungen
- NeurotransmitterDokument15 SeitenNeurotransmitterShahran KumarNoch keine Bewertungen
- Infancy and ToddlerhoodDokument25 SeitenInfancy and ToddlerhoodMark SultanNoch keine Bewertungen
- 10-Biopotential Sources Signal ProcessingDokument27 Seiten10-Biopotential Sources Signal ProcessingJZ8923Noch keine Bewertungen
- Chapter 8: Somatosensory Neurotransmission: Touch, Pain, & TemperatureDokument21 SeitenChapter 8: Somatosensory Neurotransmission: Touch, Pain, & Temperatureanon_794697676100% (1)
- Sensations and Sensory Pathways General Senses Test Procedure Normal Result Abnormal Result Clinical InterpretationDokument5 SeitenSensations and Sensory Pathways General Senses Test Procedure Normal Result Abnormal Result Clinical InterpretationAbby MataNoch keine Bewertungen
- Nervous System Lab ReportDokument6 SeitenNervous System Lab Reportapi-269993638Noch keine Bewertungen
- Veterinary Neuropharmacology VPT 321 Lecture Notes TANUVASDokument101 SeitenVeterinary Neuropharmacology VPT 321 Lecture Notes TANUVASSunil89% (18)
- BioPsych Lecture Notes CH 7Dokument6 SeitenBioPsych Lecture Notes CH 7Generic_Persona100% (1)
- Non-Depolarising Blockers Depolarising Blockers Botox: Anticholinesterase IMPORTANTDokument2 SeitenNon-Depolarising Blockers Depolarising Blockers Botox: Anticholinesterase IMPORTANTjsdlzjNoch keine Bewertungen
- Mirror Therapy PosterDokument1 SeiteMirror Therapy Posterapi-335381896Noch keine Bewertungen
- Report - Brain Computer InterfaceDokument13 SeitenReport - Brain Computer InterfaceSethi AshishNoch keine Bewertungen